High succinate producing bacteria
A technology of bacteria and cells, applied in the direction of bacteria, fermentation, etc., can solve problems such as limitations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0016] The carboxylic acids may be salts, acids, bases or derivatives, depending on structure, pH and ions present. For example, the terms "succinate" and "succinic acid" are used interchangeably herein. Succinic acid is also called succinic acid (C 4 h 6 o 4 ). The chemicals used here included formic acid, glyoxylic acid, lactic acid, malic acid, oxaloacetic acid (OAA), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and pyruvate. Bacterial metabolic pathways including the Krebs cycle (also known as the citric acid, tricarboxylic acid, or TCA cycle) can be found in Lehninger's "Principles of Biochemistry" and other biochemistry textbooks.
[0017] The terms "operably associated" or "operably linked" are used to refer to functionally paired nucleotide sequences.
[0018] "Reduced activity" or "inactivation" as defined herein means at least a 75% reduction in the activity of the protein compared to an appropriate control strain. Preferably, at least 80, 85, 90, 95% reduction in activity is ach...
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Inhibition of Lactic Acid, Acetic Acid and Ethanol
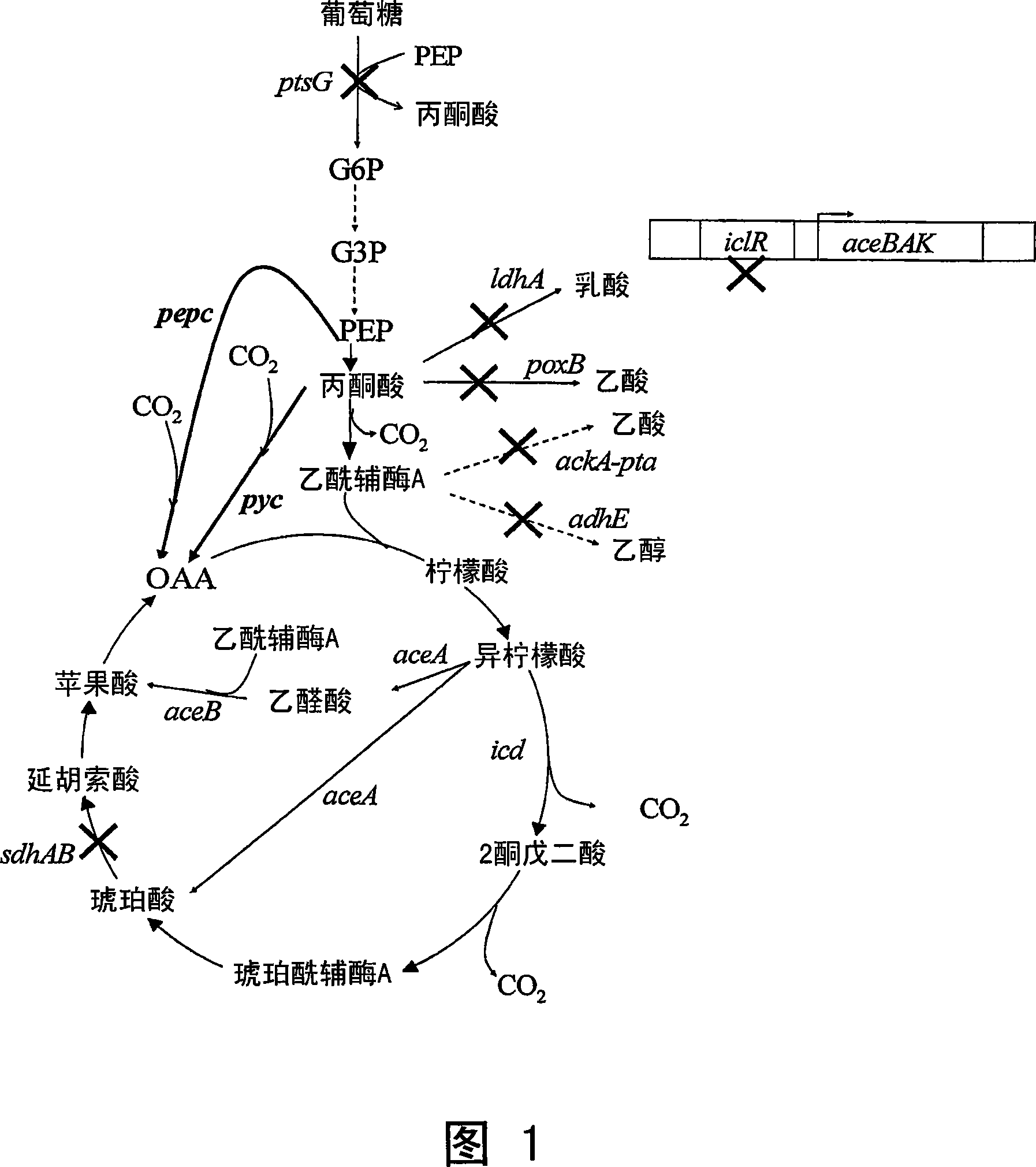
[0032] Hybrid bacterial strains that produce carboxylic acids under aerobic and anaerobic conditions are able to overcome the limitations of low biomass generation on anaerobic production processes. Biomass can be produced under aerobic conditions at the beginning of the fermentation process. During this period, a large number of carboxylic acids are generated through the aerobic synthetic pathway, saving time and cost. Once high biomass is achieved, the environment can be switched or allowed to switch to anaerobic conditions for additional conversion of carbon sources to carboxylic acids in high yield. Using a redesigned anaerobic succinate fermentation pathway, carboxylic acid production is expected to increase to well above 2 or 3 moles of product per mole of glucose.
