Anti-human cd69 antibody, and use thereof for medical purposes
a technology of human cd69 and antibody, applied in the field of antihuman cd69 antibody, can solve the problems of substantially impossible inability to evaluate the pharmacological effect of existing antibodies in vivo, and the method of efficiently evaluating in vitro the pharmacological effect of an antibody to human cd69 is not availabl
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of Antigen and Antibody
(1) Production of Human CD69 Recombinant Protein
[0112]Since human CD69 forms a homodimer via cysteine 68, cDNA (NM—001781) encoding the extracellular region (amino acid sequences; 62-199) containing cysteine 68 was inserted into a vector for Escherichia coli periplasm expression. Competent cells of Escherichia coli TG1F(−) strain prepared in advance (Z-competent E. Coli Transformation Buffer Set: manufactured by ZYMO RESEARCH) were transformed with this expression vector, and cultured on a LB agar plate containing chloramphenicol (final concentration 34 μg / mL) at 37° C. overnight. This Escherichia coli cells were inoculated in a 2×YT medium, and cultured at 37° C. for 3-5 hr (OD600=0.5-0.8). IPTG (final concentration 0.1 mM) was added, and the mixture was cultured at 25° C. overnight. The cultured Escherichia coli cells were collected by centrifugation, and lysed with lysis buffer (200 mM borate, 160 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 1 mg / ml lysozyme, pH 8.0), an...
