Patents
Literature
423results about "Animal material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
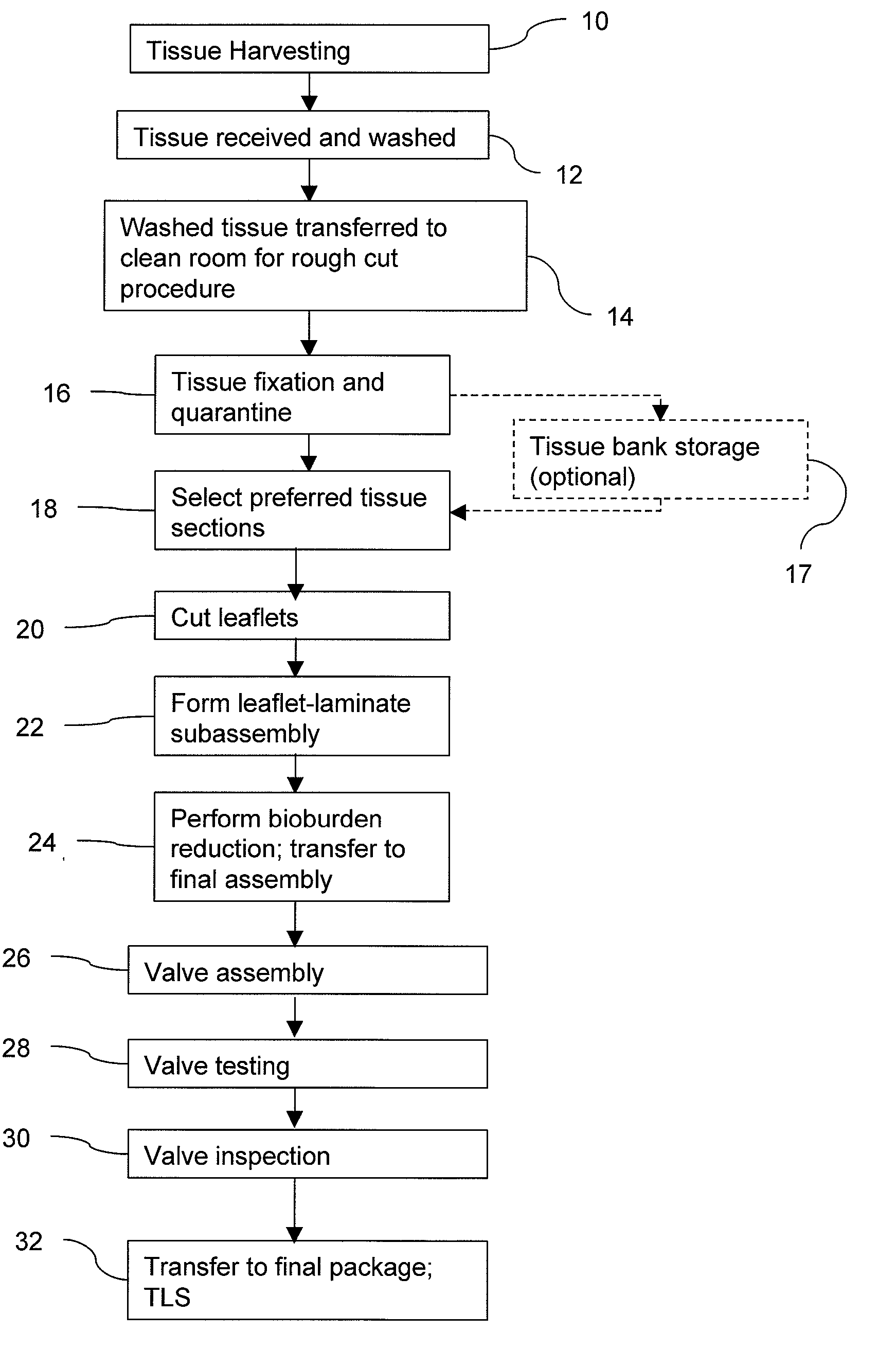
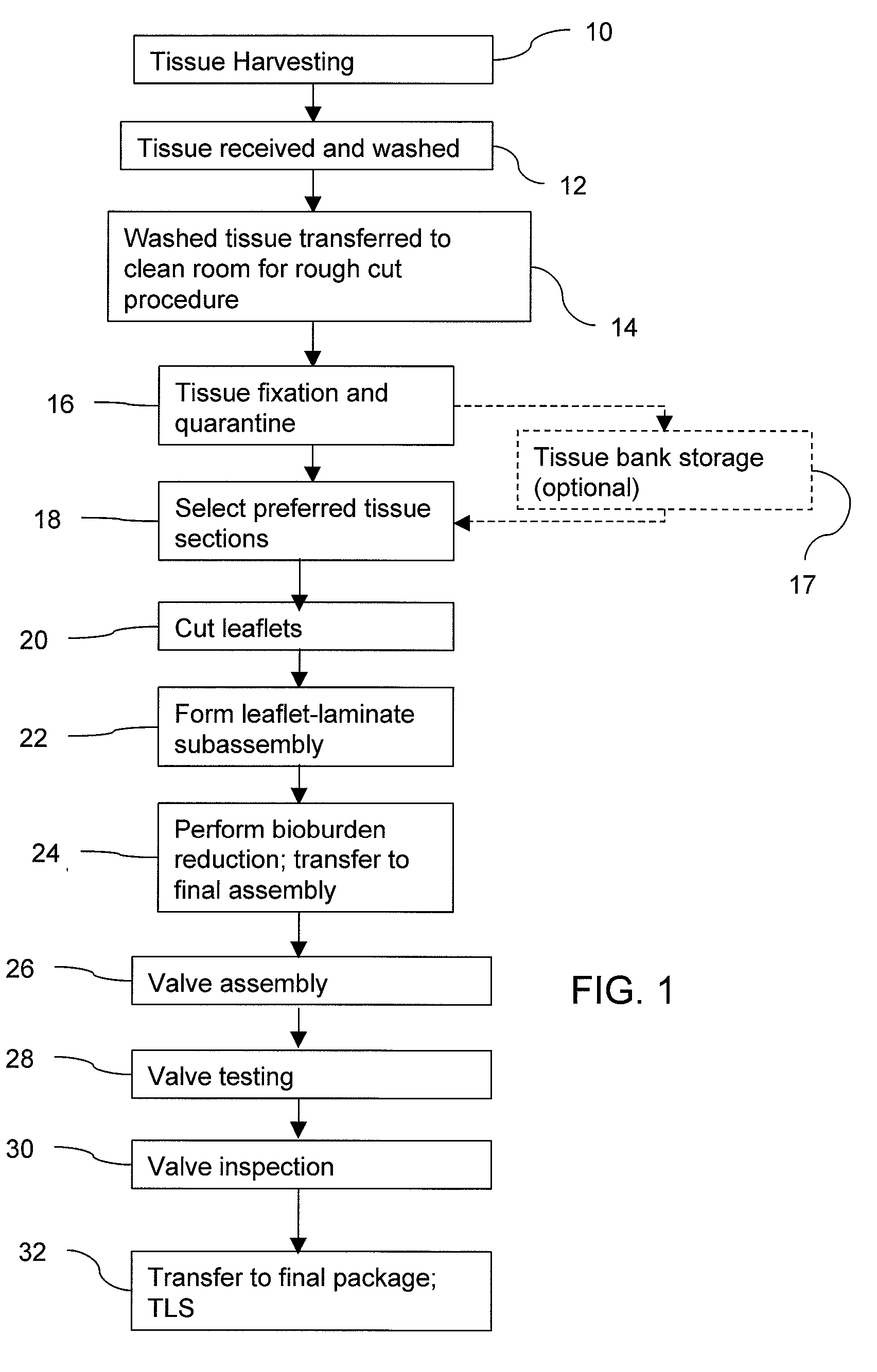
Methods for treating a patient using a bioengineered flat sheet graft prostheses
InactiveUS20020103542A1Easy to assembleEasy to cleanSuture equipmentsAnimal materialTissue architectureProsthesis
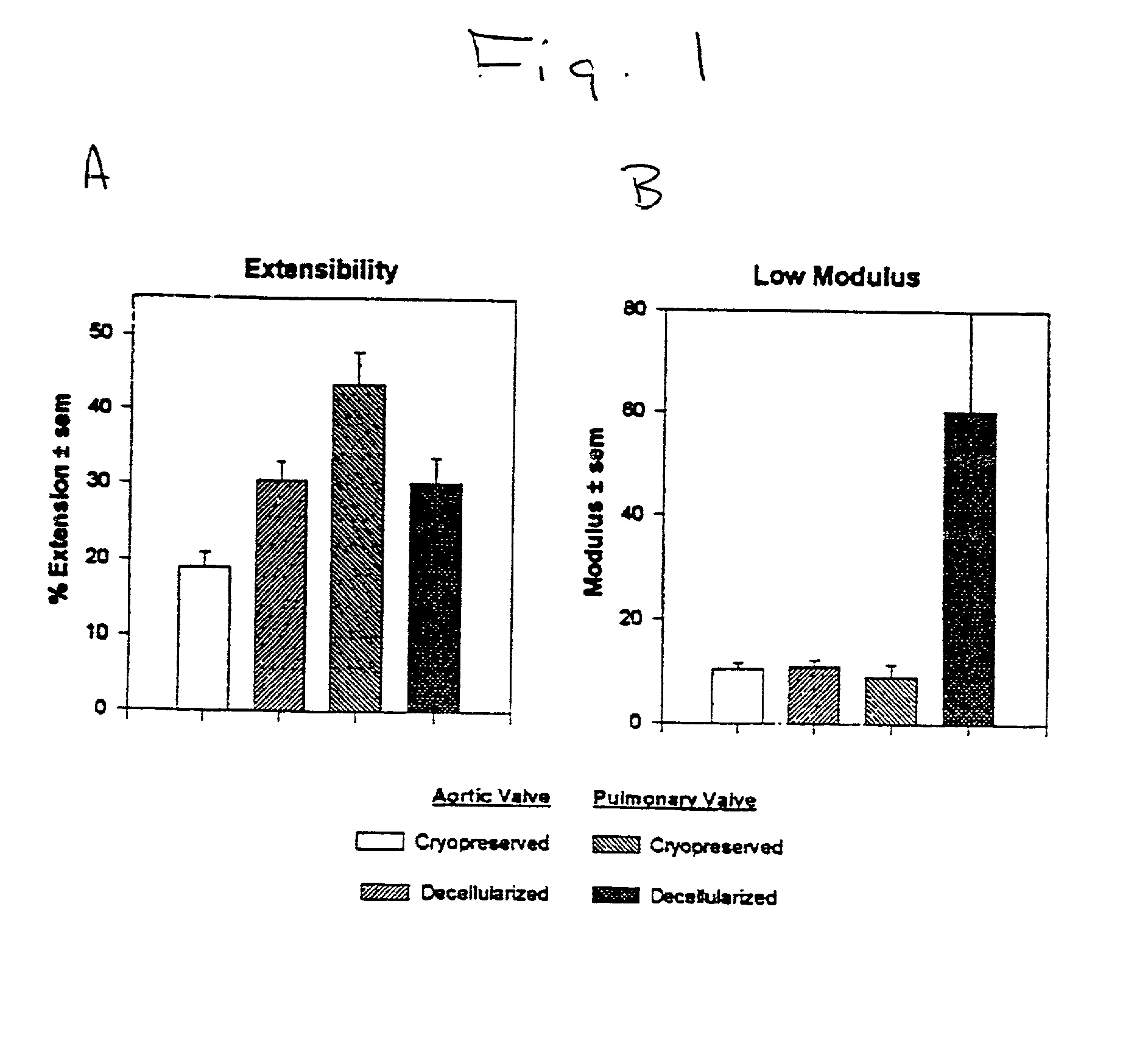
This invention is directed to tissue engineered prostheses made from processed tissue matrices derived from native tissues that are biocompatible with the patient or host in which they are implanted. When implanted into a mammalian host, these prostheses can serve as a functioning repair, augmentation, or replacement body part or tissue structure.
Owner:ORGANOGENESIS
Anti-calcification treatments for heart valves and vascular grafts
InactiveUS20060047343A1Reduces calcification potentialReduce calcificationSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCalcificationProsthesis
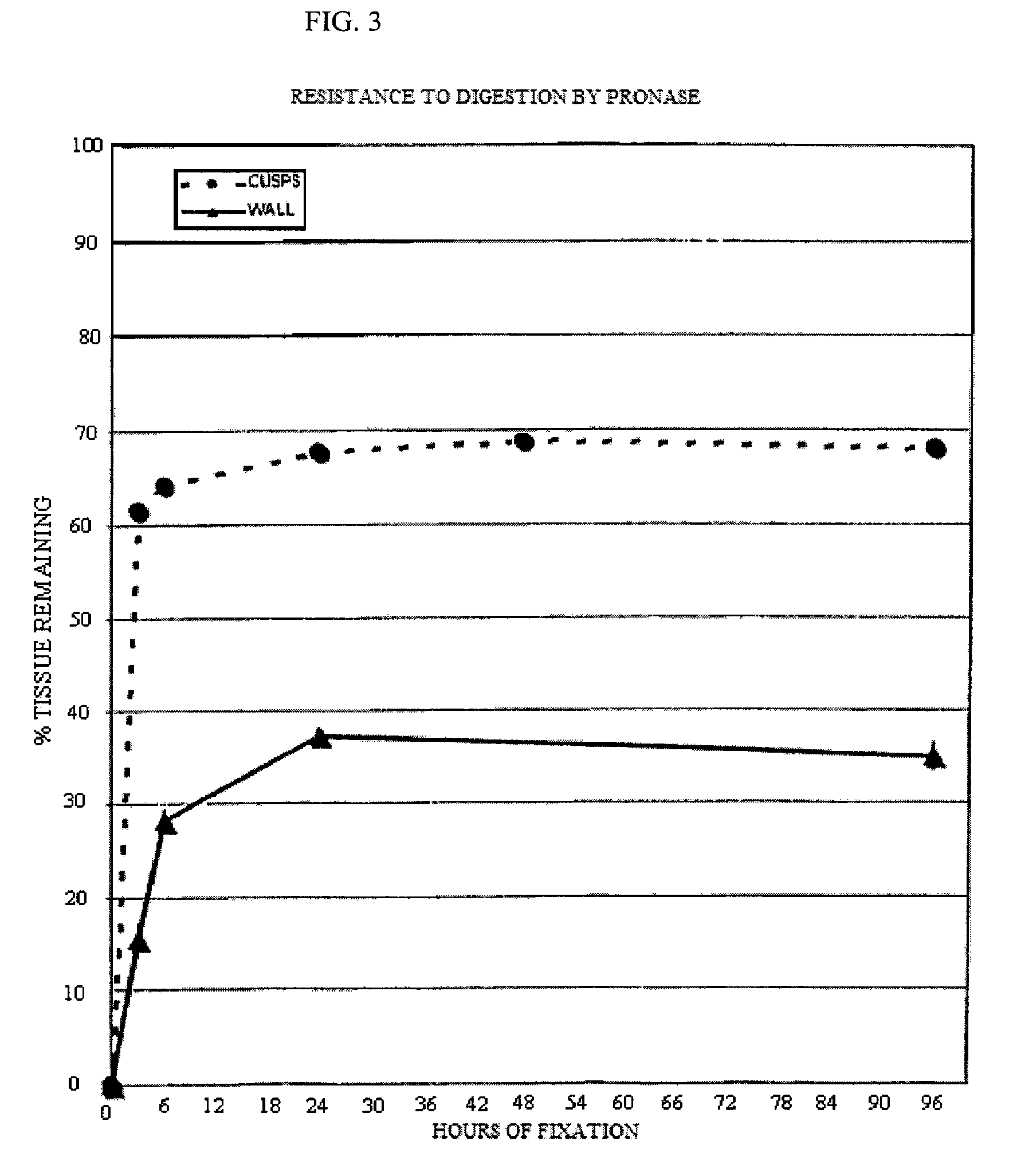
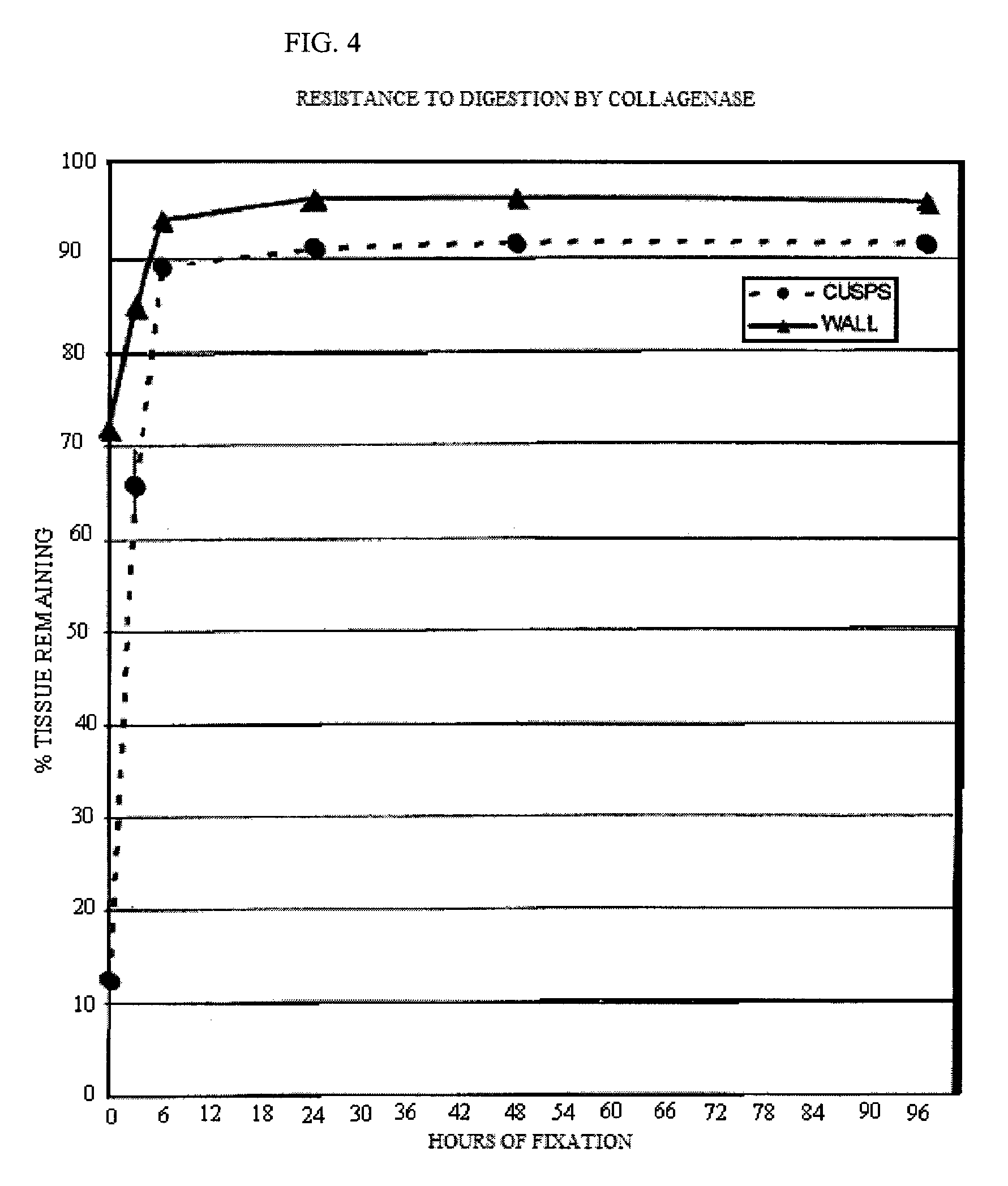
The present invention provides processes for fixation of biological tissue and / or post-fixation treatment of such tissue that result in modified tissues with reduced susceptibility to in vitro calcification when used in prosthetic devices. The invention also relates to calcification resistant biological tissue and to methods of using such tissue.
