Method for detecting unwanted interface charge of mercury cadmium telluride thin film photovoltaic device
A technology of interface charge and thin-film photovoltaics, applied in the direction of measuring electric variables, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as unimportant, limiting the effect of C-V method, unable to extract interface charge information, etc., and achieve the effect of non-damage judgment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] Below in Hg 0.702 CD 0.298 Te thin-film photovoltaic device is an embodiment in conjunction with the accompanying drawings to describe in detail the specific implementation of the present invention:
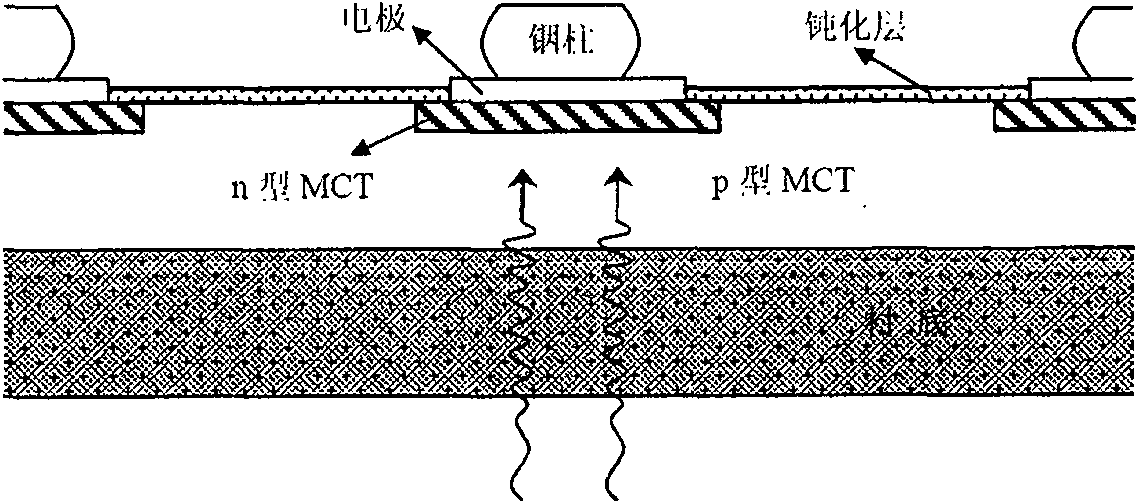
