Compositions and methods to improve the therapeutic benefit of indirubin and analogs thereof, including meisoindigo
a technology of indirubin and analogs, applied in the field of hyperproliferation diseases including oncology, can solve the problems of inability to meet preclinical testing and federal regulatory requirements for clinical evaluation, failure or disappointment of chemical agents in human clinical trials, and inability to rationally and successfully discover useful therapies, etc., to improve the utility of chemical agents with suboptimal performance, improve the effect of dose determination and schedule, and improve the therapeutic benefi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of Meisoindigo
[1056]Prior Process
[1057]To synthesis meisoindigo, typically, add equal molar amount of 2-hydroxyindole and N-methyl-indolinyl-diketone, glacial acetic acid (2.0 L of glacial acetic acid for one mole of the reaction substances), and hydrochloric acid (concentrated, 6.67 ml of HCl for one mole of the reaction substances) into three-neck flask, heat to 70-80° C., stir for 2 h, cool to room temperature. Bulk brown crystal precipitates are then formed. Filter, and sequentially wash with glacial acetic acid, dH2O, and ethanol. The melting point is measured. It should be between 235-237° C. Filter, and sequentially wash with glacial acetic acid, dH2O, and ethanol. Melt point is measured. It should be between 235-237° C.
[1058]Newly Developed Process
[1059]An outline of the process is shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Reaction solution*Reaction ConditionsPurification ProcessAcetic acid (15v)70-80° C. for 3 hrsCool to 25-30° C., filter,Conc. HCl (0.05v)wash with acetic acid (5v)...
example 2
Effect of Meisoindigo on Viability of Cancer Cell Lines
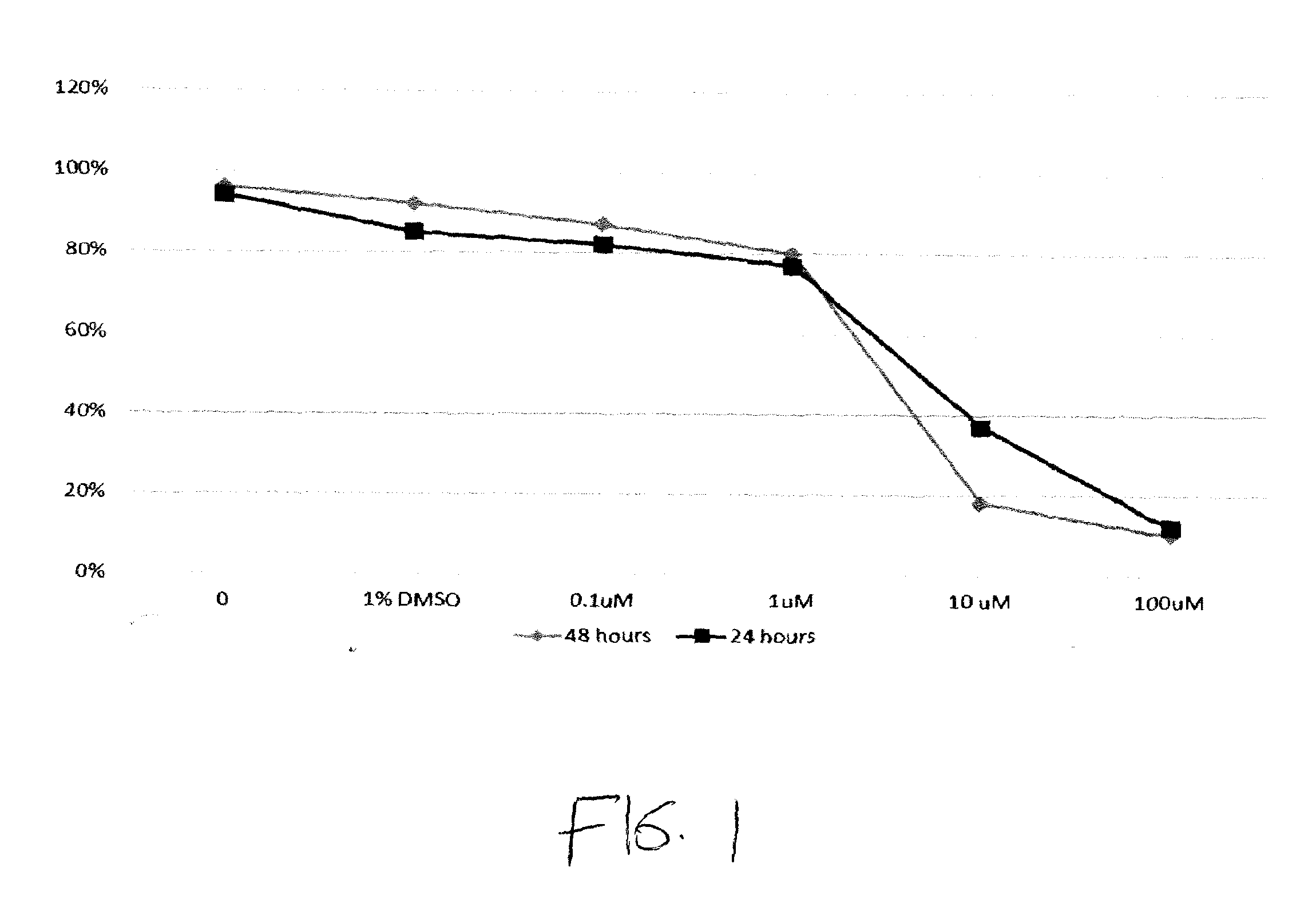
[1077]FIG. 1 shows the viability of the AML cell line MV 4-11 (FLT-3 ITD) after meisoindigo treatments. Viability at 48 hours is shown by (♦); viability at 24 hours is shown by (▪). Results are shown for a control, 1% DMSO without meisoindigo, 0.1 μM meisoindigo, 1 μM meisoindigo, 10 μM meisoindigo, and 100 μM meisoindigo.