Owner:OVIATT HENRY W +1
Bioprosthetic tissue preparation with synthetic hydrogels
ActiveUS20050119736A1Reduce calcificationReduce stiffnessSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCross-linkIn situ polymerization
Methods for treating xenogenic tissue for implantation into a human body including in-situ polymerization of a hydrogel polymer in tissue, and tissue treated according to those methods, where the polymerization takes place in tissue that has not been fixed with glutaraldehyde. The polymerization may only fill the tissue, bind the polymer to the tissue, or cross-link the tissue through the polymer, depending on the embodiment. One method includes free radical polymerization of a first vinylic compound, and can include cross-linking through use of a second compound having at least two vinyl groups. Another method utilizes nucleophilic addition polymerization of two compounds, one of which can include PEG and can further include hydrolytically degradable regions. In one embodiment, applicants believe the in-situ polymerization inhibits calcification, and that the polymerization of tissue un-fixed by glutaraldehyde allows for improved penetration of the polymer. The methods find one use in the treatment of porcine heart valve tissue, intended to extend the useful life of the valves by inhibiting calcification. The incorporation of degradable hydrogel regions may initially fill the tissue and reduce any initial inflammatory response, but allow for later infiltration by cells to remodel the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Process and apparatus for treating implants comprising soft tissue
ActiveUS20050229323A1Simple structureImprove mechanical propertiesSuture equipmentsSolid sorbent liquid separationLigamentBiomedical engineering
The present invention is directed to the field of implants that include soft tissue. More particularly, the present invention is directed to processes for treating implants that include soft tissues such as tendons and ligaments, and to implants produced by such processes. The present invention is also directed to processes and apparatus for improved processing of implants that include soft tissue, by applying kinematic restraint, preferably tension, to the implant or specific portions of the implants during the treatment, and to implants produced by such processes and apparatus. The present techniques yield soft tissue implants having superior structural, mechanical, and / or biochemical integrity.
Owner:RTI BIOLOGICS INC
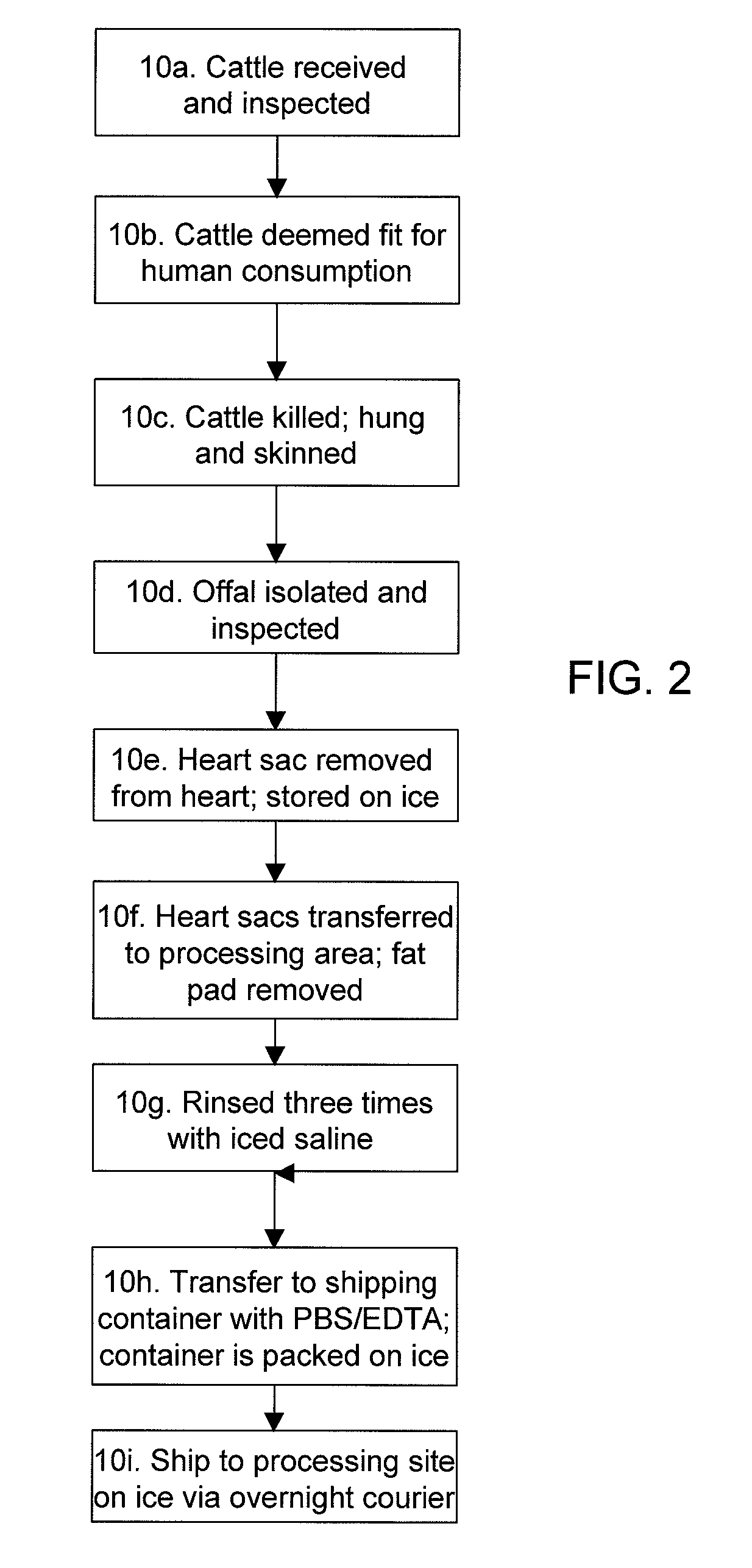
Methods for processing biological tissue
ActiveUS20060207031A1Remove background levelAvoid degradationSuture equipmentsDead animal preservationCalcificationPhospholipid
