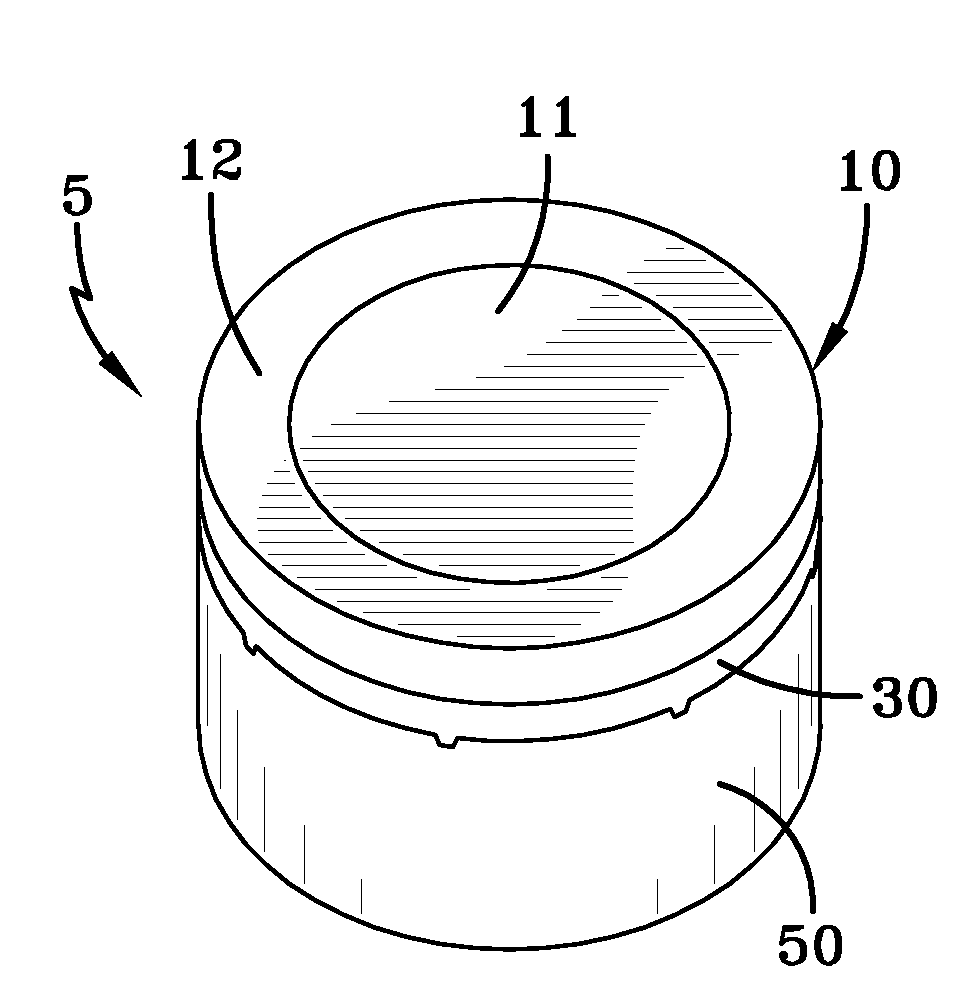
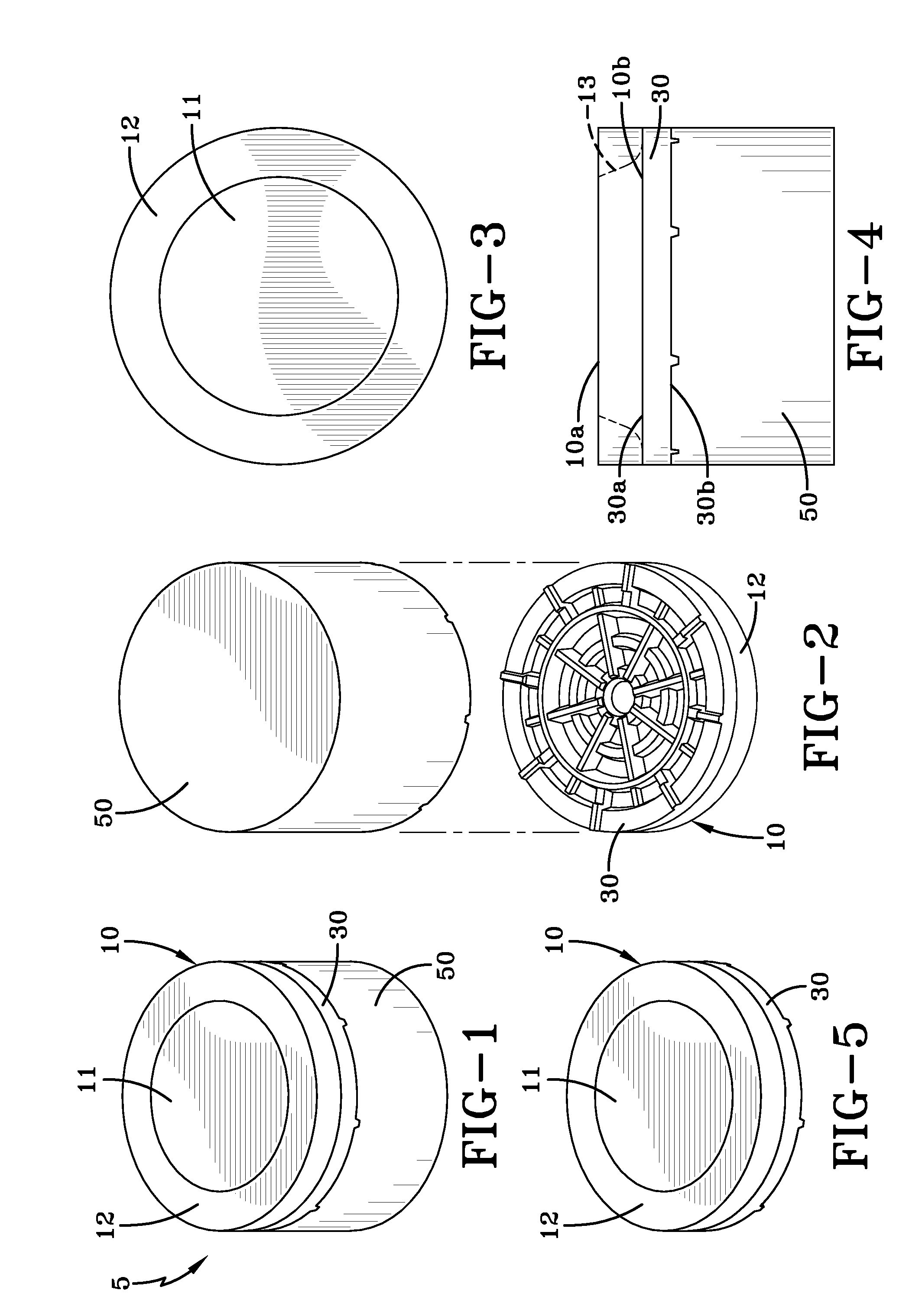
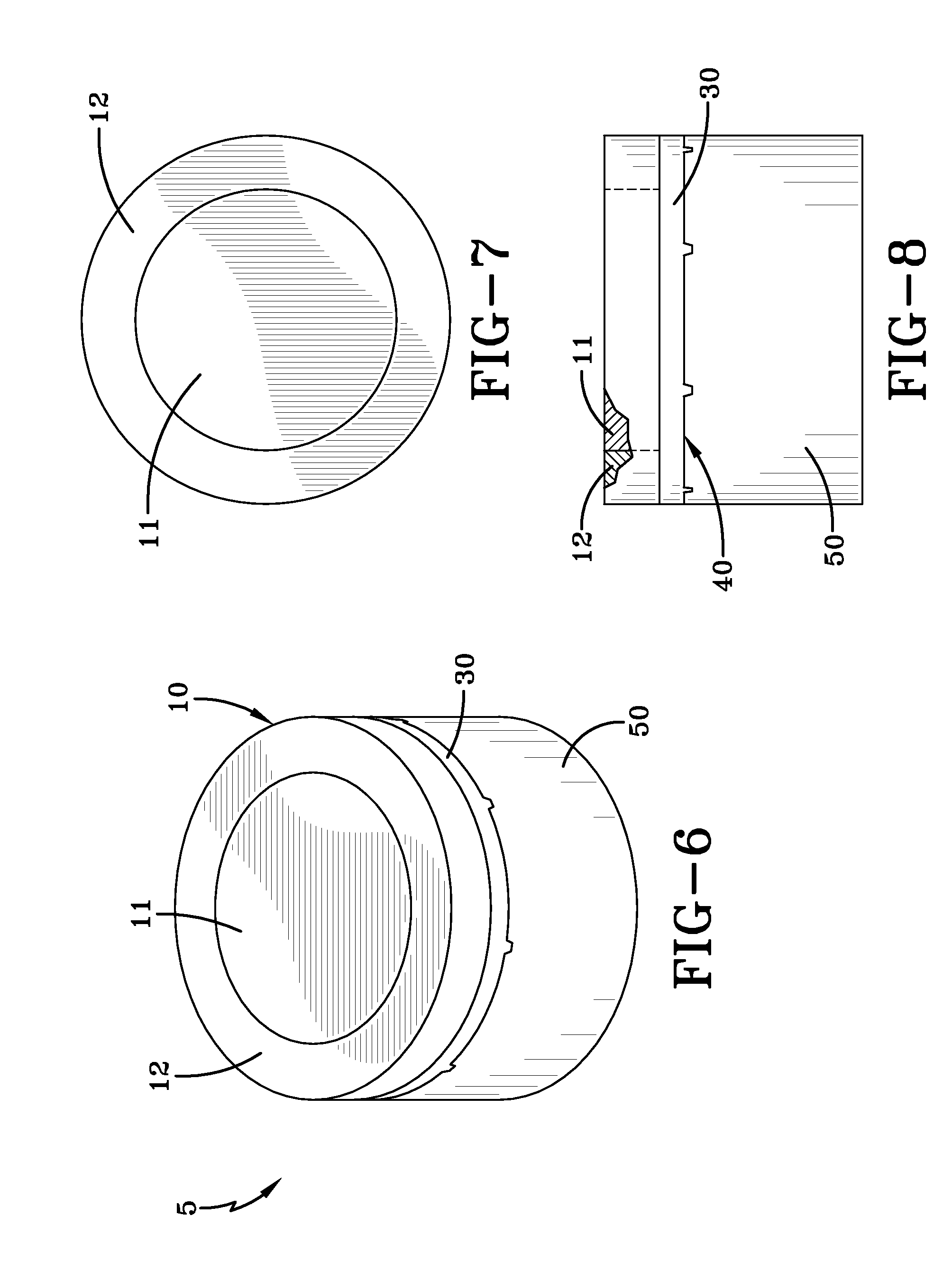
Composite polycrystalline diamond body
a polycrystalline diamond and composite technology, applied in the field of composite polycrystalline diamond bodies, can solve the problems of pdc being unable to cut rock or stone, affecting the quality of the material,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0106]A number of samples with different diamond configurations were prepared and evaluated for impact and abrasion resistance. The impact and abrasion resistance tests performed on these samples are standard tests in the PDC industry.
[0107]Description of impact test: This test evaluates the resistance of the PDC cutter to damage due to being struck by a solid object with a specific amount of energy. The impact test was performed by dropping a certain mass from specific height to produce 20 joules on energy on the impacted PDC. The PCD edge which was held at a 15° angle. Each time the mass is dropped on the PDC cutter, the cutter is examined visually and the area damaged (the area of the top surface of the PDC) after each hit is