A thymus-specific protein
A technology based on isoleucine and selection, applied in the field of new thymus-specific proteins, can solve the problem of unclear mechanism of CD4+CD25+ T cell regulatory function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0193] The amino acid and nucleotide sequences of the full-length T101 are shown in FIG. 1 . Using the Phobius signal peptide prediction tool (available at www.phobius.cgb.ki.se available above) to analyze the amino acid sequence to predict the transmembrane topology and signal peptide sequence.
[0194] Phobius predicted the 33 amino acid C-terminal sequence of the full-length T101 peptide to be a hydrophobic, transmembrane signal peptide domain. The signal peptide is indicated in Figure 1 with conventional block letters.
[0195] Also by using conventional bioinformatics tools, the 24 amino acid subsequence of SEQ ID NO: 4 was found,
[0196] SKRVSDKQLISKAVWWTFFLPSTL (SEQ ID NO: 12)
[0197] Corresponds closely to the following sequences from other mammalian species:
[0198] Dog: SKQVSDKQLISKAVQRIFFFLQPS (SEQ ID NO: 13); and
[0199] Rat: SKFMSDKQLISKAVQRIFFLSSTL (SEQ ID NO: 14).
[0200] When comparing SEQ ID NOs: 12 to 14, the following consensus amino acid residues...
Embodiment 2
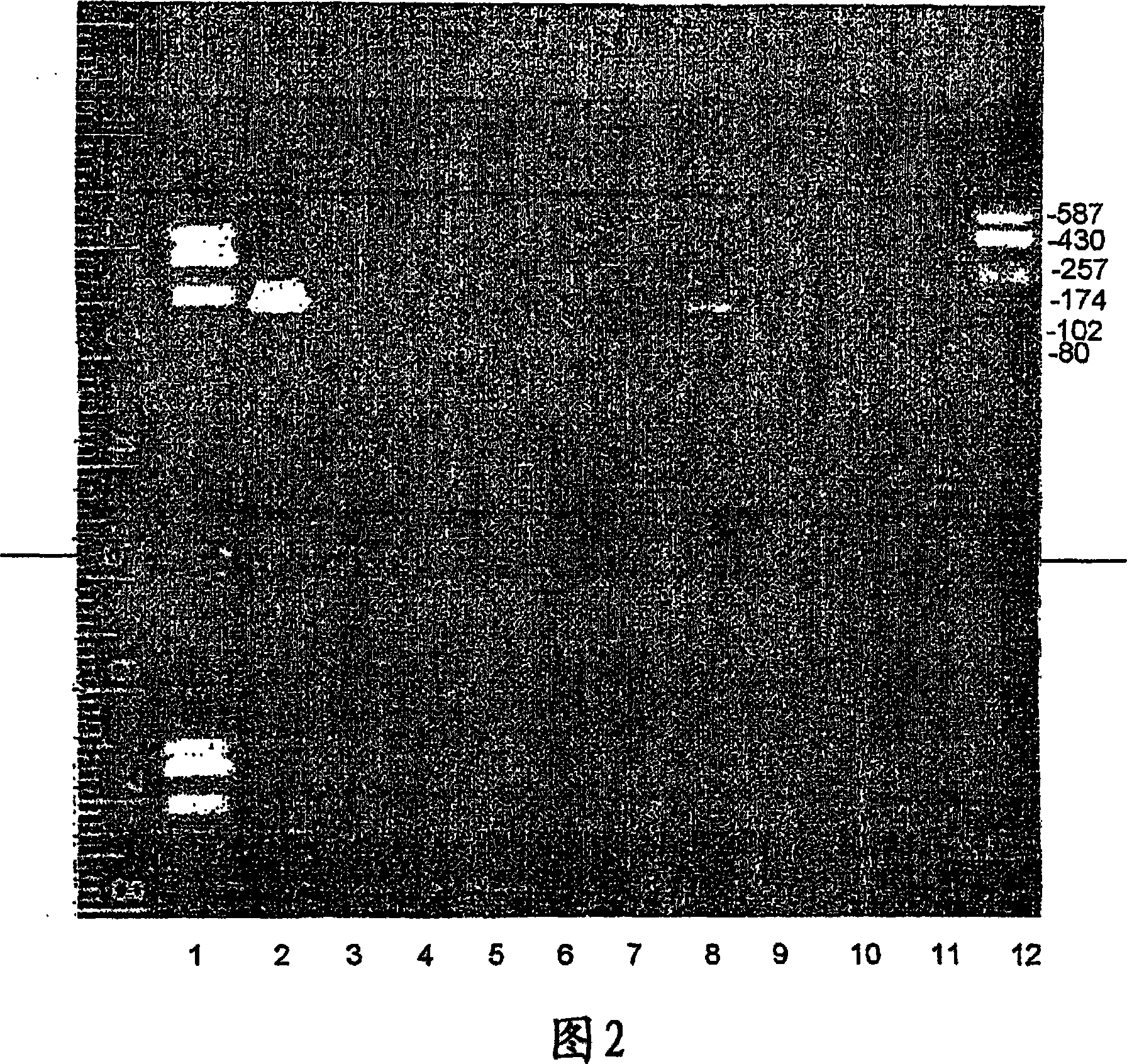
[0205] cDNA libraries from 16 different tissues were used to screen for T101. The library was purchased from Clontech Company, including libraries of leukocyte, testis, colon, prostate, small intestine, thymus, ovary, spleen, liver, kidney, brain, lung, pancreas, bone, placenta, and heart.