A method for processing biological tissue used in biological prostheses includes providing a tissue procurement solution formed from a phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution and a chelating agent. The tissue is transferred from the tissue procurement solution and undergoes chemical fixation. The fixed tissue is then immersed in a series of fresh bioburden reduction process (BRP) solutions to extract phospholipids. The tissue procurement solution reduces the bioburden on the stored tissue and preserves tissue architecture by minimizing tissue swelling. The tissue procurement solution further reduces calcium from the incoming water and / or tissue, and inhibits enzymes that digest the collagen matrix. The serial immersion of the tissue in the fresh bioburden solutions ensures optimal extraction of phospholipids thereby mitigating subsequent calcification of the tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Osteoimplant and method for making same
A method of manufacturing an osteoinductive osteoimplant is provided which comprises the steps of: demineralizing part or all of at least one surface of a monolithic section of cortical bone to a depth of at least about 100 microns; and, configuring the monolithic section of cortical bone to provide an osteoimplant possessing an outer surface possessing at least one demineralized zone and a non-demineralized zone. An implant produced according to the above method demonstrates improved osteoinduction without producing any clinically significant reduction of strength in critical regions of the osteoimplant.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Vertebral disc repair
InactiveUS7879103B2Eliminate osteoinductivitySuture equipmentsBone implantShape-memory alloyBone Cortex
A sterile implant for treatment of a spinal disc defect comprising an allograft cortical bone demineralized to a Type I collagen having a specific shape which is treated to eliminate osteoinductivity. The implant is lyophilized and compressed into smaller first shape which 20 to 80% from its original shape in at least one dimension and hardened. The implant expanding when hydrated into a second shape having the shape memory of the first shape and expanded in dimensional size from the first compressed shape.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Treatment of bioprosthetic tissues to mitigate post implantation calcification
InactiveUS6878168B2Lower potentialReduce the temperatureSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTreatment resultsMedicine
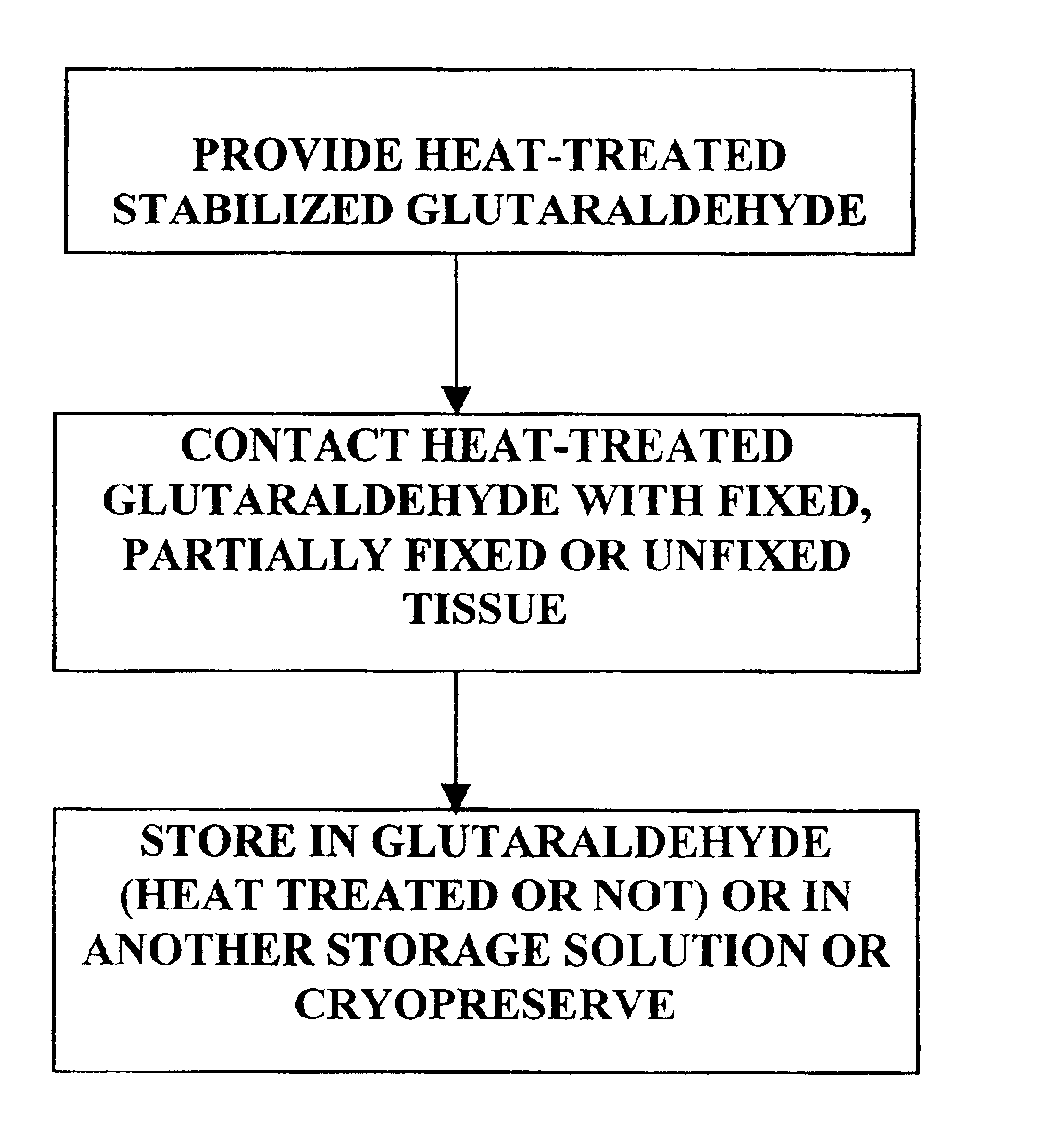
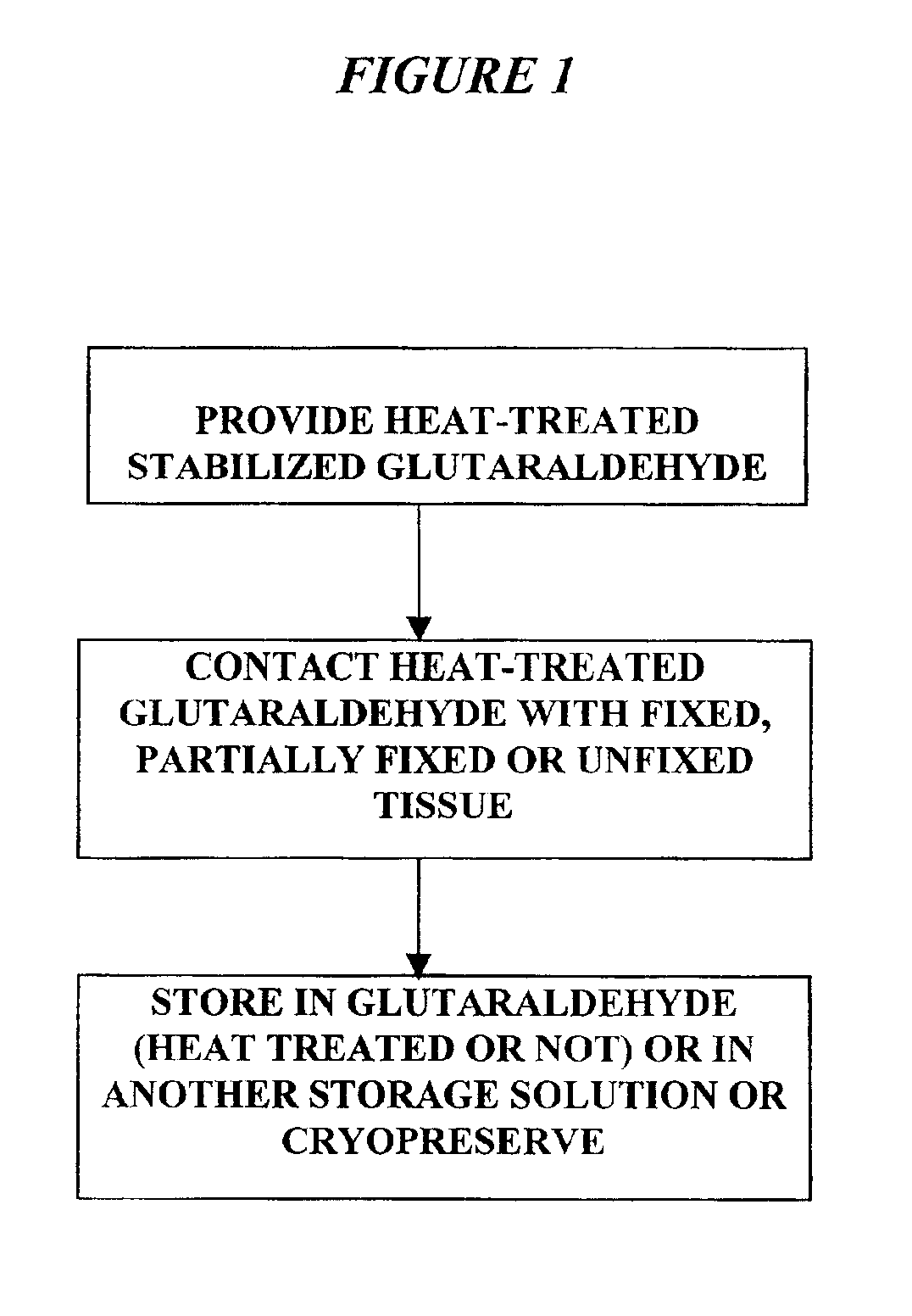
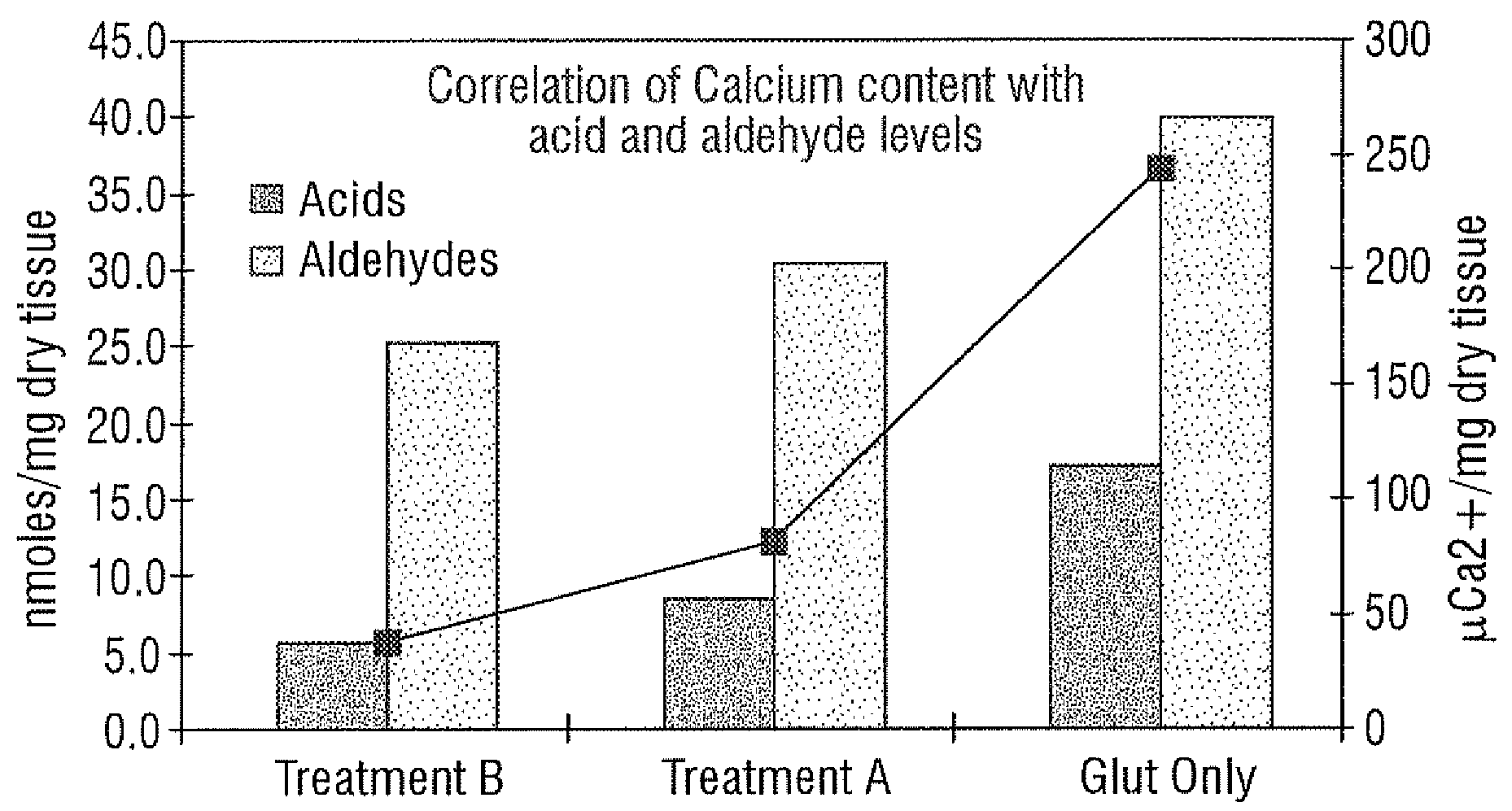
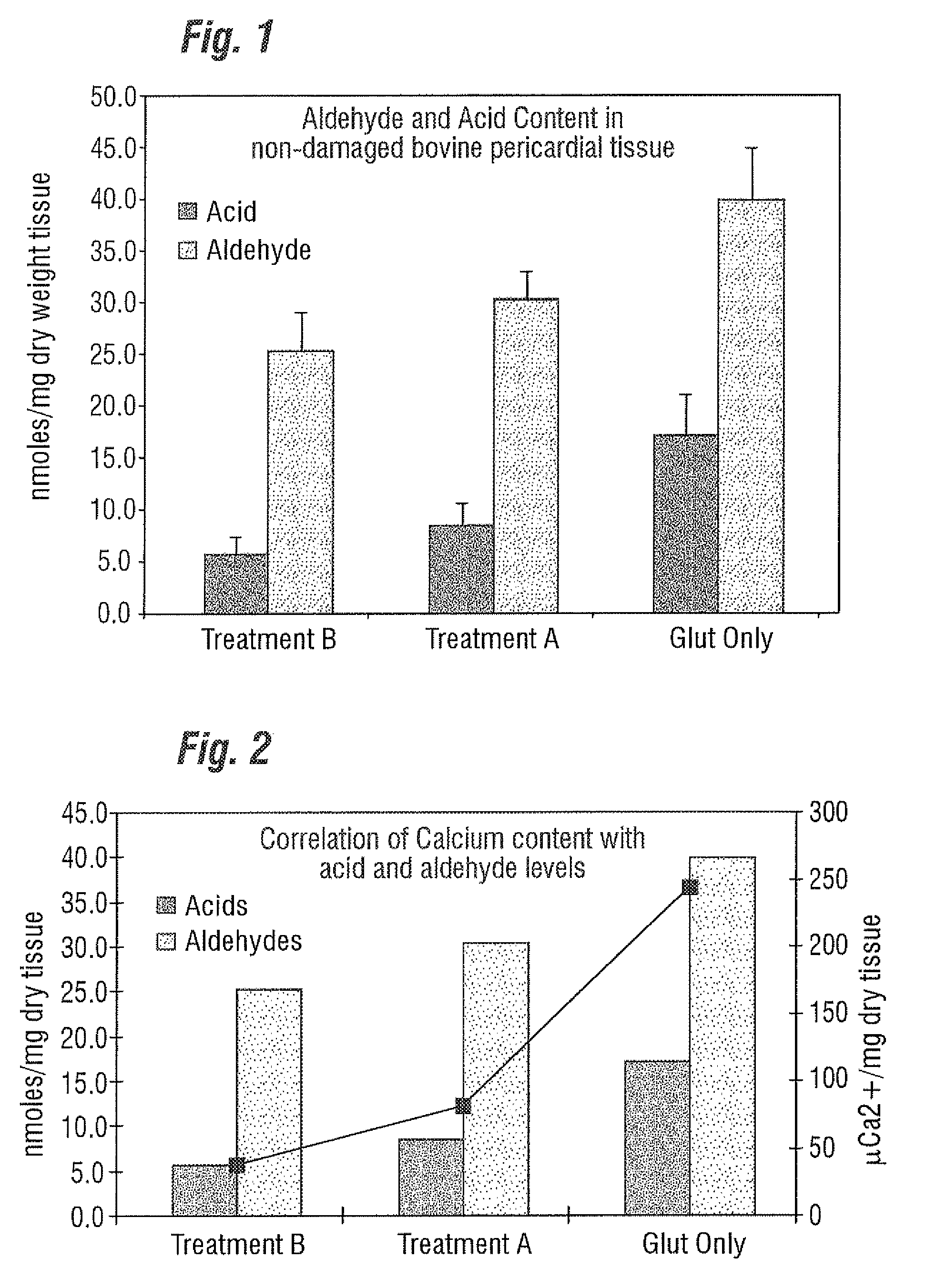
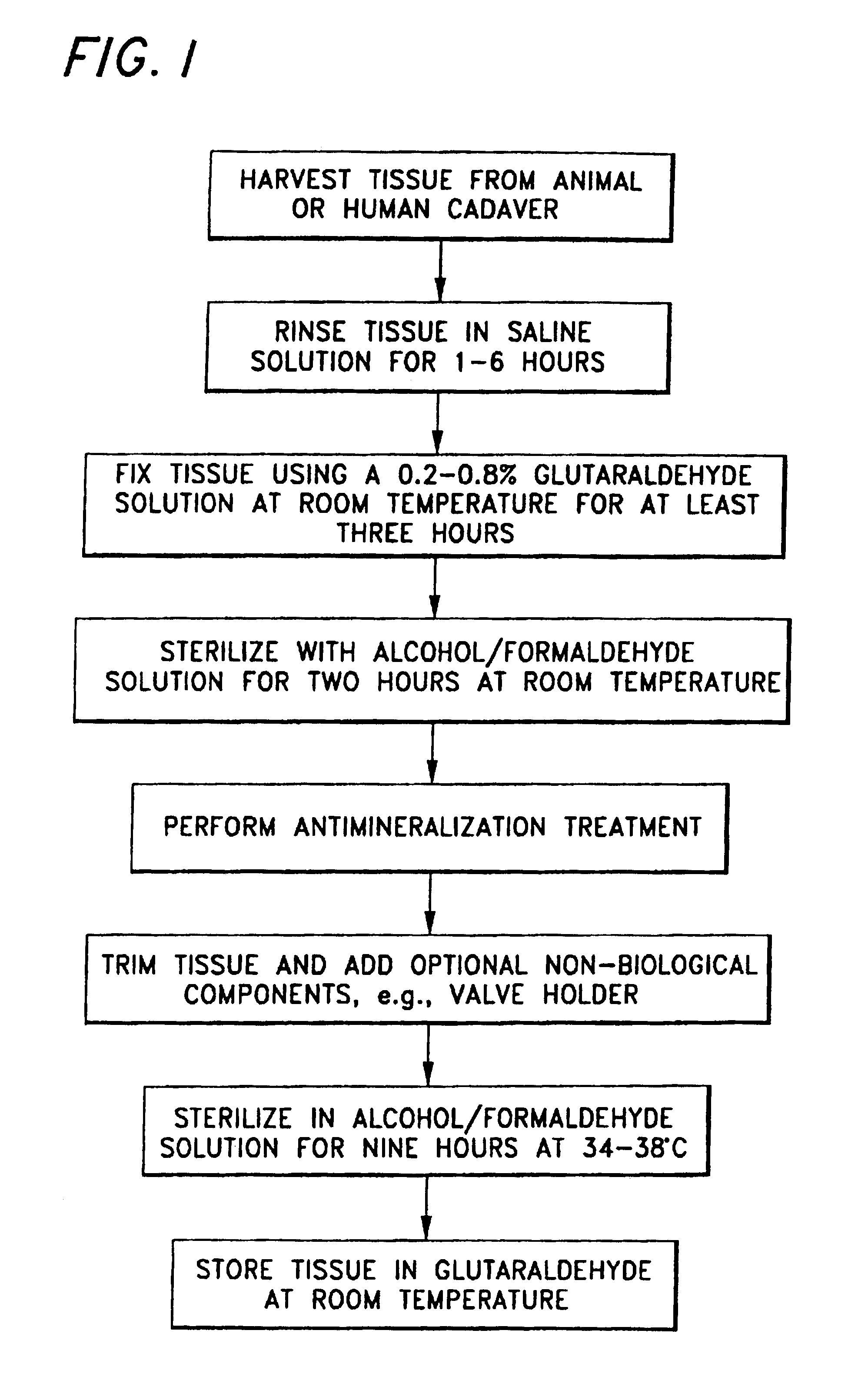
Bioprosthetic tissues are treated by immersing or otherwise contacting fixed, unfixed or partially fixed tissue with a glutaraldehyde solution that has previously been heat-treated or pH adjusted prior to its contact with the tissue. The prior heat treating or pH adjustment of the glutaraldehyde solution causes its free aldehyde concentration to decrease by about 25% or more, preferably by as much as 50%, and allows a “stabilized” glutaraldehyde