Wearable and convertible passive and active movement training robot: apparatus and method
a passive and active movement, wearable technology, applied in the field of motor function training devices, can solve the problems of affecting the patient's daily life, severe pain, affecting the patient's voluntary movement, etc., and achieves the effect of convenient use in the home, effective and accurate stretching training, and facilitating patient voluntary movemen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
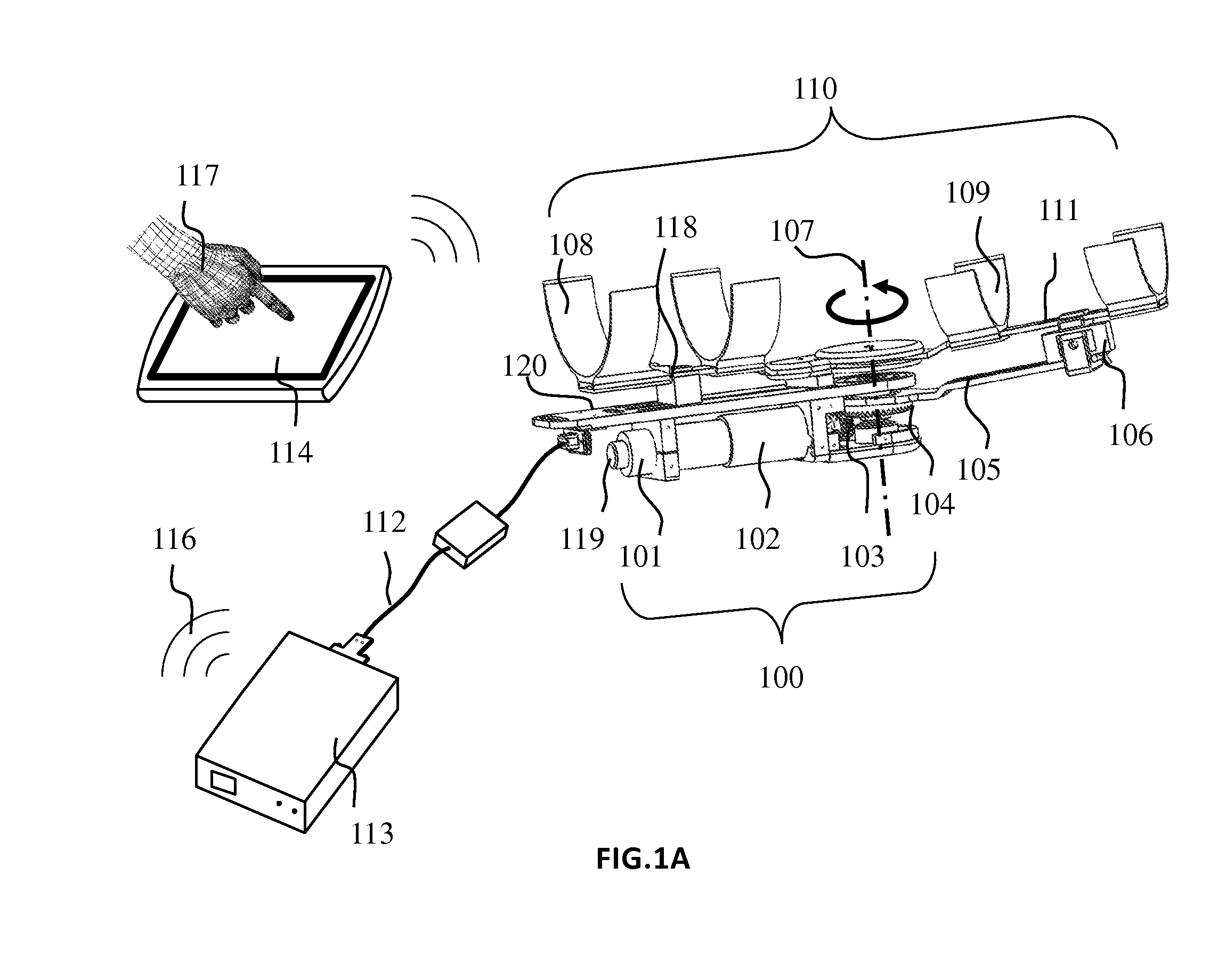
[0048]FIG. 1A shows a diagrammatic view of passive / assistive wearable device for elbow joint.
