Process for obtaining antibodies
A recombinant antibody, partial antibody technology, applied in separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in obtaining high recovery percentages, and achieve the effect of saving production time and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
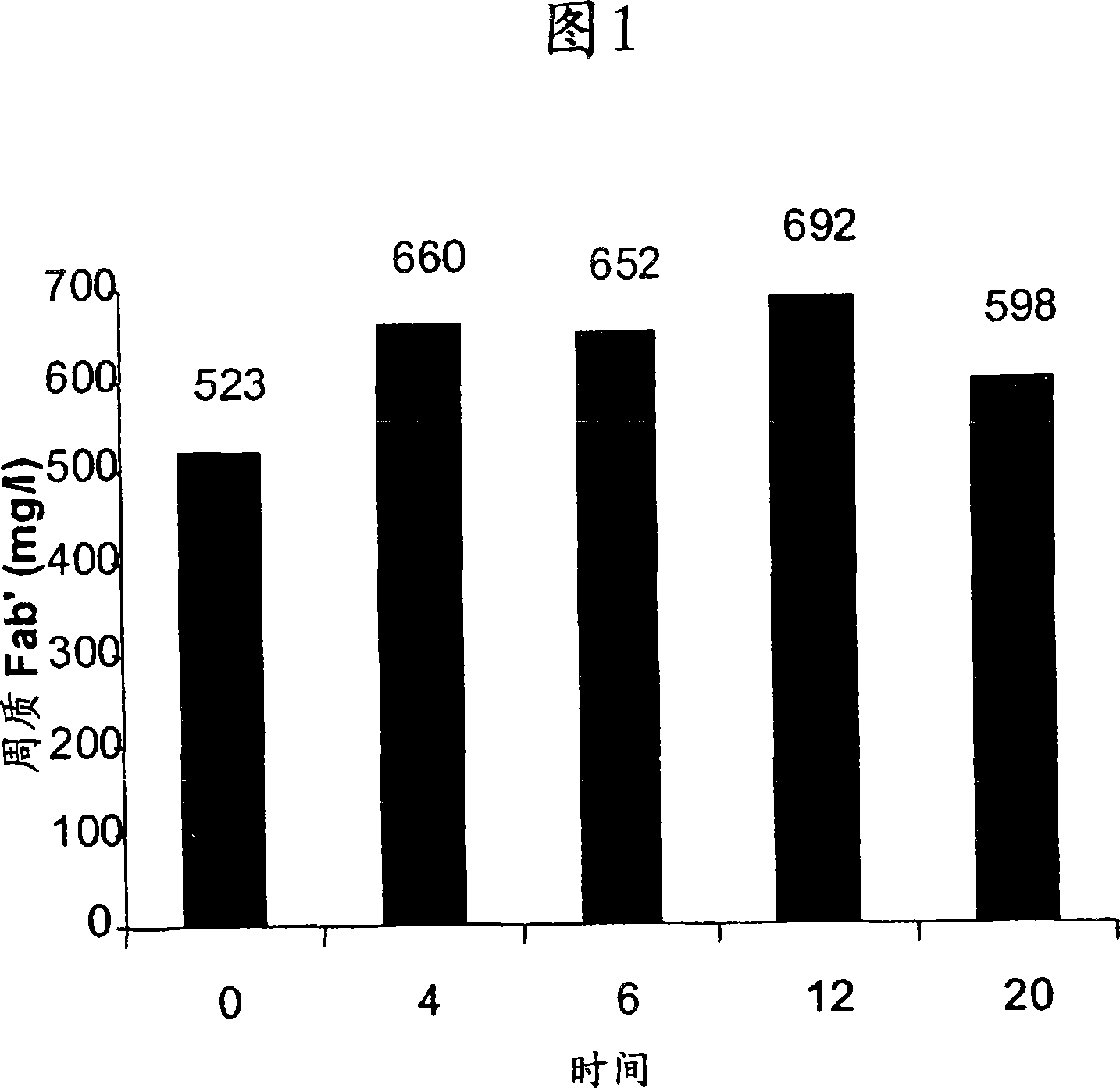
[0044] Embodiment 1: the effect of non-lysing treatment (pretreatment)
[0045] (a) Antibody A (a Fab') was expressed in Escherichia coli W3110 cells using vector pTTOD inserted with DNA encoding antibody A. Fermentation (in DD53) at 25°C until OD 600 For 111.6 and ready to collect. Aliquots of the culture were harvested by centrifugation in 50 ml at room temperature and the cell pellet was resuspended in 5 ml culture supernatant + 29 ml HO 20 and 5 ml of 1M Tris, pH 7.4, containing 100 mM EDTA. The resuspended cell pellet was subjected to pretreatment agitation at 60 rpm for the times indicated in Figure 1. After pretreatment, the resuspended cell pellet was subjected to heat treatment at 50°C while stirring at 170 rpm for 14 hours. After heat treatment, the resuspended cell pellet was clarified by centrifugation in a Beckman J.6 centrifuge