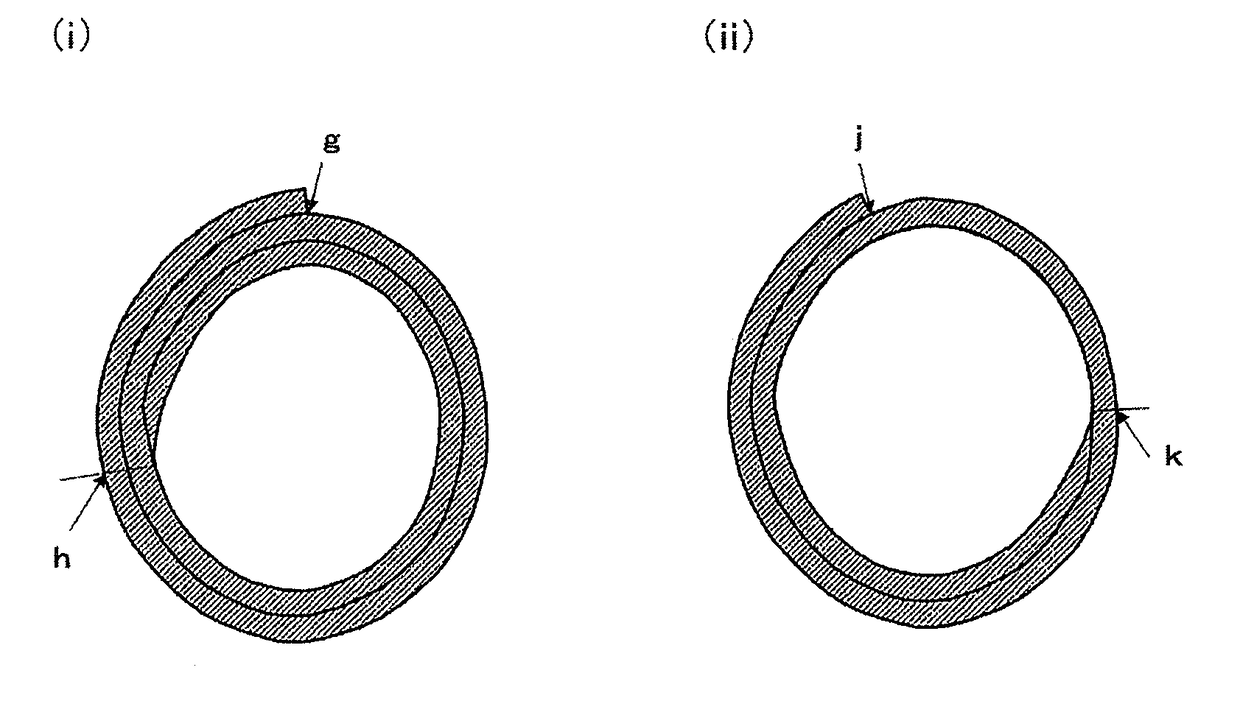
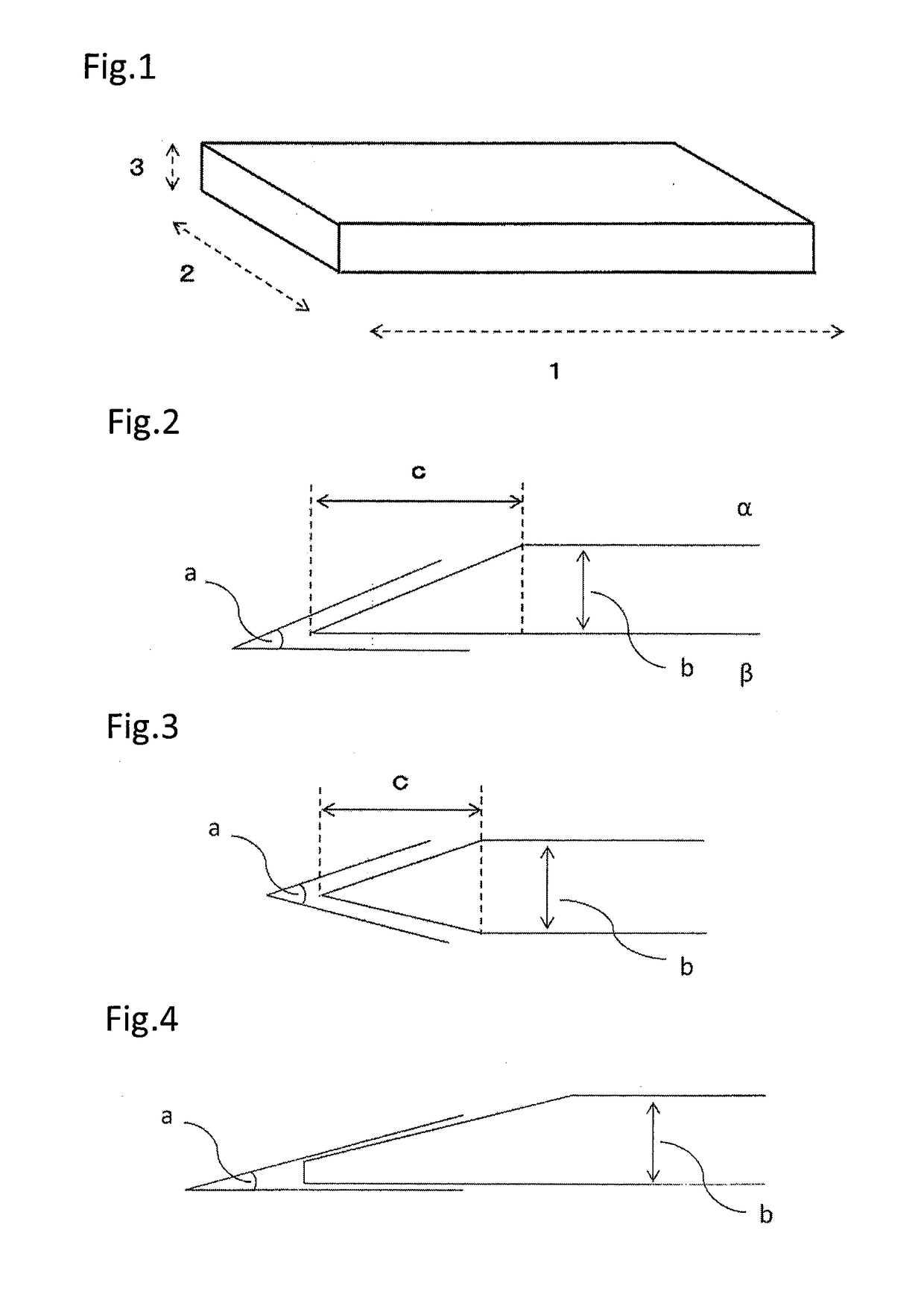
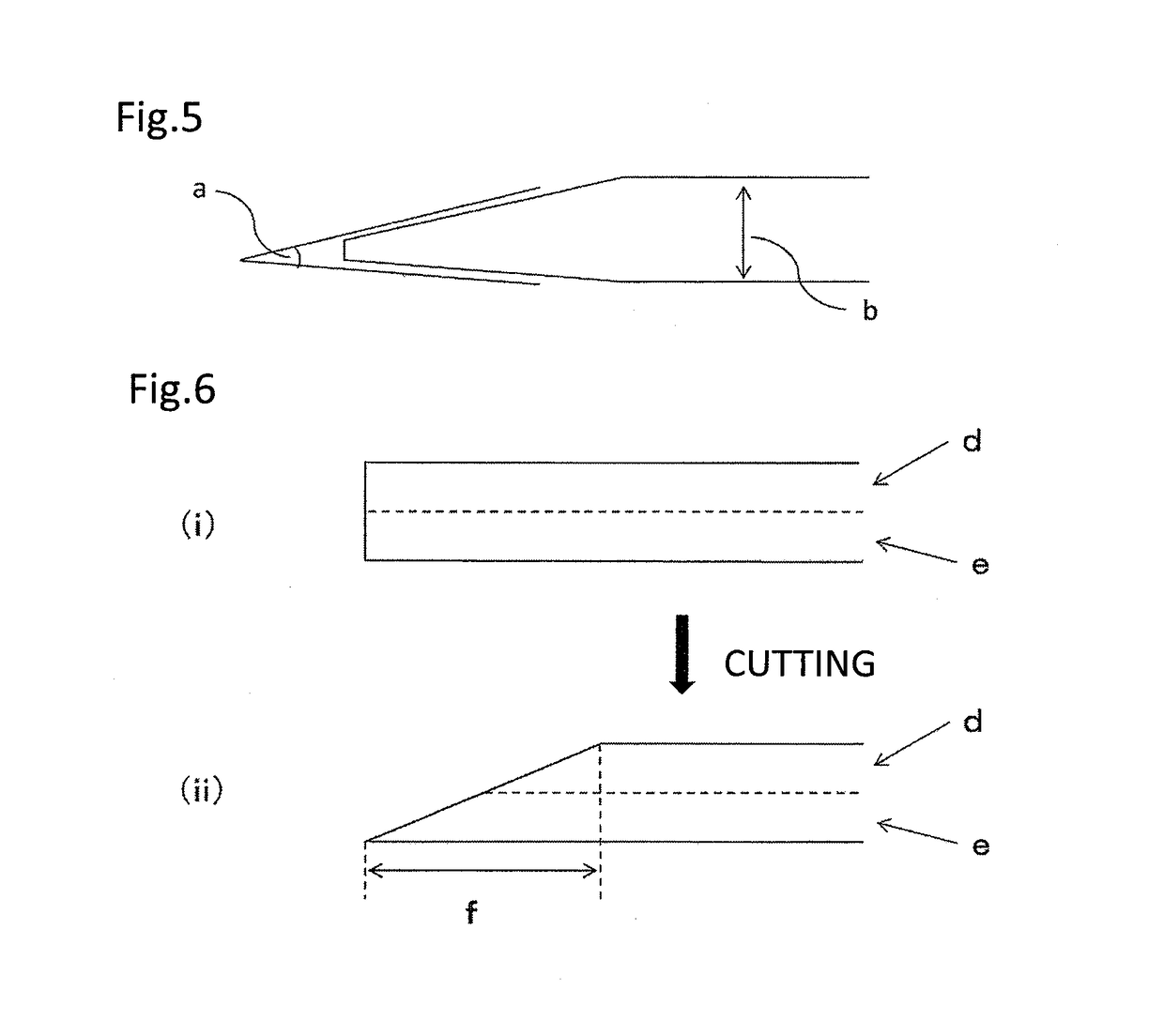
Sheet of biological tissue, tubular structure obtained from said sheet, and artificial blood vessel comprising said tubular structure
a biological tissue and tubular structure technology, applied in the field of biological tissue and tubular structure obtained from the sheet, can solve the problems of inability to avoid, significant burden on the patient's body, inevitable variability in the length and quality of the blood vessel, etc., and achieves excellent pressure resistance and handleability, no peeling or curling readily, and increase flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of Tubular Structure No. 1
(Sheet Formation Step, Decellularization Step)
[0096]A porcine aorta was purchased from a slaughterhouse, and was transported at 4° C. The adventitia was completely stripped off the aorta, which was then cut open. The aorta thus cut open was then cut out to