solution to be obtained at the desired concentration and pH for an optimal fixation of the tissue at high or low temperature. This treatment results in a decrease in the tissue's propensity to calcify after being implanted within the body of a human or animal patient. The heat-treated or pH adjusted glutaraldehyde solution may, in some cases, also be used as a terminal sterilization solution such that the calcification-decreasing treatment with the previously treated glutaraldehyde and a terminal sterilization may be carried out simultaneously and / or in a single container.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Implant derived from bone
An implant which is particularly suitable for the repair and / or replacement of a skeletal joint, e.g., a vertebral joint, includes a unit of monolithic bone possessing at least one demineralized region exhibiting properties of flexibility and resilience, the demineralized region having diminished or insignificant capacity for promoting new bone growth.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Vertebral disc repair
InactiveUS20060235534A1Eliminate osteoinductivitySuture equipmentsBone implantBone CortexCortical bone
A sterile implant for treatment of a spinal disc defect comprising an allograft cortical bone demineralized to a Type I collagen having a specific shape which is treated to eliminate osteoinductivity. The implant is lyophilized and compressed into smaller first shape which 20 to 80% from its original shape in at least one dimension and hardened. The implant expanding when hydrated into a second shape having the shape memory of the first shape and expanded in dimensional size from the first compressed shape.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Methods for pre-stressing and capping bioprosthetic tissue
ActiveUS20080302372A1Reduce in vivo calcificationSuture equipmentsHeart valvesDamages tissuePhosphate
A treatment for bioprosthetic tissue used in implants or for assembled bioprosthetic heart valves to reduce in vivo calcification is disclosed. The method includes preconditioning, pre-stressing, or pre-damaging fixed bioprosthetic tissue in a manner that mimics the damage associated with post-implant use, while, and / or subsequently applying a calcification mitigant such as a capping agent or a linking agent to the damaged tissue. The capping agent suppresses the formation of binding sites in the tissue that are exposed or generated by the damage process (service stress) and otherwise would, upon implant, attract calcium, phosphate, immunogenic factors, or other precursors to calcification. The linking agent will act as an elastic reinforcement or shock-absorbing spring element in the tissue structure at the site of damage from the pre-stressing. In one method, tissue leaflets in assembled bioprosthetic heart valves are preconditioned by simulating actual flow conditions for a predetermined number of cycles, during or after which the valve is exposed to the capping agent.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