example 2
Effect of Anti-Human CD69 Antibody on Intraalveolar Mononuclear Cell Infiltration
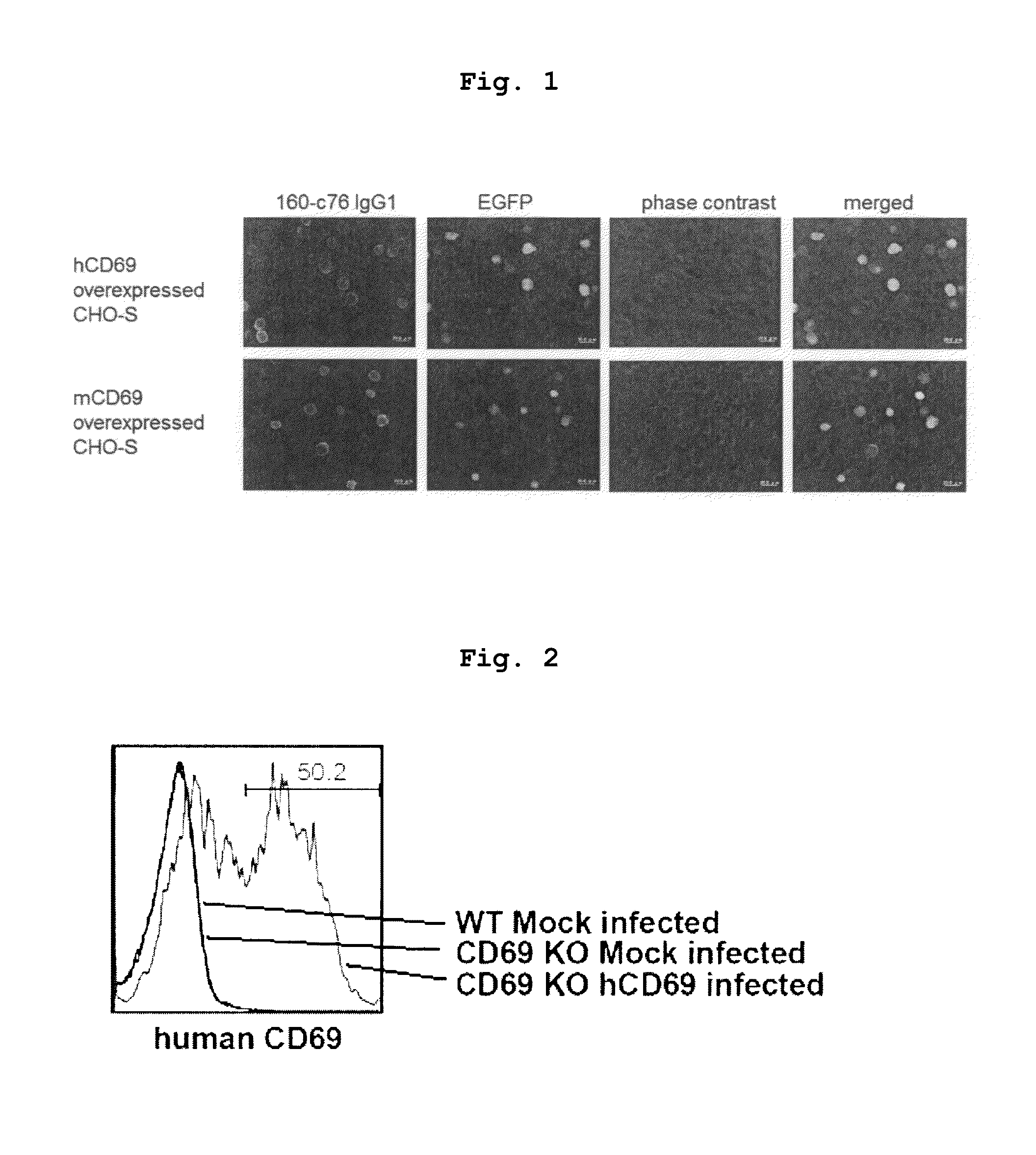
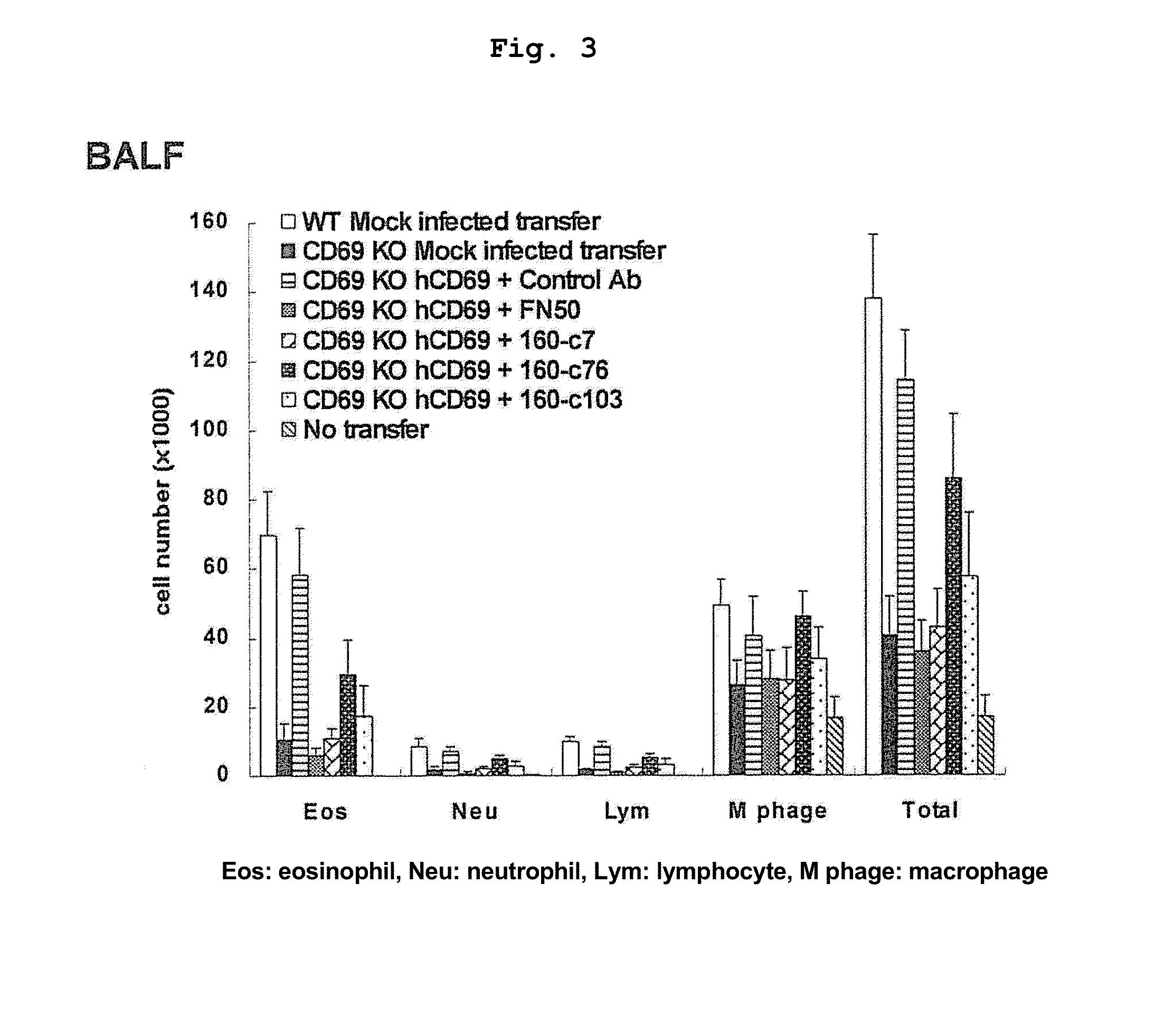
[0119]Mice obtained by crossing BALB / c mouse or CD69 deficient (CD69KO) mouse back-crossed not less than 10 times onto BALB / c (Murata, K. et al. 2003. Int. Immunol. 15: 987-992) with D011.10 transgenic mouse were used. The spleen CD4T cells of these mice were purified by AutoMACS sorter (Miltenyi Biotec) to a purity of >98%. The isolated CD4T cells were cultured with stimulation with immobilized anti-TCR and anti-CD28 monoclonal antibodies under Th2 conditions (IL-2 10 u / ml, IL-4 100 U / ml). Two days after the start of the culture, and human CD69 gene was introduced by a retrovirus vector containing human CD69 (hCD69) gene. The method of introducing human CD69 gene followed the method described previously (Kimura, M. et al. 2001. Immunity 15: 275-287). Five days after the start of the culture, the cultured cells were recovered, and the expression of human CD69 was confirmed by flow cytometry (FIG. 2). 50...
