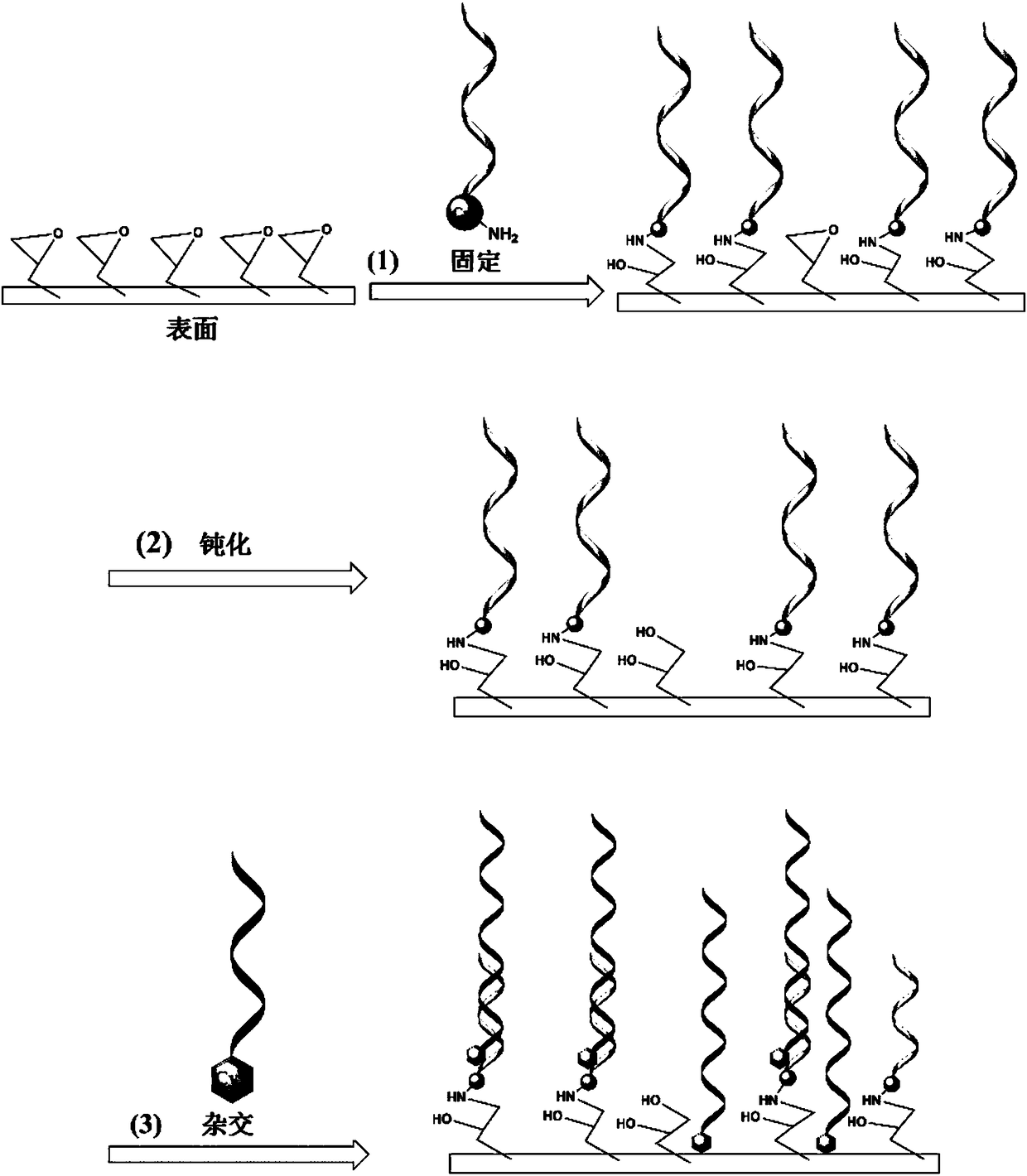
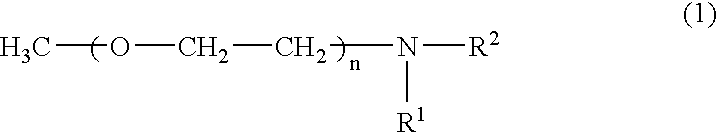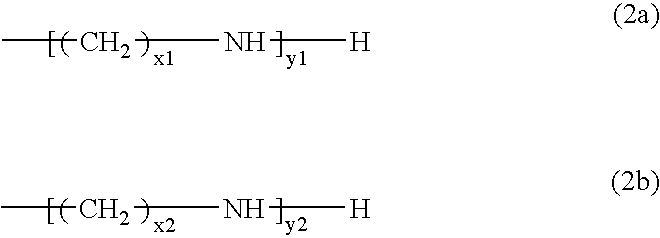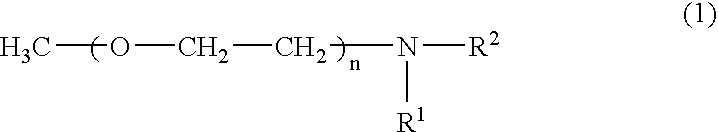Patents
Literature
293 results about "Non specific adsorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-specific adsorption (NSA) is a persistent problem that negatively affects biosensors, decreasing sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility. Passive and active removal methods exist to remedy this issue, by coating the surface or generating surface forces to shear away weakly adhered biomolecules, respectively.
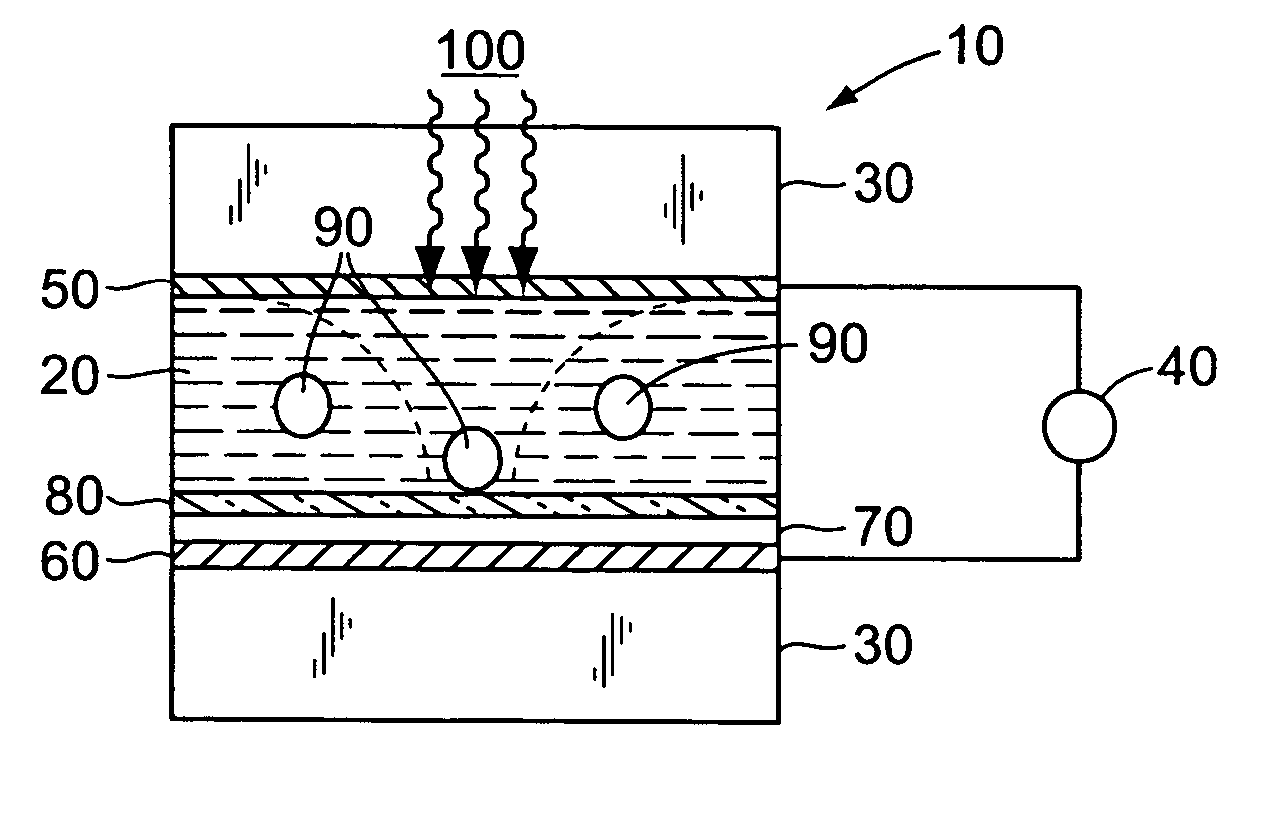
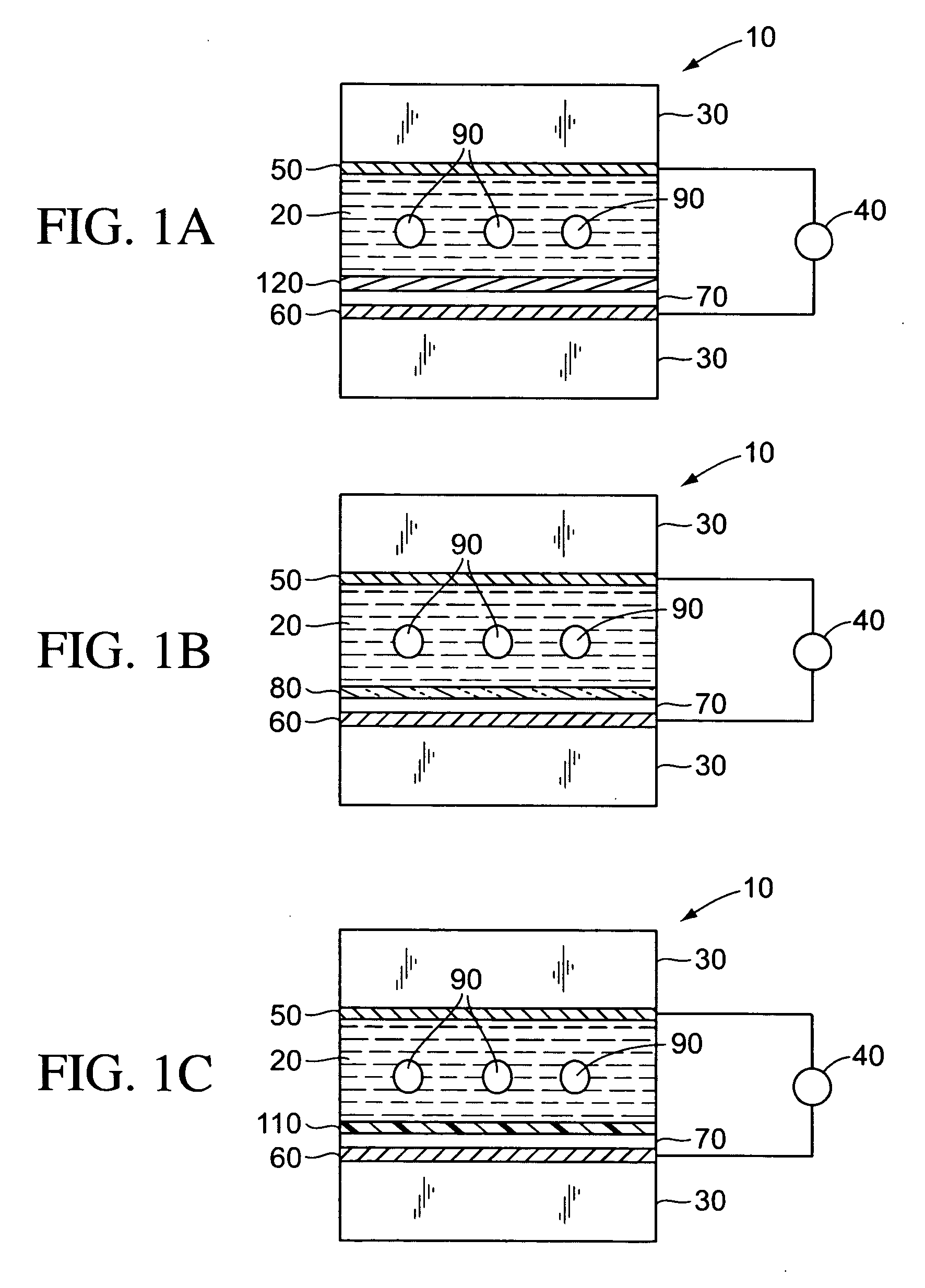
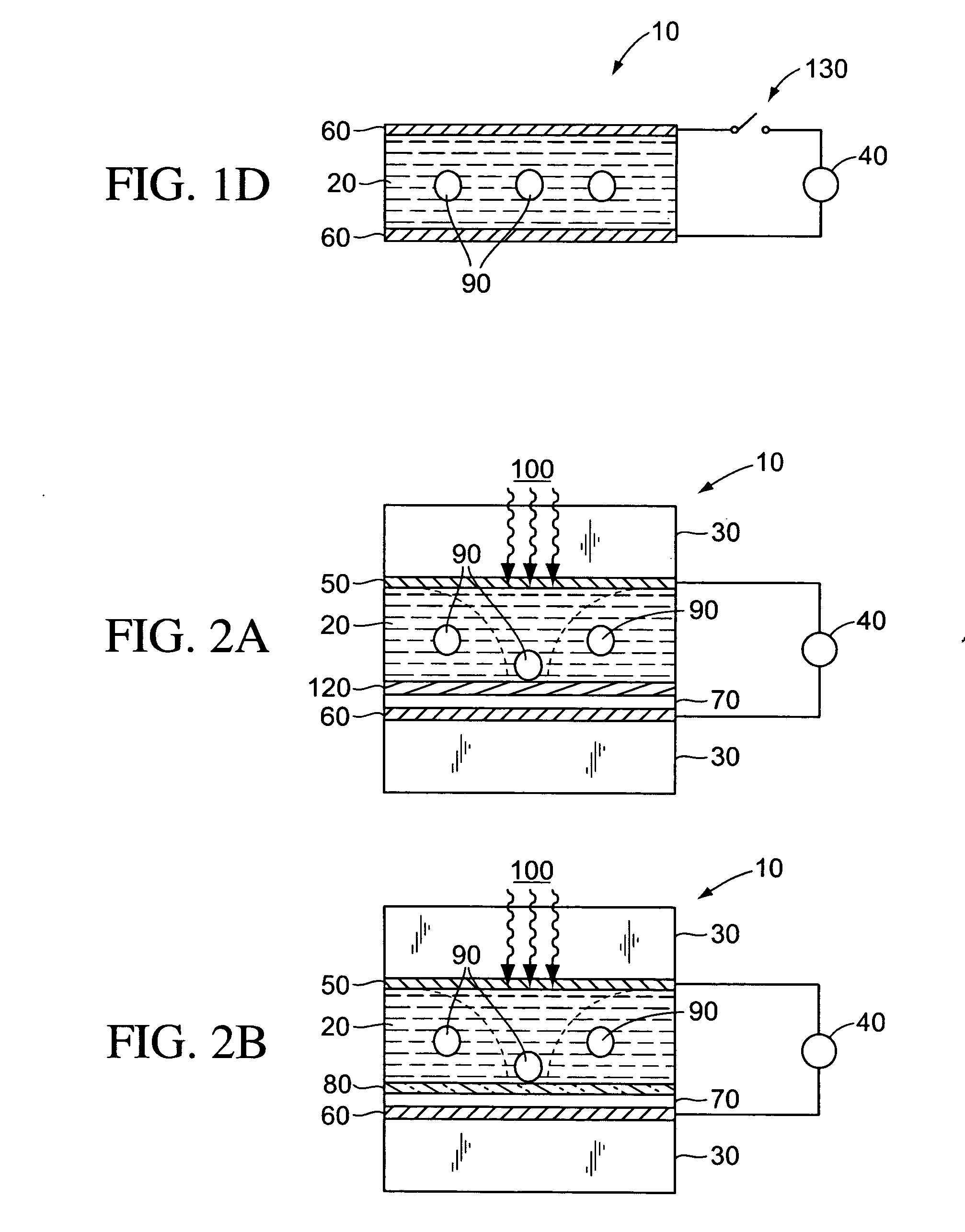
Surface modification for non-specific adsorption of biological material
InactiveUS20060091015A1Prevent non-specific adsorptionDecrease non-specific adsorptionElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentBiological materialsSurface modification
The present teachings provide a manipulation chamber, device, and method related to surface modifiers added to an electrode exposed to the biomolecules or a layer adjacent to an electrode exposed to the biomolecules to decrease non-specific adsorption of the biomolecules such as proteins or nucleic acids in a biological sample.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Functional nano particle composite microsphere, preparation and applications thereof
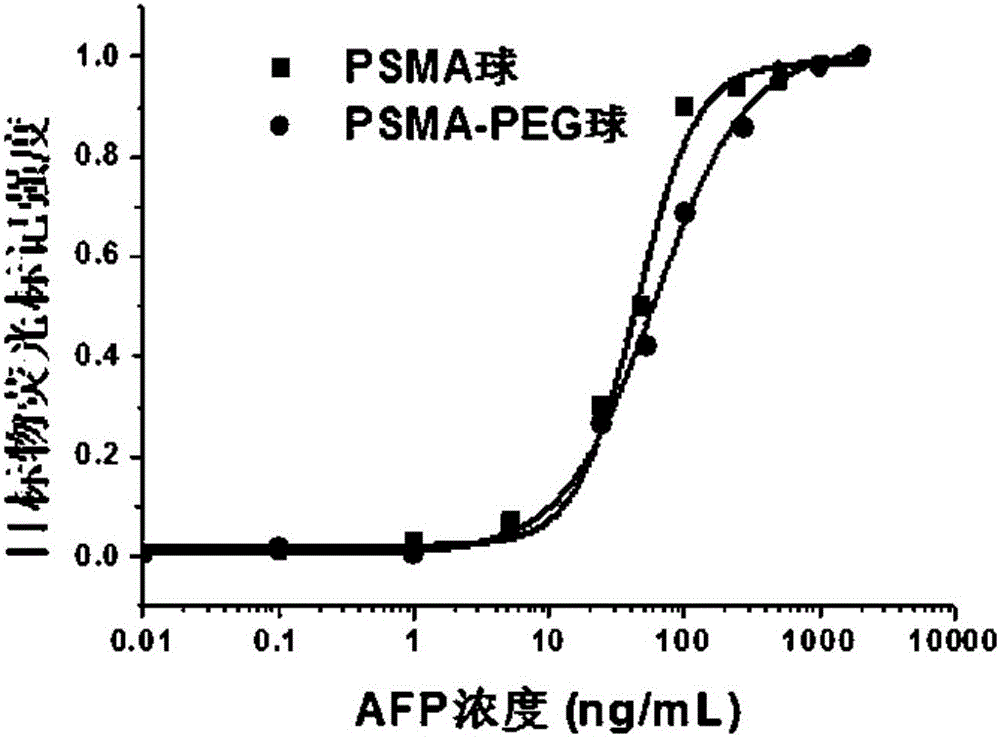
The invention discloses a functional nano particle composite microsphere. The functional nano particle composite microsphere is a functional nano particle composite PEG microsphere, which comprises functional nano particles and polymer containing a PEG chain segment; wherein the functional nano particle composite PEG microsphere has an average particle size of 0.1 to 1000 [mu]m, and the particle size distribution variable coefficient is less than 10%. According to the invention, functional nano particles and PEG chain segment grafted polymer are made into composite microspheres with a uniform particle size, the PEG chain segment can effectively inhibit the non-specific adsorption; and thus the provided composite microsphere has a wide application prospect in the fields of biological detection and biomedicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ORIENT GENE BIOTECH
Biochip sensor surface carrying polyethylene glycolated nanoparticles
InactiveUS20050106570A1Good dispersionHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologySensor materialsBiochip
The invention provides high sensitivity bioassay sensor systems in which non-specific adsorption of impurities such as, for example, proteins, in biological samples is inhibited. Polyethylene glycolated particles enclosing metal or semi-conductor which is in common with the sensor material are used for amplification.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Surface of base material being inhibited in non-specific adsorption