[0206] The cDNA library was screened by PCR using oligonucleotides specific for T101. The sequence of the oligonucleotide was deduced from the sequence of T101.
[0207] In PCR experiments, 3 microliters of each cDNA library, 5 microliters of specific oligonucleotides (total), 20 microliters of Readymix Taq polymerase and 17 microliters of DDW were used.
[0208] Use the following more described PCR steps:
[0209] - 1 minute at 95°C
[0210] -30 loops:
[0211] 1 minute at 95°C;
[0212] 1 minute at 52°C;
[0213] at 72 °C for 1 min.
[0214] - After completing the cycle, keep the sample at 72°C for 10 minutes.
[0215] The sequences of the oligonucleotides used were:
[0216] (i...
Embodiment 3
[0223] The T101 peptide was tested for its ability to activate the proliferation of mouse splenocytes or thymocytes (using two mouse strains: CD1 and Ba1b / C), as well as human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL). Proliferative activity was measured by the incorporation of 5-bromo 2'-deoxy-uridine (BrdU) into these cells.
[0224] method
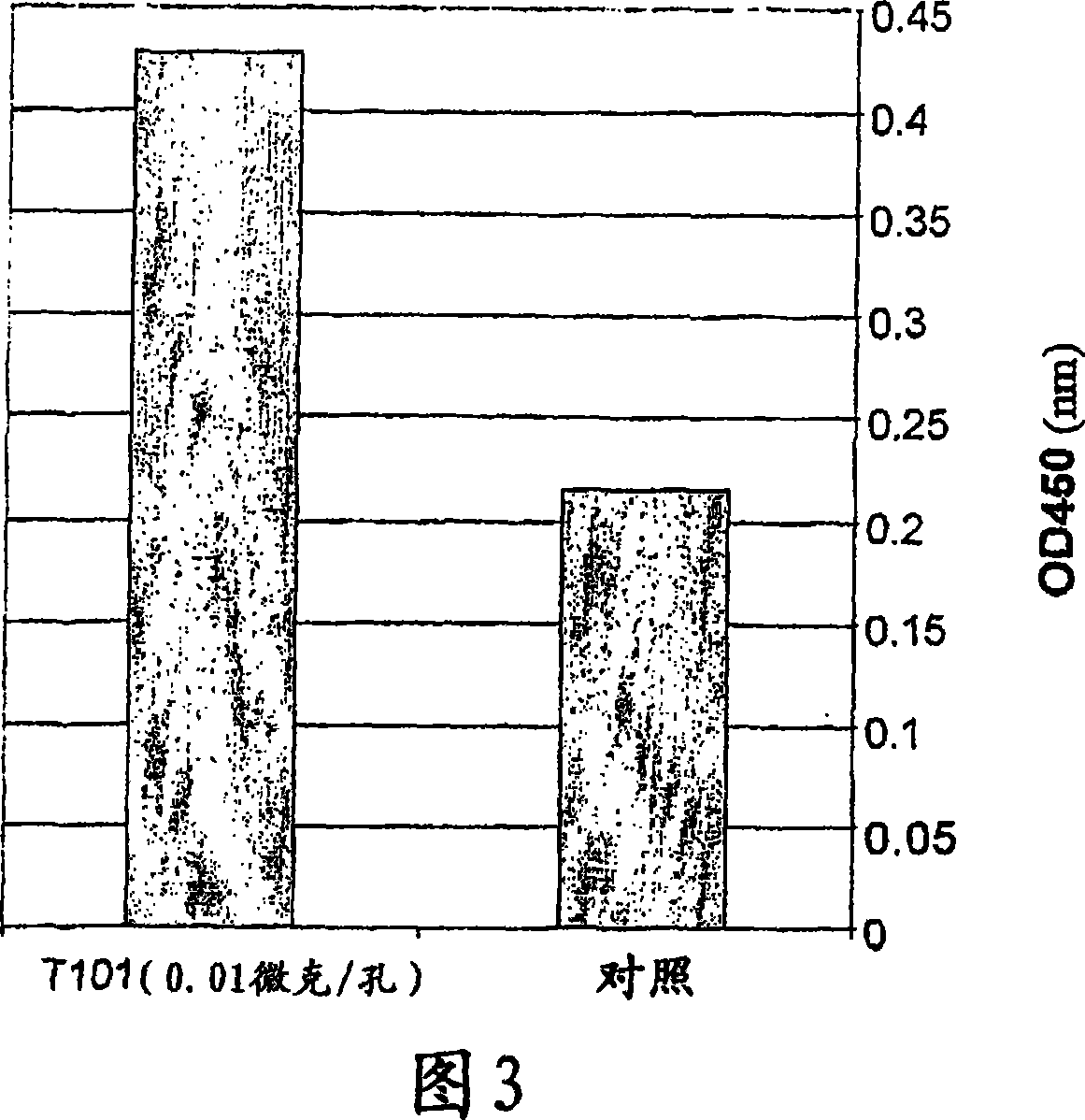
[0225] Mouse splenocytes or thymocytes were isolated from the spleen or thymus of Ba1b / C mice. use 10 7 Cells / well were plated in 96-well plates. RPMI 1640 medium + 10% FCS and Pen / Str were used. The cells were treated with different concentrations of T101 peptide (0.1 or 0.01 μg / well) or with saline (control), and after 48 hours, were labeled with BrdU for 6 hours and detected for BrdU incorporation into their nuclei.
[0226] Human PBL cells were isolated from volunteer blood on a Ficole gradient and plated in 96-well plates, again using RPMI 1640+10% FCS+Pen / Str.
[0227] Cells were treated with different concentrations of peptide or s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com