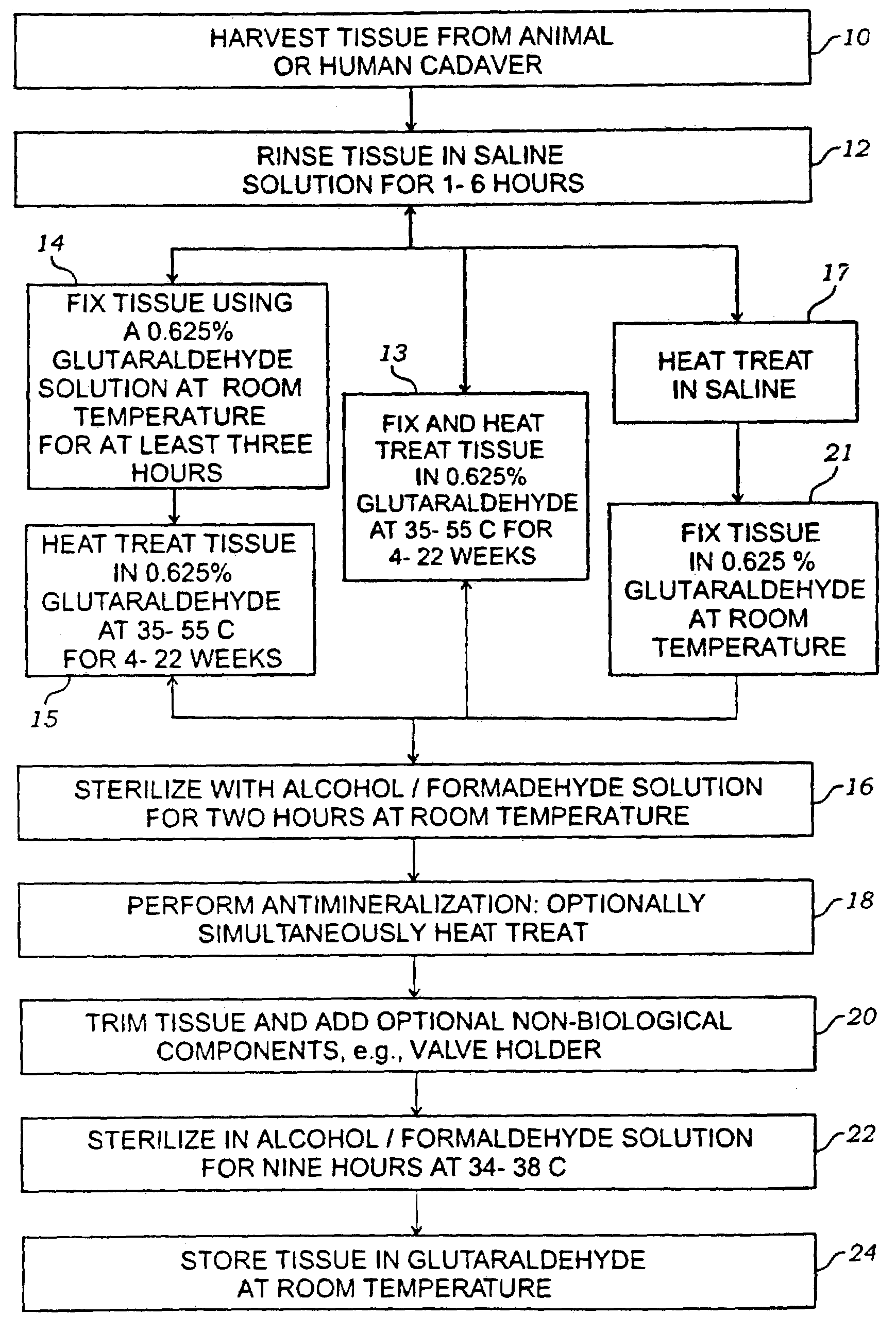
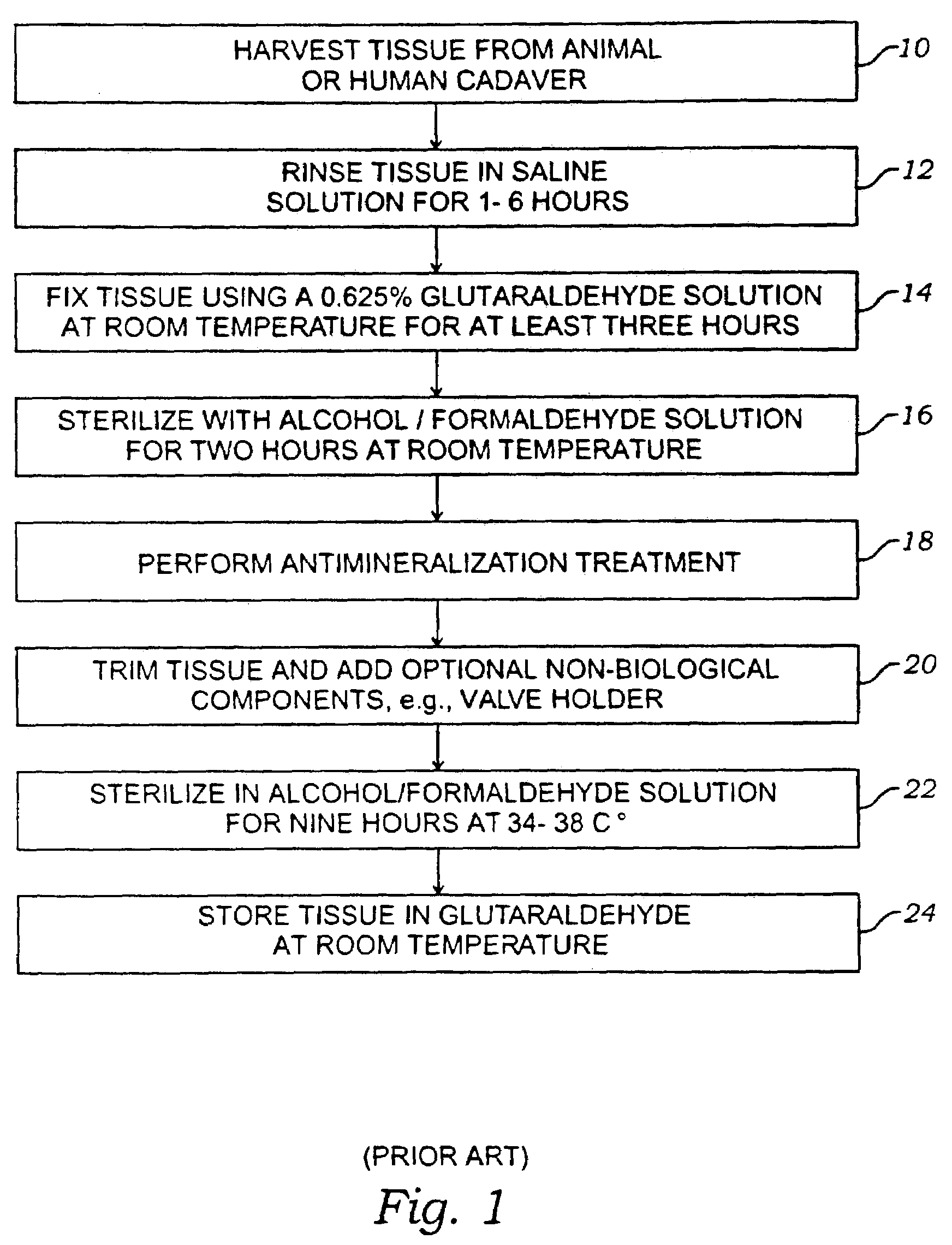
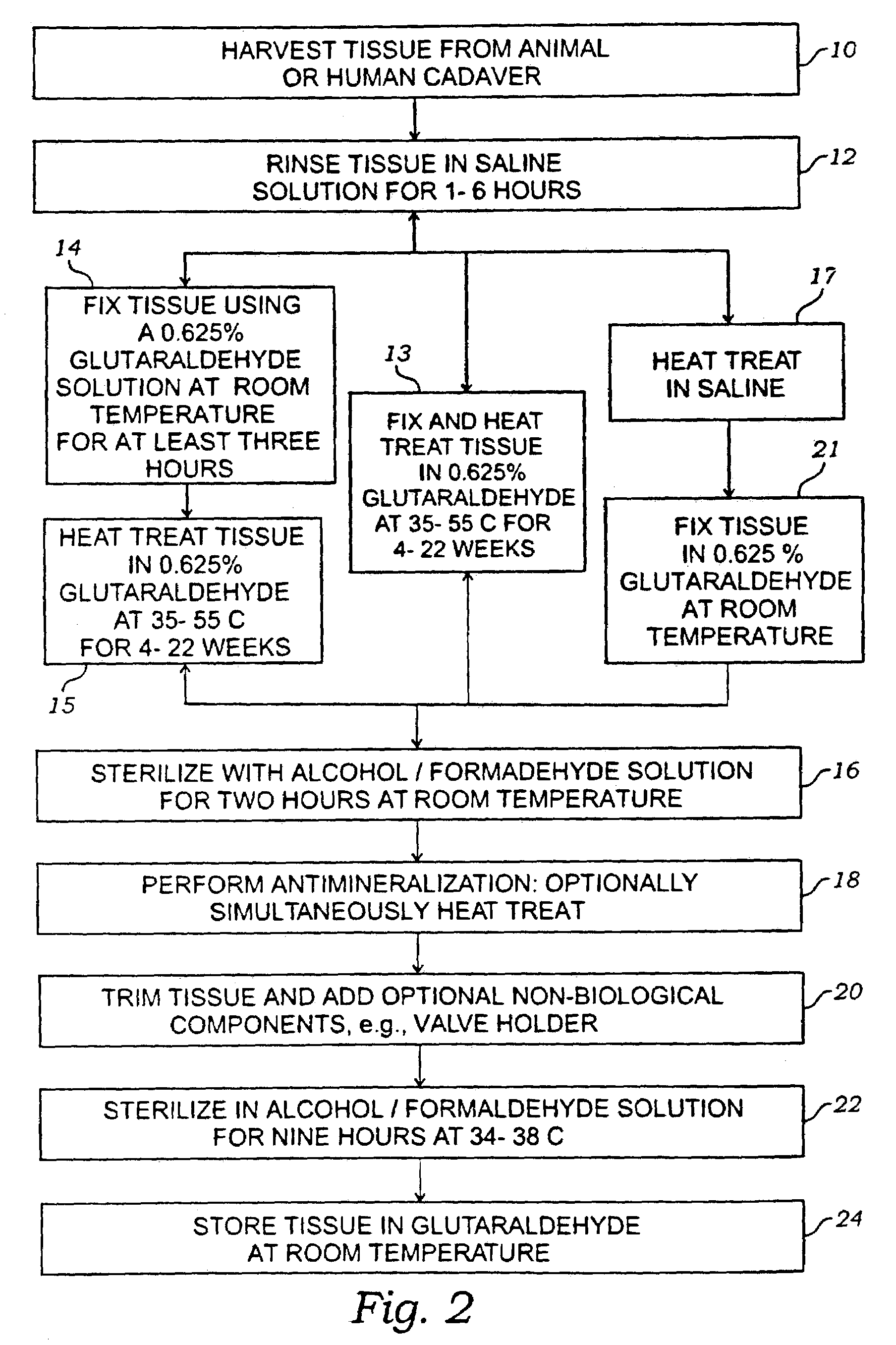
Method for treatment of biological tissues to mitigate post-implantation calcification and thrombosis
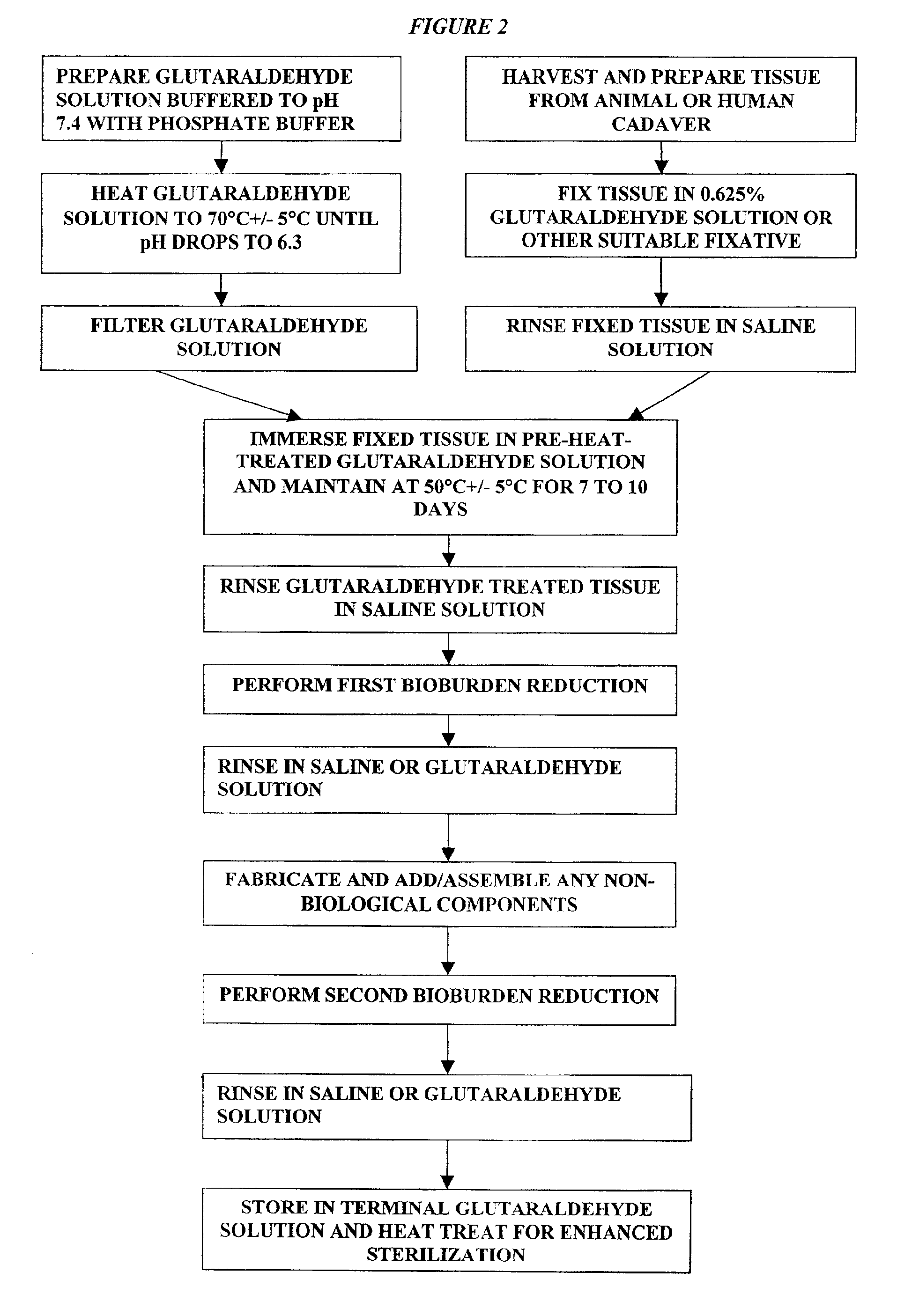
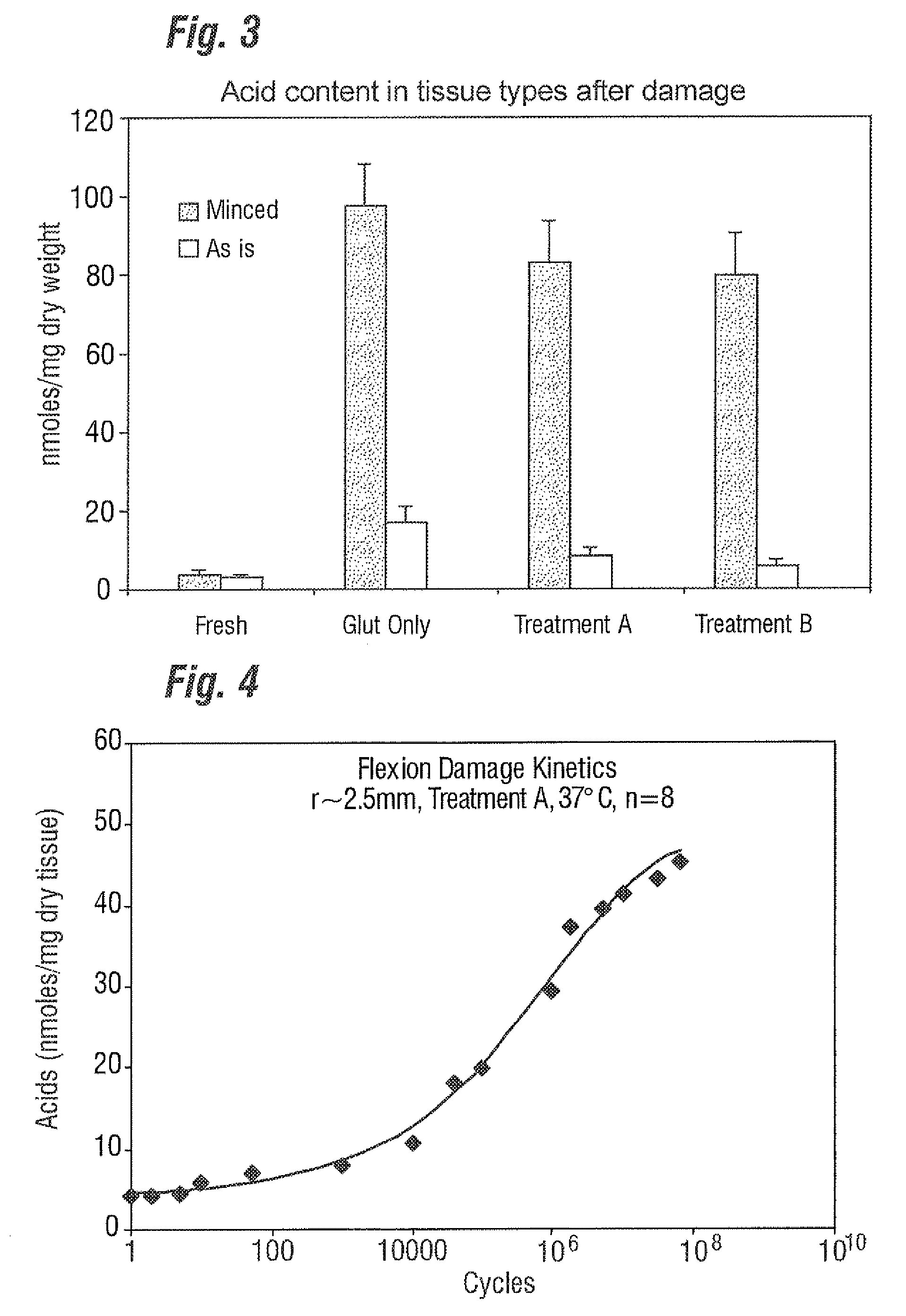
A method of treating a biological tissue including contacting the biological tissue with an aqueous sterilizing solution, and maintaining the aqueous sterilizing solution at a temperature of about 50° C. for a time period of about 1 to 2 days. The method of treating a biological tissue may be utilized as a terminal sterilization step in a method for fixation of biological tissues, and bioprosthetic devices may be prepared by such fixation method. The fixation method may include the steps of A) fixing the tissue, B) treating the tissue with a mixture of i) a denaturant, ii) a surfactant and iii) a crosslinking agent, C) fabricating or forming the bioprosthesis (e.g., forming the tissue and attaching any non-biological components thereto) and D) subjecting the bioprosthesis to the terminal sterilization method. The aqueous sterilizing solution may be glutaraldehyde of about 0.625 weight percent buffered to a pH of about 7.4.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Tissue decellularization
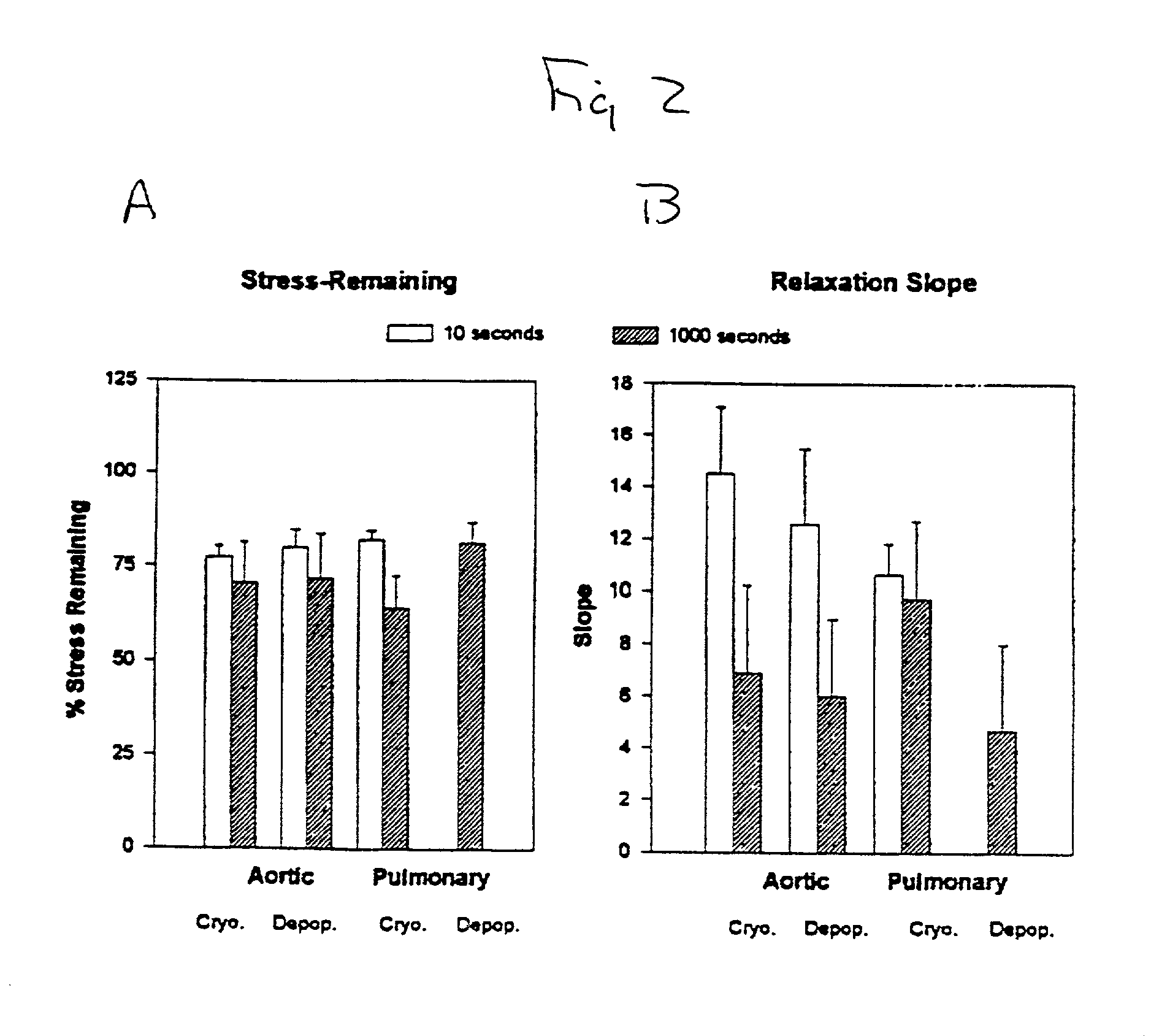
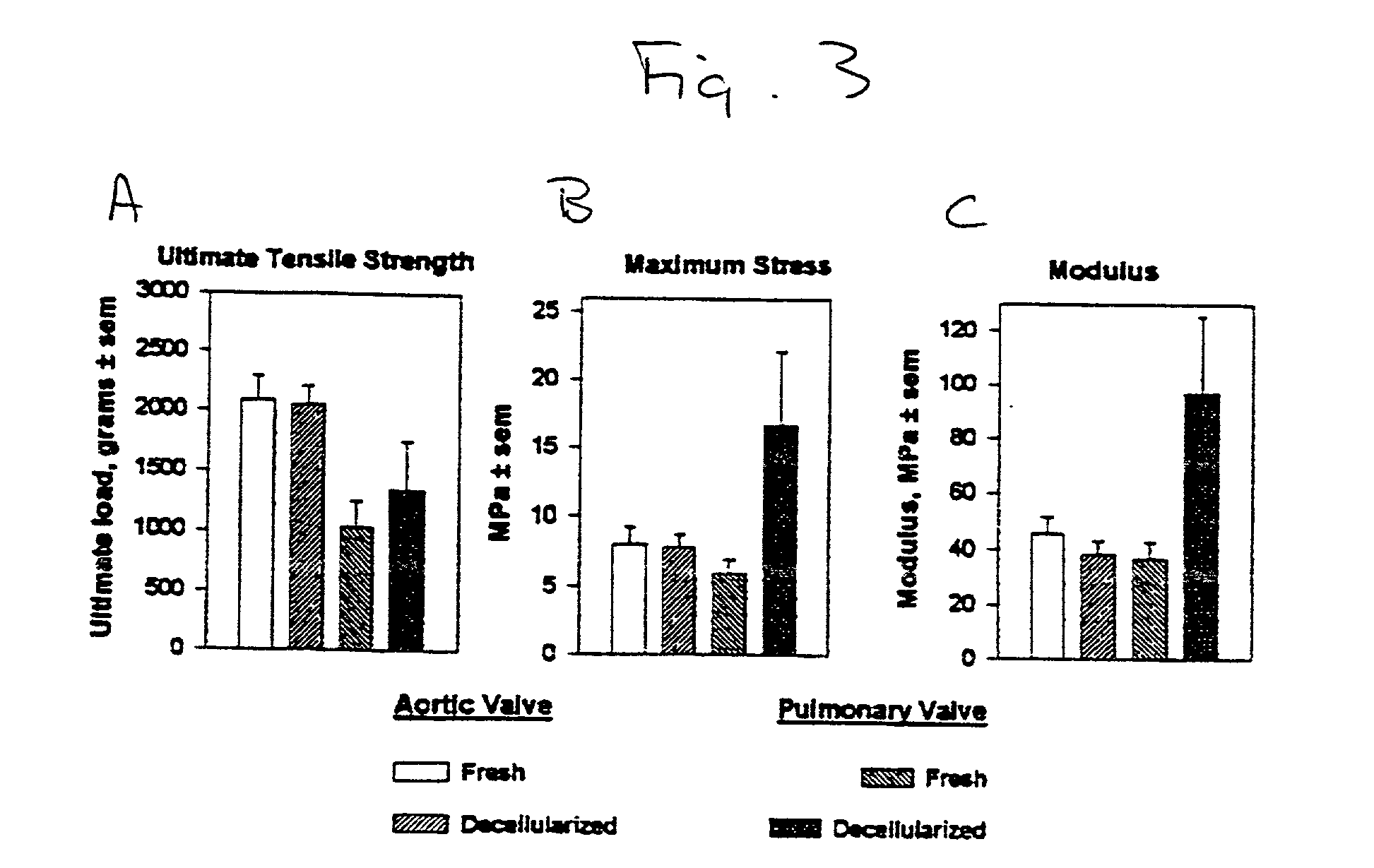
InactiveUS20010000804A1Increased durabilityDecreased immunoreactivitySuture equipmentsHeart valvesTissue DecellularizationLigament structure
The present invention relates, in general, to tissue decellularization and, in particular to a method of treating tissues, for example, heart valves, tendons and ligaments, so as to render them acellular and thereby limit mineralization and / or immunoreactivity upon implementation in vivo.
Owner:CRYOLIFE
Implant derived from bone
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Process and apparatus for treating implants comprising soft tissue
ActiveUS7648676B2Superior structural and mechanical and biochemical integrityAvoid damageSuture equipmentsSolid sorbent liquid separationLigament structureBiomedical engineering
The present invention is directed to the field of implants that include soft tissue. More particularly, the present invention is directed to processes for treating implants that include soft tissues such as tendons and ligaments, and to implants produced by such processes. The present invention is also directed to processes and apparatus for improved processing of implants that include soft tissue, by applying kinematic restraint, preferably tension, to the implant or specific portions of the implants during the treatment, and to implants produced by such processes and apparatus. The present techniques yield soft tissue implants having superior structural, mechanical, and / or biochemical integrity.