ActiveUS20060240438A1Easy to prepareHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific adsorptionAnalyte
A substrate surface on which either a substance to detect analyte or an analyte per se is immobilized, which surface is formed by a treatment of substrate surface with a liquid which contains uncrosslinked polymer based on polyethylene glycol chain segment, said treatment conducted either simultaneously with the immobilization of said substance or analyte or after said substance or analyte has been immobilized on said surface. The non-specific adsorption of impurity protein or the like which is co-existent in sample for assay is significantly restrained.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Method for preparing shell-core micrometer/nanometer spheres capable of preventing functional materials
InactiveCN101721964APrevent leakageAvoid destructionMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationOperabilityBiological macromolecule
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic nanometer materials, in particular to a method for preparing shell-core micrometer / nanometer spheres capable of preventing functional materials. The method comprises the step of coating a compact silicon dioxide shell layer on the surfaces of the traditional micrometer / nanometer spheres wrapping functional materials to seal and protect the functional materials with an anti-leakage ratio of 98 percent. The shell layer of silicon dioxide is easy to modify by introducing rich chemical functional groups and convenient to couple biomacromolecules in the field of biomedicines. The shell-core micrometer / nanometer spheres, prepared by the method, have the advantages of avoiding the damage caused by the infiltration of the environmental medium into the micrometer / nanometer spheres to the properties of the functional materials, avoiding the direct contact with the bioactive materials, introducing the rich chemical functional groups to the surfaces of the micrometer / nanometer spheres, and being conveniently crosslinked with biological proteins and nucleic acid molecules, along with smooth surfaces and little non-specific adsorption; and the preparation method has the advantages of simpleness, easy operation, strong operability, good repeatability, and low cost. The shell-core micrometer / nanometer spheres coated with silicon dioxide are stable in performance and long in holding time, and can be widely applied in biochemical analysis fields of biological marking, biological separation, cell imaging and development, biological sensors and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Micro-nano material, product of covalent modification of hydrophilic substances for surface of micro-nano material, and preparation method
ActiveCN106519147AReduce non-specific adsorptionIncrease coverageCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationMicro nanoHydrophilic polymers
