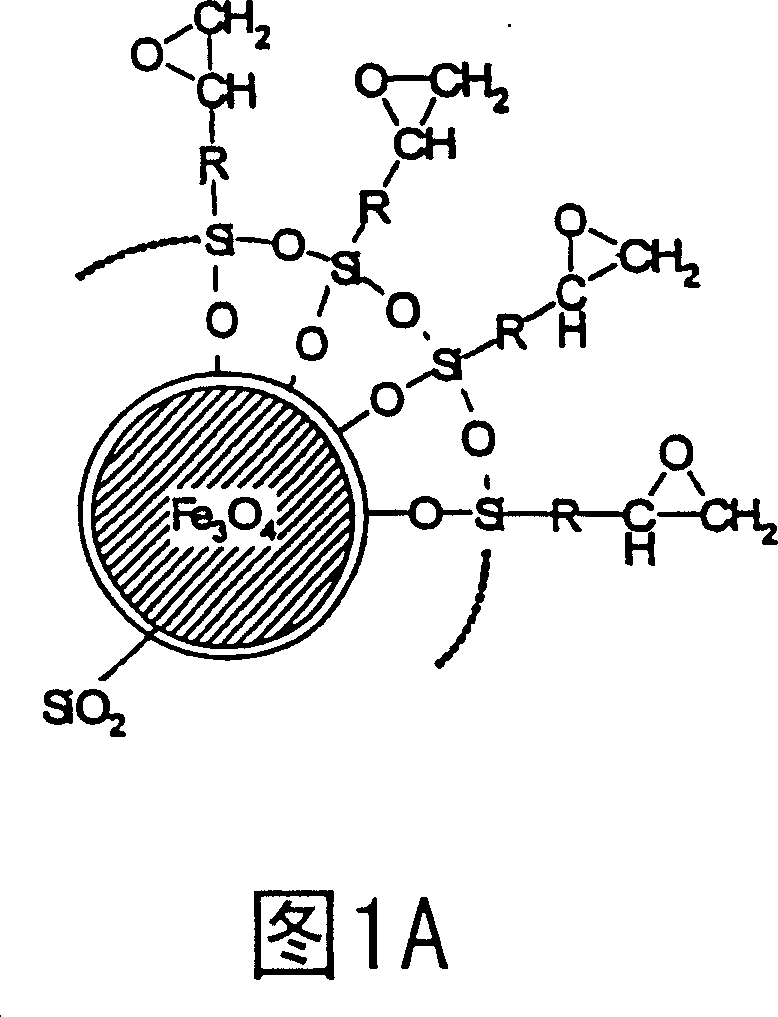
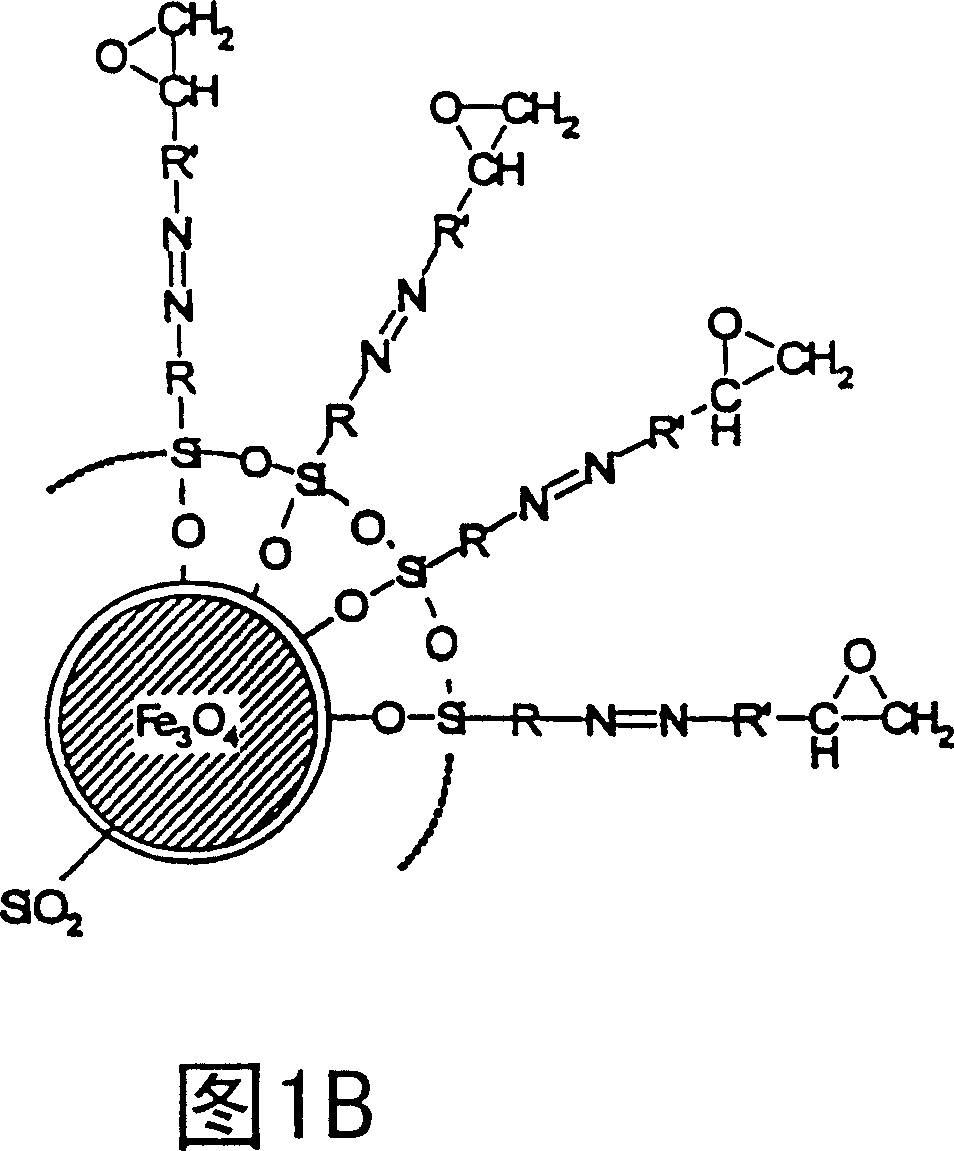
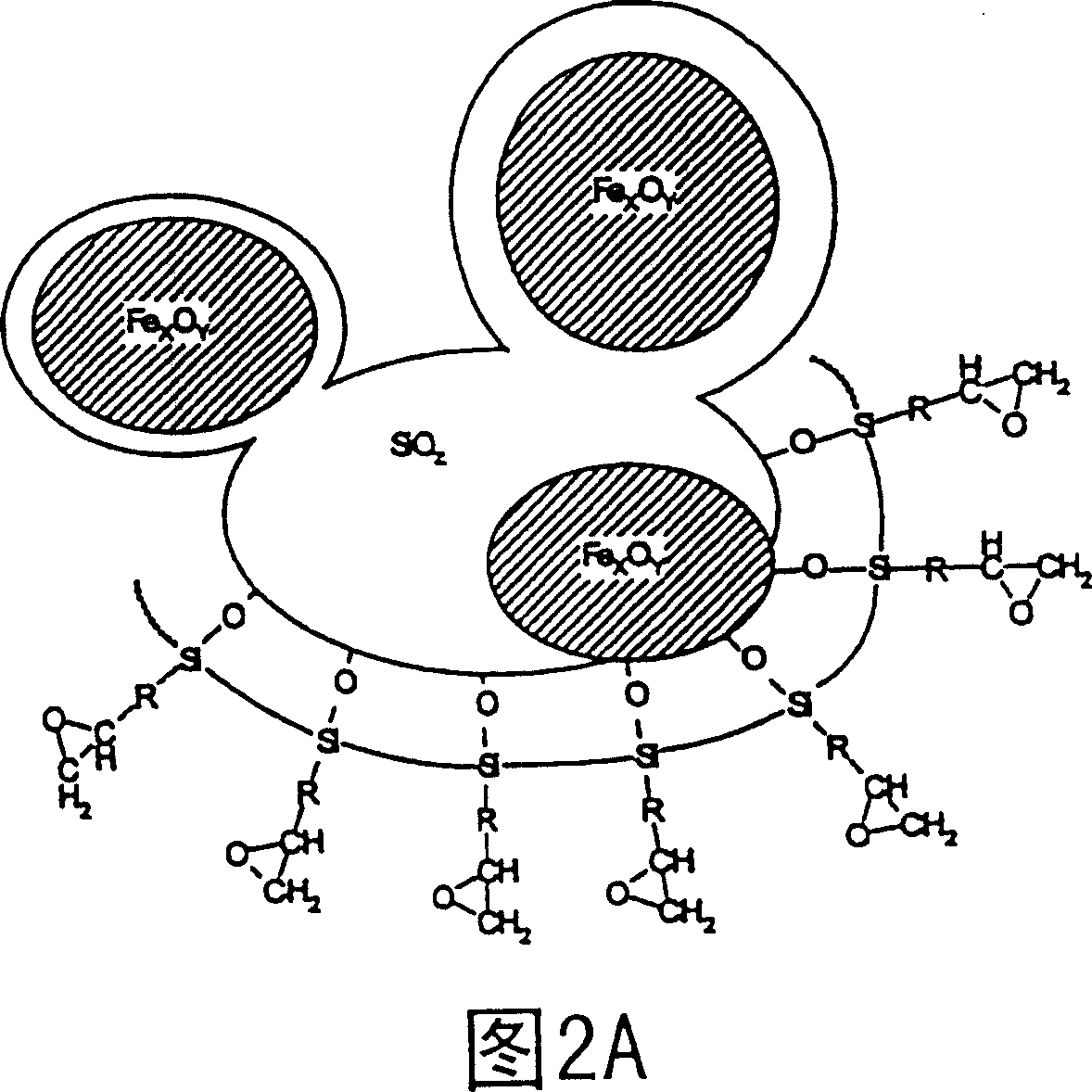
Curable bonded assemblies capable of being dissociated
An adhesive and composition technology, which is applied in the direction of adhesive heating, non-polymer adhesive additives, adhesives, etc., can solve the problem of limited strength of adhesive joints and irregular distribution of heat-activatable substances , adhesive thermal decomposition and other problems, to save time and energy, avoid non-selective thermal decomposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1: Curing and Separation of Adhesive Joints Containing Inductively Excitable Filler Particles Bonded to Crosslinkers
[0069] 1a) Nano-sized magnetite coated with silica
[0070] 43.3 g of iron (III) chloride hexahydrate was dissolved in 370 ml of water, and then dissolved oxygen was removed by blowing nitrogen gas through the solution. 15.9 g of iron(II) chloride tetrahydrate were added, followed by a solution of 25.6 g of sodium hydroxide in 100 ml of water dropwise in a stream of nitrogen over 2 hours while stirring with a precision glass stirrer. thus forming Fe 3 o 4 fine granular black precipitate. Add 22 