Owner:RTI BIOLOGICS INC
Spun laced fabric and processing method thereof
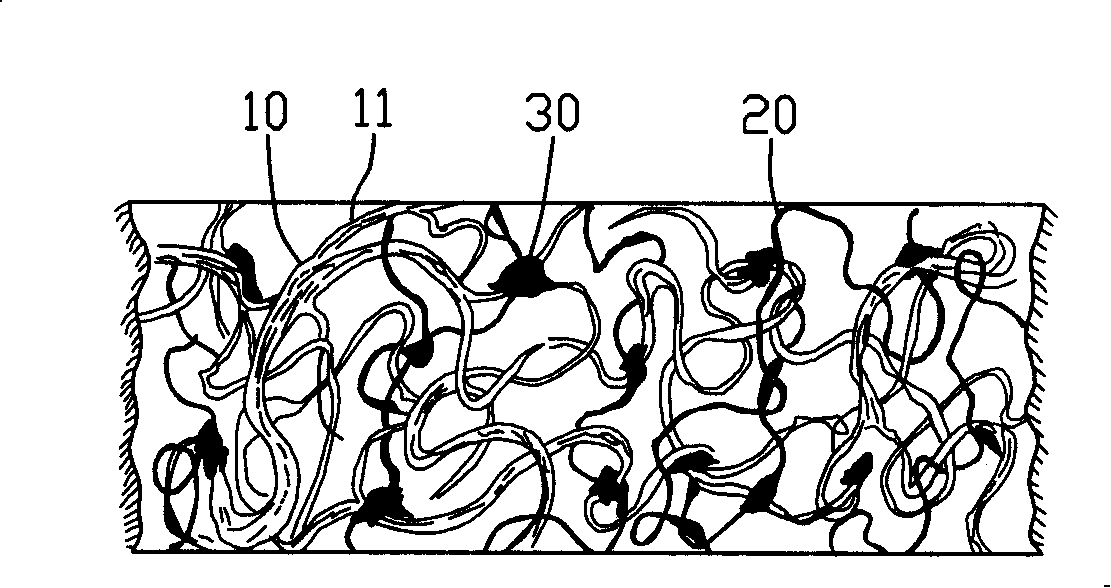
InactiveCN101235579ANot easy to slip offRich varietyAnimal materialNon-woven fabricsFiberCollagen fiber bundle
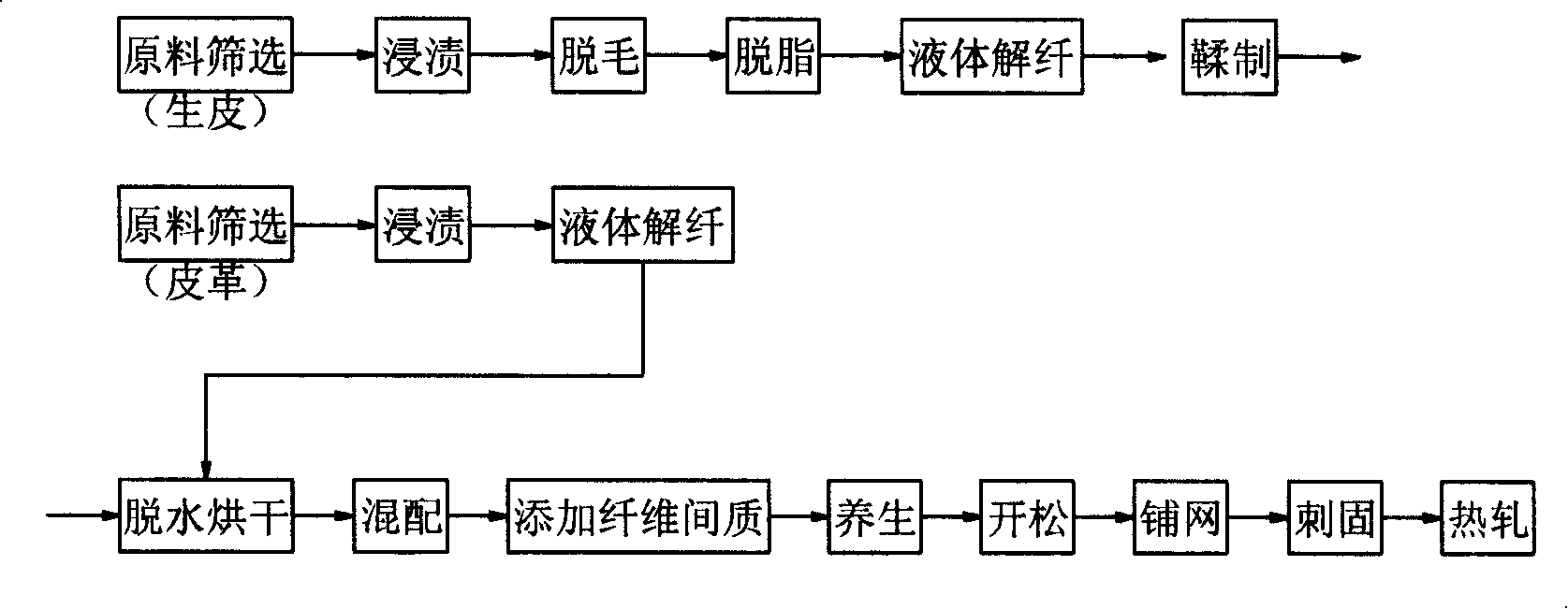
The invention discloses spun-laced cloth and a method for manufacturing the spun-laced cloth. The spun-laced cloth is composed of collagen fiber bundles, other textile-used staple fibers and interstitial fibers, wherein the collagen fiber bundles are mutually interpenetrated and interweaved with branches of the collagen fiber bundles to form stereo reticular braided structures, other textile-used staple fibers are located on skeleton of the stereo reticular braided structures, reticular entwining is formed between the textile-used staple fibers mutually or between the textile-used staple fibers and the collagen fiber bundles and the branches of the collagen fiber bundles, and fiber is adhered or bound by the interstitial fibers. The method of the invention can take animal raw hide as raw materials and can be realized through following technical steps: screening the raw materials, dipping, unhairing, degreasing, defibering liquid, tanning, dewatering and drying, mixed liganding, adding the interstitial fibers, health preserving, opening, combing,laying net, spunlacing, and hot rolling, furthermore, the method of the invention can also take the animal leather after tanning as the raw material and can be realized through following steps: screening the raw materials, dipping, defibering the liquid, dewatering and drying, mixed liganding, adding the interstitial fibers, health preserving, opening, combing, laying net, spunlacing, and hot rolling.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HONGZHAN NEW MATERIALS
Apparatuses and methods for treating biological tissue to mitigate calcification
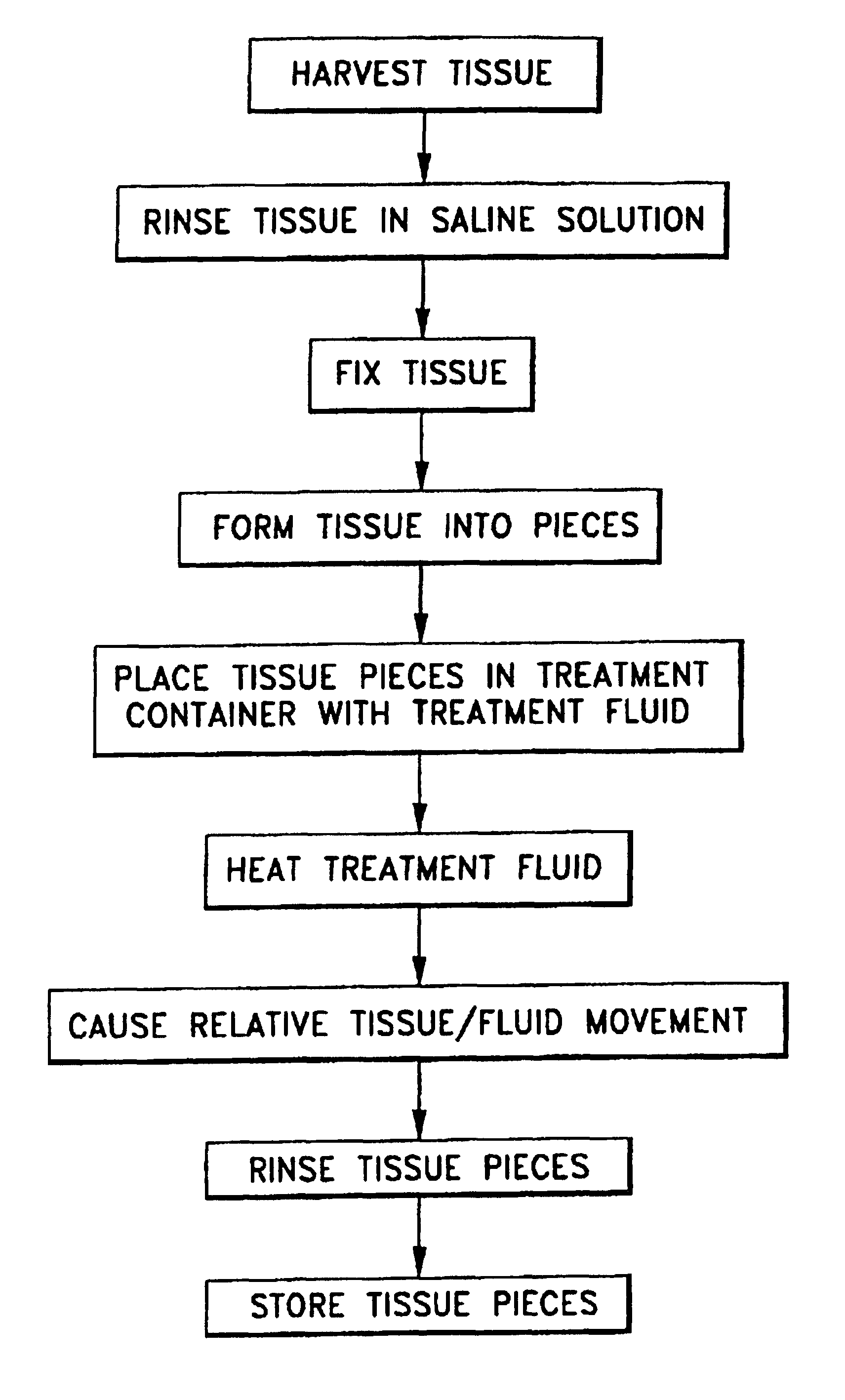
An apparatus for treating fixed biological tissue to inhibit calcification of the biological tissue following implantation thereof in a mammalian body. The apparatus includes a container for placing the biological tissue in contact with a treatment solution, structure to induce relative tissue / solution movement, and structure to heat the solution. The relative movement may be induced by shaking a container in which the tissue is immersed in the treatment solution, or by stirring the solution within the container. The movement may also be induced by flowing a treatment solution past the tissue to be treated. The tissue may be free to move in the treatment container, or may be restrained from gross movements. The flow may be part of a circulation system having a reservoir, with a heater being provided to heat the treatment solution in the reservoir. Alternatively, a treatment apparatus, including a fluid circulation system if desired, may be enclosed in an incubator. The tissue may be mounted in a planar configuration generally parallel to the direction of fluid flow. A flow column having a plurality of sections divided by perforated baffles may be used to treat multiple tissues at once.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
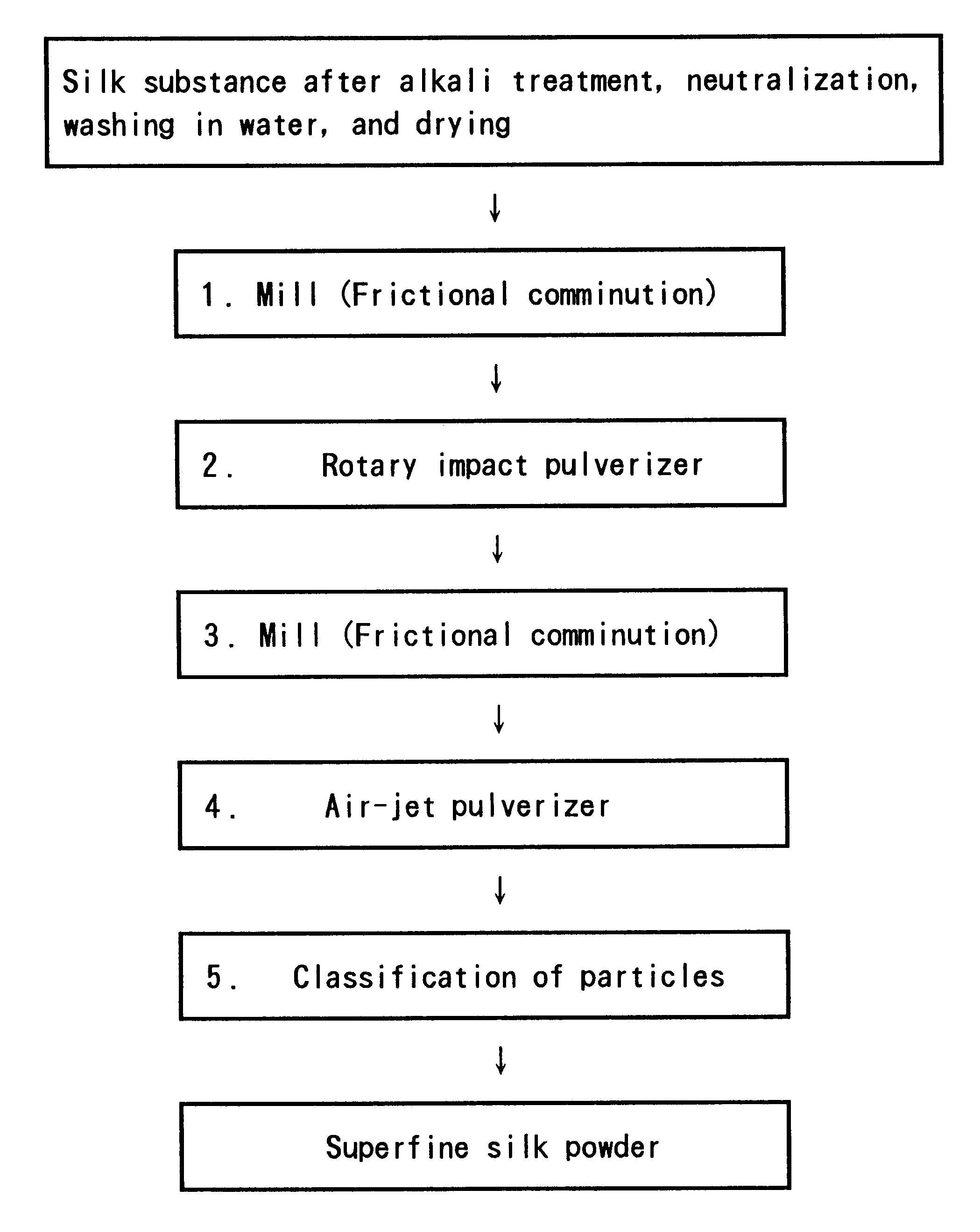
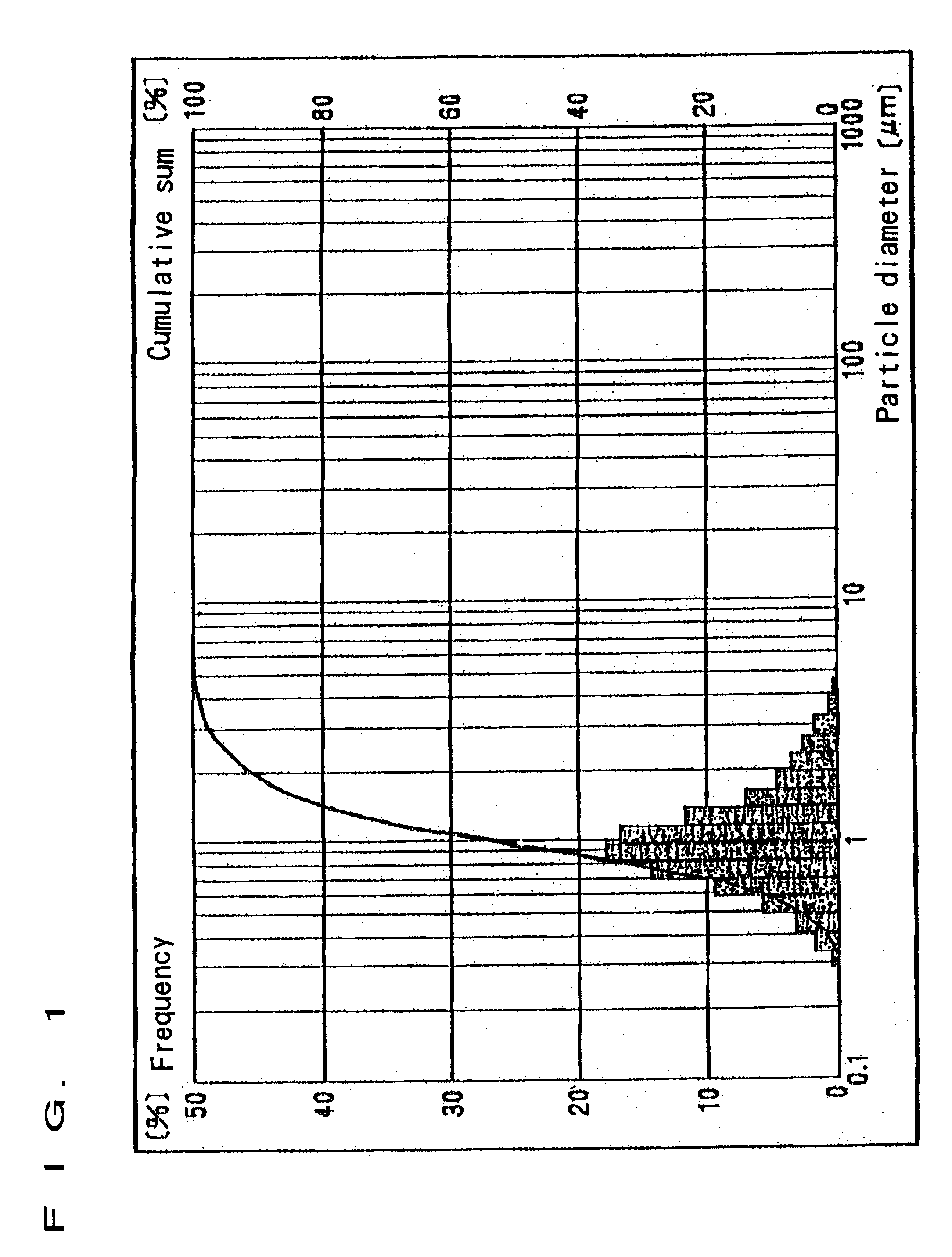
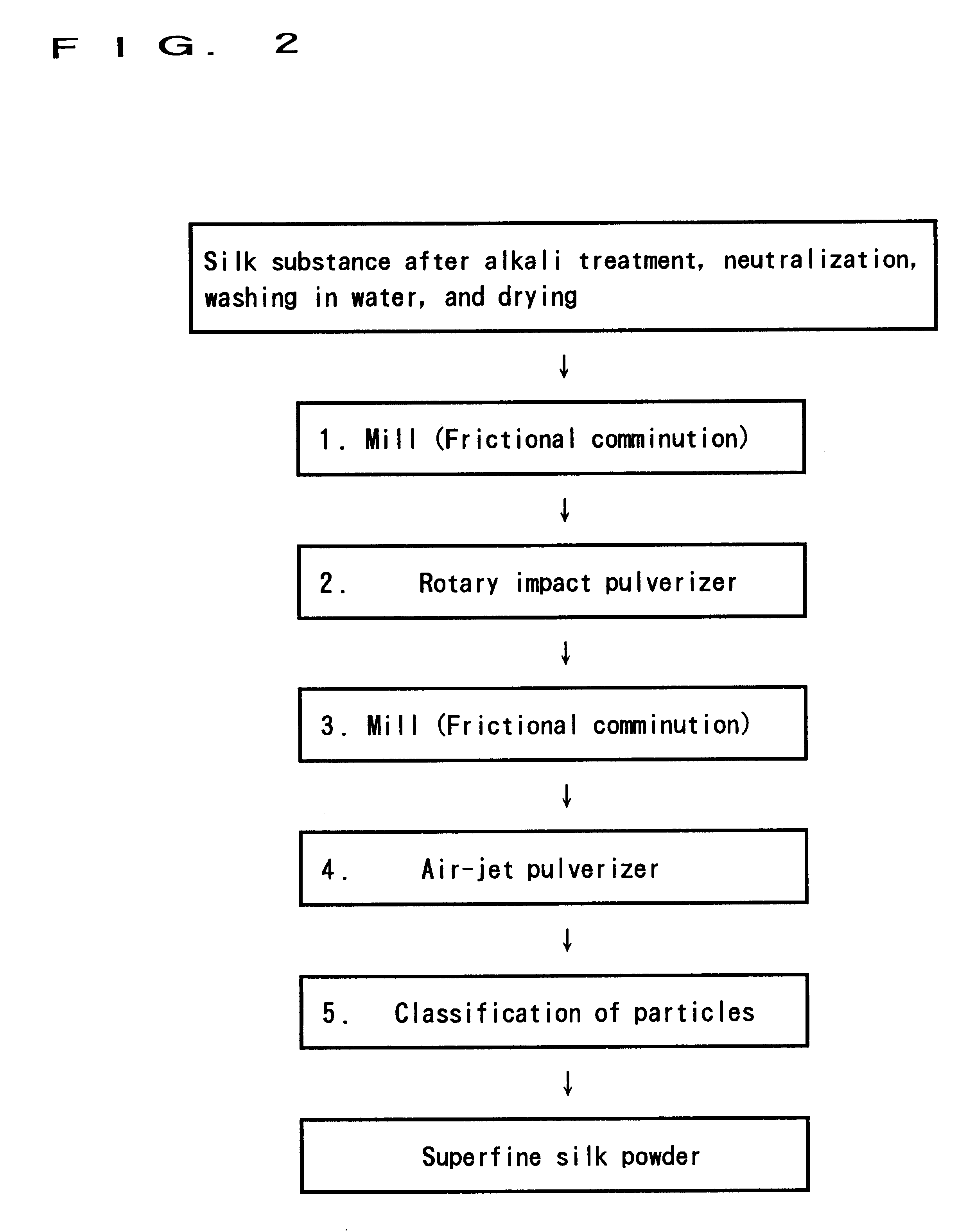
Method for manufacturing crystalline superfine silk powder
The main theme of the invention is to provide a method for manufacturing industrially, by mechanically comminuting silk yarn, crystalline silk fibroin powder below 3 mum in an average particle diameter, which can be used for various applications. A silk substance such as cocoon filament, silk yarn, or raw silk is brought into an alkali aqueous solution under a pressure of 1 through 5 atmospheric pressure at temperatures from 100° C. through 150° C. to reduce the tensile strength of the silk substance to around 0.02 g / d or less. Thereafter, the resultant silk substance is subjected to dealkalization and drying. Subsequently, the resultant dried silk substance is comminuted into powder below 3 mum in an average particle diameter. Thus, the crystalline silk fibroin powder below 3 mum in an average particle diameter is manufactured.
