Conversion of ion-beam mediated Chinese ephedra general DNA in microzyme and acquired tr-gene yeast engineering fungus
A yeast and transgenic technology, applied in the field of genetic transformation, can solve the problems such as the inability to construct ephedrine, and achieve the effects of easy cultivation, convenient genetic manipulation, and overcoming genetic transformation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
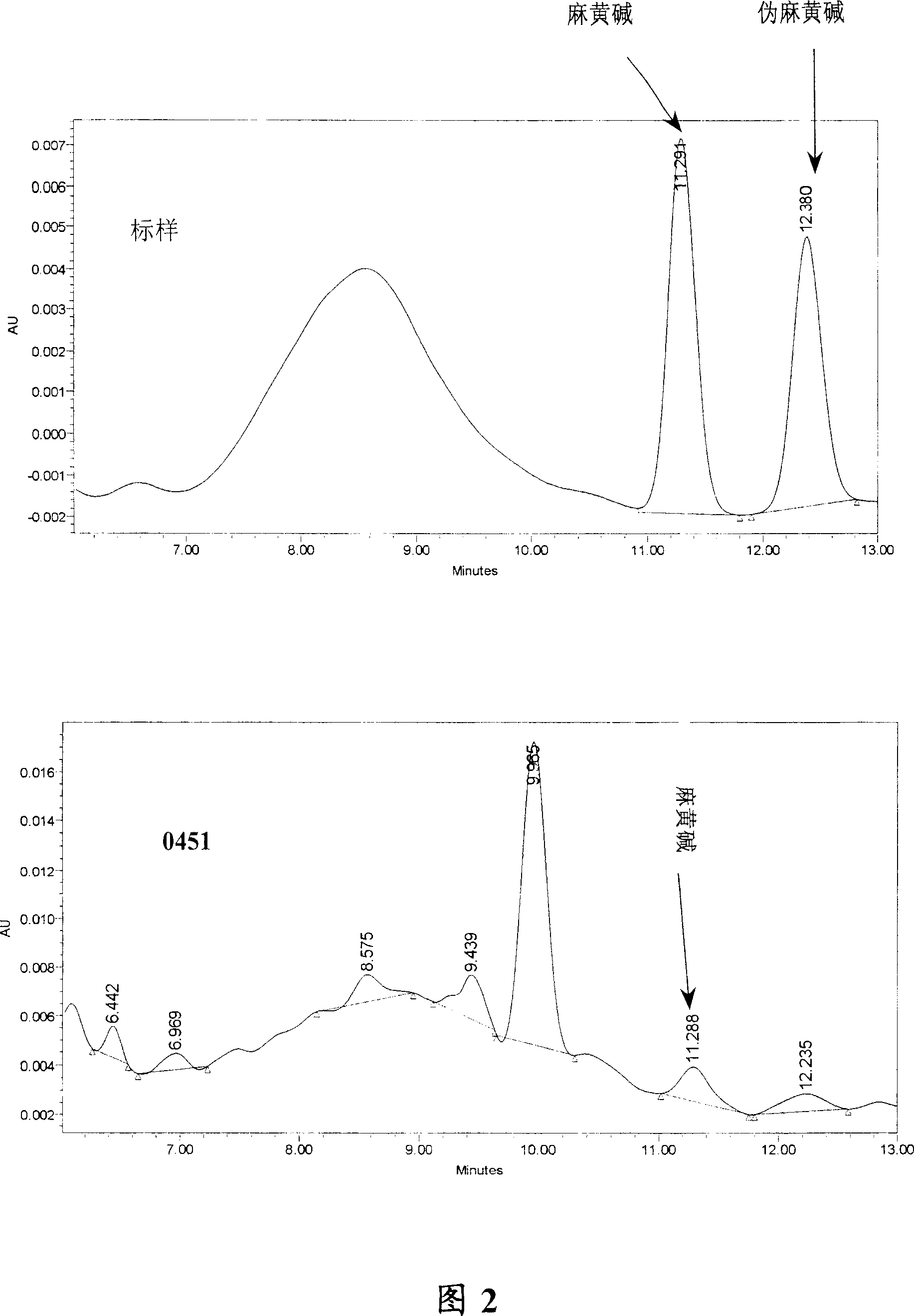
[0047] Example 1: Introduction and transformation of the total DNA of Ephedra to obtain Hansenula anomaly engineering strain 0451
[0048] (1), collection of medicinal plant ephedra, preparation of total DNA
[0049] Use 10 times the amount of color-changing silica gel (origin: Shanghai) of the blue ephedra (Ephedra glauca) sample and put the blue ephedra twigs with scaly triangular leaves (collected from the desert area of Yamalik Mountain, Xinjiang) into a sealed bag at room temperature. Guaranteed to be dry within 12 hours. If the silica gel has changed from dark blue to pink, replace it in time. After returning to the laboratory, immediately seal the dried ephedra material and store it in a desiccator.
[0050] After the castor ephedra material was quick-frozen in liquid nitrogen, it was co-researched with quartz sand, and the total DNA was extracted by CTAB method (see reference 7). Detection of DNA purity by UV spectrophotometer A 260 / A 280 It was 1.8, and it was a...
