Method for detecting DNA by stacking hybridization fluorescent amplify magnetic separation
A magnetic separation and fluorescence technology, applied in the field of DNA detection, can solve the problems of cumbersome condition optimization, false positives, false negatives, etc., and achieve the effect of rapid on-site sampling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
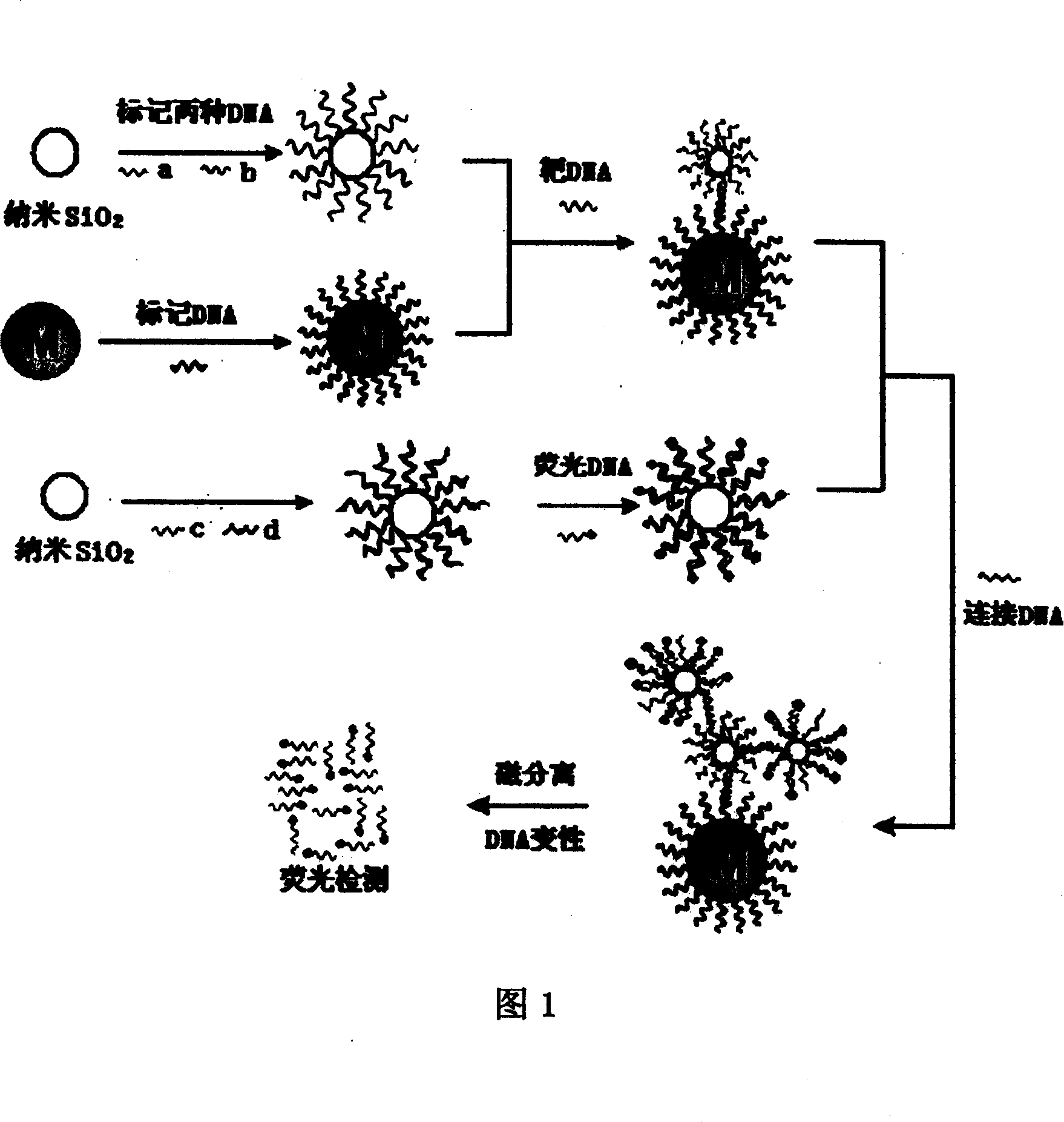
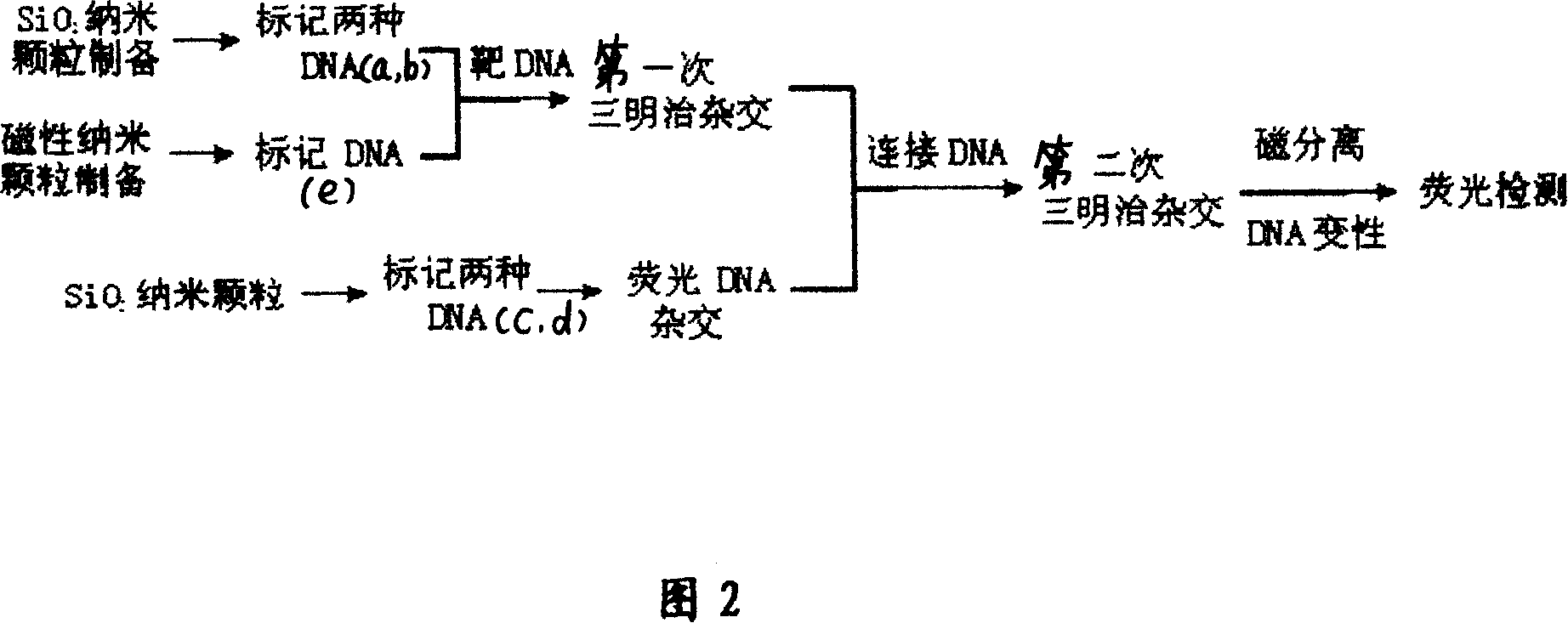
[0025] See Figures 1 and 2 for the principle diagrams of cascade amplification DNA detection. SiO 2 Two kinds of DNA with different sequences a and b are marked on the nanoparticle at the same time, wherein sequence a is completely positively matched with one end of the connecting DNA, and sequence b is completely positively matched with one end of the target sequence DNA. The amount of marking of sequence a is much larger than that of sequence b. Another DNA sequence e is marked on the surface of the magnetic nanoparticle, and its sequence is completely positively matched with the other end of the target DNA. Two kinds of nanoparticles modified with DNA hybridize with the target DNA for the first time, and the sequences b and e on the surface of the nanoparticles form a “sandwich” hybridization structure with the target sequence. At this time, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com