The invention discloses a micro-nano material, a product of covalent modification of hydrophilic substances for the surface of the micro-nano material, and a preparation method. Carboxyl groups or potential carboxyl groups are contained on the surface of the micro-nano material and transformed into active esters; the product of covalent modification of the hydrophilic substances for the surface is obtained through taking a hydrophilic compound or / and a hydrophilic polymer containing aliphatic primary amines or / and aliphatic secondary amines as a modifier, forming amido bonds from the active esters for the surface and the hydrophilic compound or / and the hydrophilic polymer, and carrying out covalent modification; during preparation, enough carboxyl groups or potential carboxyl groups are generated on the surface of a polymeric material from monomers containing carboxyl groups or / and potential carboxyl groups and transformed into active esters, then amido bonds are formed from the active esters and a modifier with aliphatic primary amines and / or aliphatic secondary amines, potential facultative ionic groups and hydrophilic connection arms, and having a moderate volume, and covalent modification layers are obtained; and multilayer covalent modification is realized during a process of repeatedly generating the active esters on the surface of the product of covalent modification and then forming the amido bonds from the active esters and the hydrophilic modifier, and the surface of the micro-nano material is efficiently covered with the hydrophilic modifier having a medium volume, thus the non-specific adsorption of the modification product for biological molecules is remarkably reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING FARSIGHTED BLUE DRAGON FBD BIOTECH CO LTD CHINA
Preparation method and application of magnetic microsphere for biological protein separation
ActiveCN104031201AGood dispersionReduce non-specific adsorptionPeptide preparation methodsBiological testingEmulsionMicrosphere
The invention provides a preparation method of a magnetic microsphere for biological protein separation, which comprises the following steps: preparing and using a suitable emulsion to treat a magnetic microsphere matrix, and performing emulsion polymerization to modify the surface of the magnetic microsphere matrix, thus obtaining the magnetic microsphere of which the surface is coated with a polyacrylate polymer layer, wherein the emulsion comprises the following components: a monoacrylate compound, a diol acrylate compound, an initiator, and optional anionic surfactant and water. When being used for biological protein separation, the magnetic microsphere obviously reduces the non-specific adsorption of other proteins on the premise of not influencing the capability of linking to a specific protein, thus providing a new choice for separation engineering of high-protein-specificity adsorption.
