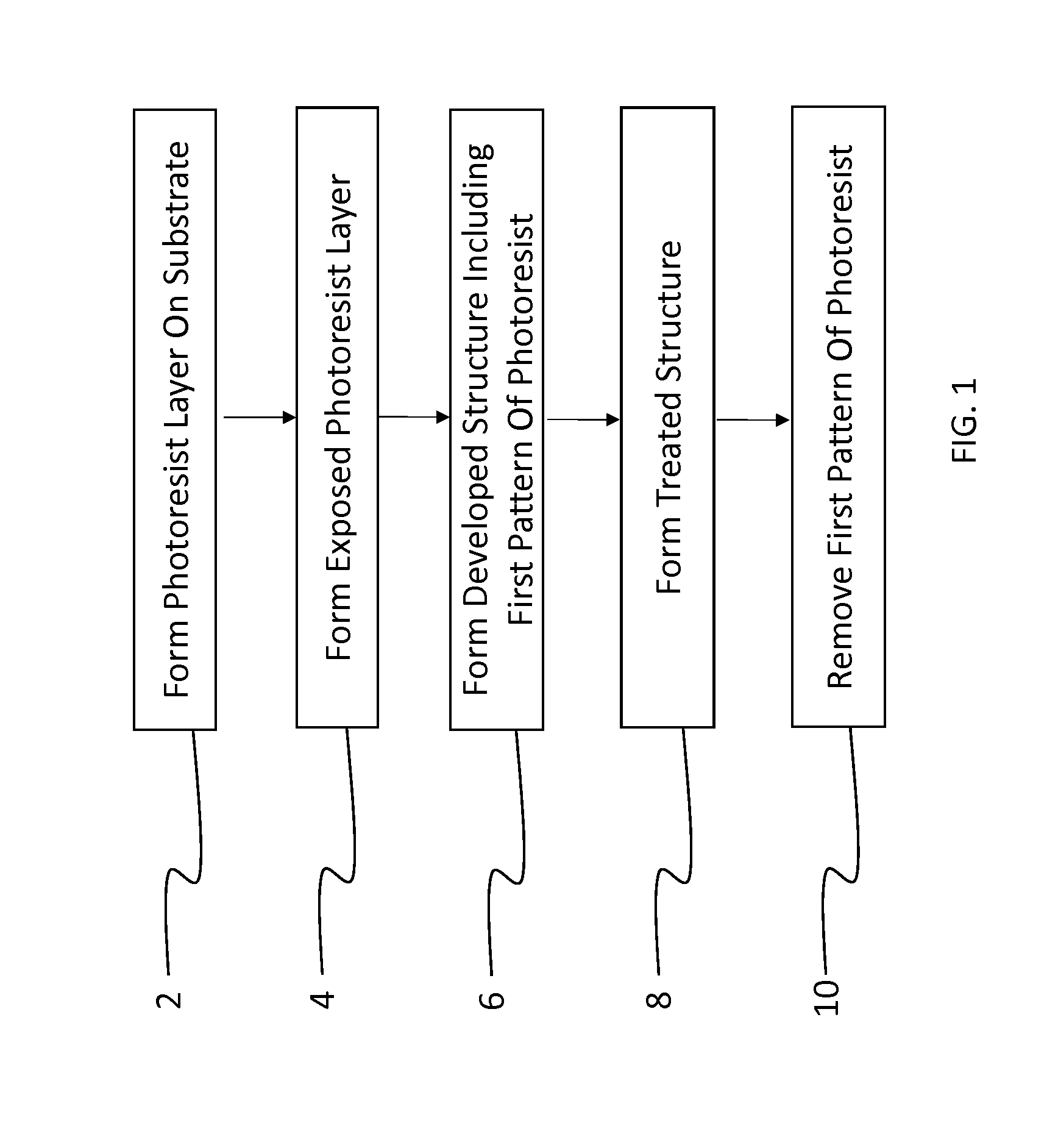
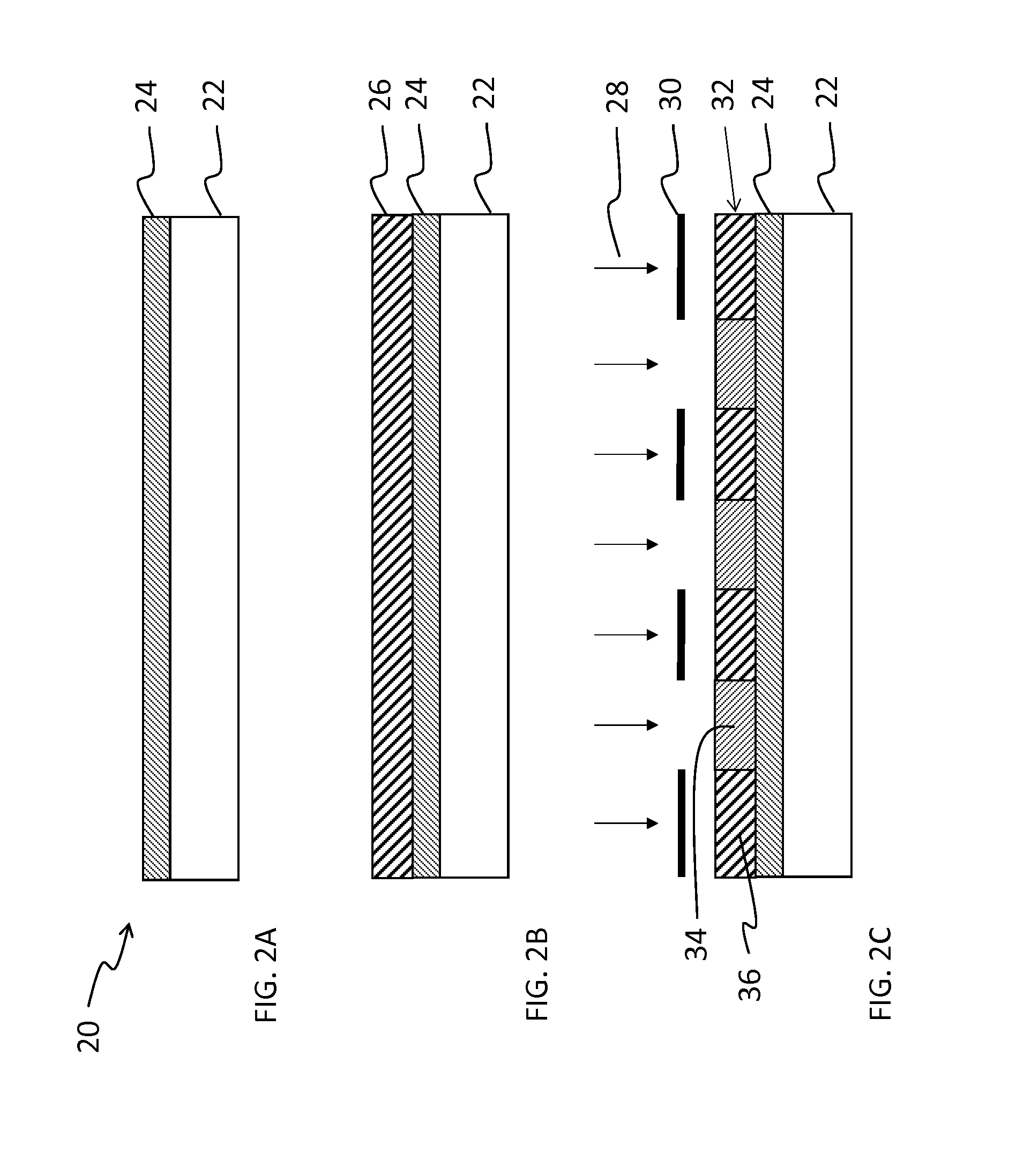
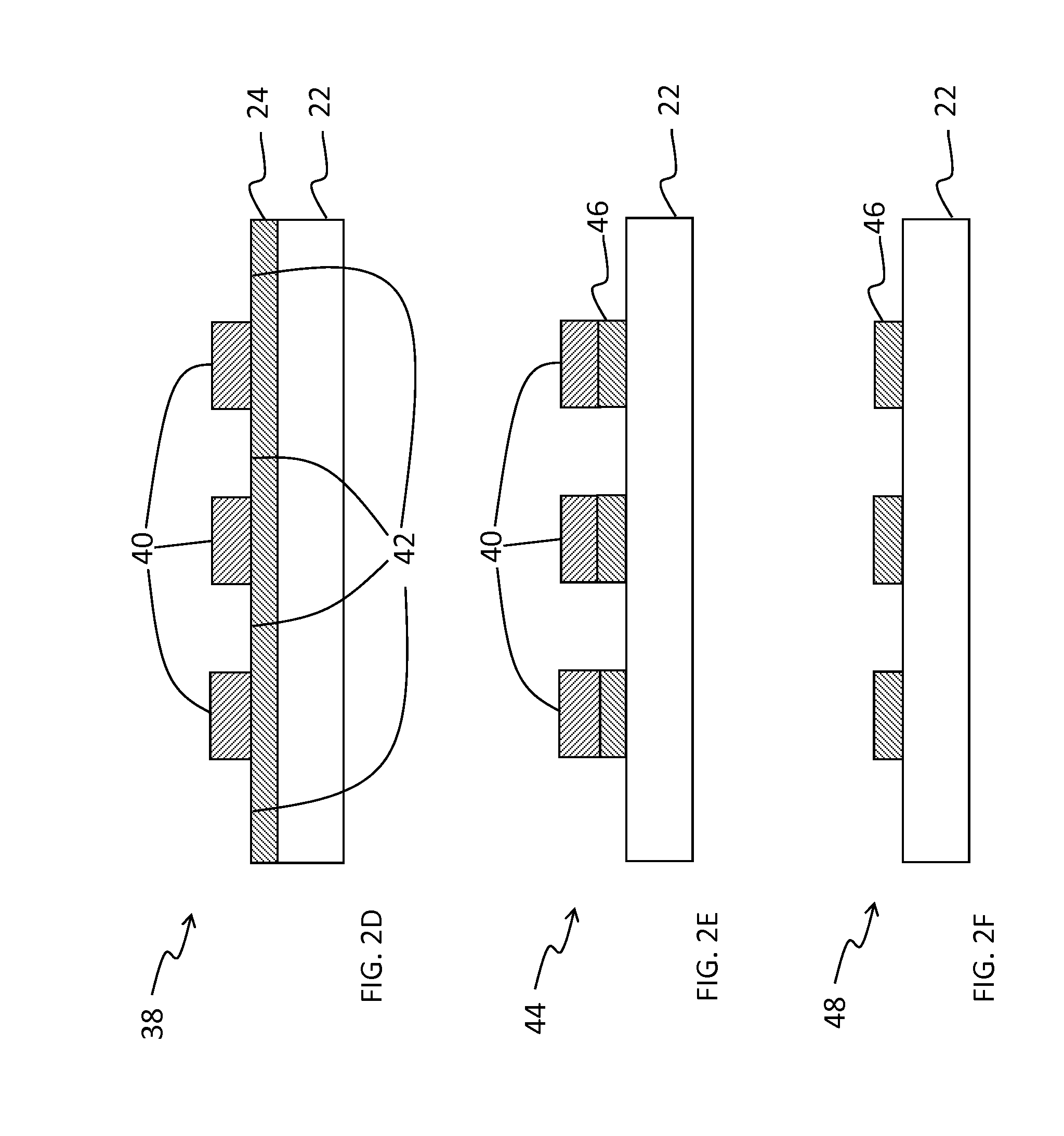
Method of patterning a device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
General Embodiment 1
[0062]In this embodiment, the first solvent is one that has a high degree of discrimination between solubilizing exposed and unexposed regions of the photoresist layer. Typically, the first solvent dissolves the unexposed regions at a moderate rate, but dissolves the exposed (switched) region at a much lower rate, preferably at least 10× lower. This helps produce an image with reasonable contrast and tolerable processing latitude, but an image may take longer than desired to develop appropriately. The second solvent is one that dissolves the unexposed regions at a rate greater than the first solvent rate, and preferably, also dissolves the exposed regions a rate higher than the first solvent rate. That is, the second solvent is generally a stronger solvent than the first solvent for both exposed and unexposed areas. Both should be selected to have a low interaction with sensitive, active organic materials if present during processing. Preferably the first and sec...