at 4200 rpm for 30 min at 4°C. Fab' in the supernatant containing functional antibody A was determined using protein GHPLC analysis ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Effect of non-cracking treatment (pressure)
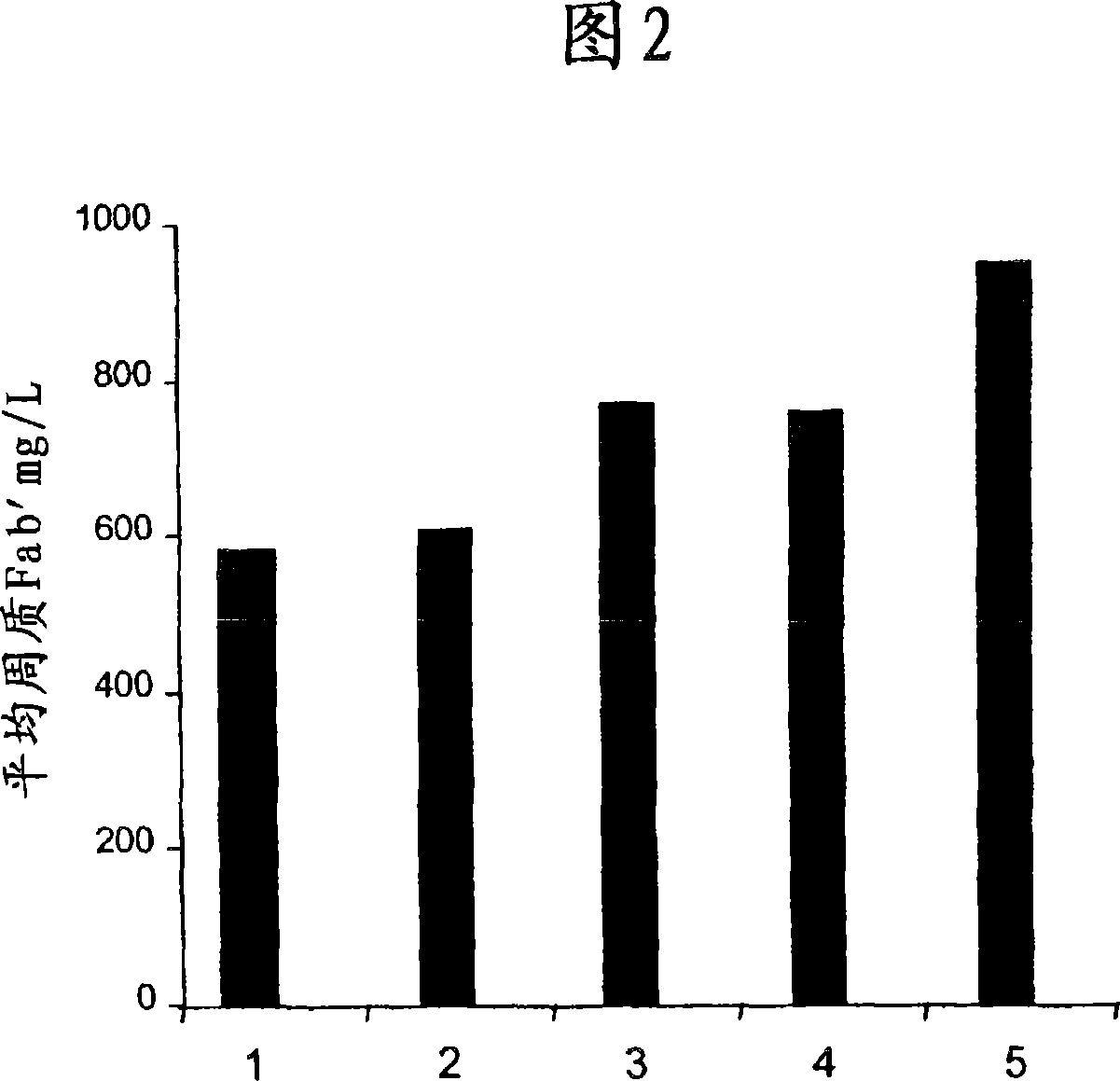
[0050] (a) Antibody A was expressed in E. coli as described in Example 1. As described in Example 1, in the culture supernatant, H 20 Resuspended cell pellets were prepared in Tris / EDTA and thereafter pressure treated at different pressures using a French cell press. Heat treatment was performed and the yield of functional antibody was calculated as described in Example 1.
[0051] An increase in the yield of functional antibody was observed at all pressures except 500 psi compared to the case where no pressure was used (Figure 2). Increased yields of functional Antibody A were obtained by using this non-lysing treatment, particularly at 1000 psi and 2000 psi. Some cell lysis was seen at 4000 psi, but this was not significant (ie less than 20%).
[0052] (b) Antibody B (a Fab') was expressed in Escherichia coli W3110 cells using vector pTTOD inserted with DNA encoding antibody B. Fermentation was carried out ...
