Use of cannabidivarin in the treatment of autism spectrum disorder, associated disorders and schizophrenia
a technology of cannabidivarin and autism spectrum disorder, applied in the field of use, can solve the problems of not being fully manifested, unfavorable to adapt to tone and content, and react unusually negatively, and achieve the effect of improving symptoms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
nnabidivarin (CBDV) in a Mouse Model of Autism Spectrum Disorder
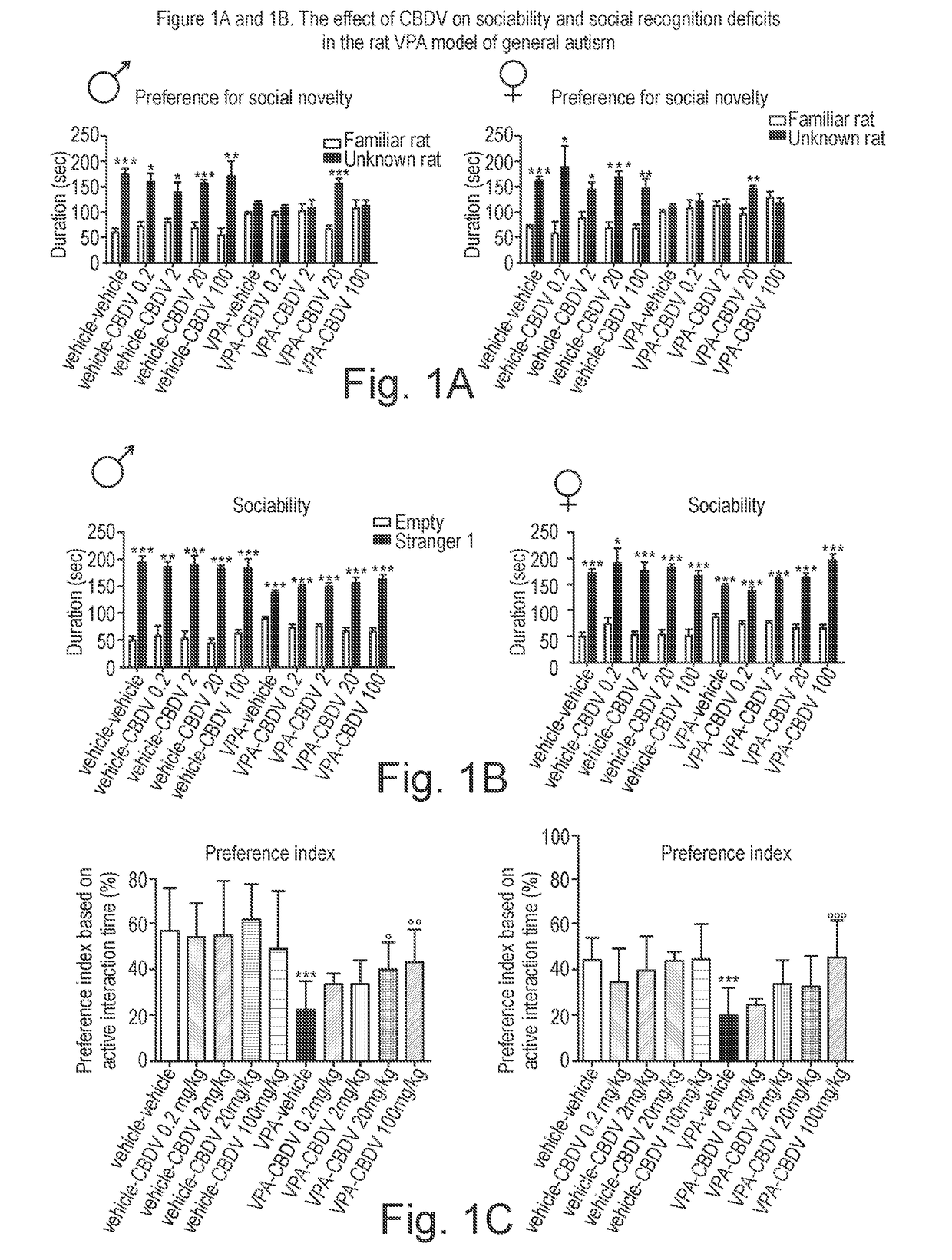
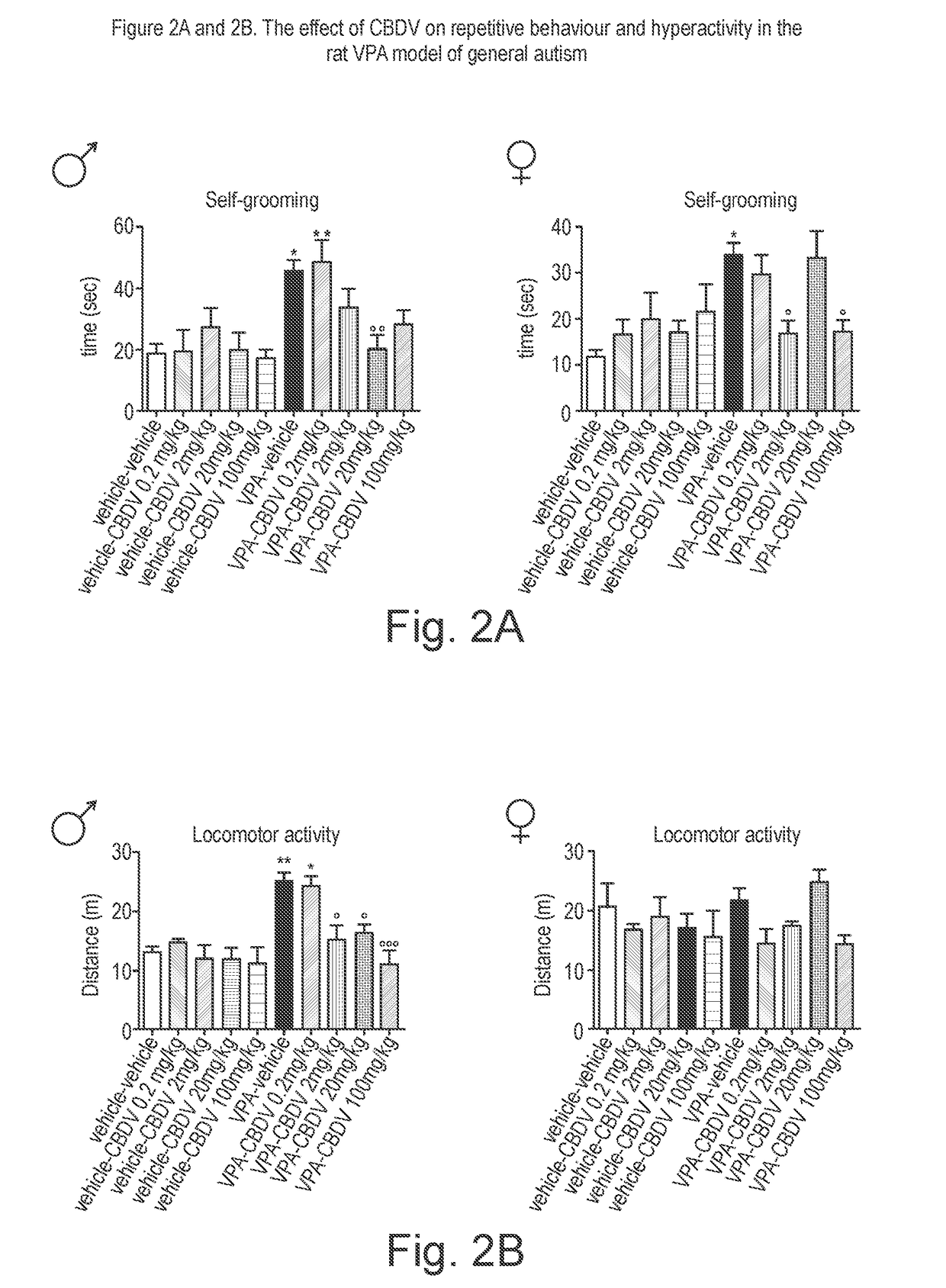
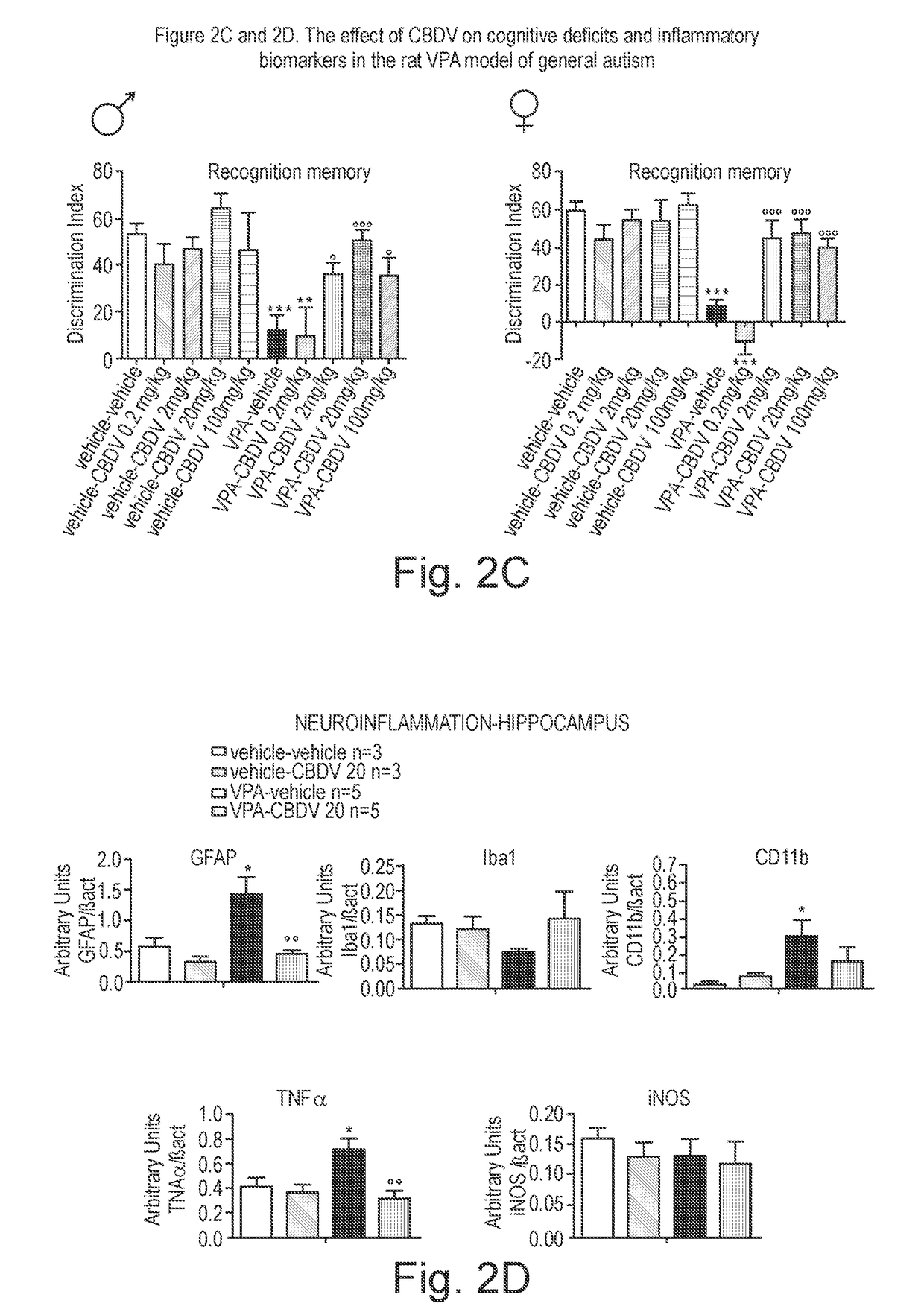
[0170]The phytocannabinoid cannabidivarin (CBDV) was evaluated in a rodent model of autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
[0171]In utero exposure of rodents to valproic acid (VPA) has been shown to induce a phenotype with behavioural characteristics similar to those observed in ASD and provides a robust animal model for social cognitive impairment understanding and a potential screen for the development of novel therapeutics for this condition (Foley et al. 2012).
