Secondary battery
a secondary battery and battery technology, applied in the field of secondary batteries, can solve the problems of deterioration of the negative electrode, reliability of the secondary battery, and suppress the output characteristics of the secondary battery, and achieve the effects of high output, high capacity, and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0051]In this embodiment, a secondary battery of one embodiment of the present invention is described with reference to FIGS. 1A to 1C and FIGS. 2A and 2B.
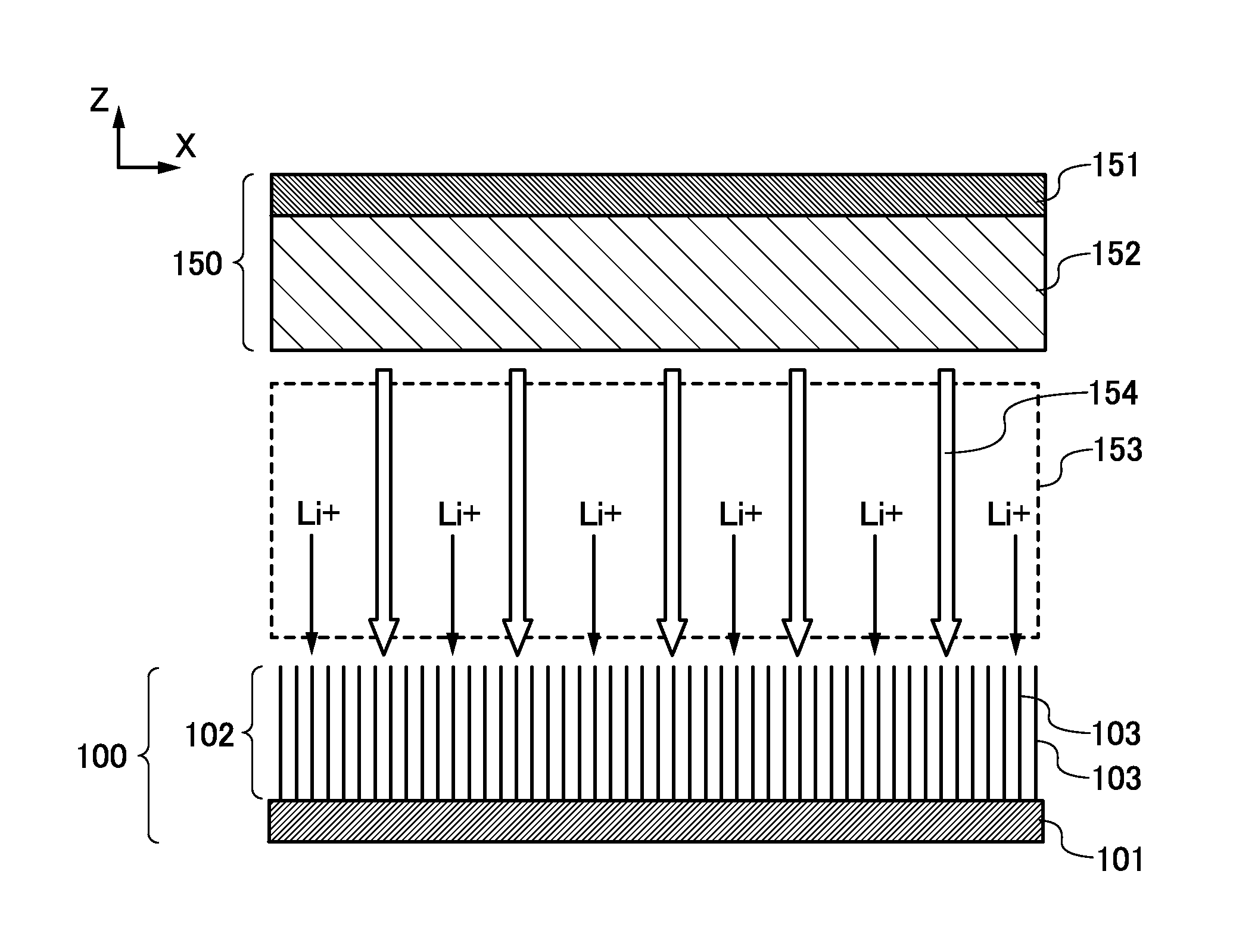
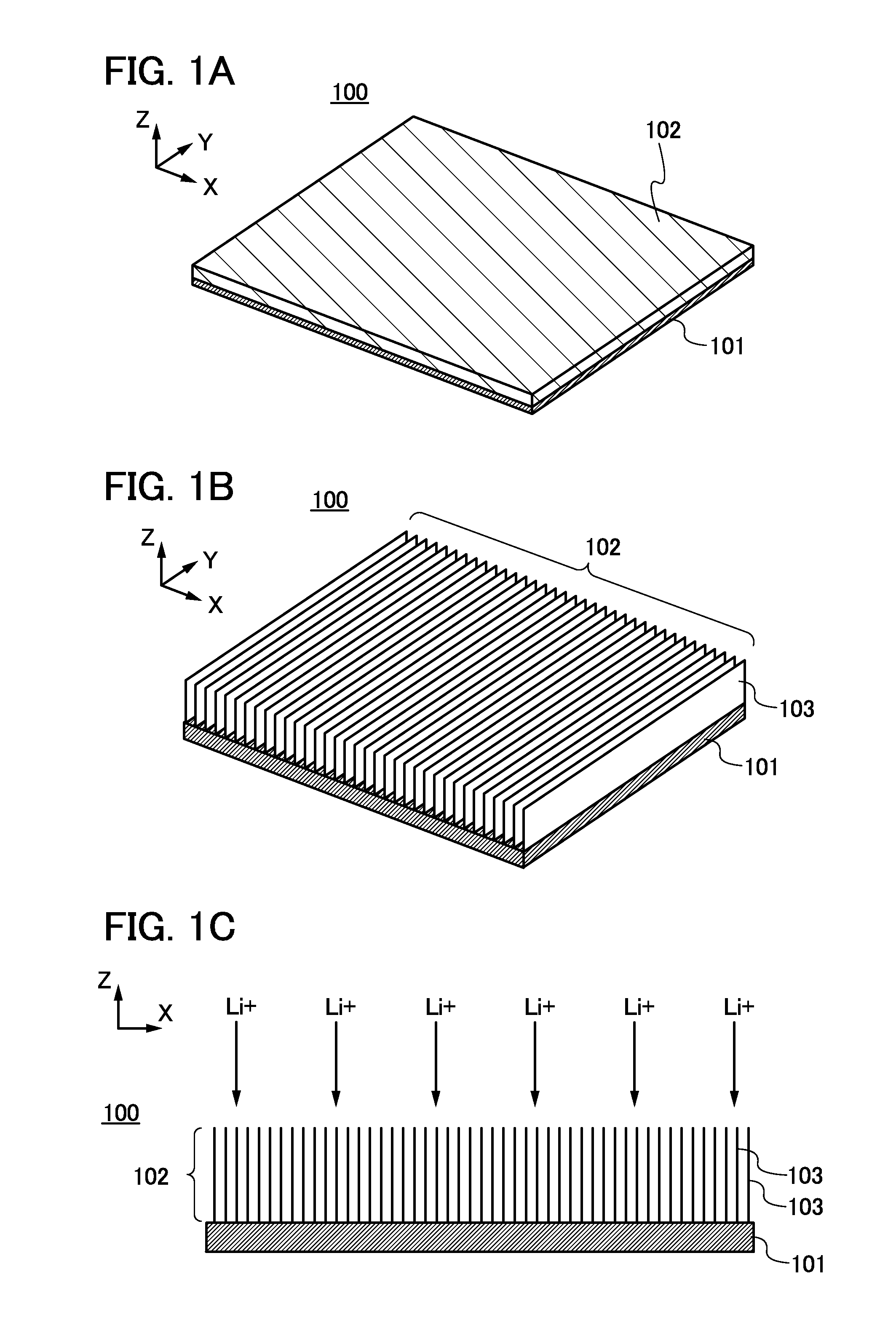
[0052]FIG. 1A is a perspective view of a negative electrode. A negative electrode 100 has a structure in which an active material layer 102 is provided over a current collector 101. Note that although the active material layer 102 is provided on one surface of the current collector 101 in FIG. 1A, the active material layer 102 may be provided on both surfaces of the current collector 101.
[0053]The current collector 101 can be formed using a material which has high conductivity and is not alloyed with carrier ions such as lithium ions, e.g., a metal typified by stainless steel, gold, platinum, zinc, iron, copper, aluminum, titanium, or tantalum, or an alloy thereof. Alternatively, the current collector 101 can be formed using an aluminum alloy to which an element which improves heat resistance, such as silicon, titanium, neodymium,...
embodiment 2
[0080]In this embodiment, termination of edges of a plurality of graphene layers included in graphite that is crystalline carbon is described with reference to FIGS. 8A to 8C.