embodiment 2
General Embodiment 2
[0064]Here, the first solvent is one that has a high degree of discrimination between solubilizing exposed and unexposed regions of photoresist layer. Typically, the first solvent dissolves the unexposed regions at a moderate rate, but dissolves the exposed (switched) region at a much lower rate, preferably at least 10× lower. This helps produce an image having reasonable contrast and with good processing latitude, but an image may sometimes take longer than desired to develop appropriately. The second solvent in this embodiment is one that has higher solubilizing power than the first solvent with respect to removing the unexposed regions, but generally lacks sufficient solubilizing power to dissolve the exposed photoresists alone. For example, the first solvent, although it shows some development and good discrimination, may be too slow to be practical on its own. Conversely, the second solvent may be too fast to control, and although it is not capable of stripp...
embodiment 3
General Embodiment 3
[0066]Here, the first solvent generally provides low solubilizing strength with respect to both the exposed and unexposed regions of the photoresist. The second solvent is one that can solubilize both exposed and unexposed portions, but has a higher dissolution rate for the unexposed portions. When sufficient second solvent is added to the first solvent, the developing solution is capable of selectively solubilizing unexposed regions, i.e., dissolving unexposed regions at a rate that is at least 10 times higher than solubilization of the exposed areas. In this embodiment, the volume percentage of the second solvent is in a range from 20 to 80%, preferably 25 to 60%. The stripping solution will include the second solvent, optionally with a small amount of the first solvent or protic solvent or both. The volume of the second solvent in the stripping solution in this embodiment is at least 80%, preferably at least 90%.
[0067]An advantage of certain embodiments of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com