Controlling client access to networked data based on content subject matter categorization
a networked data and content technology, applied in the field of controlling client access to networked data based on content subject matter categorization, can solve the problems of affecting the service life of the client, so as to achieve the effect of constant maintenan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
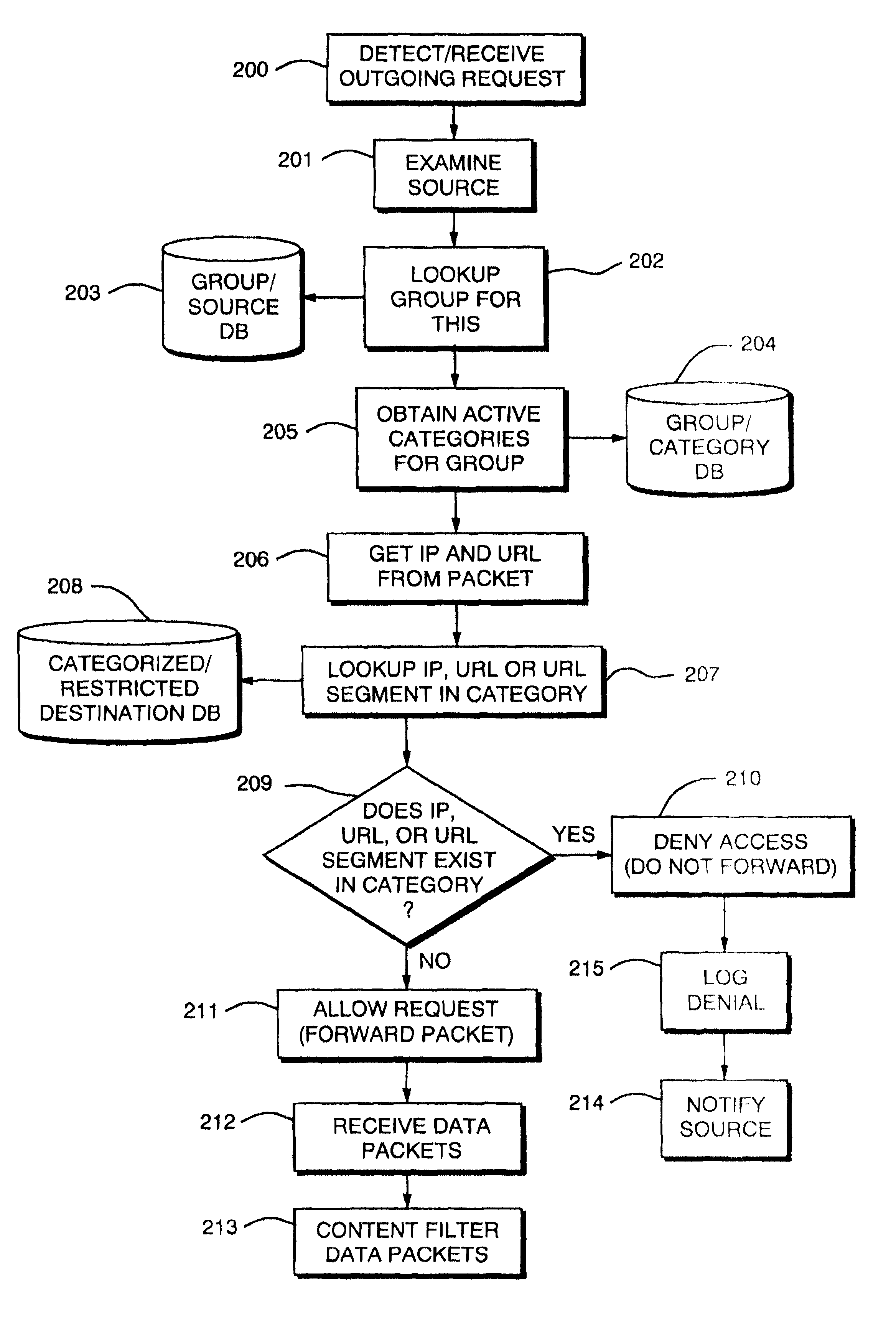
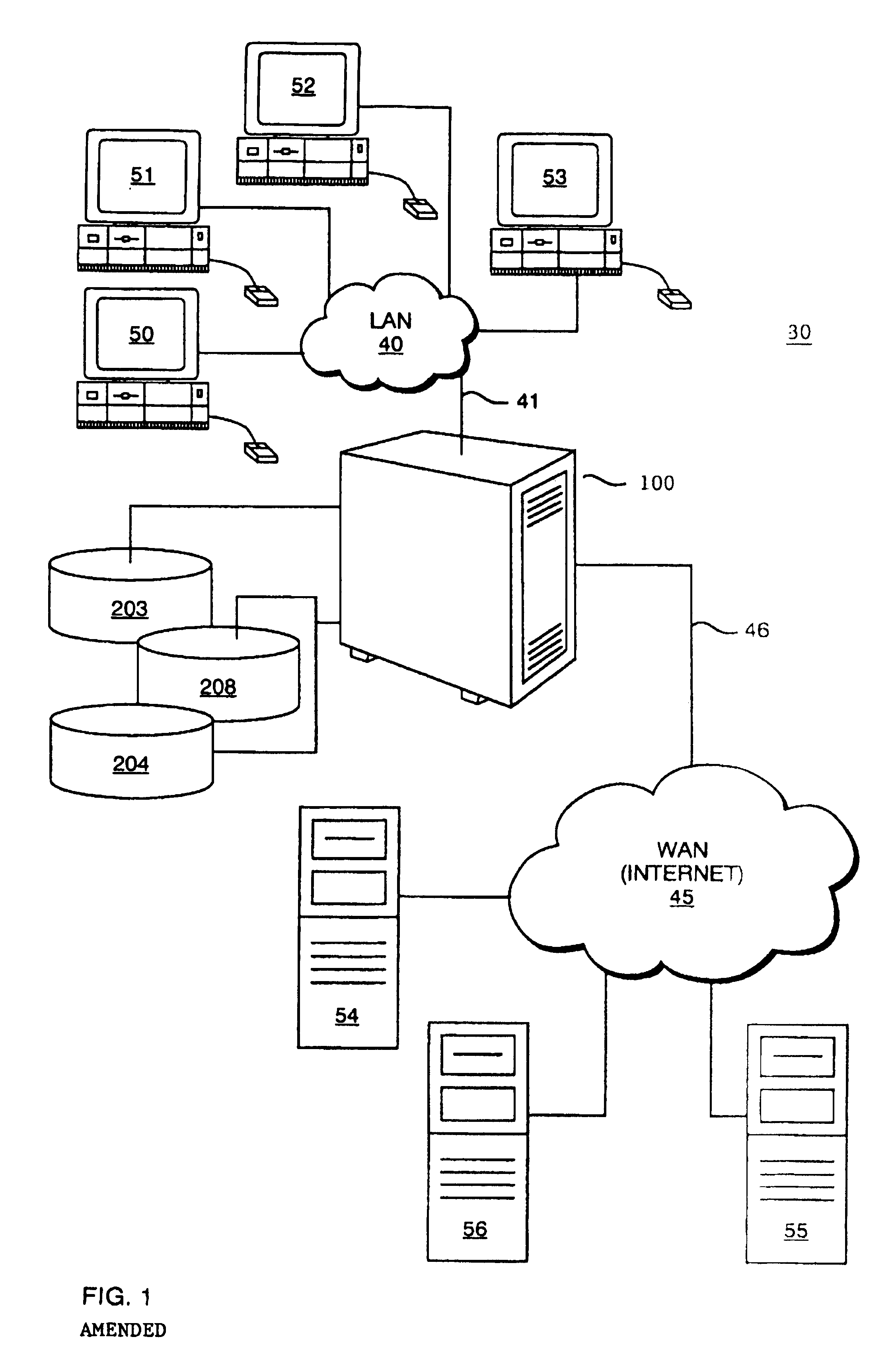
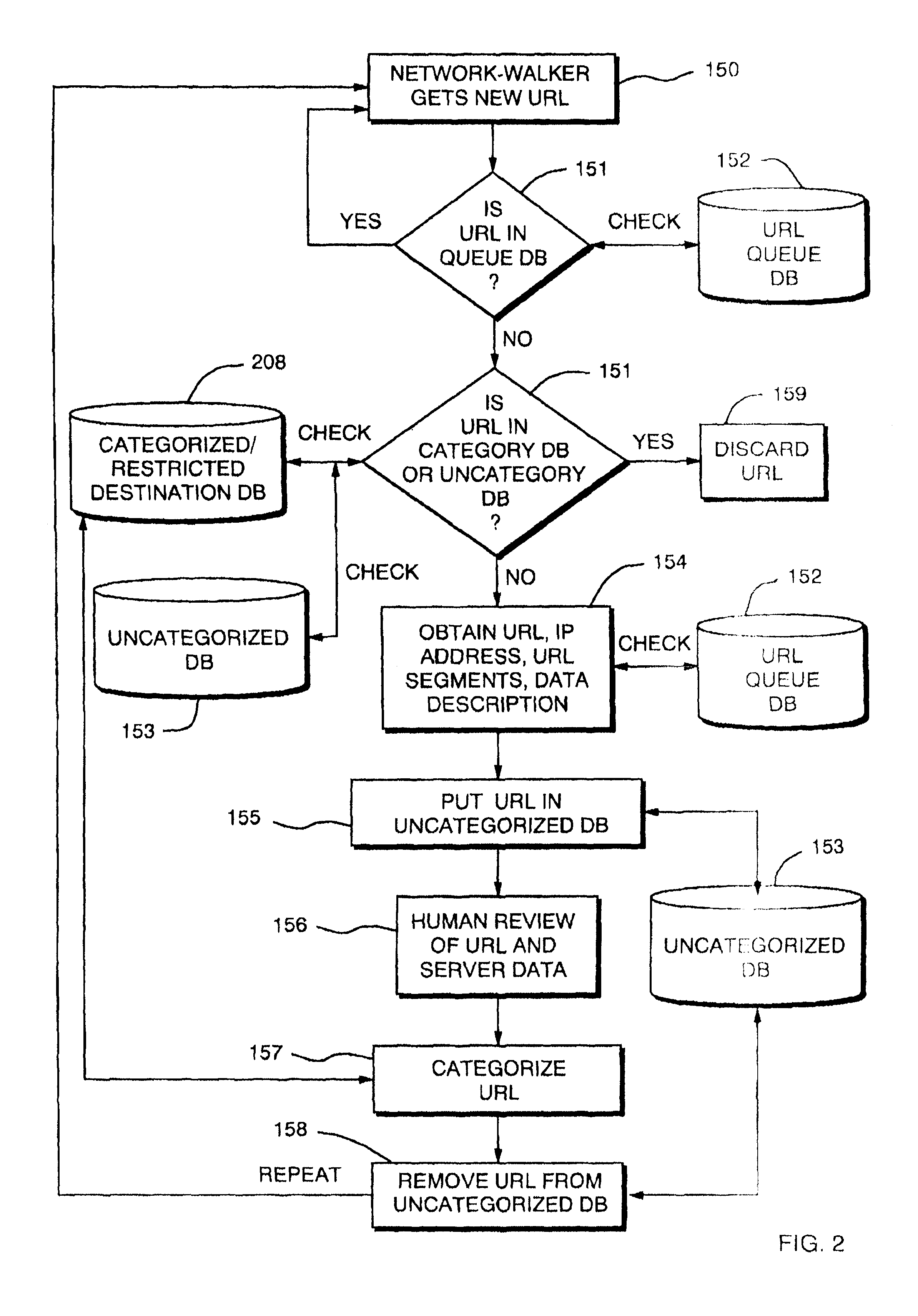
[0026]FIG. 1 illustrates an example networked computer environment 30 in which the present invention may be implemented. The networked computer environment 30 includes a first or Local Area Network (LAN) 40 composed of client computer hosts (“clients”) 50 through 53, a second or Wide Area Network (WAN) 45 including server computer hosts (“servers”) 54 through 56, and a network device 100 having access control databases 230203, 204 and 208. The network device 100, is connected to permit data communication between the Local Area Network 40 and Wide Area Network 45, and is in particular configured according to the present invention to provide an access control mechanism for all data information requests made from clients to servers, such as, for example, web page, news server, or FTP data or application download requests.
[0027]While the invention is applicable to many types of data transfer operations made from client to server computers, the preferred embodiment described herein relat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com