[0172]Thus, in utero exposure to VPA has been used as a reliable model to increase the understanding of behavioural effects evaluated by specific tests as sociability, social preference and stereotypic behaviour, also observed in human patients (Schneider and Przewlocki, 2005).
[0173]Example 1 describes the use of prenatal VPA exposure in rats to evaluate the efficacy of chronic CBDV administration in reversing the autism-like behaviours present in this model.
Materials...
example 2
nnabidivarin (CBDV) in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
[0201]The phytocannabinoid cannabidivarin (CBDV) was evaluated in a mouse model of Fragile X syndrome (FXS). Such model evaluates the treatment on cognitive deficits and seizures present in Fmr1 knockout (KO) mice.
Materials and Methods
Animals
[0202]Fmr1 KO mice and wild type mice were obtained and housed four per cage in a temperature of 21° C.±1° C. and humidity of 55%±10% controlled environment. Food and water were available ad libitum. All experiments were performed during the light phase of a 12 hour light / dark cycle (08:00 to 20:00). Animals were handled for one week before the start of experiments. All behavioural tests were performed by researchers blind to the different experimental groups.
Novel Object Recognition Task
[0203]On day one mice were habituated for 10 minutes to the empty V-maze in which the task was to be performed. On the second day the mice went back to the maze for 10 minutes which contained two identica...
example 3
nnabidivarin (CBDV) in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome
[0215]The phytocannabinoid cannabidivarin (CBDV) was evaluated in a mouse model of Rett syndrome (RS). Such model evaluates the treatment on motor alterations and cognitive deficits present in MeCP2 KO mice.
[0216]CBDV was administered daily at the dose of 2, 20 and 200 mg / kg i.p. starting from PND 28 and the following signs were scored every other day: hindlimb clasping (indication of motor imbalance), tremor, gait (measure of coordination), breathing, mobility and general condition.
[0217]Furthermore, the efficacy of CBDV in reverting / attenuating the short- and long-term memory deficits present in these mice was evaluated. The Novel Object Recognition (NOR) test was performed before the starting of the treatment Post Natal Day 28 (PND 28), at PND 41 when the first motor symptoms appear and at PND 56 and 66 when the disease is fully manifested.
Materials and Methods
[0218]The CBDV was dissolved in ethanol, cremophor and saline (1:1:1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com