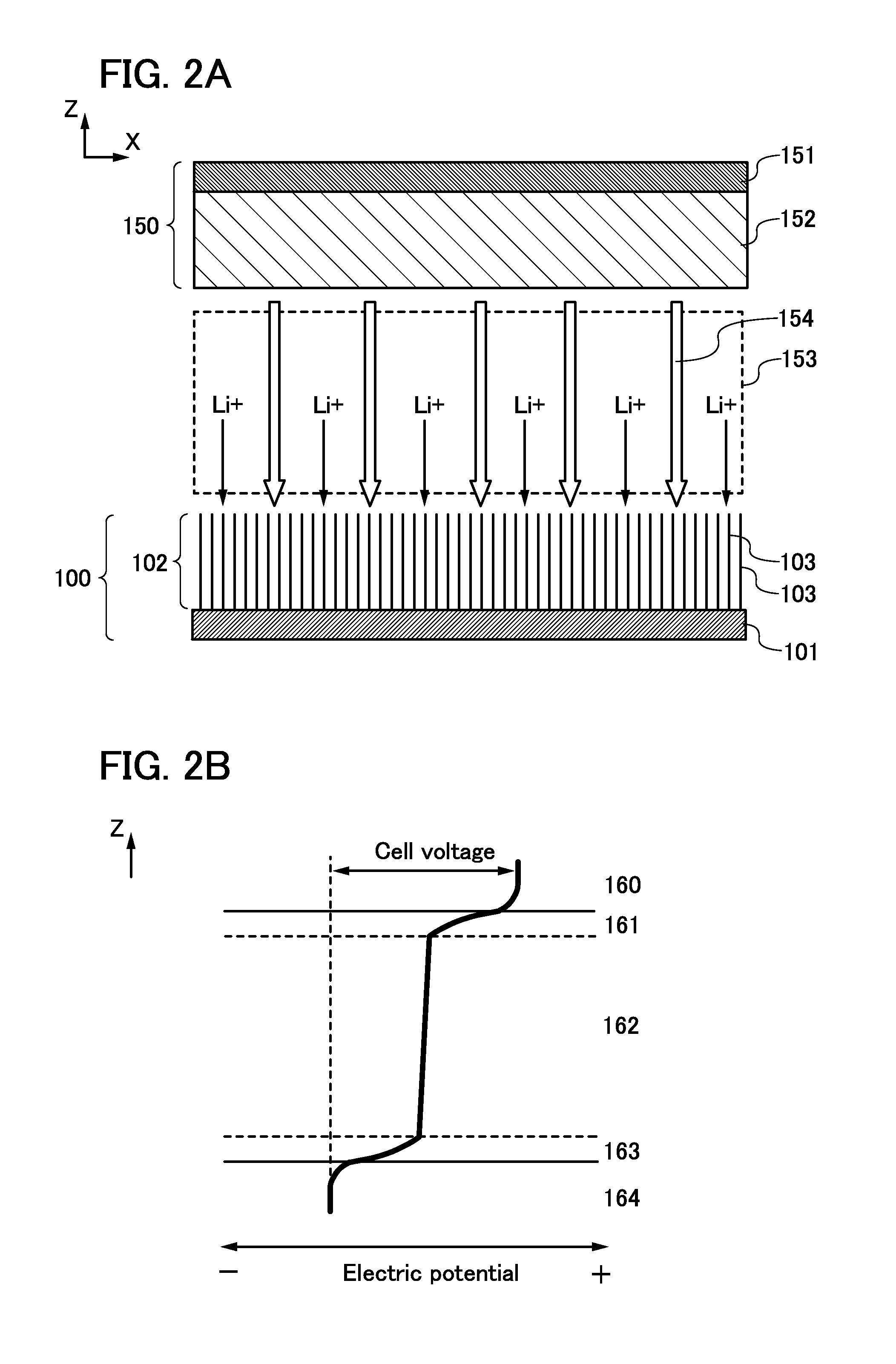
[0081]FIG. 8A illustrates the negative electrode 100 in FIG. 1B described in Embodiment 1. The current collector 101 is illustrated at the back of the drawing and the active material layer 102 is illustrated at the front for convenience. The active material layer 102 includes the plurality of graphene layers 103, and surfaces of the plurality of graphene layers are stacked in parallel to each other.
[0082]There are carbon atoms having one or more dangling bonds in edges of the plurality of graphene layers 103 exposed to an electrolyte solution. The dangling bond can be regarded as a defect in the edge of the graphene layer. To deactivate and stabilize the graphene layer having such a dangling bond, the defect is repaired by terminating the dangling bond. Specifically, one or more of groups such as —O—Si, —O—P, —...
embodiment 3
[0093]In this embodiment, a variety of structures of secondary batteries described in Embodiments 1 and 2 are described with reference to FIGS. 9A and 9B and FIGS. 10A and 10B.
(Coin-Type Secondary Battery)
[0094]FIG. 9A is an external view of a coin-type (single-layer flat type) secondary battery, part of which also illustrates a cross-sectional view of part of the coin-type secondary battery.
[0095]In a coin-type secondary battery 450, a positive electrode can 451 serving also as a positive electrode terminal and a negative electrode can 452 serving also as a negative electrode terminal are insulated and sealed with a gasket 453 formed of polypropylene or the like. A positive electrode 454 includes a positive electrode current collector 455 and a positive electrode active material layer 456 which is provided to be in contact with the positive electrode current collector 455. A negative electrode 457 is formed of a negative electrode current collector 458 and a negative electrode acti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com