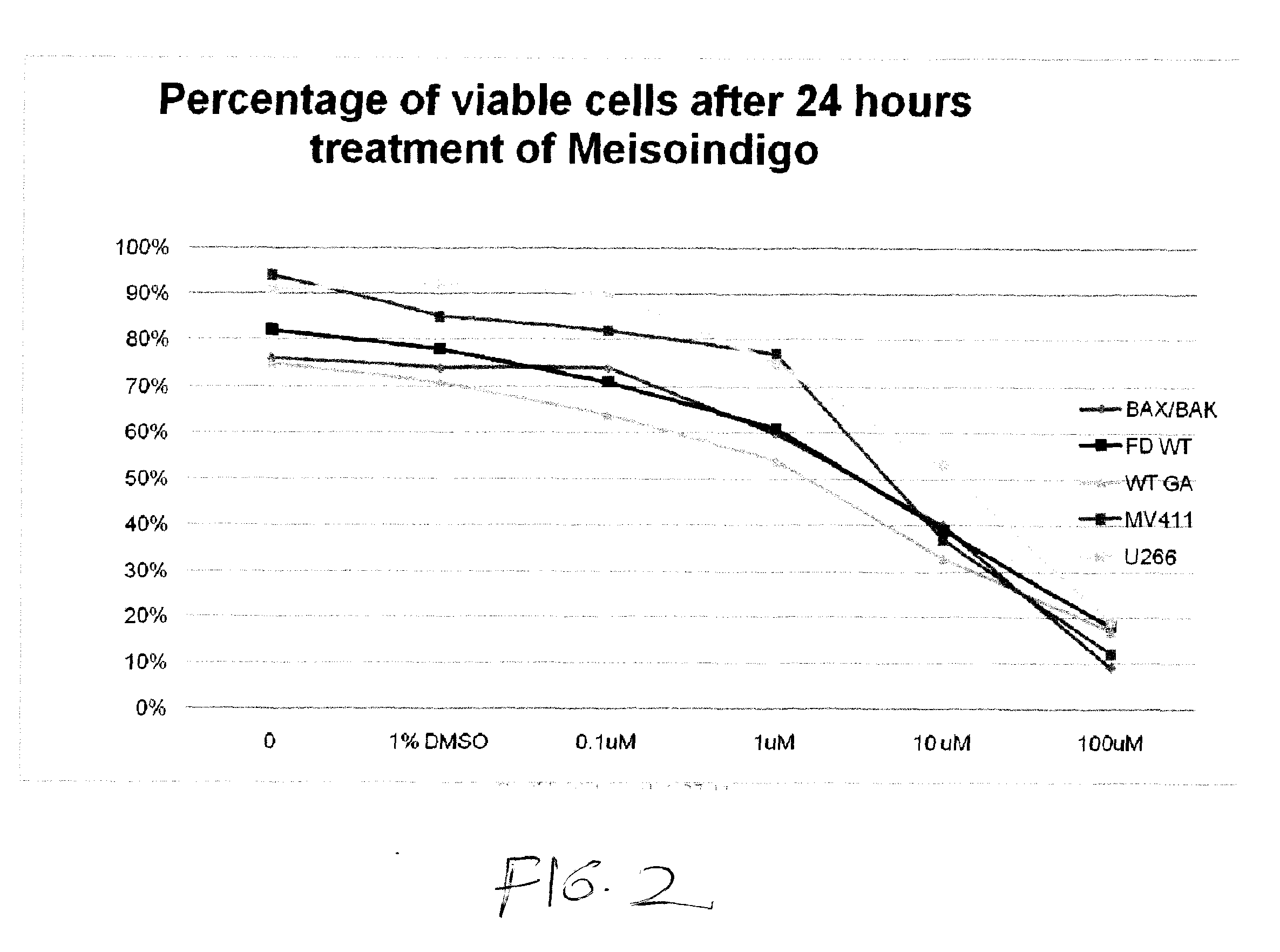
[1078]FIG. 2 shows the viability of a number of myeloid cell lines in terms of the percentage of viable cells after 24 hours of treatment with meisoindigo. Results are shown for a control, 1% DMSO without meisoindigo, 0.1 μM meisoindigo, 1 μM meisoindigo, 10 μM meisoindigo, and 100 μM meisoindigo.