example 3
Selection of High Affinity Anti-Human CD69 Antibody
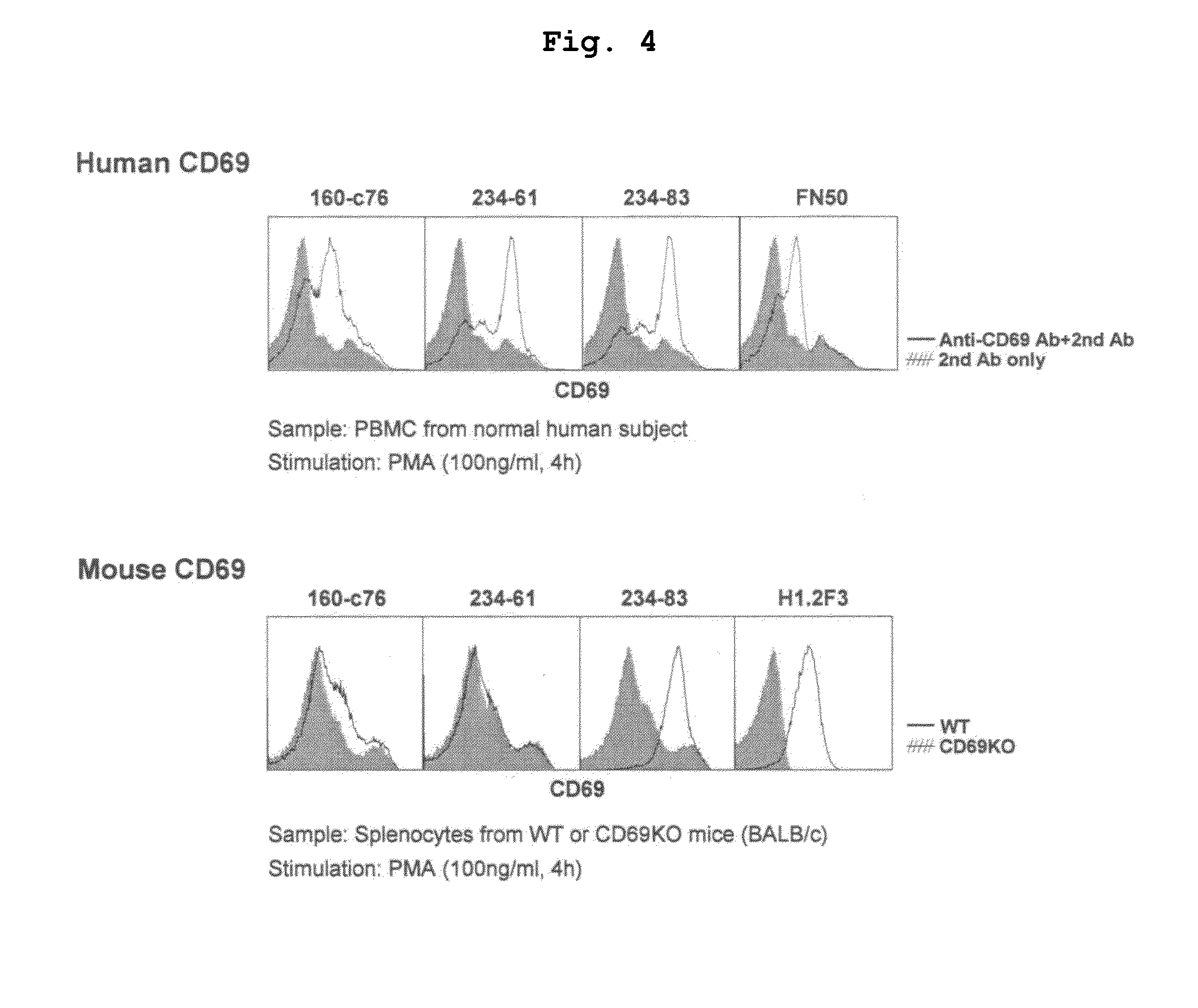
[0124]Selection of an antibody having higher affinity for human CD69 was tried by introducing a mutation into the light chain CDR3 of the antibodies selected in Example 1. To be specific, the methods described in Prassler J, Steidl S, Urlinger S. Immunotherapy. 2009 July; 1(4):571-83. and Hillig R C, Urlinger S, Fanghanel J, Brocks B, Haenel C, Stark Y, Sulzle D, Svergun D I, Baesler S, Malawski G, Moosmayer D, Menrad A, Schirner M, Licha K. J Mol Biol. 2008 Mar. 14; 377(1):206-19 were employed. The antibody selection round was repeated twice, the base sequences of the light chain CDR3 of the obtained antibody clones were examined and antibody clones having a novel sequence were identified. They were expressed in Escherichia coli, and ELISA was performed for the antigen by using the lysate and the amount of the antibody in the lysate was simultaneously measured by sandwich ELISA. The relative specific binding activity of each clone ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com