Graft copolymer, crosslinked particles, graft crosslinked particles, rubbery polymer, and thermoplastic resin composition using same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment of first invention
[Graft Copolymer (C)]
[0098]A graft copolymer (C) of the first invention is obtained by graft-polymerizing one or two or more monomers (B) selected from (meth)acrylic acid esters, aromatic vinyls, vinyl cyanides, N-substituted maleimides, and maleic acid onto a composite rubber-like polymer (A) (hereinafter also referred to as “the composite rubber-like polymer (A) of the first invention”) obtained by miniemulsifying a mixture (Ac) containing a polyorganosiloxane (Aa) and an acrylic acid ester (Ab) in water solvent and then polymerizing the polyorganosiloxane (Aa) and the acrylic acid ester (Ab) in the miniemulsion.
[0099]By polymerizing the mixture (Ac) of the polyorganosiloxane (Aa) and the acrylic acid ester (Ab) after being miniemulsified, the composition of each of the resulting composite rubber-like polymer (A) particles tends to be uniform. A thermoplastic resin composition obtained by incorporating the graft copolymer (C) produced using the composite rubber-like polymer (A) ha...
embodiment of second invention
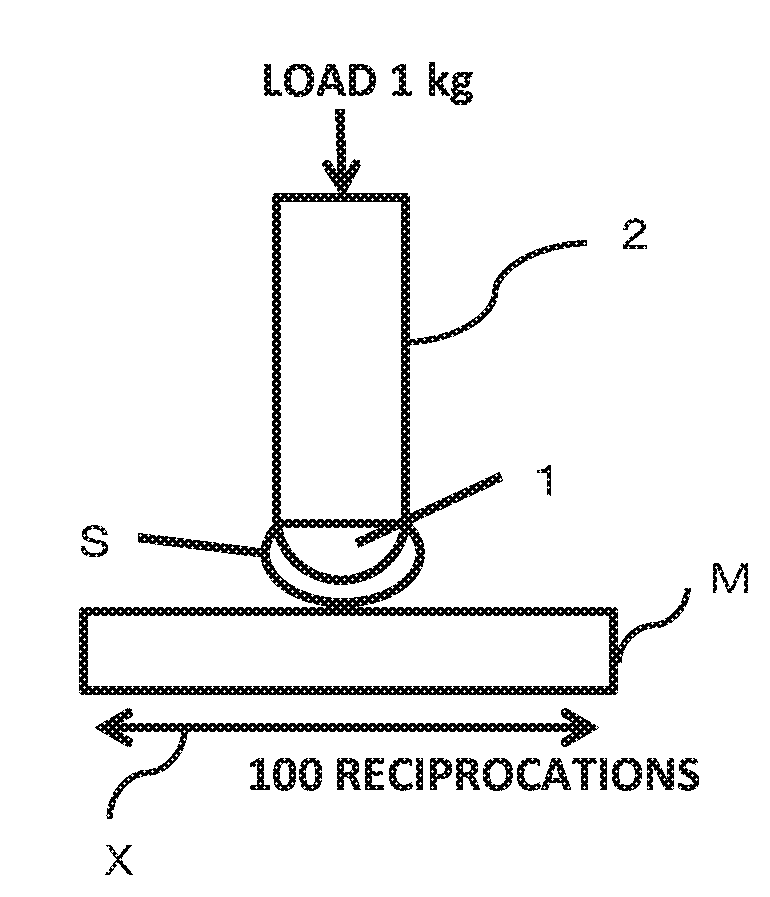
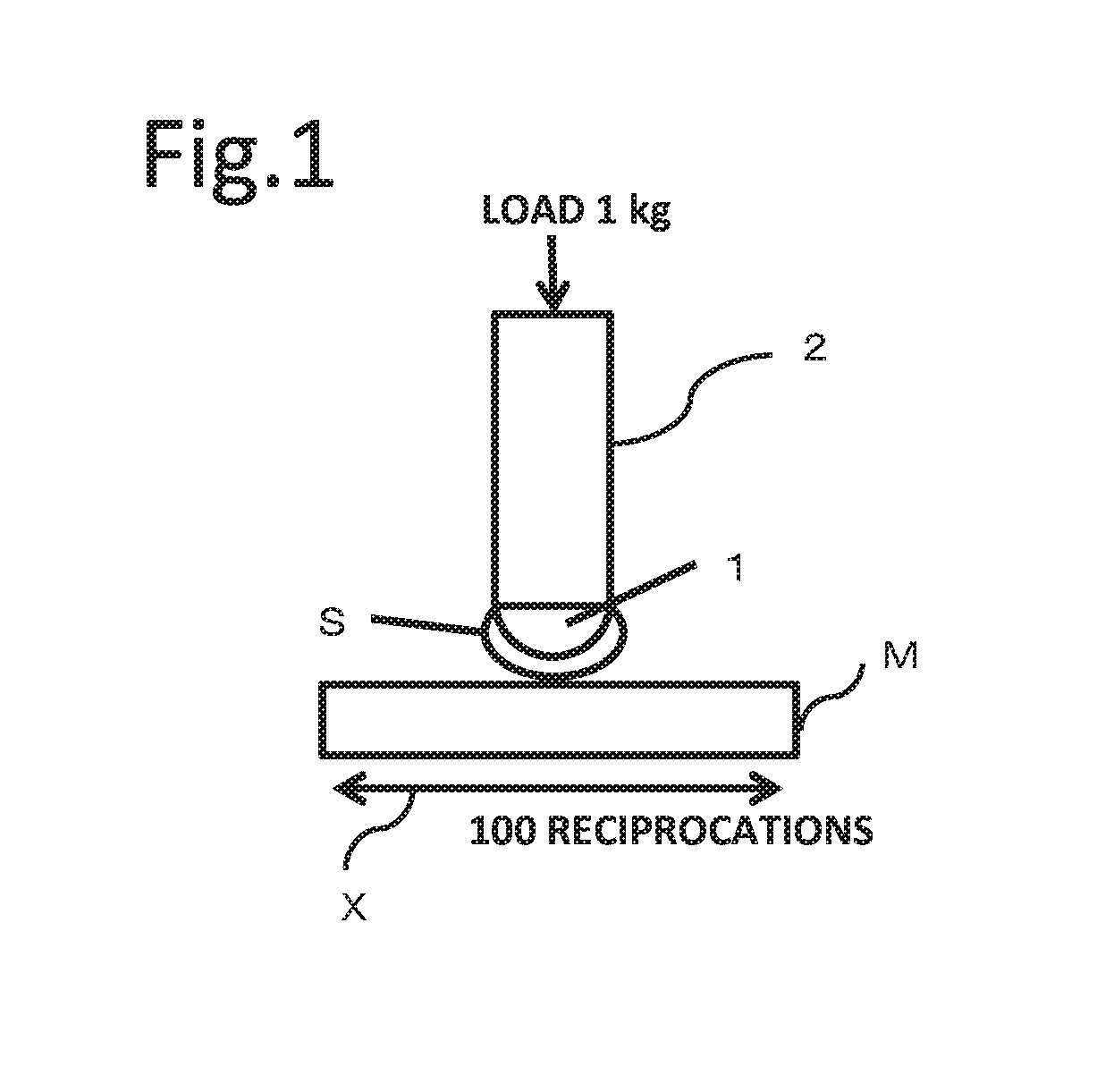
[0179]Hereinafter, “abrasion resistance” means resistance to damage (abrasion, wear) that can occur when a surface of a molded article is rubbed with a soft material such as cotton work gloves, gauze, or a cloth.