Embodiment 2
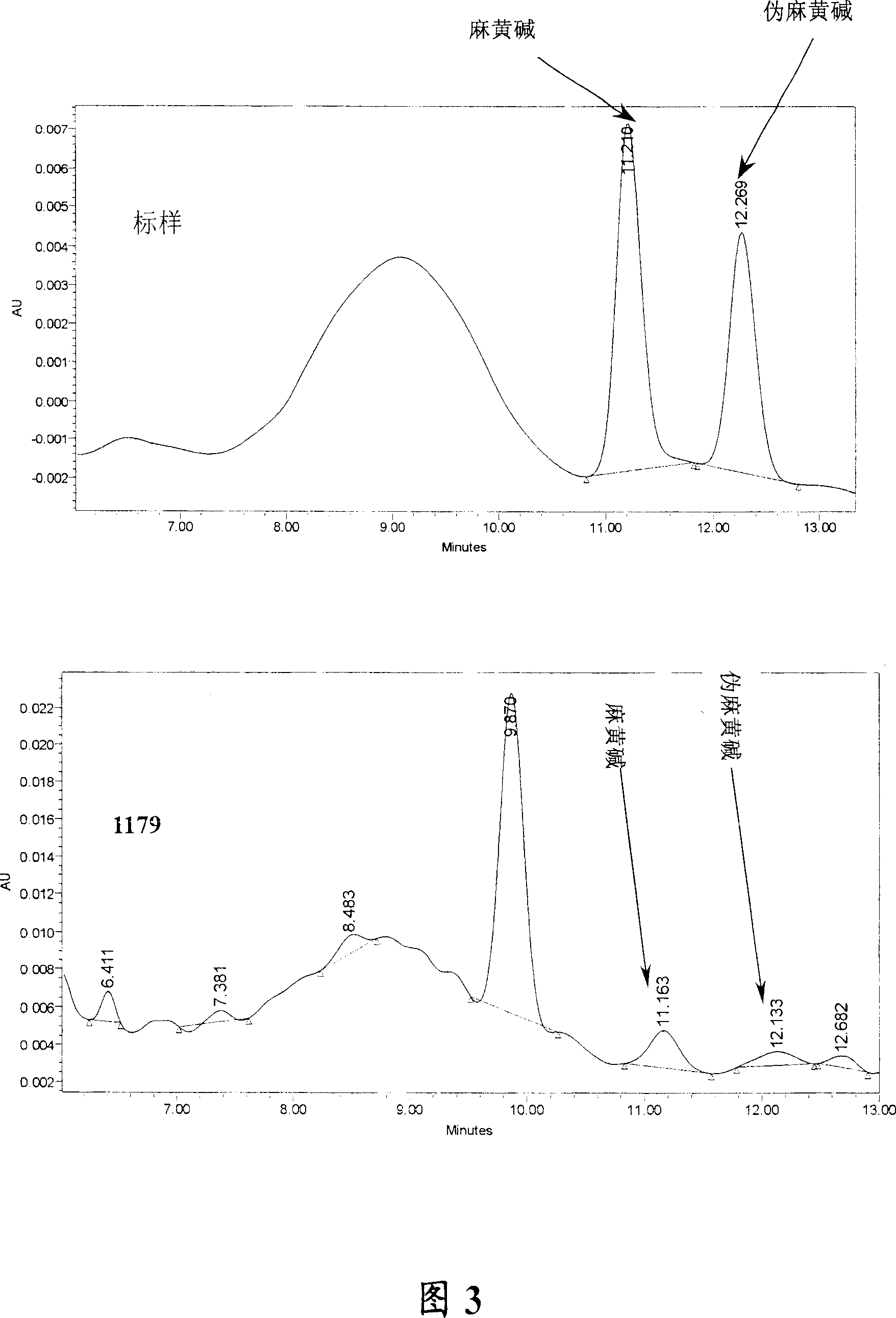
[0065] Example 2: Introduction and transformation of total DNA of Ephedra to obtain Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered strain 1179
[0066] (1), collection of medicinal plant ephedra, preparation of total DNA
[0067] Total DNA was prepared in the same manner as described in Part (1) of Example 1, except that shoots of Ephedra sinica (collected from the northern desert area of the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang) with scaly triangular leaves were used. Detection of DNA purity by UV spectrophotometer A 260 / A 280 It was 1.9, and it was a single band in agarose electrophoresis (Fig. 5b).
[0068] (2), the treatment of yeast cells
[0069] Put the strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (purchased in Beijing: China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, No. 2.1882) into the wort culture solution (see reference 8) on the slant, and put it on a rotary shaker at 230r / min, and cultured at 30°C for 12 hours. With 0.1% soluble starch (domestic, analytically pure) an...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3: The introduction and transformation of the total DNA of ephedra to obtain the fermenting Pichia pastoris engineered strain 3161
[0081] (1), collection of medicinal plant ephedra, preparation of total DNA
[0082] Part (1) of Example 1 was repeated to extract total DNA, except that shoots of Ephedra intermadia (collected from the western desert area of Jungar Basin, Xinjiang) with scaly triangular leaves were used. Detection of DNA purity by UV spectrophotometer A 260 / A 280 It was 1.7, and it was a single band in agarose electrophoresis (Fig. 5c).
[0083] (2), the treatment of yeast cells
[0084] Put the strains of fermenting Pichia fermentans (purchased in Beijing: China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, No. 2.1706) into the wort culture solution (see reference 8), and put it on a rotary shaker 230r / min, 30°C for 12 hours. With 1.0% soluble starch (domestic, analytically pure) and 1.0% glucose (C 6 h 12 o 6 ·H 2 O...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com