Methods of treating heavy menstrual bleeding
a menstrual bleeding and receptor antagonist technology, applied in the direction of sexual disorders, drug compositions, medical preparations, etc., can solve the problems of pelvic pressure and pelvic organ compression, back pain, and cost of $238 million to $7.76 billion annually, so as to reduce the volume of menstrual blood loss, reduce the fibroid and uterine volume, and treat non-bleeding-related symptoms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Summary of Efficacy and Safety Findings in Completed Phase 2 Studies in Endometriosis Subjects
[0220]Efficacy
[0221]Six Phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-, and / or active-controlled, parallel-group, multiple dose studies were completed to evaluate elagolix as a treatment for endometriosis associated pain. Efficacy was assessed for dysmenorrhea (DYS), nonmenstrual pelvic pain (NMPP), dyspareunia, and general pelvic pain with a range of instruments.
[0222]Additional efficacy assessments included quality of life and the use of analgesics for control of endometriosis pain.
[0223]Across these Phase 2 studies, the enrollment criteria were similar and were intended to select premenopausal women aged 18 to 49 years of age with endometriosis confirmed by visual inspection (laparoscopy or laparotomy within 5 to 8 years of screening) who experienced moderate to severe endometriosis-associated pain. Women were included if they had regular menstrual cycles and no significant uterine fibroids ...
example 2
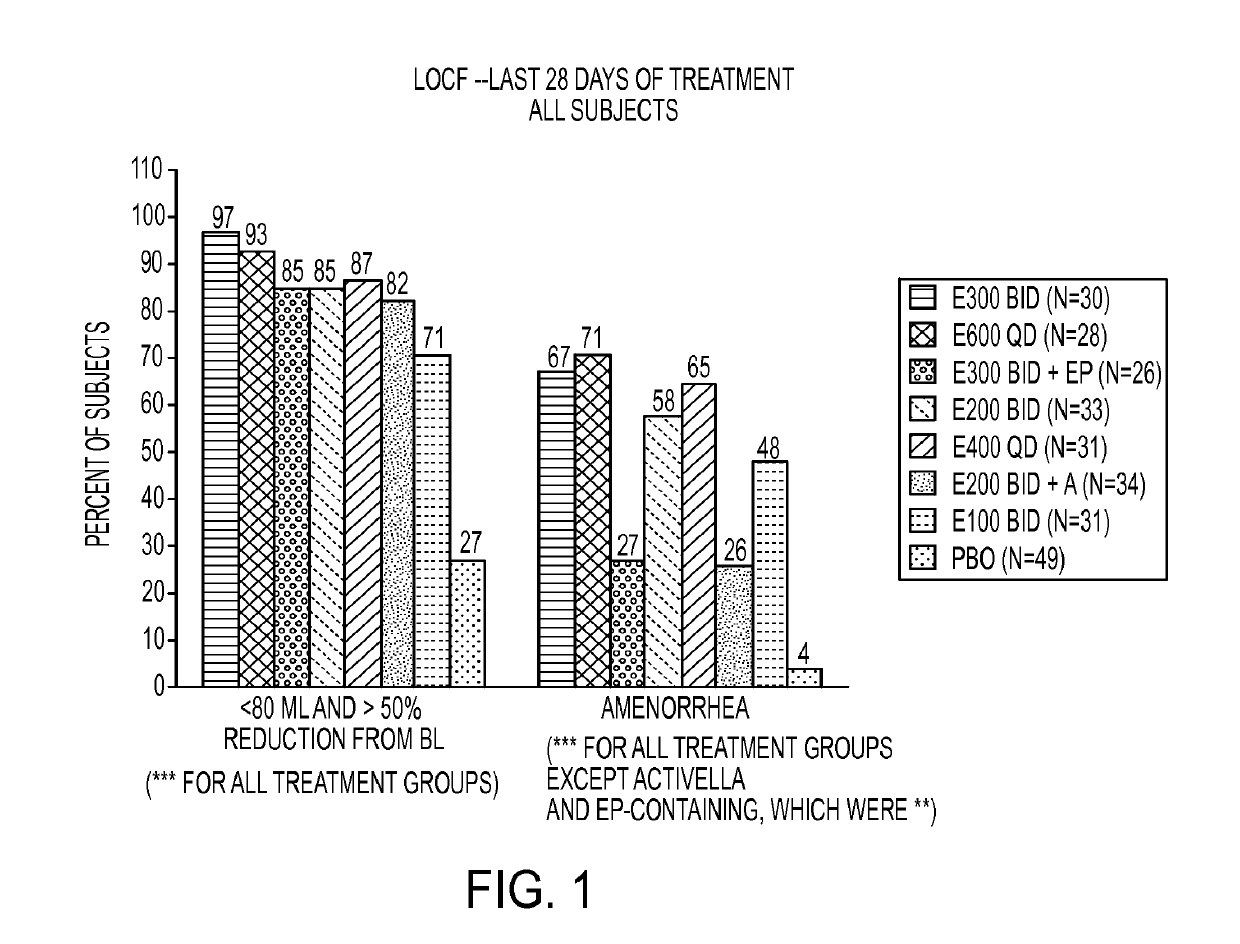
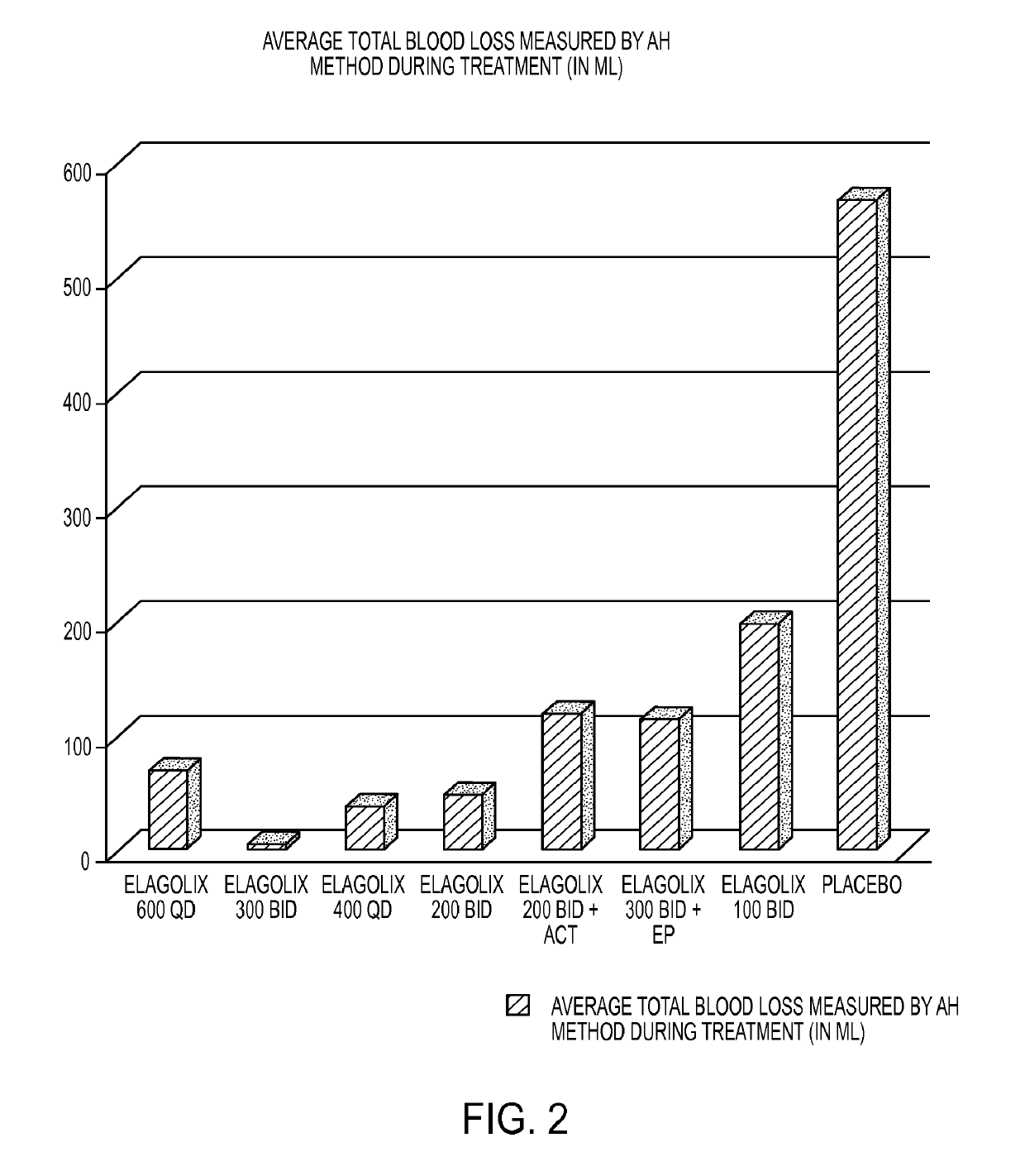
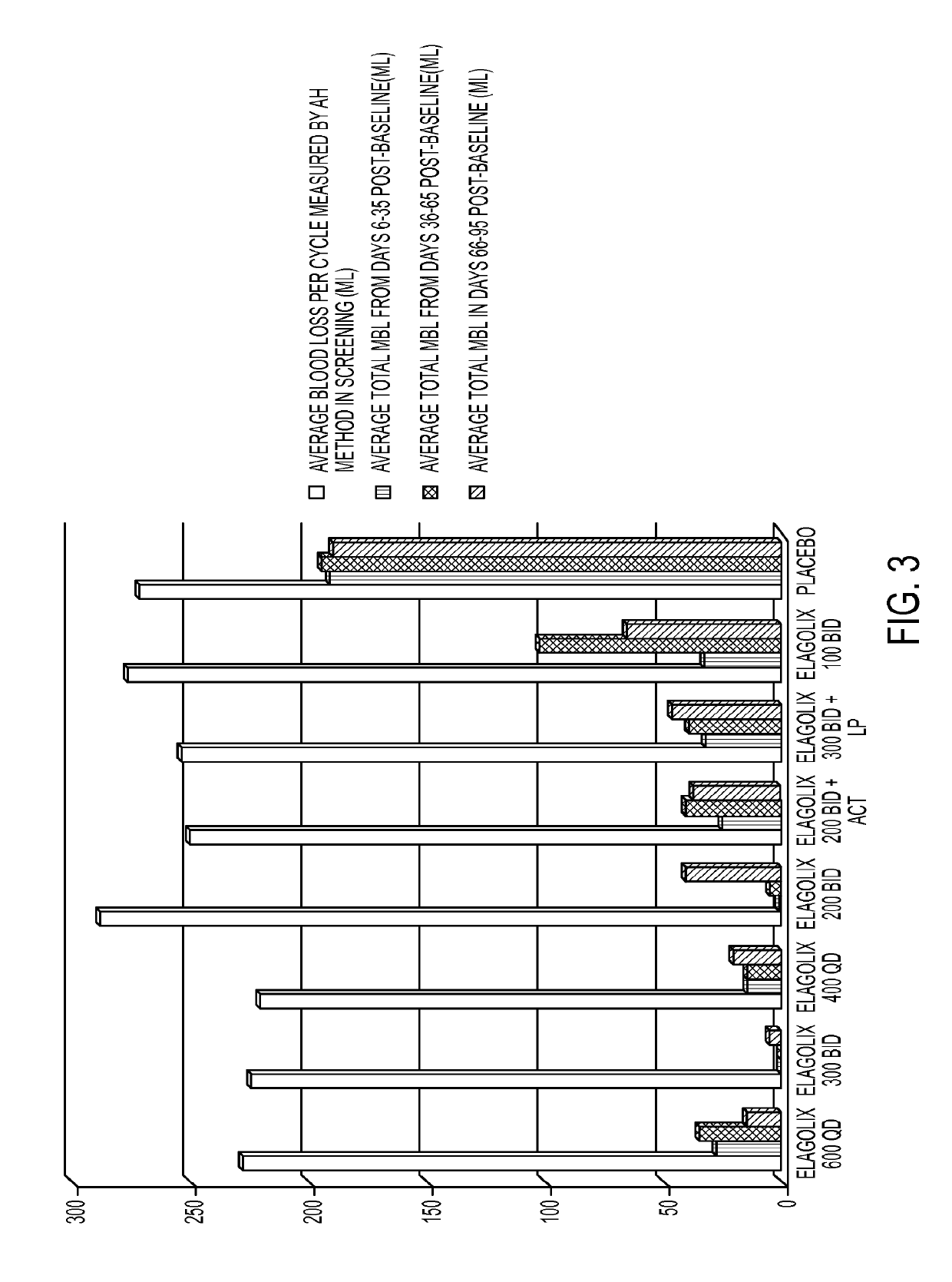
[0233]This example is a Phase 2a, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial (N=280) with a 3-month treatment duration evaluating the safety and efficacy of Elagolix administered with or without Activella® in premenopausal women with uterine fibroids.
[0234]It evaluates the safety and efficacy of 6 doses of Elagolix (100 mg BID, 200 mg BID, 200 mg BID plus low dose Activella® (a combination of 0.5 mg estradiol and 0.1 mg northindrone acetate), 300 mg BID, 300 mg BID plus 1.0 mg of Estrace and 200 mg cyclical Prometrium (collectively referred to as “EP”), 400 mg QD and 600 QD) versus placebo (PBO) to reduce uterine bleeding associated with uterine fibroids and to reduce fibroid volume and uterine volume in premenopausal women 20 to 49 years of age with heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB; >80 mL blood loss per menstrual cycle). The study involved the following six (6) cohorts:
[0235]Cohort 1: Elagolix 200 mg BID or placebo (PBO).
[0236]Cohort 2: Elagolix 300 mg BID or pla...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com