Owner:SHENZHEN NEW INDS BIOMEDICAL ENG
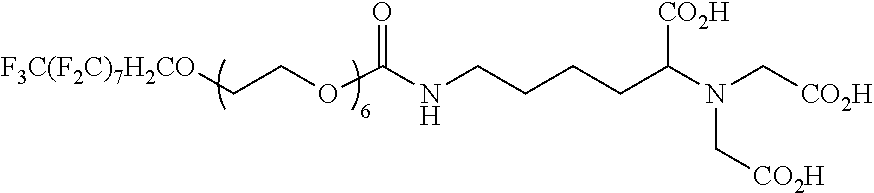
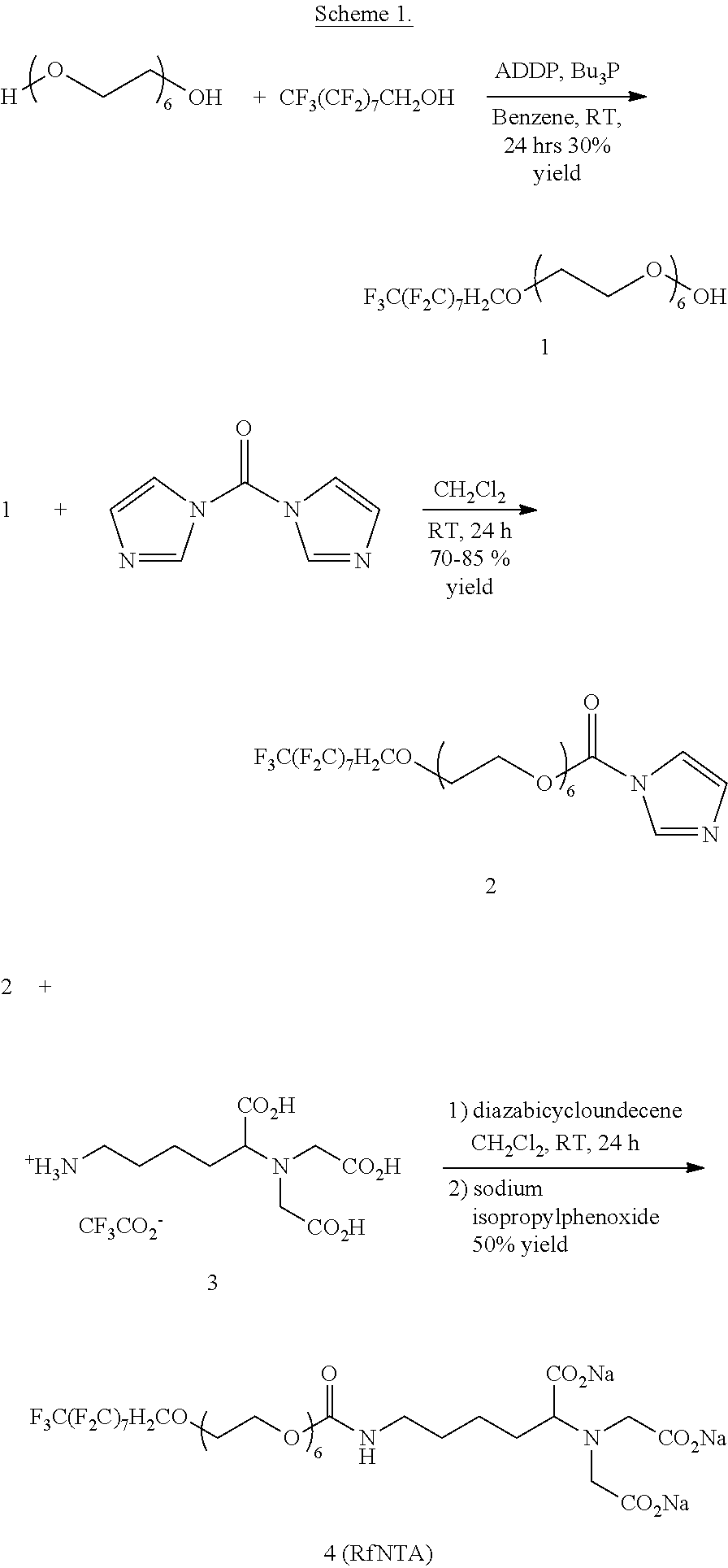
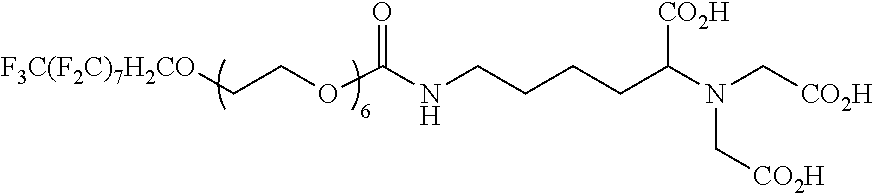
Interfaces that eliminate non-specific adsorption, and introduce specific interactions
InactiveUS20110165037A1Carbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationCarrier fluidSURFACTANT BLEND
A microfluidic system comprising a microchannel, a carrier fluid comprising a fluorinated oil in the microchannel, at least one plug comprising an aqueous plug-fluid in the microchannel and substantially surrounded on all sides by the carrier-fluid, and a fluorinated surfactant comprising a functional group capable of selectively binding a target molecule is disclosed. A compound for use therewith and a method of synthesizing a fluorinated surfactant are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Biochip sensor surface carrying polyethylene glycolated nanoparticles
InactiveCN1646912AInhibition of non-specific adsorptionMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst regeneration/reactivationSensor materialsBiochip
The invention provides high sensitivity bioassay sensor systems in which non-specific adsorption of impurities such as, for example, proteins, in biological samples is inhibited. Polyethylene glycolated particles enclosing metal or semi-conductor which is in common with the sensor material are used for amplification.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
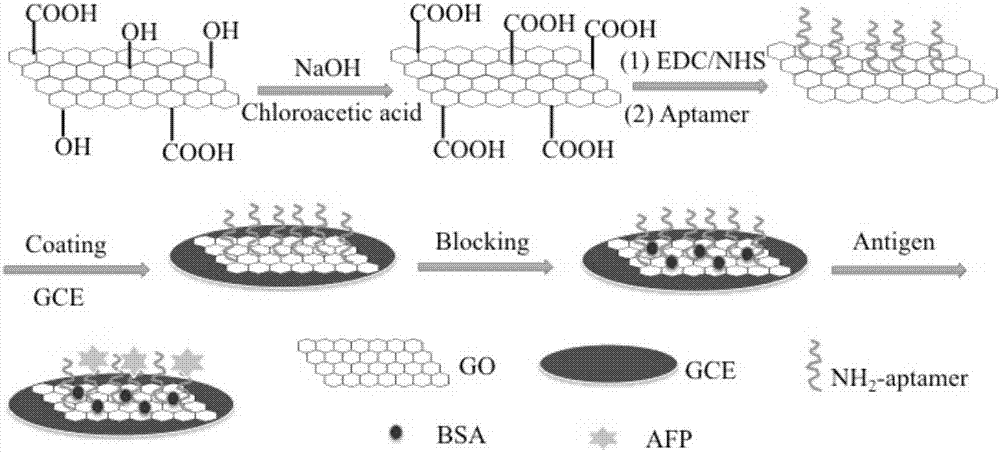
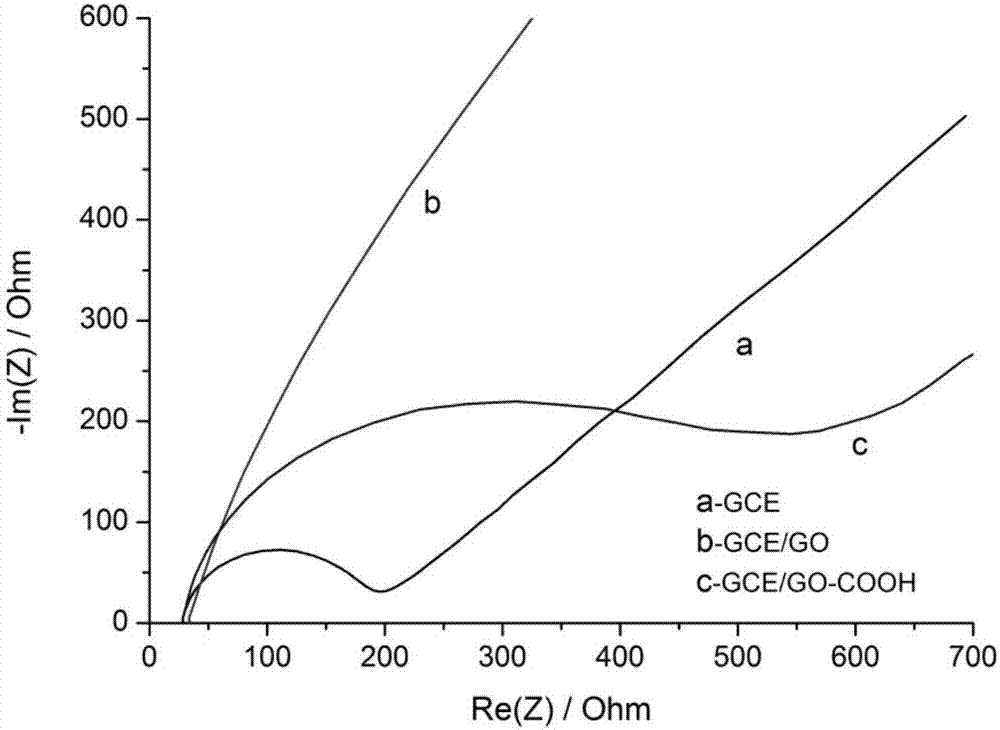
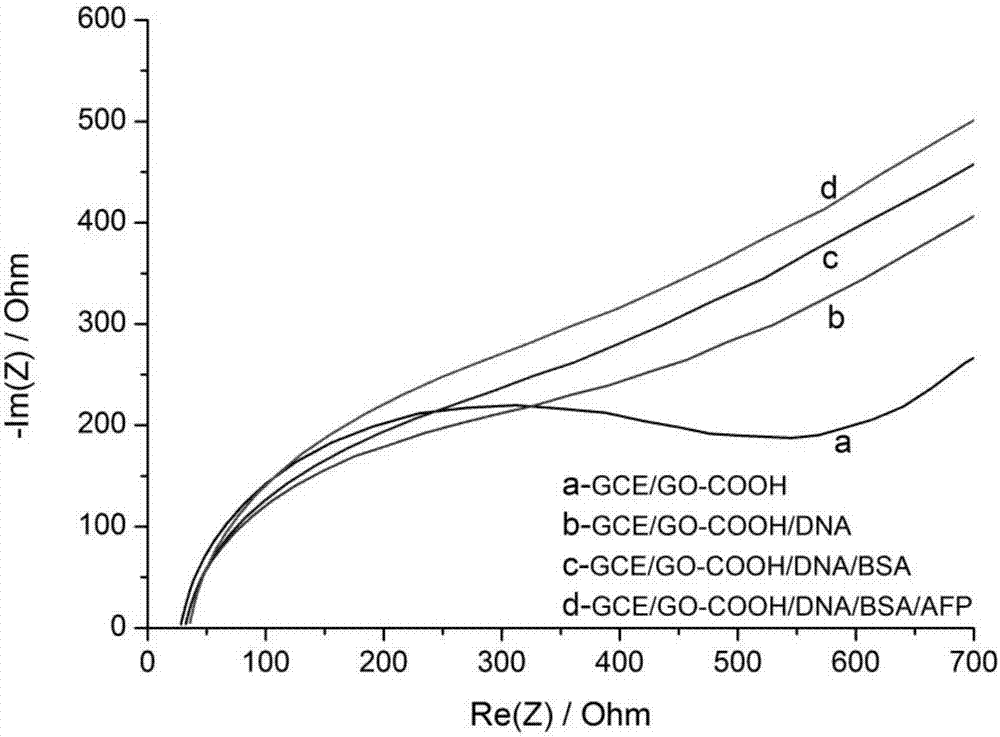
Preparation method of graphene oxide/ alpha fetoprotein aptamer electrochemical sensor
ActiveCN107144617ALarge specific surface areaImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtein targetSignal on
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene oxide / alpha fetoprotein aptamer electrochemical sensor. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking carboxylated graphene oxide as a substrate, grafting an aminated alpha fetoprotein aptamer chain on the substrate through carbodiimide reaction, then modifying the obtained compound on an electrode, closing a non-specific adsorption site on the modified electrode with bovine serum albumin, so that a graphene oxide / alpha fetoprotein aptamer electrochemical sensing interface is formed; and taking the modified electrode as a working electrode, and investigating variation, caused by alpha fetoprotein solution with different concentrations, of an impedance signal on the sensing interface by adopting an impedance method. Compared with an existing alpha fetoprotein detection method, the preparation method has the advantages that an alpha fetoprotein aptamer is adopted for analyzing a target protein, harms such as redundant multiple labeling operation, radiation and pollution do not exist, and the sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, good selectivity, simplicity in preparation, high analysis speed, mild reaction conditions, low preparation cost and the like.