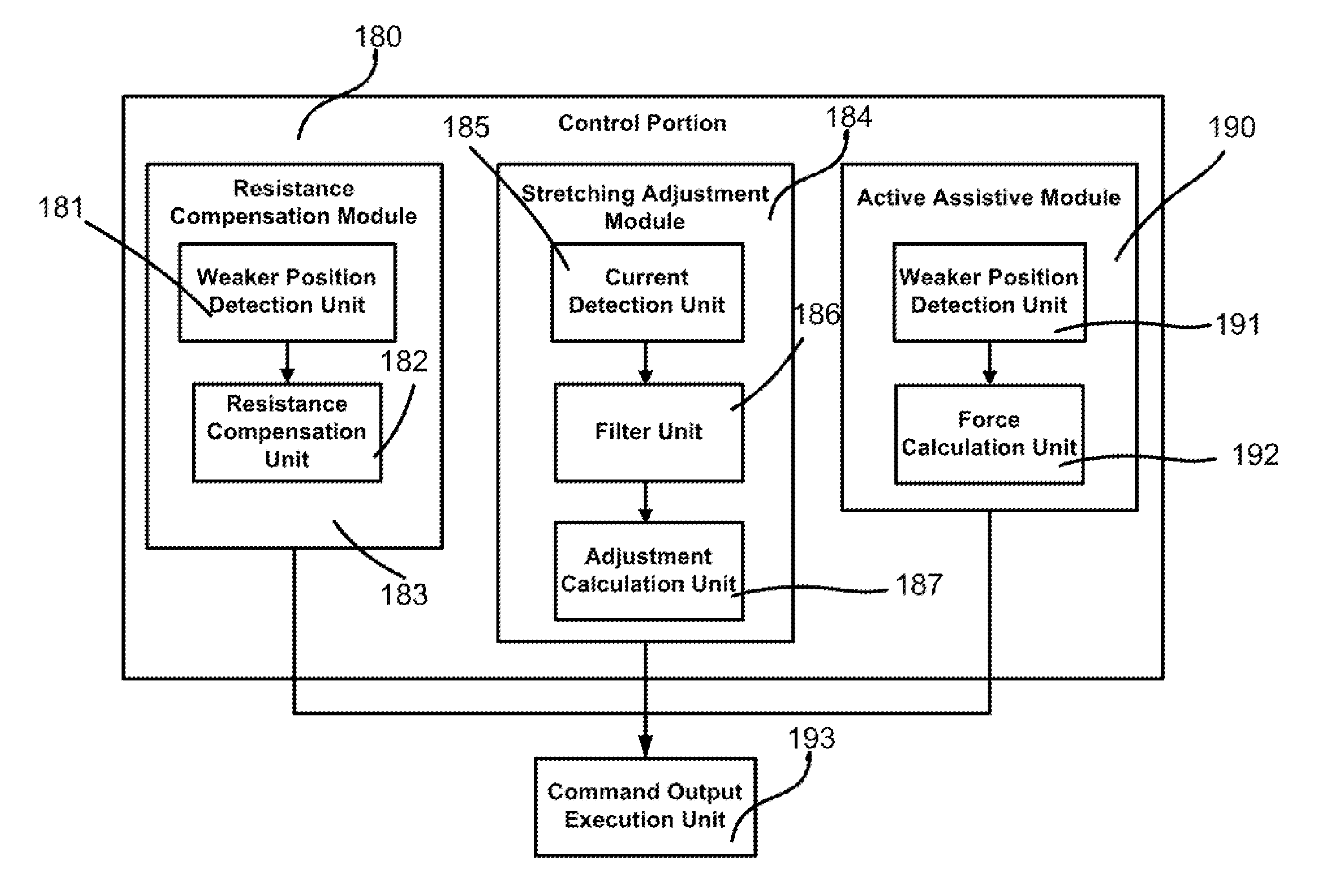
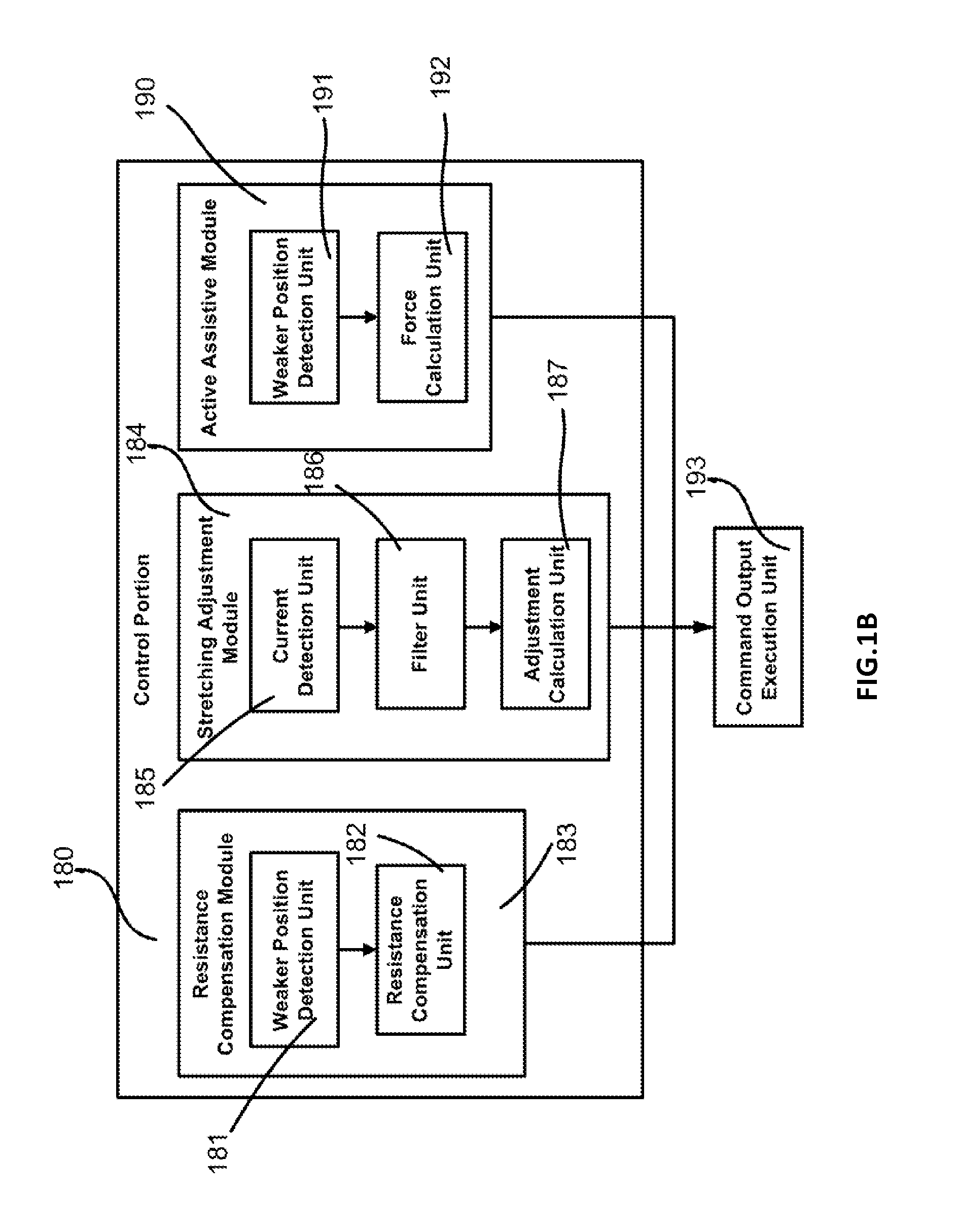
[0049]In one particular embodiment of the device, the wearable elbow device comprises: 1) a securing portion for securing the training device; 2) a movement portion for securing the limb and is rotatably connected to the securing portion; 3) a motor driving portion secured at the securing portion and is driven by electrical current, wherein the current changes when the limb applies a torque to the movement portion; 4) gearing means for connecting the motor driving portion and the movement portion, wherein the gearing means and the motor driving portion can be moved when the limb applies a torque to the movement portion; 5) a control portion connected to the training device via a control bus, wherein a) the control portion can control the motor driving portion to drive the movement portion to rotate via the gearing means; b) the motor driving portion has a position sensor, which can detect th...
second embodiment
[0060]FIG. 4 shows the second illustrative embodiment of the invention for ankle joint. The wearable ankle device is similar to the structure of the first illustrative embodiment, and the differences are: the securing component 110 (including 108,118,109 and 111) is replaced by the securing component 140 (including 141,142,144 and 145). In the second embodiment of the invention, the securing part comprises the securing plate 120, the first securing strap 144 and the first retainer 142. The movement portion comprises the securing plate 105, the second retainer 141 and the second securing strap 145. The second retainer 141 can rotate with respect to the first retainer 142 along the rotation axis 143, and the securing component 140 can be replaced by other securing setups, such as knee securing portion or wrist securing portion to achieve different limbs training functions.
[0061]As shown in FIG. 5A, FIG. 5B, and FIG. 5C, patients use the same lower limb training device while they are s...
third embodiment
[0063]FIG. 6 shows a third embodiment of the invention installed on the ground for different joints of the limb training device. This device can be installed in different ways to achieve assisted and resistance training for different joints (elbow flexion / extension, wrist flexion / extension, supination / pronation, ankle dorsiflexion / plantarflexion).
[0064]Similar to above first and second embodiment, the third embodiment is a training device comprising a securing portion, a movement portion, a motor driving portion, gearing means and a control portion Said securing portion comprises a securing base 616, a first securing plate 614 for securing the motor driving portion, and a height adjusting mechanism 606, the height of the first securing plate 614 can be adjusted via the height adjusting mechanism 606 so as to suit different heights of the joints. Said movement portion comprises a limb securing comprises a limb retainer 607 and a second securing plate 612; said limb retainer 607 is se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com