[0018] The measured sample is a planar junction HgCdTe linear photovoltaic detector grown by molecular beam epitaxy, see figure 1 . p-Hg 0.702 CD 0.298 Te grows on the CdTe buffer layer with GaAs substrate. Boron ions are implanted on the p-type surface to form n + type mutation n + -p knot. Samples were flip-bonded on sapphire substrates.
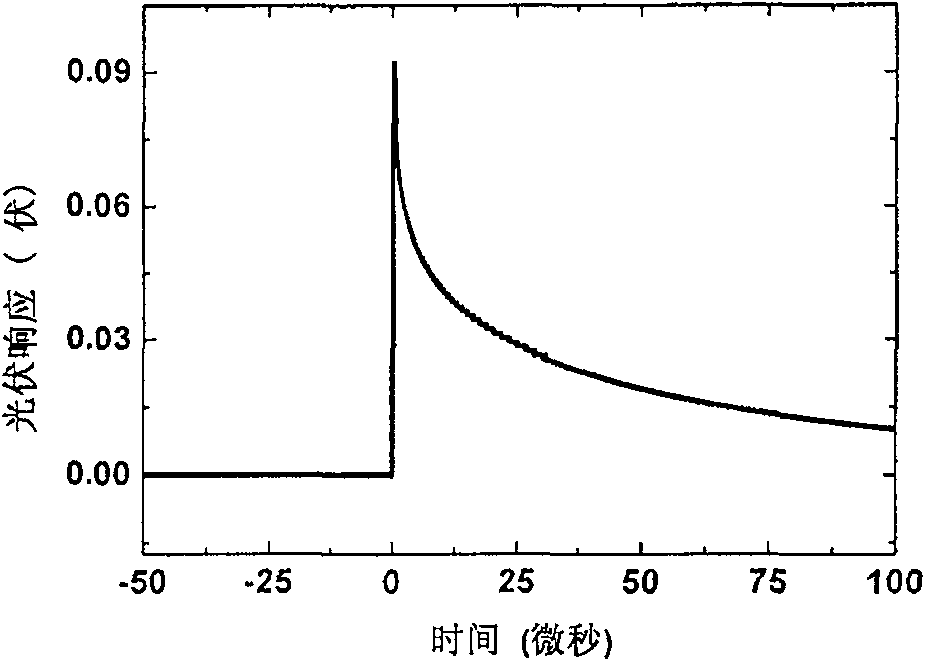
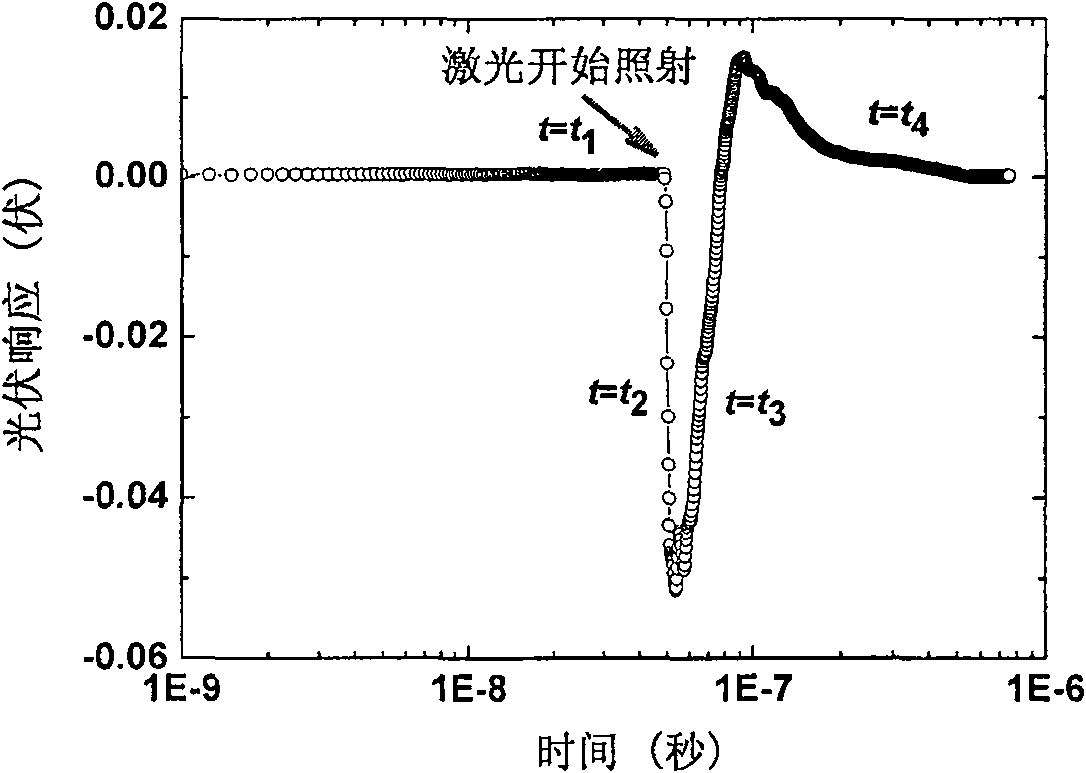
[0019] The tunable pulse laser is pumped by PL2143BSS Nd:YAG laser produced by Lithuania EKSPLA company to pump PG401 / DFG optical parameter generator / difference frequency amplifier. The laser pulse width is 30ps, repetition frequency is 10Hz, and its output wavelength is adjusted to 4.5μm. Calculated, Hg at 4.5μm incident wavelength 0.702 CD 0.298 The absorption coefficient of Te is α 4.5μm =4870cm -1 , Hg 0.702 CD 0.29...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com