Owner:青岛远诚创智科技有限公司
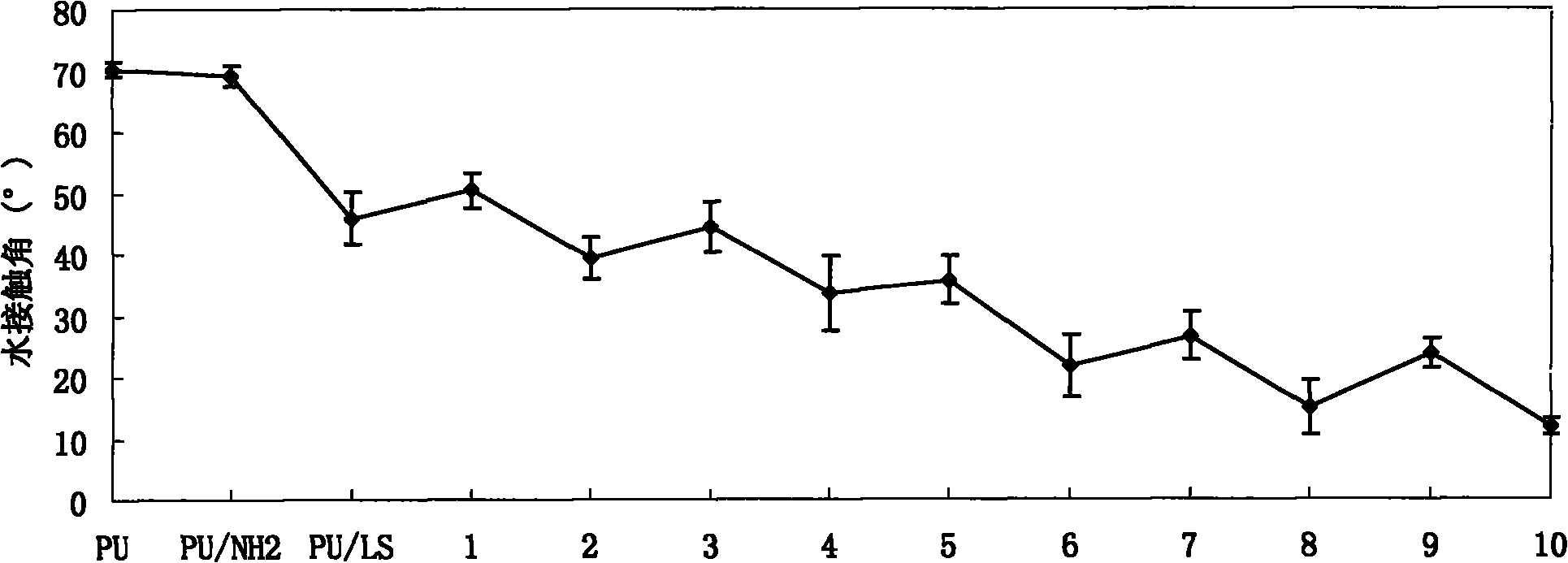
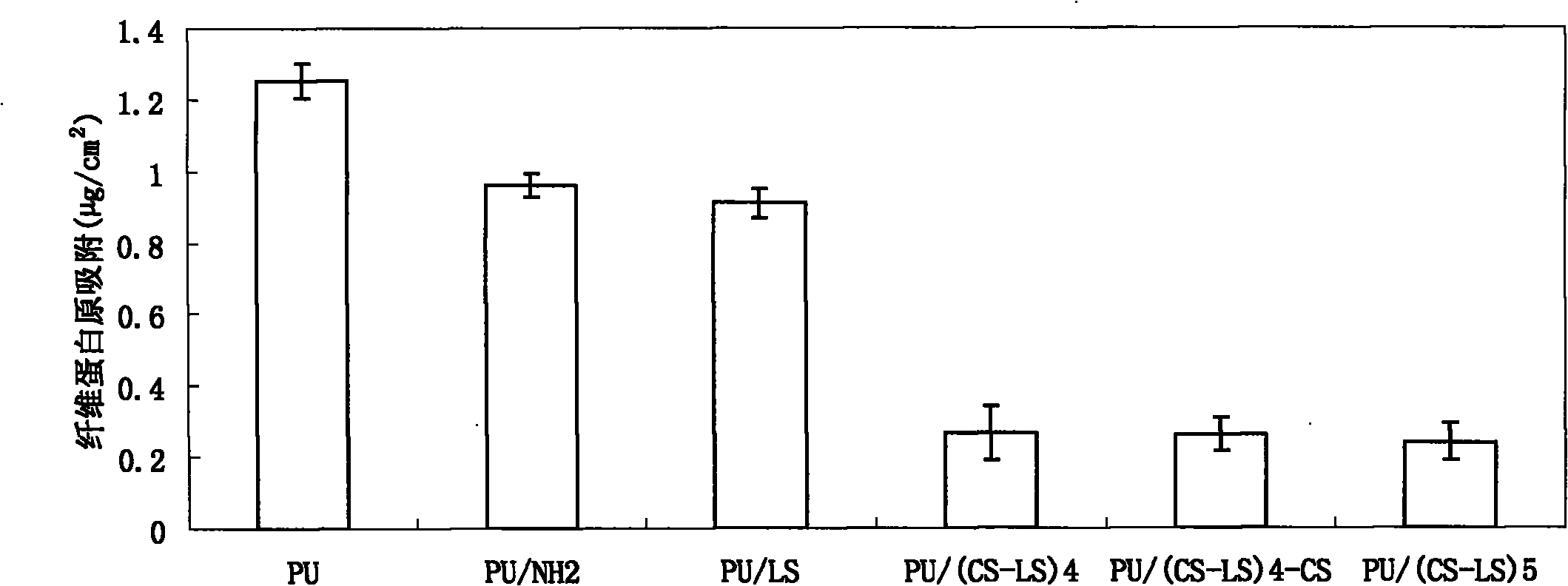
Bioactive polysaccharide self-assembly modified polyurethane material and preparation method thereof
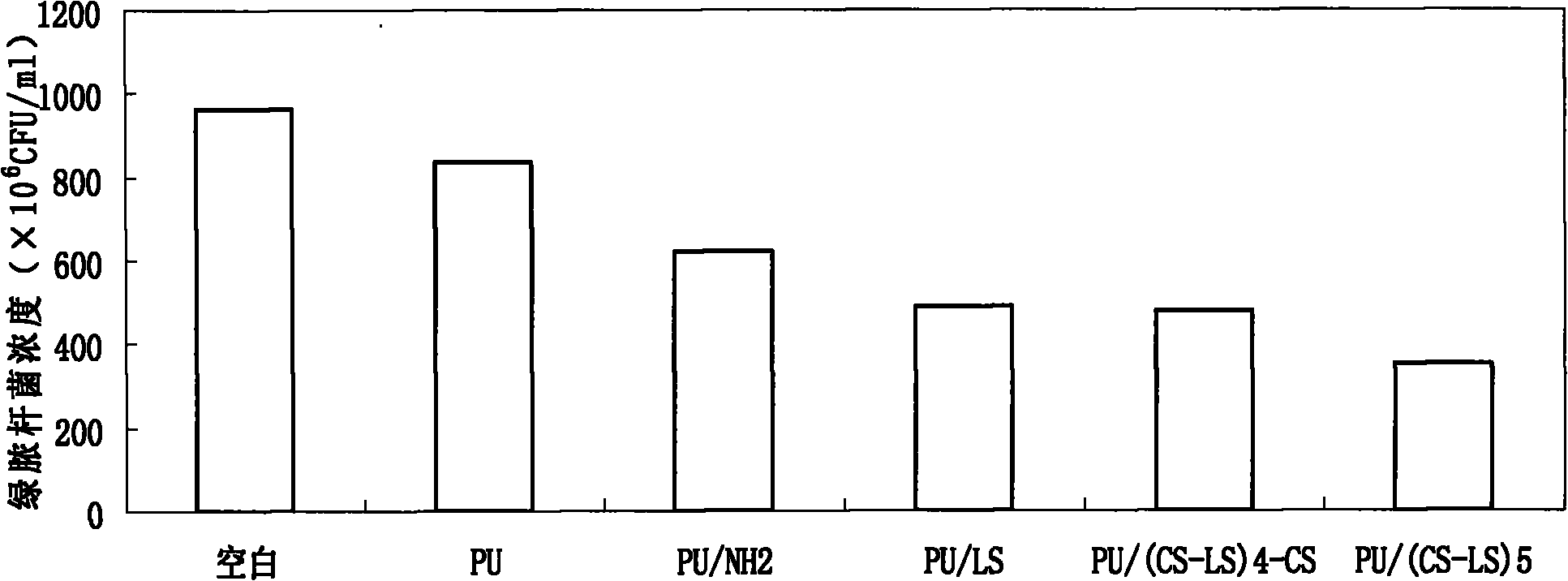
InactiveCN101810879AImprove hydrophilicityGood biocompatibilitySurgeryCoatingsAntibacterial activityLayer by layer self assembly
The invention relates to a bioactive polysaccharide self-assembly finishing polyurethane material and a preparation method thereof. The bioactive polysaccharide self-assembly finishing polyurethane material is characterized by comprising a substrate and a finishing layer, wherein the substrate is made of a polyurethane material, and the finishing layer is prepared by finishing the surface of the substrate by using a layer-by-layer self-assembly technique; and the finishing layer contains electronegative lentinan sulfate and electropositive chitosan which are alternately self-assembled layer by layer on the surface of the substrate. The surface of the polyurethane material has favorable hydrophilicity, favorable function of resisting fibrinogen non-specific adsorption, high antibacterial activity for inhibiting Bcillus pyocyaneus and other bacteria, and favorable cell compatibility. In addition, the polyurethane material has the advantages of simple preparation technology, easy control, mild preparation conditions and low cost, and is especially suitable for preparing biomedical materials for artificial organs and devices with complicated shape and structure.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
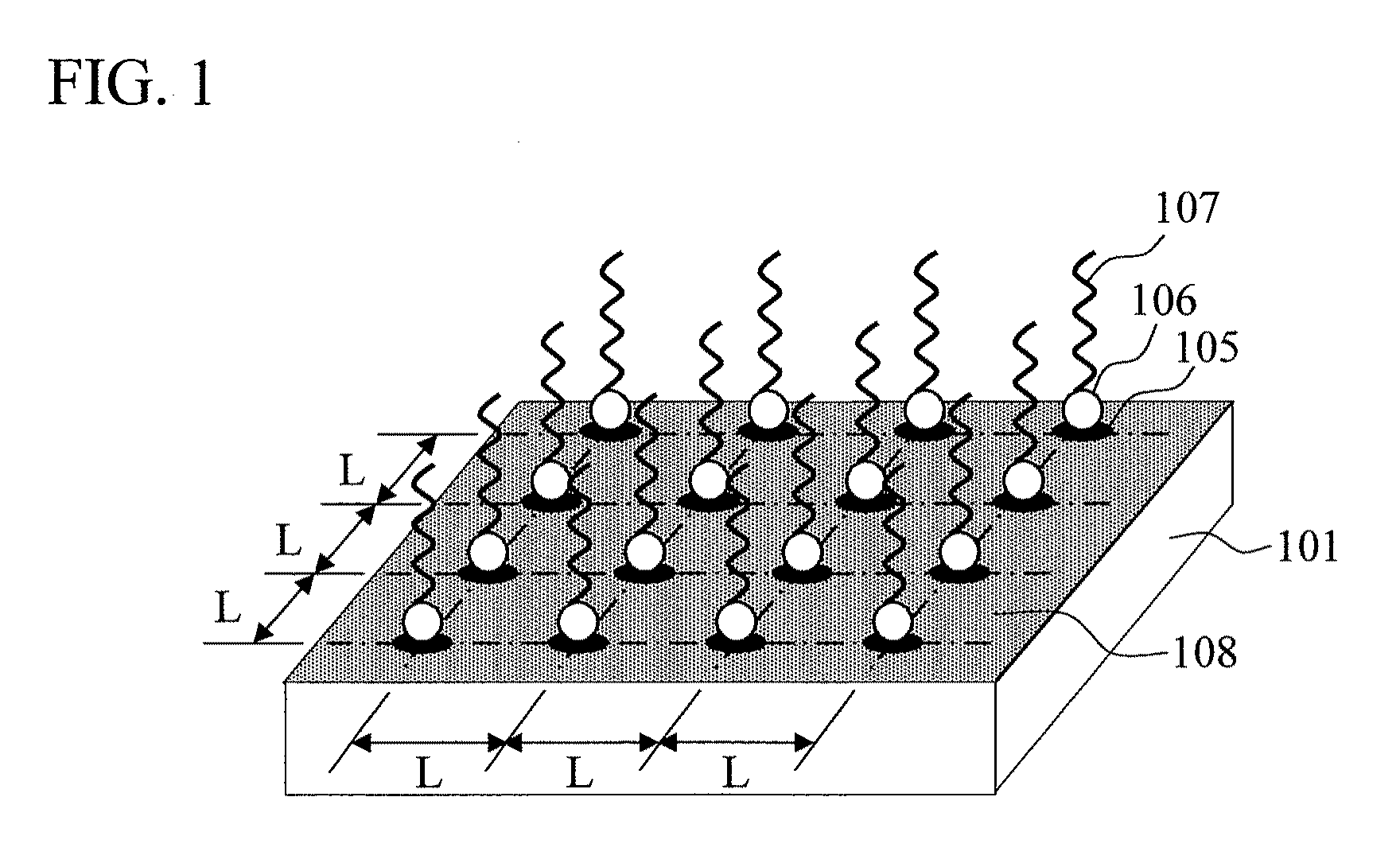
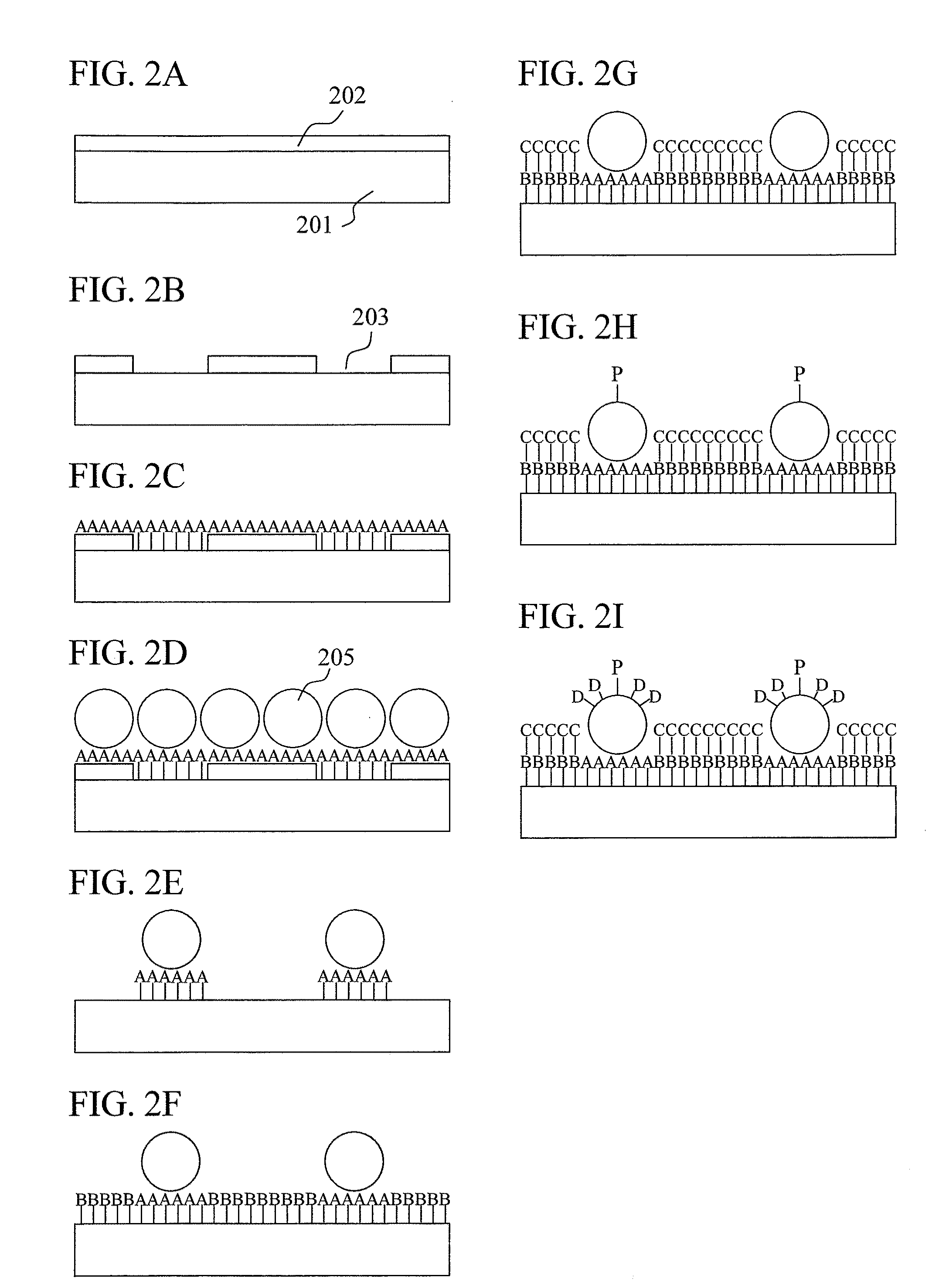
Biomolecule sensor, method for manufacturing the same, biomolecule detection method, and biomolecule detection system
InactiveUS20100009862A1Convenient and accuratePrevent non-specific adsorptionNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningFluorescenceMicroparticle
The present invention aims to improve detecting accuracy and reproducibility of a biomolecule sensor. The biomolecule sensor of the present invention includes single probe molecules orderly aligned and fixed on grid points on the surface of a substrate. Accordingly, in the biomolecule sensor of the present invention: probe molecules for detecting a biomolecule are orderly aligned and separately fixed; blocking for preventing non-specific adsorption is applied to a region other than the region of the probe molecules for detecting a biomolecule; and fluorescence enhancement is achieved by metal microparticles.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Polystyrene microsphere
ActiveCN109988333ANot easy to fall offEasy to operateMicroballoon preparationMaterial analysisMicrosphereFunctional modification