Owner:JAPAN AS REPRESENTED BY DIRECTOR GENERAL OF NAT INST OF SERICULTURAL & ENTOMOLIGICAL SCI MINIST OF AGRI FORESTRY & FISHERIES +1
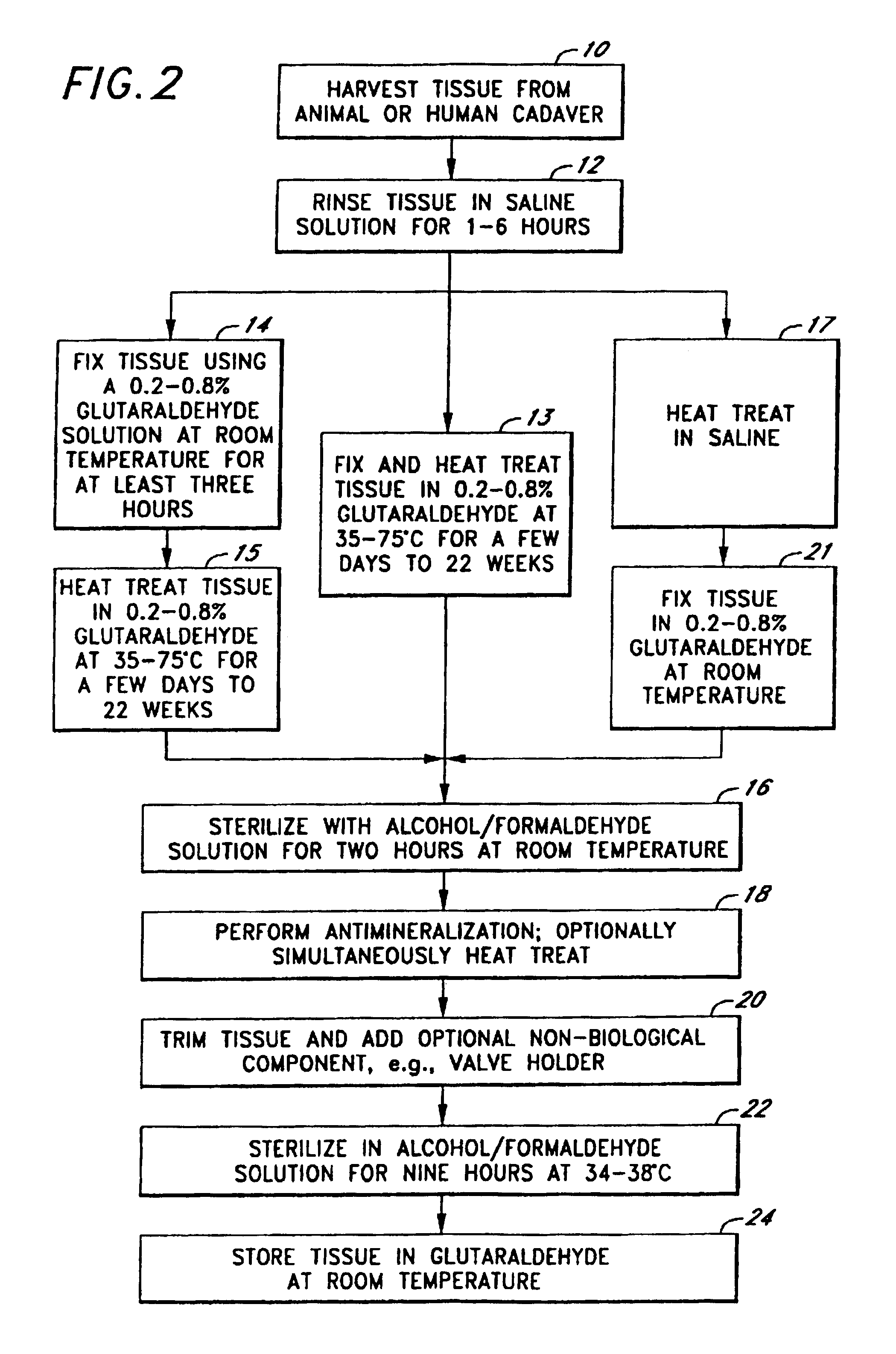
Methods for treating implantable biological tissues to mitigate post-implantation calcification
A method for treating fixed biological tissue inhibits calcification of the biological tissue following implantation thereof in a mammalian body. The method includes placing the biological tissue in contact with glutaraldehyde and then heating the glutaraldehyde. Alternatively, methods other than heating (e.g., chemical or mechanical means), for effecting polymerization of the glutaraldehyde may also be utilized. Alternatively, the tissue may be heat treated prior to fixing thereof. Alternatively, methods other than glutaraldehyde may also be used for fixing the tissue. The biological tissue may be so treated at any time prior to implantation thereof in a mammalian body.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
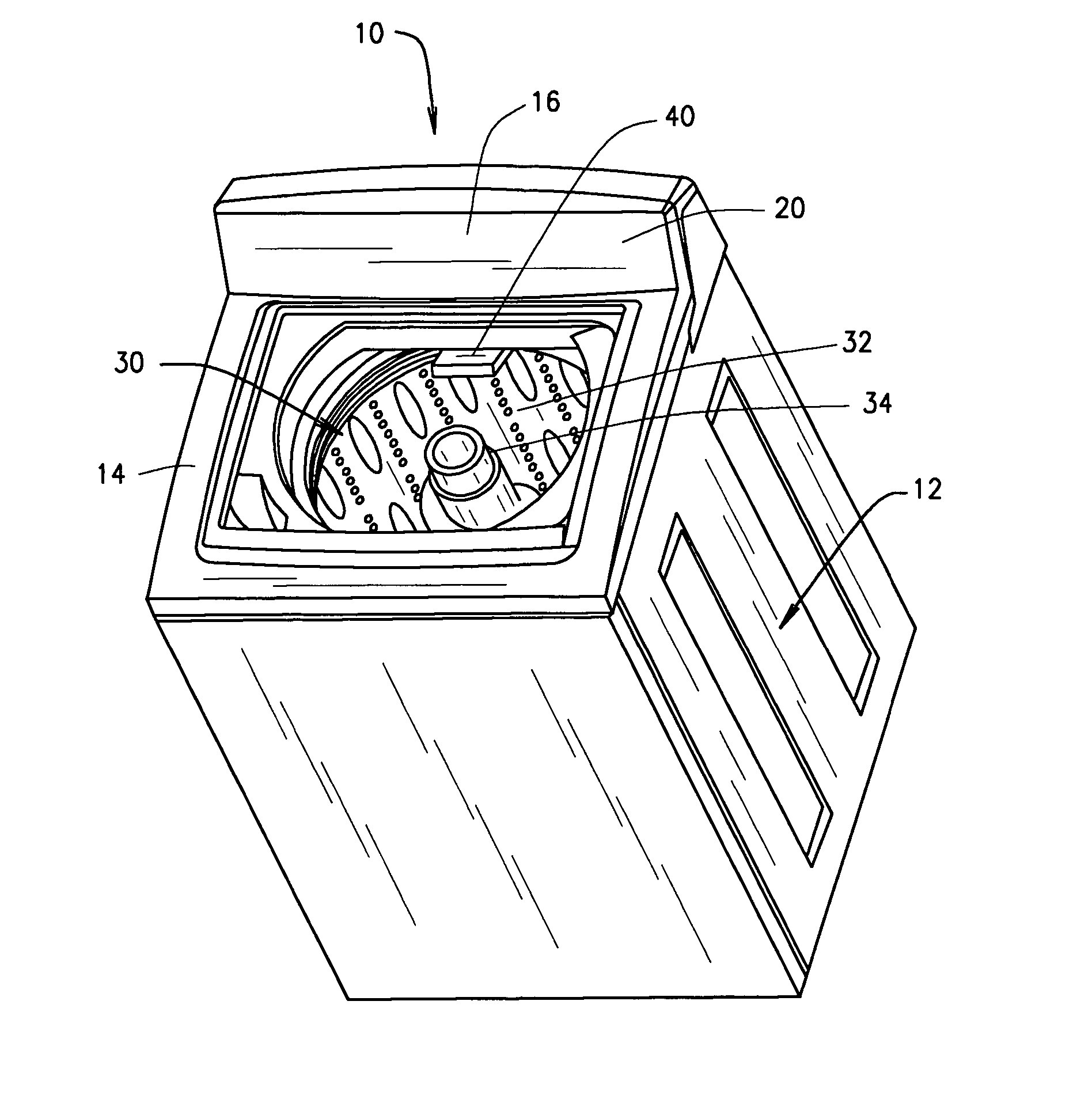
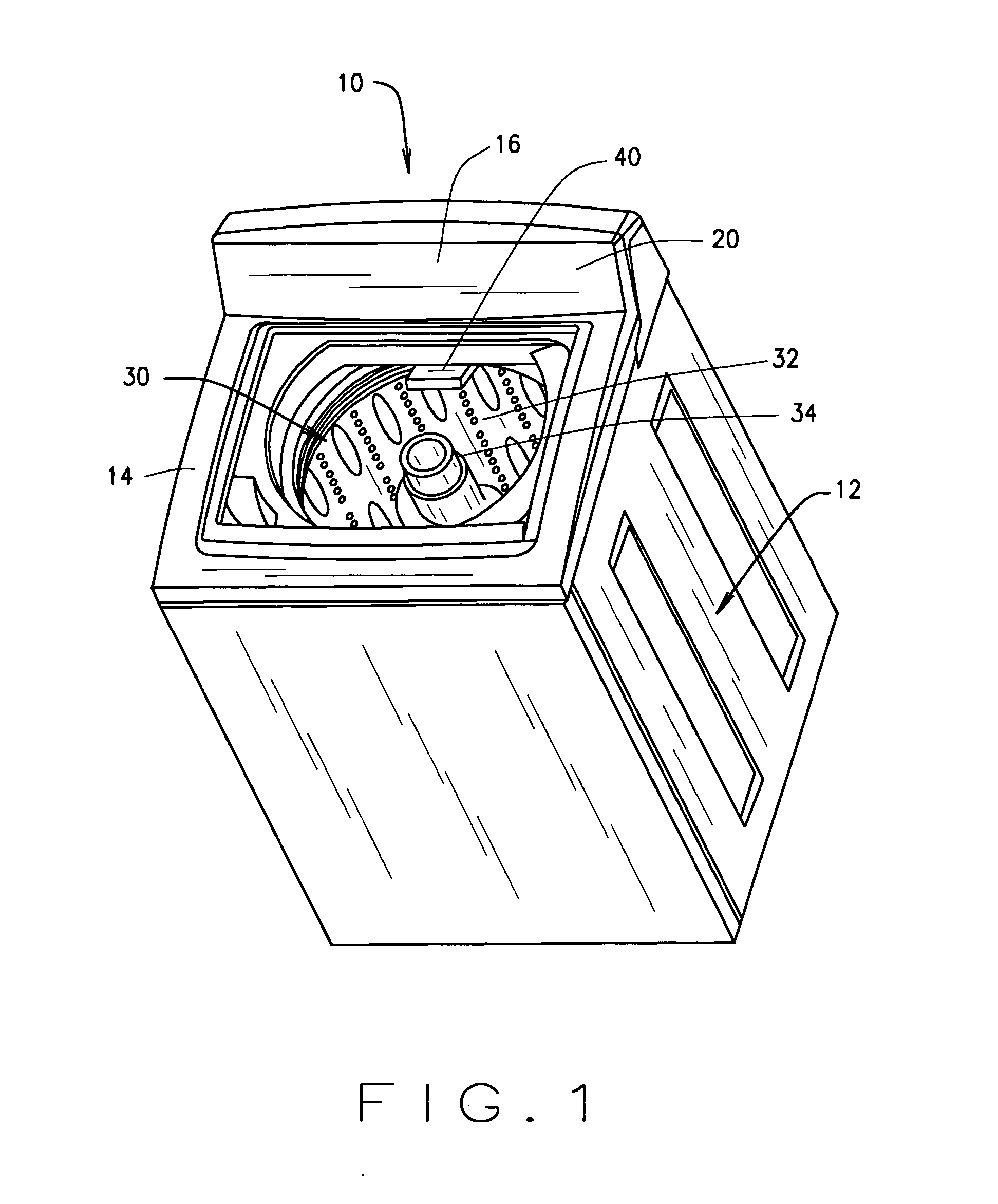
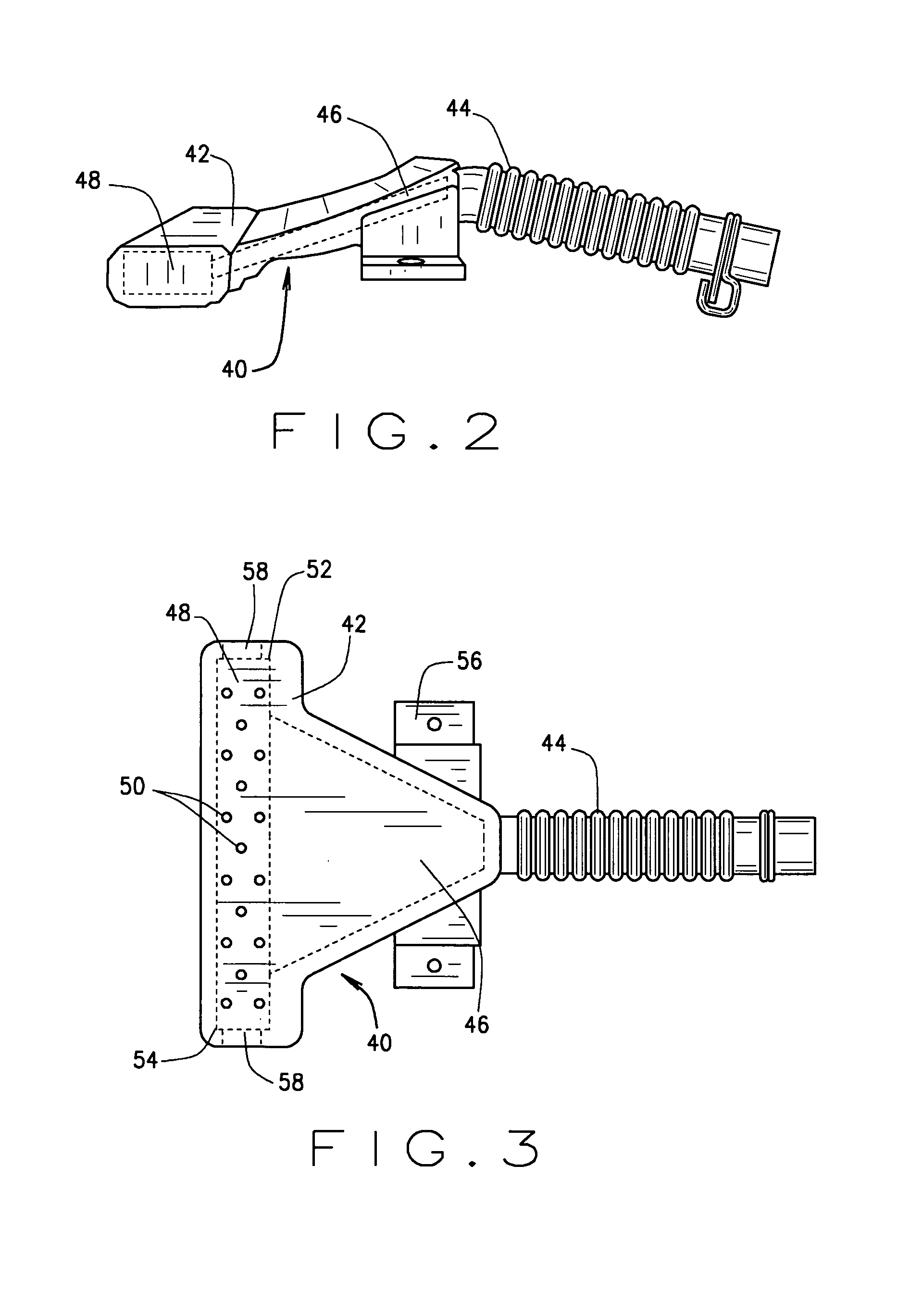
Spray fill device and method for using the same
A spray fill device for delivering water to a washing machine is provided. The spray fill device includes a body defining an inlet, an outlet port, a mounting port, and a plurality of outlet apertures in flow communication with the inlet. The spray fill device also includes a first valve coupled to the inlet, the valve configured to control a flow rate of water into the inlet. The spray fill device also includes a pressure relief mechanism coupled to the mounting port, the pressure relief mechanism inhibiting flow through the outlet port when a pressure within the body is less than a predetermined pressure.