[0033] First, to increase flux into the TCA cycle for carboxylic acid production, two acetate pathways in aerobic metabolism are ina...
Embodiment 2
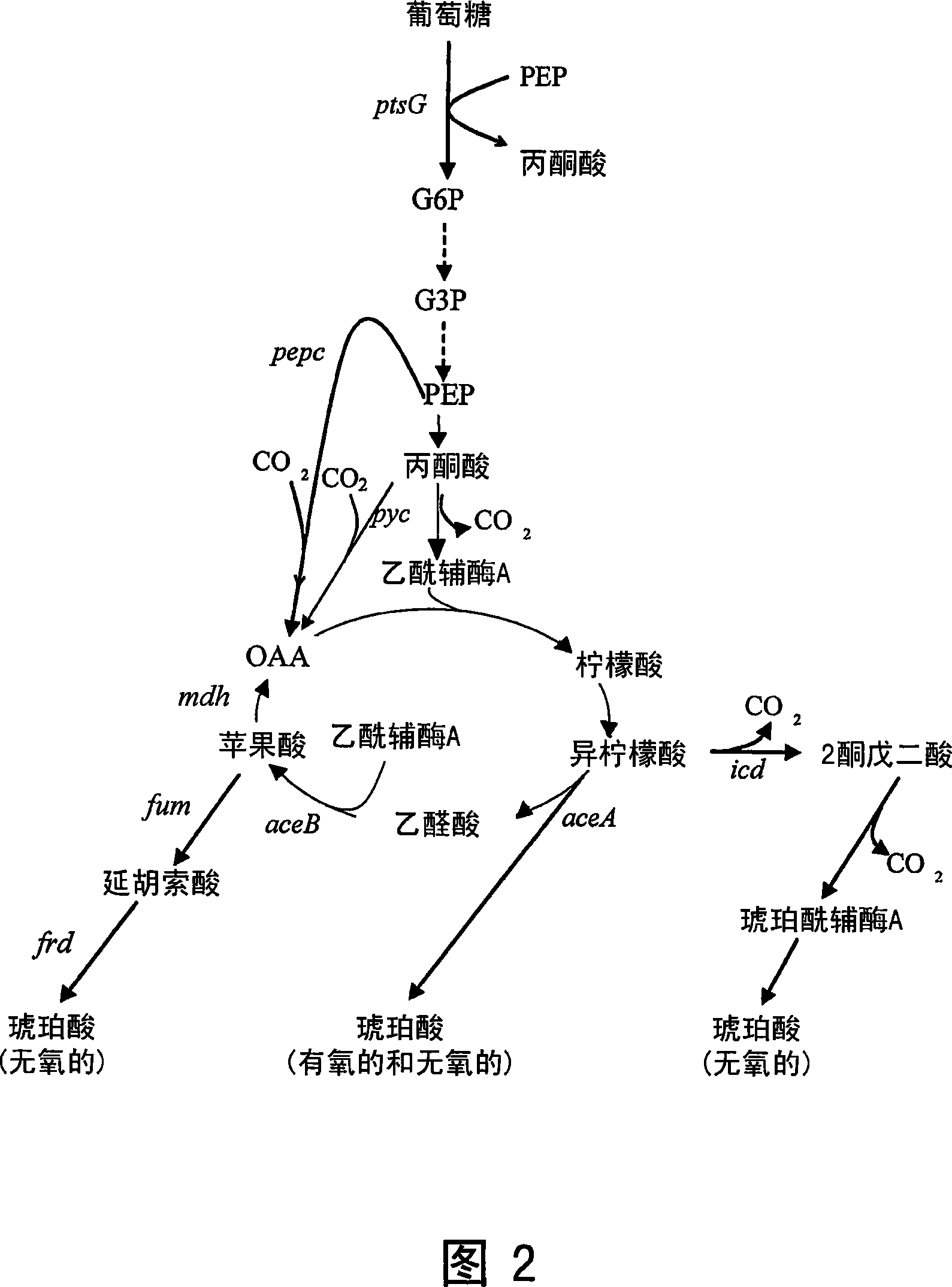
[0037] Example 2: Increasing glyoxylate bypass flux
[0038] As previously shown, the presence of native ACEA and ACEB is sufficient to drive carboxylic acid production without additional expression. However, native expression levels are susceptible to feedback inhibition and are sensitive to the aerobic or anaerobic conditions of the environment. Constitutive activation of the glyoxylate shunt is important to maintain high levels of aerobic metabolism for carboxylic acid synthesis. This activation is made possible by inactivating the aceBAK operator repressor (ICLR). As shown in Figure 1, activation of the glyoxylate bypass provides a mixed fermentation environment that achieves high levels of carboxylic acid production.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com