Embodiment 3
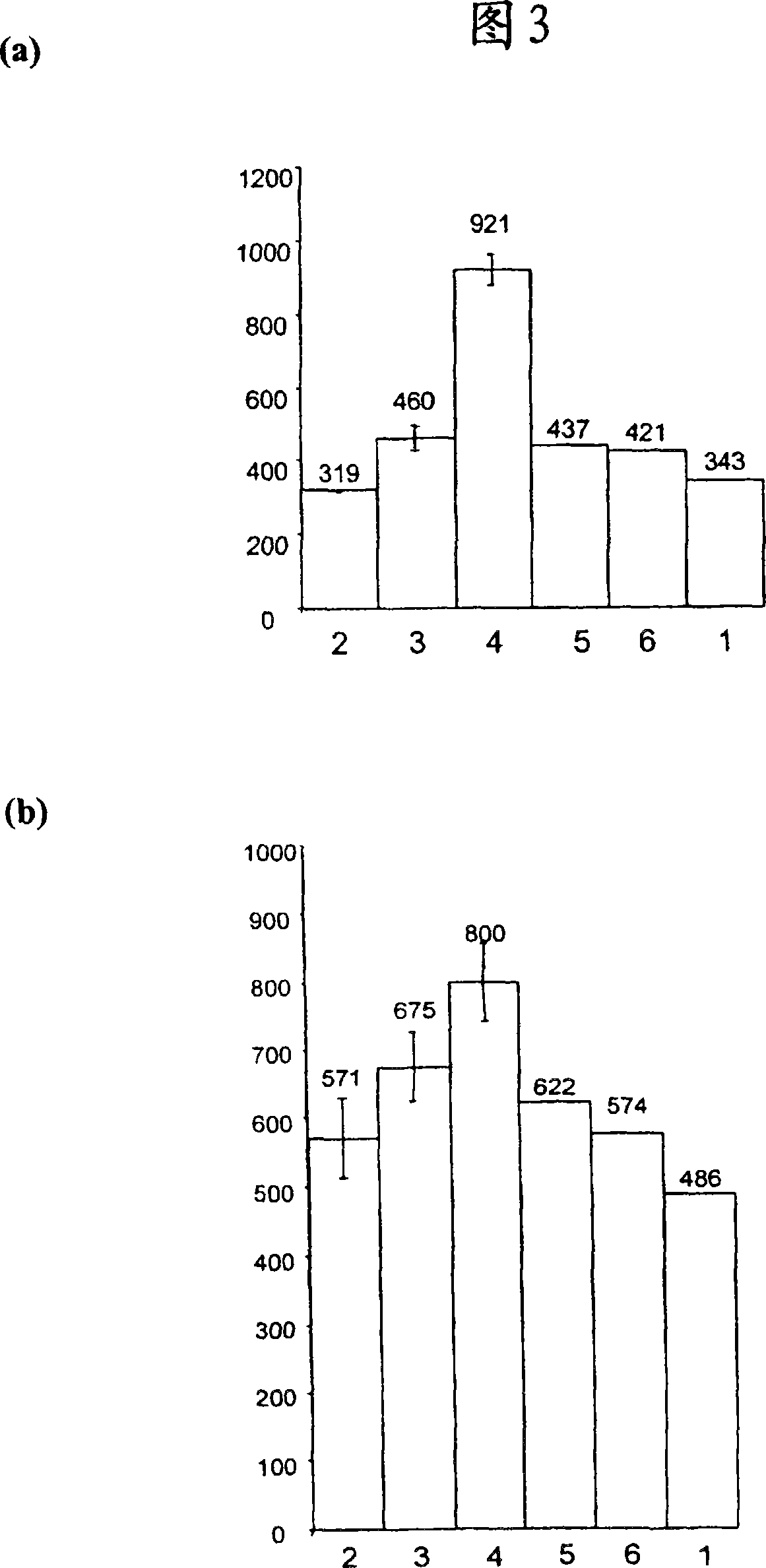
[0059] Example 3: Determination of Cell Lysis Using FACS Analysis
[0060] Antibody A (a Fab') was expressed in Escherichia coli W3110 cells using vector pTTOD into which DNA encoding antibody A was inserted. Cell slurries were prepared to original volume in tris / EDTA extraction buffer as described in Example 1 and passed through a MG homogenizer (single pass) at different pressures (see Figure 5).
[0061] The feed stream from the homogenizer was collected and diluted to OD in phosphate buffered saline 600 is 0.2. To each sample (500 μl) was added the fluorescent dye propidium iodide (200 μg / ml) (2 μl). Propidium iodide binds DNA but cannot cross the intact plasma membrane. Each reaction was evaluated using a Becton Dickinson FACSCalibur to determine lysed and non-lysed cells. Harvested cultures and Opsi controls are included and total intact cells before stress treatment are indicated. The data presented in Figure 5 indicate that pressure treatment up to and including 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com