A polystyrene microsphere is provided. The polystyrene microsphere is micron or nano-scale, and the surface of the microsphere is coated with a polyacrylic resin Eudragit. The polystyrene microsphereof the present invention is a polystyrene microsphere with very low non-specific adsorption, and the surface of the microsphere contains a functional group carboxyl group, so that further functional modification of the surface of the polystyrene microsphere is not required, the operation is further greatly simplified, and the loss is reduced.
Owner:成都爱兴生物科技有限公司
Membrane assisted separation of glycoprotein all N-linked carbohydrate chain and identification method thereof
InactiveCN102788720AAvoid bringing inClearly separate sugar chain effectPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical reactionCell separation
The invention provides a membrane assisted separation of glycoprotein all N-linked carbohydrate chain and an identification method thereof, and solves problems of low reaction efficiency and identification of few types of carbohydrates in prior art. According to the invention, a molecular sieve effect of a membrane of 8-12KD is employed to separate carbohydrate chain released from glycoprotein from protein; on a molecular sieve of 10KD, an N-linked carbohydrate chain of the glycoprotein is released by a PNGase F enzyme; the N-linked carbohydrate chain flows out through repeated centrifugation, but the protein is retained on the membrane, thereby realizing separation of the carbohydrate chain. The method has obvious carbohydrate chain separation effect, and avoids by-products caused by non-specific adsorption and chemical reactions; besides, the method has high reaction efficiency and concise reaction steps.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Magnetic nanoparticle and immunomagnetic nanoparticle with cell-like structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109507418AGood magnetic responseReduce non-specific adsorptionMaterial analysisPolyethylene glycolMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a magnetic nanoparticle and an immunomagnetic nanoparticle with a cell-like structure as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The magnetic nanoparticle with the cell-like structure uses a superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle as a core and is wrapped with a white cell membrane on the surface, so that the magnetic nanoparticle has excellent magnetic responseperformance, furthermore, the white cell membrane wrapping on the surface of the magnetic nanoparticle is homologous with white cells, thereby effectively weakening non-specific adsorption to the white cell; an antibody is modified onto the white cell membrane wrapping on the surface of the magnetic nanoparticle through mediating of lipid molecules-polyethylene glycol-biotin molecules and avidin,so as to obtain the immunomagnetic nanoparticle with the cell-like structure. CTCs cells can be enriched and separated with high efficiency and high purity.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Nano gold doped integral material for enriching glycoprotein and applications thereof
