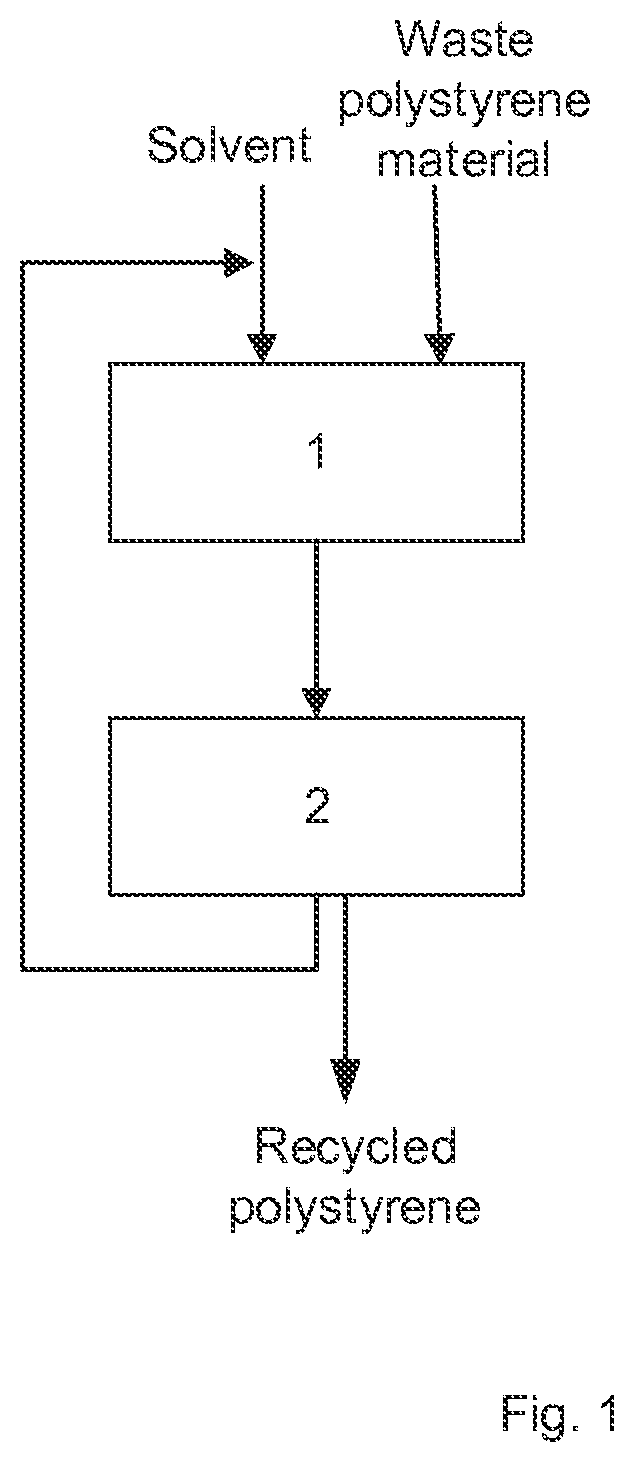
Method for recycling polystyrene and solvent for dissolving polystyrene
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0036]In this Example, polystyrene recycling was studied with the solvents according to the present invention and with limonene as a reference.
[0037]Foamed polystyrene, 1 g, was added to 20 g of each solvent, weighted into an individual rounded bottom flask. Mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 minutes to completely dissolve foamed polystyrene to the solvent. After polystyrene was dissolved, the round bottom flask was equipped with distilling bridge and a receiving flask and placed on oil bath. Mixture was heated gradually towards the boiling temperature of the solvent until the solvent started to evaporate. Distillation was continued for 1 hour at 1 atm pressure. Solvents and their boiling point are presented in Table 1. Limonene was used as reference. Polystyrene and residue solvent remaining in reaction flask and distilled solvent in receiving flask were weighted. Results are summarized in Table 2.
[0038]Compared to Limonene (reference solvent), both isoamul acetate and 1...
example 2
[0039]In this Example, polystyrene recycling was studied with the solvents according to the present invention and with limonene (reference solvent) under diminished air pressure for studying the effect of vacuum on distillation.
[0040]Foamed polystyrene, 1 g, was added to 20 g of each solvent, weighted into an individual rounded bottom flask. Mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 minutes to completely dissolve foamed polystyrene to the solvent. After polystyrene was dissolved, the round bottom flask was equipped with distilling bridge, receiving flask and vacuum pump and placed on oil bath. Pressure of the system was set to 50 mbar.
[0041]When using 1,3-dioxolane as the solvent, after setting the vacuum solvent started to evaporate. Distillation was continued for 1 hour at 50 mbar pressure at room temperature.
[0042]When using isoamyl acetate as the solvent, mixture was heated gradually to 55-75° C. to evaporate the solvent. Distillation was continued for 1 hour.
[0043]When usin...
example 3
[0046]Solubility of foamed polystyrene to the solvents according to the present invention and to limonene as a reference solvent was determined. 20 g of each solvent was weighted to an individual rounded bottom flask. Solvents were stirred at room temperature and foam polystyrene pieces were added to the mixtures until it no longer dissolved to the solvents. Mixtures were weighed and the amount of polystyrene foam dissolved was determined. Limonene was used as a reference solvent. Solubility test results are summarized in Table 4.
TABLE 4Solubility of polystyrene foam in different solvents.Solvent (20 g)Dissolved polystyrene foam (g)1,3-Dioxolane4.18Isoamyl acetate7.22Limonene (reference)2.25
[0047]The solvents according to the present invention dissolve polystyrene foam better as limonene.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com