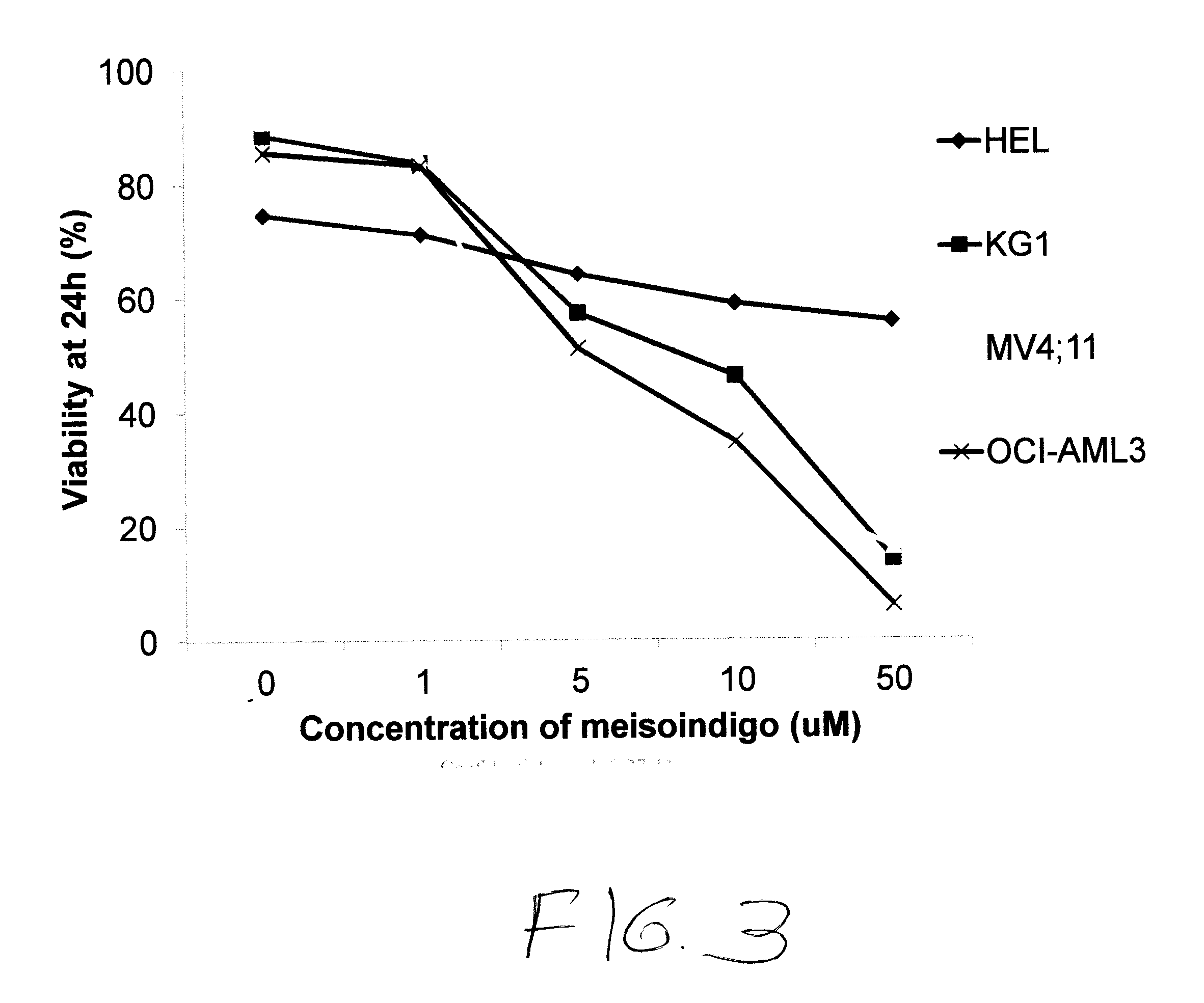
[1079]FIG. 3 shows the viability of a number of additional myeloid cell lines in terms of the percentage of viable cells after 24 hours of treatment with meisoindigo. Results are shown for a control, 1% DMSO without meisoindigo, 0.1 μM meisoindigo, 1 μM meisoindigo, 10 μM meisoindigo, and 100 μM meisoindigo.
[1080]FIG. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com