ActiveCN103877949AImprove hydrophilicityReduce non-specific adsorptionOther chemical processesPeptide preparation methodsGlycidyl methacrylateGold particles
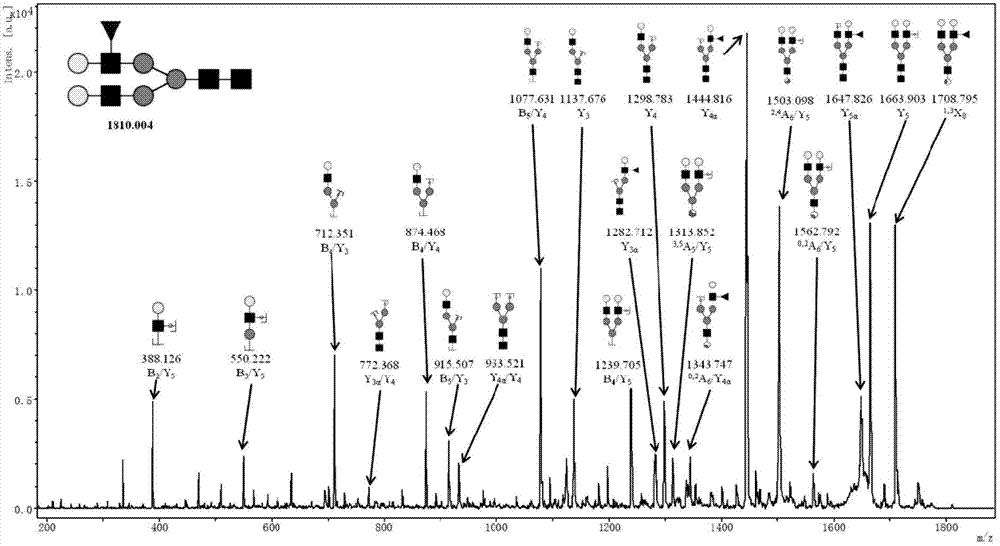
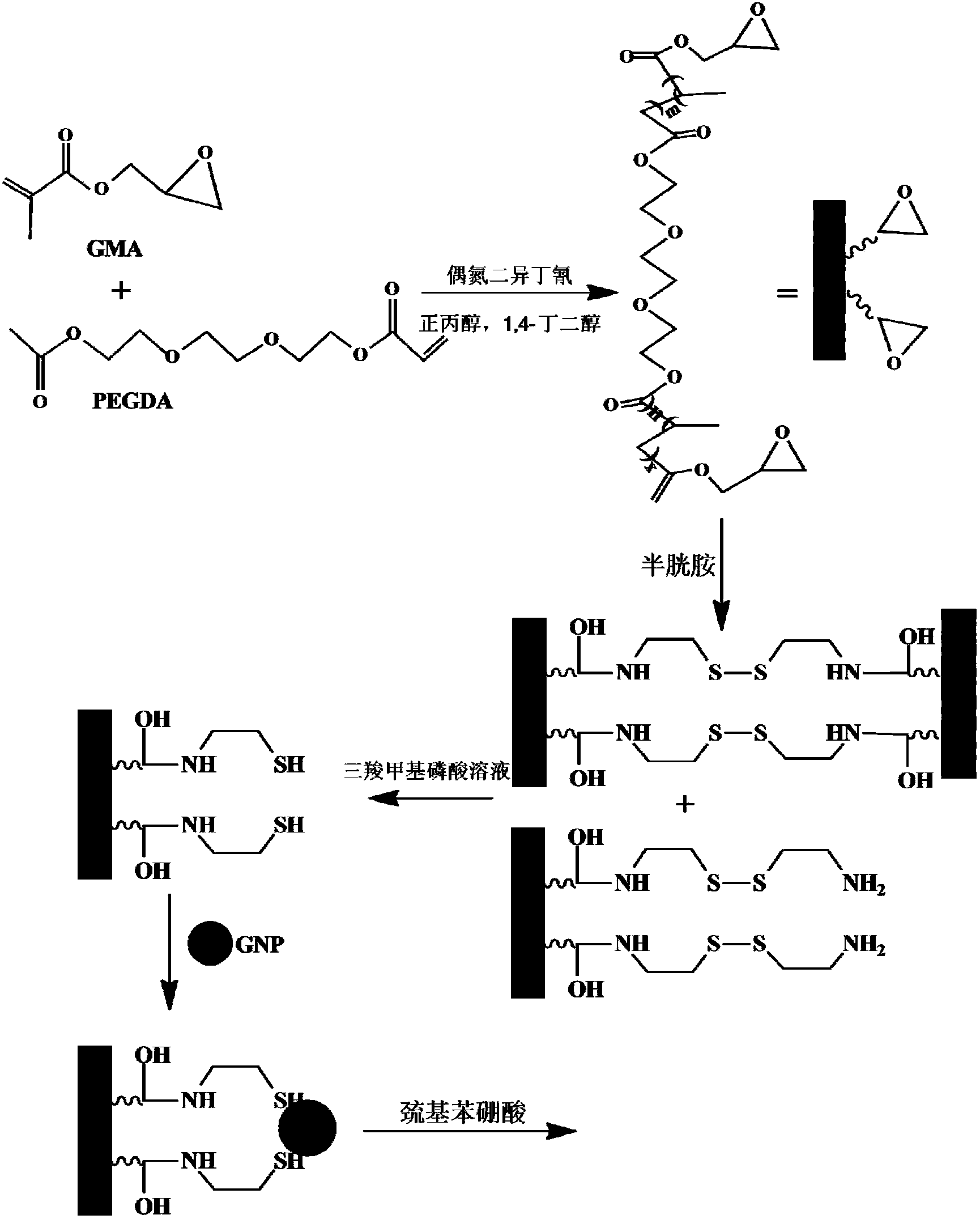
The invention relates to a preparation method of a nano gold doped integral material for enriching glycoprotein. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) and polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) as the monomers to synthesize a hydrophilic polymer integral material substrate through an in-situ polymerization method; utilizing the epoxy groups in the substrate surface to enrich the substrate surface with mercapto groups through a chemical derivatization method, then modifying the substrate surface with nano gold particles; finally co-modifying 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid and mercaptoethylamine on the nano gold surfaces on the substrate, and enriching glycoprotein on the basis of phenylboronic acid affinity chromatography. The hydrophilicity of the monomer polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) is utilized so as to reduce the non-specific adsorption of substrate on proteins, and thus the enrichment selectivity is improved. At the same time, the high specific surface area of nano particles is utilized at the same time, thus the enrichment capacity is increased, and finally the high-efficient and high-selective enrichment of glycoprotein is achieved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microchannel surface coating
InactiveUS20090130746A1Improve efficiencyNon-specific degradationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrofluidic channelContamination
The present invention relates to a method for improving the efficiency of biochemical reactions in channels of microfluidic devices. More specifically, the present invention relates to the use of chitosan or a chitosan derivative for coating channel surfaces to reduce non-specific adsorption of reagents to microfluidic channels. This reduction of non-specific adsorption improves the efficiency and reproducibility of the reaction, e.g., amplification reactions, such as PCR, and reduces cross-contamination.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
Kit and method for detecting hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg)
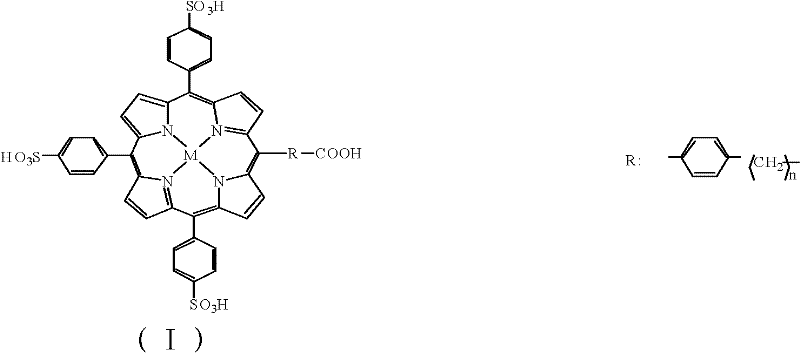
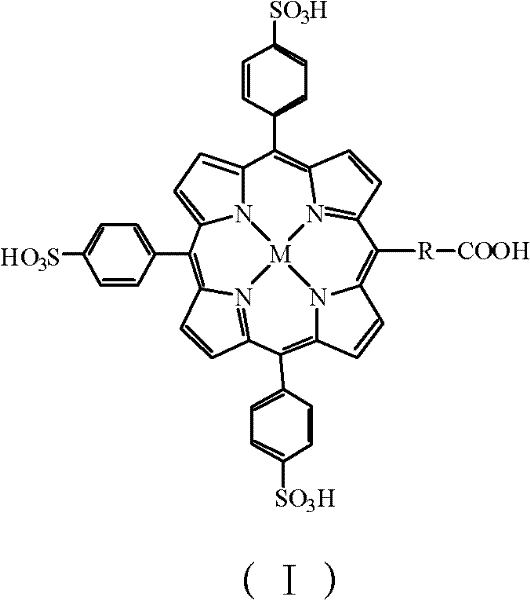
InactiveCN102183647AHigh purityReduce system errorOrganic chemistryMaterial analysisHepatitis B Virus Surface AntibodyPorphyrin