Owner:HAIER US APPLIANCE SOLUTIONS INC
Fabric strip for spinning and its processing method
The invnetion relates to a spinning fiber rod comprised of 5-100% collagen fiber and residual textile fiber. Wherein, the process method comprises: screening material, dipping, defibering, degreasing, cleaning, dewatering, drying, opening to remove impurity, mixing, carding, and drafting. This invention can obtain material from wide source, has well applicability, high tensile strength, well moisture / oil absorption properties, and fit to spread in textile industry.
Owner:张立文
Reducing leather and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101851828ARandom croppingNo location differenceNon-adhesive dressingsTanning treatmentFiberApparent density
The invention discloses reducing leather and a preparation method thereof. The leather is mainly and three-dimensionally weaved by collagenous fiber obtained by defibrination of leather materials, and the apparent density thereof is 0.35g / cm3-1.4g / cm3. The preparation method of the leather comprises the steps: carrying out defibrination on the leather materials to prepare the collagenous fiber, forming web, carrying out hydroentanglement and wet-hot shrinkage and forming. The leather is reducing leather, the weaving structure, the apparent density, all strength indexes and wear resistance of which are approximate to those of true leather. Compared with the true leather, the reducing leather has the advantages that the leather is large and tidy and can be cut randomly, the weaving apparent density is consistent without location difference; and simultaneously, the raw materials of the reducing leather mainly adopt corner wastes in the leather-working industry. The promotion of the method can enhance the circulation and reutilization of resources in the leather-working industry, and is beneficial to realizing transformation from the traditional leather-working industry to the energy-saving and environment-friendly industry.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WUYUAN NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Silk nanofiber manufacturing method
InactiveCN104532365APromote swellingAvoid influenceAnimal materialSilk filament obtainingInorganic saltsFiber
The invention relates to a silk nanofiber manufacturing method, and belongs to the technical field of nano material manufacturing. The manufacturing method includes the steps that silk obtained after degumming treatment is transferred to a solution composed of an inorganic salt or weak acid or weak alkali small molecule compound, deionized water and alcohols, after binding force between nano fibrils in the silk is weakened through soaking, the silk solution is transferred to a high-voltage cell crushing machine or an emulsification machine or a pulp refiner or a crushing machine of a high-speed stirring device, and the soaked silk is mechanically crushed to obtain silk nanofibers. A silk nanofiber solution obtained through the method is similar to the shape of hydrogel, the silk nanofibers are obtained through centrifuging or filtering separation, manufacturing time is short, equipment is simple, operation influence factors are few, and control is convenient. The adopted small molecule compound avoids influences of strong acid or strong alkali on the silk nano fibrils, and the crushing machine can be used for quickly manufacturing the silk nanofibers on a large scale.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Method and device for producing a thread from silk proteins
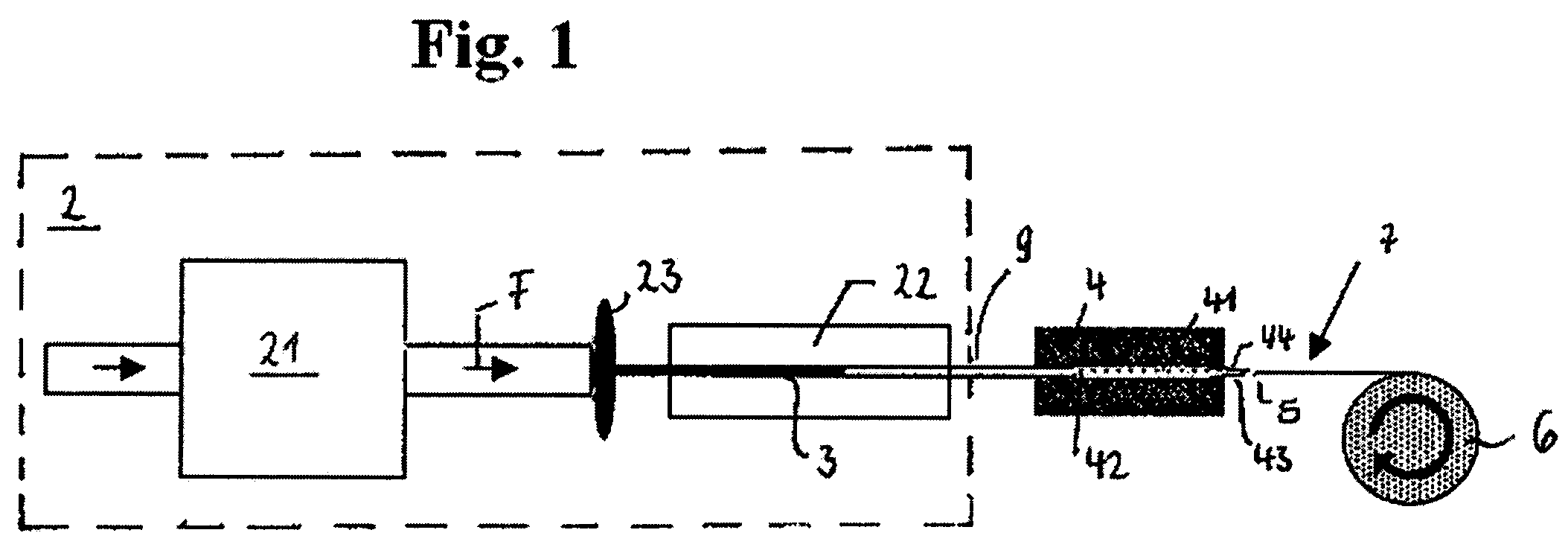
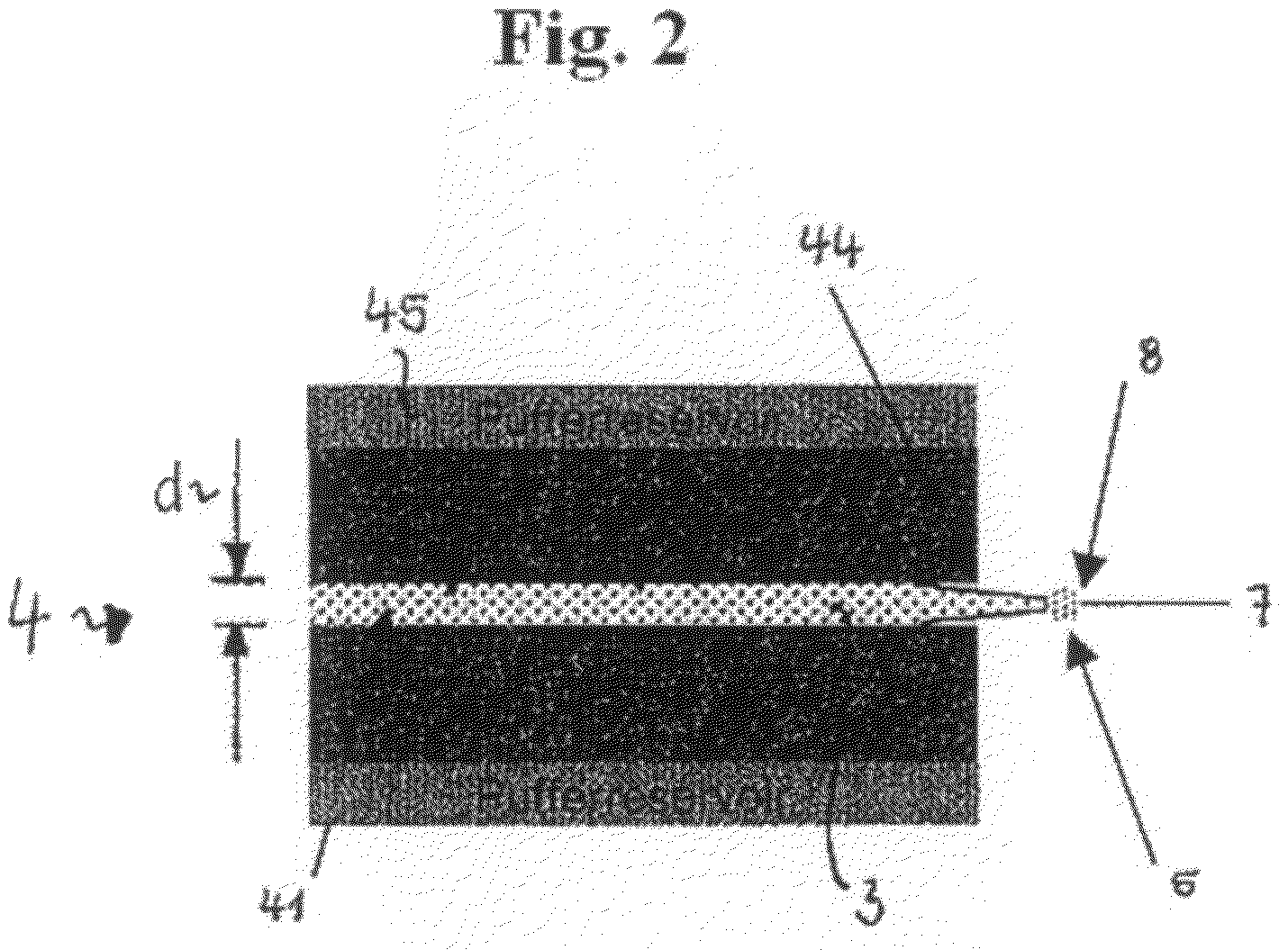
ActiveUS7868146B2Enhancing stability and processabilityEnsure continuous processingPeptide/protein ingredientsMonocomponent fibroin artificial filamentProduction lineEngineering
The present invention relates to a thread preparation process from silk proteins including an apparatus which is appropriate for performing the method. Furthermore, the invention is directed to the threads obtained therewith as well as the use thereof. The invention uses a diffusion unit leading to the production of high-quality silk threads with high yield.
Owner:AMSILK
Method of creating biological and biosynthetic material for implantation
InactiveUS7022348B2Maintain alignmentSuture equipmentsUnknown materialsCalcificationGradual increase
A method of creating an implantation material from biological and tissue engineered biosynthetic and biological tissue of autogenic, allogenic and xenogenic origin suitable for implantation into humans or animals as surgical and vascular prostheses. The resultant material inhibits in vivo calcification and provides a non-porous biomatrix which is impervious to angiogenesis and tissue ingrowth and suitable for the adhesion and retention of transplanted living cells such as endothelial cells, without the need for additional extracellular matrix protein coating. The method, which incorporates a gradual increase in glutaraldehyde concentration from 0% to no more than 5% weight / volume in a pH which is gradually changed from acid to alkaline at room temperature, maintains the micro-architecture and the cellular lining of the material. Additionally flexibility, compliance and haemo-compatibility along with strength and durability can be varied according to the end use. The glutaraldehyde penetrates the material gradually and completely, cross linking the collagenous components of the tissue.
Owner:KRYOCOR PTY LTD
Method for preparing collagen microfiber by use of ionic liquid mixing solvent
ActiveCN103554247AWide variety of sourcesSuitable for large-scale productionConnective tissue peptidesAnimal materialFreeze-dryingSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing collagen microfiber based on an imidazole type ionic liquid / dimethyl sulfoxide system. The animal leather is used as a raw material, and an imidazole type ionic liquid / dimethyl sulfoxide mixture is used as a treatment agent. The method comprises the following steps of treating at 90-130 DEG C to obtain a suspension, performing high-speed centrifugation to obtain a precipitate, and cleaning the obtained precipitate and freeze-drying to obtain the collagen microfiber. The collagen microfiber can be applied to the fields such as textile, high-molecular materials and the like. The adopted reagent ionic liquid is non-volatile and can be recycled, and dimethyl sulfoxide is a low-toxicity solvent, therefore, the preparation method is environment-friendly and has a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN ZHONGHUIDA SCI INSTR
Variably crosslinked tissue
InactiveUS7918899B2Minimal shrinkageImprove the immunitySuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHigh concentrationAnatomy
Non-glutaraldehyde fixation of an organ or a prosthesis for implantation in a mammal is based upon carbodiimide treatment. A solution containing a sterilizing agent, such as EDC, in combination with a coupling enhancer, such as Sulfo-NHS, and a high concentration of a diamine cross linking agent is used. As a result, only minimal surface reduction occurs during fixation, and the resultant products show a dramatic increase in resistance to calcification.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL DESIGN
Method for debriding bone, and bone debrided thereby
InactiveUS6837907B2Easy to disassembleSuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsPositive pressureSodium hydroxide
The invention is directed to a method of debriding bone including incubating the bone and associated soft tissue, with one or more debriding solutions where the debriding solution may include one or more alkaline solutions. Incubation is optionally carried out with one or more debriding agents including inert dry granular or particulate material including for example beads, and the granular phase of an alkaline agent, including for example granular sodium hydroxide. The incubating may be carried out with agitation. In another embodiment, the medullary canal of the bone is subjected to a positive pressure stream of debriding solution under conditions sufficient to loosen the associated soft tissue from the bone at the interface of the soft tissue and bone. In a further embodiment, the debriding solution is provided as a gel.
Owner:LIFENET HEALTH
Production method of natural colorful mulberry silk floss
InactiveCN102560696AReduce churnImprove protectionAnimal materialDe-gumming silkAlkaline waterColorful appearance
The invention discloses a production method of natural colorful mulberry silk floss. The traditional common technology is difficult to reserve the natural color of the colorful cocoons, and the color is faded into white in the processing process. The production method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: selecting cocoons and removing impurities from colorful cocoons; permeating with alkaline water; reeling silk from cocoons to remove the pupa; cleaning and dewatering; adding a degumming agent to keep color and refining; removing gum and grease; decontaminating, rinsing and dewatering; adding a spun silk softening agent; regulating the pH value to 4-8; and dewatering and drying to obtain the silk floss. The method has the advantage of simple technology, and the produced silk floss has the advantages of colorful appearance, even color and luster, low trash content, soft mouthfeel, good tearing toughness and no peculiar smell and can achieve the standard of producing high-quality mulberry silk floss quilts.
Owner:HUZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Pod discharging, bleaching process
The present invention belongs to the field of silkworm cocoon silk reeling off method in filature, and is one kind of silkworm cocoon degumming and bleaching process. The technological process includes the successive steps of: compounding degumming liquid, soaking silkworm cocoon and steaming with water vapor for 20 min, eliminating liquid, rinsing with clear water, dewatering, compounding bleaching liquid, soaking silkworm cocoon and steaming with water vapor for 40 min, eliminating liquid, rinsing with clear water, dewatering, compounding silk protecting liquid, swinging and washing for 30 min, eliminating liquid and stoving. The silkworm cocoon degumming and bleaching process has greatly shortened degumming time from traditional 24 hr to 20 min, homogeneous bleaching and few silk corrosion, and the silk treated with the silk protecting liquid is bright, smooth and without silkworm cocoon smell.
Owner:于清春
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com