g of Na dropwise over a period of 30 minutes 2 Si 3 o 7 (annealing loss 17% by weight) solution in 80 ml of hot water. The silicic acid was precipitated by the slow dropwise addition of hydrochloric acid (14 ml of 37% hydrochloric acid, made up to 50 ml with water) with further stirring. The precipitate was filtered and slurried with water 5 times...
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2: Adhesive joints separable by inductively excitable gas agents
[0078] 2a) Recipe consisting of magnetite powder and gas generator
[0079] 20 g of the material prepared according to 1 a) (40% residual water content in the filter cake) or nano-sized magnetite powder obtained from other sources was suspended in 100 ml of ethanol, and 20 g of oxy-bis( benzosulfonyl hydrazide) as an infuriating agent. The mixture was heated with stirring at 70°C for 4 hours and the solvent was removed on a rotary evaporator. The dry formulation was ground in a ball mill for 5 minutes and then sieved. The fraction with particle size nominally smaller than 63 μm was used in further experiments.
[0080] 2b) Incorporation of the mixture of example 2a) in the adhesive
[0081] Stir 8g of 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3,4-epoxycyclohexane-formic acid ester, 2g of polytetrahydrofuran (M n =250), 0.1 g of (cresyl cumyl) iodonium tetrakis (pentafluorophenyl) borate and 0.04 g of ascorb...
Embodiment 3
[0087] Example 3: Separation of glass bonded bodies based on adhesives containing inductively excitable gassing agents
[0088] 3a) Formulation of composite particles and binders prepared by flame pyrolysis
[0089] 25 g of nano-sized composite particles prepared by flame pyrolysis and composed of silica and iron oxide (the properties of which are shown in Table 1) were suspended in 100 ml of ethanol, and then 20 g of oxy-bis(benzene and sulfonyl hydrazide) as an infuriating agent. The mixture was heated with stirring at 60°C for 5 hours and the solvent was removed on a rotary evaporator. The dry formulation was ground in a ball mill for 3 minutes and then sieved. The fraction with particle size nominally less than 63 μm was used in further experiments.
[0090] 3b) Incorporation of the formulation of Example 3a) in the adhesive and the adhesive experiment
[0091] 300 g of the hydraulic one-component polyurethane binder Dinitrol PUR 501 were used in a Planimax (Molteni) m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com