a substantially rectangular shape having a length of 170 millimeters and a width of 27 millimeters. The obtained sheet was subjected to a high hydrostatic pressure treatment for 15 minutes at 100 MPa in a high pressure processing device for research and development (Dr. CHEF, by Kobe Steel, Ltd.), using saline as a medium. The treated sheet was shaken for 96 hours at 4° C. in saline containing 20 ppm of the nucleolytic enzyme DNase, followed by a treatment for 72 hours at 4° C. in 80% ethanol, and was lastly washed for 2 hours at 4° C. in saline, to yield a decellularized porcine aorta sheet.
[0097]
[0098]The thickness of the decellularized porcine aorta sheet thus obtained was 258 micrometers. A...
example 2
Production of Tubular Structure No. 2
[0104]A tubular structure No. 2 of the present invention was obtained in accordance with the same procedure as in Example 1, but herein the thickness of the decellularized porcine aorta sheet was 217 micrometers, and the incidence angle of the blade was adjusted to modify the taper angle during formation of the tapered portion. The taper angle of the obtained tubular structure No. 2 was measured in the same way as in Example 1, and a pressure resistance test and a handleability test were also carried out. The results are given in Table 1.
example 3
Production of Tubular Structure No. 3
[0105]A tubular structure No. 3 of the present invention was obtained in accordance with the same procedure as in Example 1, but herein the thickness of the decellularized porcine aorta sheet was 275 micrometers, and the incidence angle of the blade was adjusted to modify the taper angle during formation of the tapered portion. The taper angle of the obtained tubular structure No. 3 was measured in the same way as in Example 1, and a pressure resistance test and a handleability test were also carried out. The results are given in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| inner circumference | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com