[0180]“Residue” refers to a structural portion that is derived from a compound used to produce a polymer (crosslinked particles (A-I) in the second invention) and incorporated into the polymer. For example, a residue X described below corresponds to the rest of a polyalkylene glycol, a polyester diol, a polycarbonate diol, or a polymer of one or more thereof from each of the two hydroxyl groups of which one hydrogen atom is removed.
[0181]In the second invention, number average molecular weights (Mn) of the crosslinked particles (A-I) and diols incorporated as divalent residues X are values measured using gel permeation chromatography (GPC) relative to polystyrene standards.
[0182]The same applies to the third invention described below.
[0183][Crosslinked Particles (A-I)]
[0184]...
embodiment of third invention
[0248]In the third invention, “abrasion resistance” and “residue” each have the same meaning as in the second invention. Number average molecular weights (Mn) of crosslinked particles (A-II) and diols incorporated as divalent residues X are values measured using gel permeation chromatography (GPC) relative to polystyrene standards.
[0249][Crosslinked Particles (A-II)]
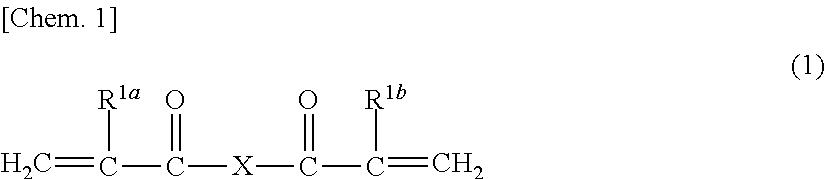
[0250]The crosslinked particles (A-II) of the third invention are obtained by polymerizing a monomer mixture (i-II) containing a di(meth)acrylic acid ester (a) represented by the following formula (1) and having a number average molecular weight of 800 to 9,000 and a mono(meth)acrylic acid ester (d). The content of the di(meth)acrylic acid ester (a) in 100% by mass of the monomer mixture (i-II) is 20% to 80% by mass. Therefore, the crosslinked particles (A-II) of the third invention are constituted by a structural unit derived from the di(meth)acrylic acid ester (a), a structural unit derived from the mono(meth)acrylic a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com