recorded, if the area damaged exceeds 25% of the total surface, the test is stopped, otherwise, the test is repeated 10 times. The total area damaged after the final hit (that would be the 10th hit if the PDC cutter does not exceed 25% area damage after any ...
example # 1
Example #1
[0109]In this example the design of the PCD layer was made with two components, a fine-grained diamond ring surrounding a coarse-grained diamond core as shown in FIG. 39a. The fine-grained diamond powder was compacted using 1000 PSI pressure. The coarse-grained diamond powder was leveled with a rod and compacted by hand; no device was used to apply extra pressure on the coarse grained diamond. When the diamond powder compaction was done the cross section of the coarse / fine diamond interface was rectangular, a straight vertical line and a straight horizontal line separated the diamond layers. There is no curvature or taper at the interface, and no corner radii. The product was processed under high pressure in excess of 55 kbar and temperature about 1500° C., The parts were afterwards machined to final dimensions, outside diameter of 0.529″ (13.44 mm) and a total height of 0.520″ (13.44 mm). FIG. 39b depicts the designed PCD layer with fine-grained diamond at the edge. FIG. ...
example # 2
Example #2
[0110]This example is similar to example #1, the design of the PCD layer was made with two components, a fine-grained diamond ring surrounding a coarse-grained diamond core as shown in FIG. 39c. However, the fine-grained diamond was not compacted; the coarse-grained diamond was leveled with a rod without any compaction. The cross section of the fine-grained diamond ring is a rectangle. Similar to the first example, when the diamond powder was loaded in the cup the cross section of the coarse / fine diamond interface was rectangular, a straight vertical line and a straight horizontal line separated the diamond layers. There is no curvature or taper at the interface, and no corner radii. The product was processed under high pressure and finished as the previous example. FIG. 40b is an SEM picture taken of the cross section of the PDC part mentioned above, after it has been processed in HPHT and finished.
[0111]It is noted that after processing in HPHT, the interface between the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com