Bispecific monoclonal antibody therapeutics against West Nile virus with improved CNS penetration
a monoclonal antibody and western nile virus technology, applied in the field of bifunctional antibodies, can solve the problems of limited efficacy of peripheral delivery of this antibody in rodents, lack of effective and specific antiviral treatment of infection by wnv or other, and limited efficacy of the ultimate application as beneficial therapeutics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods for Production of Hu-E16
[0067]Construction of pHu-E16 MAb Expression Vectors. The coding sequences of Hu-E16 MAb LC and HC (12) were optimized in silico with N. benthamiana-optimized codons using an algorithm described in (26). An 18-bp sequence coding for a ‘SEKDEL’ hexapeptide (SEQ ID NO: 13) ER-retention signal was added to the C-terminus of the HC gene. Optimized LC and HC sequences were synthesized (DNA 2.0) and cloned into the 5′ modules of plant expression vectors pICH21595 and pICH11599 of the MagnICON system as described previously (22).
[0068]Agroinfiltration of N. benthamiana. Plant expression vectors were individually transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 by electroporation as previously described (45). Wild-type N. benthamiana plants were grown in a greenhouse with 16 / 8 hr light / dark cycle at 25° C. for 5 weeks. Plant leaves were co-Agroinfiltrated with GV3101 strains containing the LC and HC 5′ modules along with their respective 3′ mod...
example 2
Expression and Assembly of Hu-E16 MAb in Plants
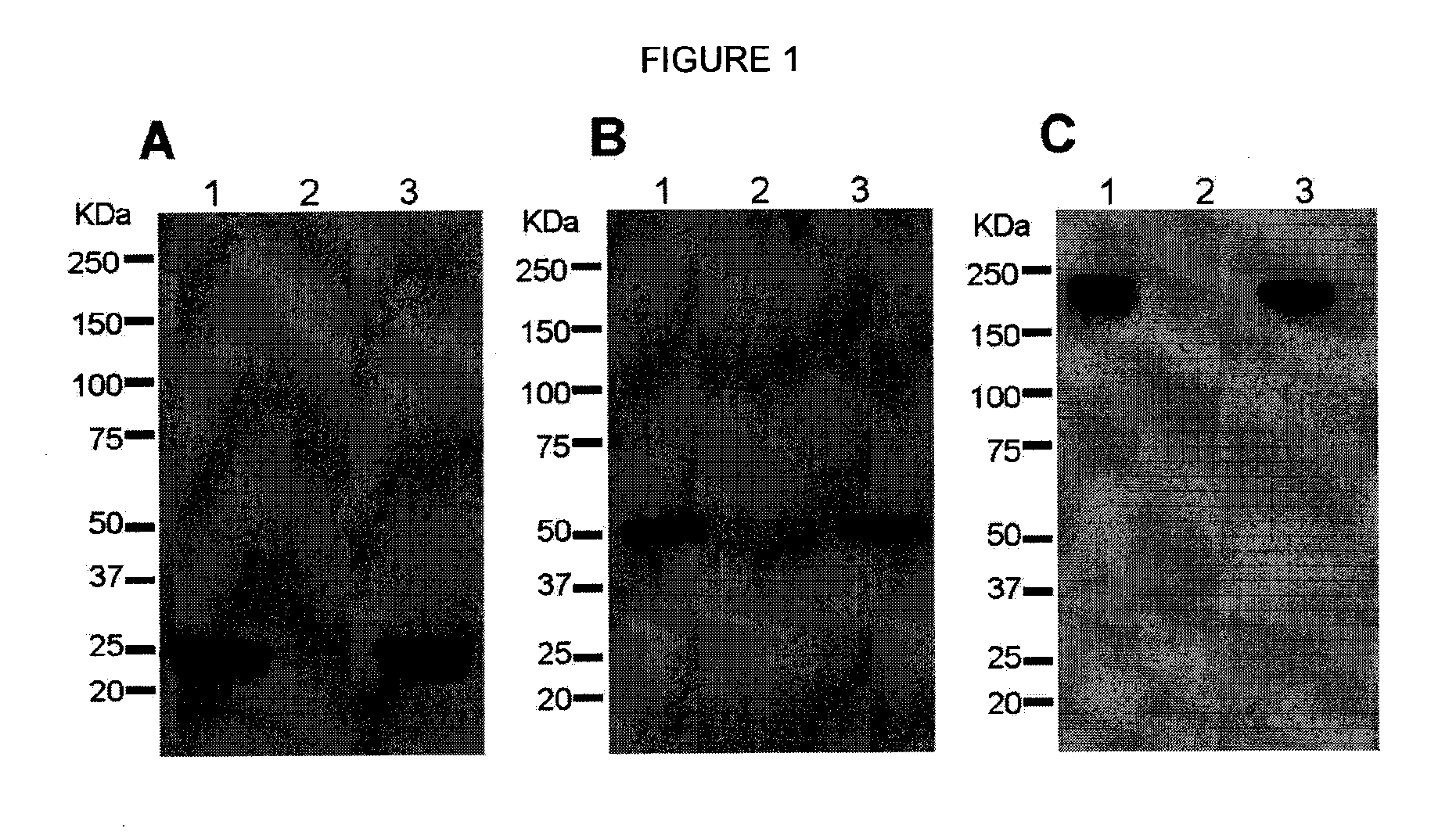
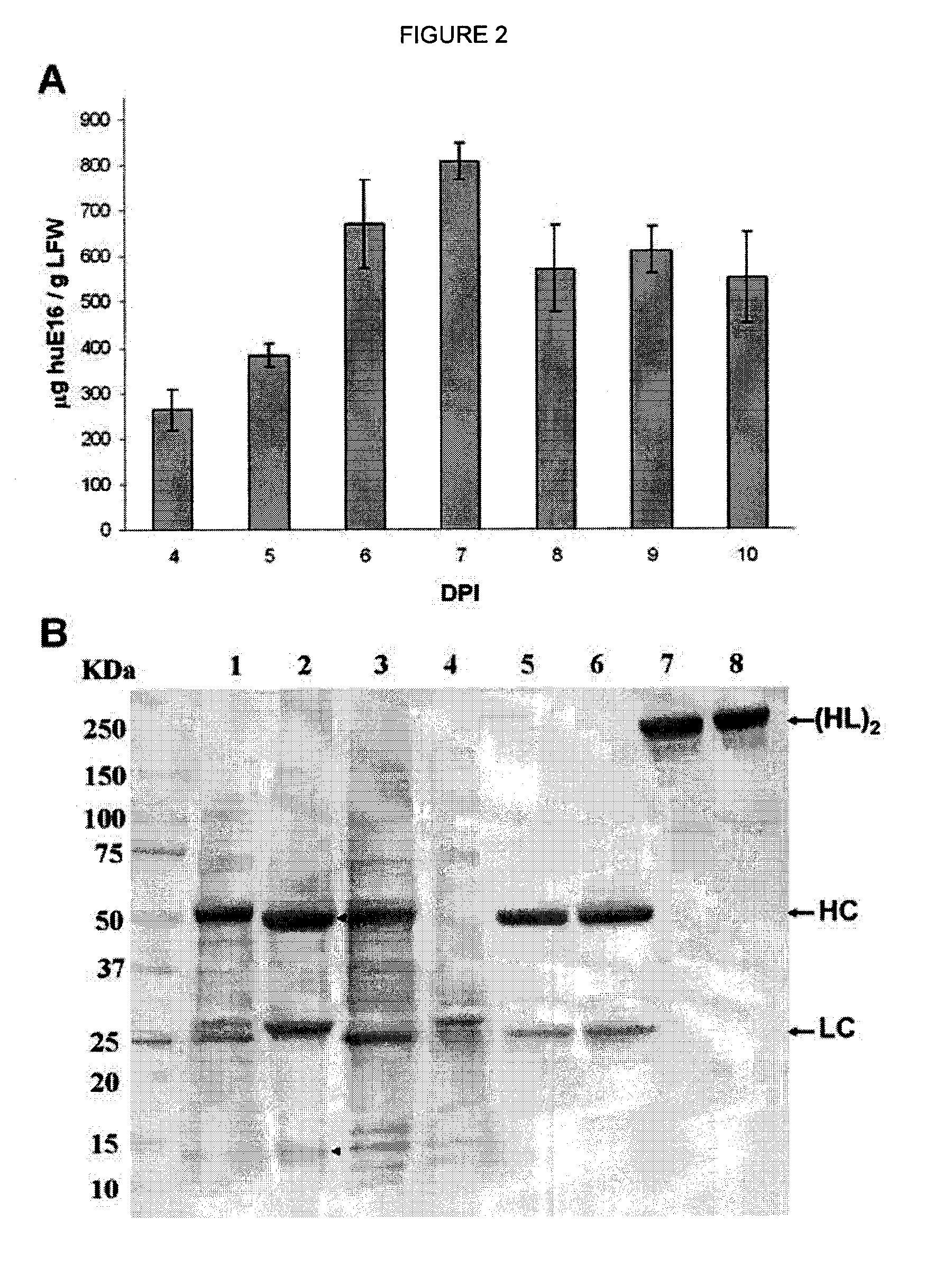
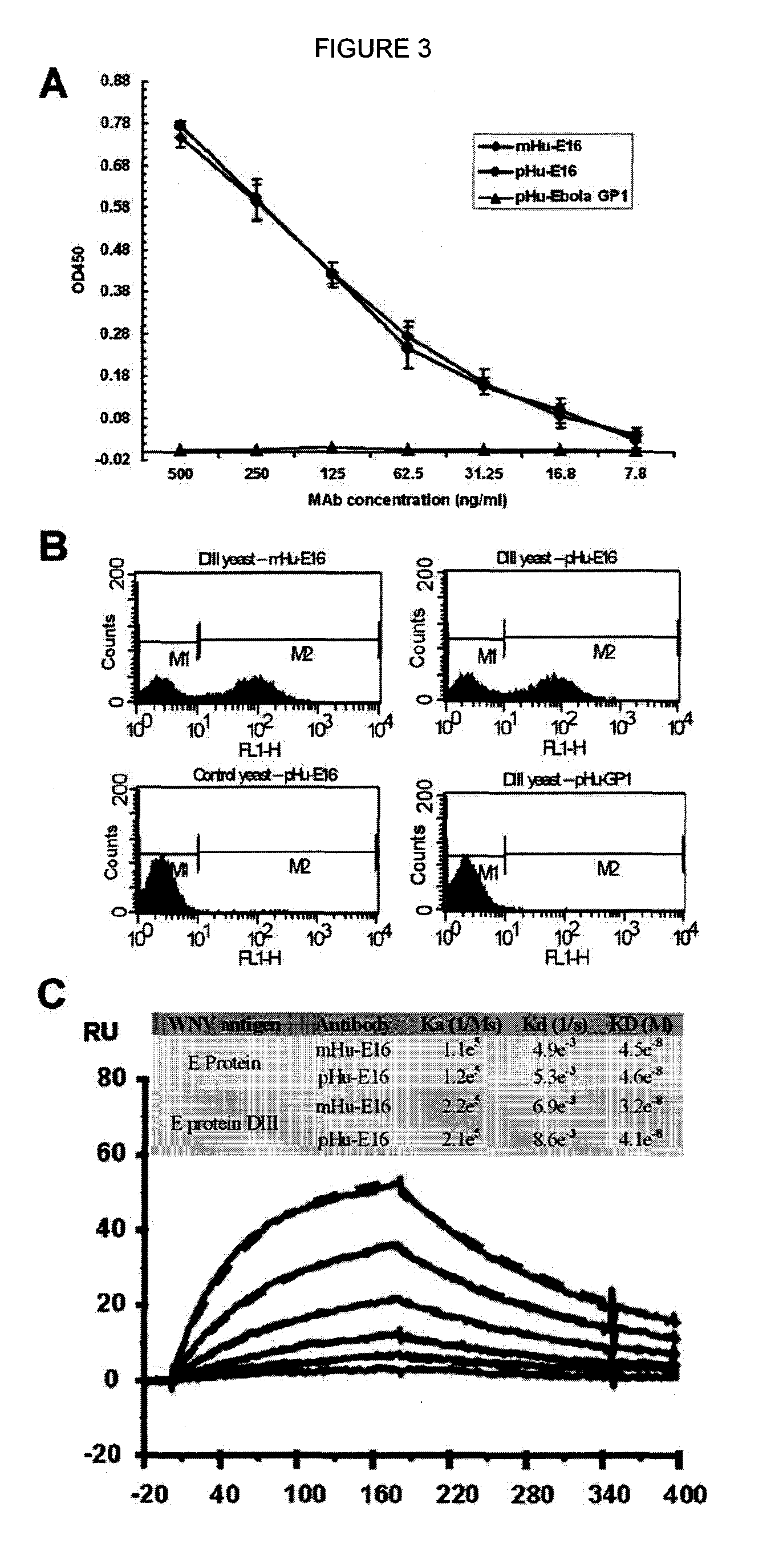
[0081]As a first test of the feasibility of developing a plant-derived Hu-E16 therapeutic, we needed to demonstrate that plants could express and assemble Hu-E16. To ensure high-level expression of Hu-E16 in plants, the coding sequences of Hu-E16 light chain (LC) and heavy chain (HC) were optimized in silico with N. benthamiana-optimized codons (26). Optimized LC and HC sequences were cloned into the 5′ modules of plant expression vectors of the MagnICON system (22) and transformed into Agrobacterium tumefacient. To co-express Hu-E16 LC and HC, A. tumefacient strains harboring the LC and HC 5′ modules were co-delivered into N. benthamiana leaves along with their respective 3′ modules and an integrase construct through vacuum infiltration (22). Western blot analysis confirmed that the LC and HC of pHu-E16 were produced in leaves with the expected molecular weights of 25 kDa and 50 kDa, respectively (FIGS. 1A and B). Western blot analysis...
example 3
Purification and Scale-Up Production of pHu-E16
[0082]For plant-produced pHu-E16 to become a viable WNV therapeutic candidate, an efficient purification scheme from plant tissue must be developed. pHu-E16 was extracted and purified by a three-step purification protocol comprised of ammonium sulfate precipitation, protein A affinity and DEAE-anion exchange chromatographies. Precipitation with 35% ammonium sulfate effectively removed the most abundant plant host protein, the photosynthetic enzyme RuBisCo, and other plant proteins (FIG. 2B, Lane 2). Protein A affinity chromatography removed the remaining contaminating proteins and enriched pHu-E16 to greater than 95% purity (FIG. 2B, Lane 5). In the presence of a reducing agent, purified pHu-E16 was detected as the HC and LC (migration at ˜50 and 25 kDa) in the same stoichiometric ratio as the Hu-E16 produced in mammalian cells (FIG. 2B, Lanes 5 and 6). Under oxidizing conditions, purified pHu-E16 antibody assembled in its tetrameric fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| v/v | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| flow rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com