The invention discloses a kit and a method for detecting hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg). The detection kit is used for marking hepatitis B virus surface antibody (HBsAb) by using metalloporphyrin obtained by using water-soluble A3B type metalloporphyrin to mark the HBsAb. The detection kit and the detection method have the advantages that: (1) free metalloporphyrin molecules are separated from a coupled substance easily after an A3B type metalloporphyrin complex is coupled with the HBsAb to obtain a high-purity labelled antibody, so that non-specific adsorption background signals are reduced when the HBsAg is detected by chemical luminescence immunodetection, and detection sensitivity is greatly improved; (2) the method is simple, convenient and quick; automation is realized easily; and specificity of immunoreaction, high sensitivity of chemical luminescence reaction and stability of a chemical marker are achieved; and (3) a new method is provided for detecting the HBsAg quickly and accurately, and preventing and treating the hepatitis B virus.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting specific and/or non-specific adsorption of nucleic acids
The invention provides a method for detecting specific and / or non-specific adsorption of nucleic acids. The method comprises the following steps: reacting a to-be-detected nucleic acid with a first probe, wherein the first probe is immobilized on the surface of a first substrate, and the to-be-detected nucleic acid and the first probe are at least partially complementary and have different labels,and the labels can generate signals; detecting signals on the surface of the first substrate to obtain first detection results; reacting the to-be-detected nucleic acid with a second probe, wherein the second probe is immobilized on the surface of a second substrate, the second probe has second labels, and the to-be-detected nucleic acid is not complementary to the second probe; detecting signalson the surface of the second substrate to obtain second detection results; and based on the first detection results and the second detection results, detecting the specific and / or non-specific adsorption of the to-be-detected nucleic acid. The method can detect the specific and / or non-specific adsorption of the nucleic acid and the surfaces of the substrates or the probes on the surfaces of the substrates, and is applicable to production quality control of chips.
Owner:GENEMIND BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
Non-specific adsorption inhibitor, probe-bonded particles, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20080160167A1Easy to produceLot of noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical containersSpecific adsorptionMonomethyl ether
A method for producing a non-specific adsorption inhibitor includes reacting (A) a tosylated compound of polyoxyethylene monomethyl ether with (B) a polyamine having either an amino group or imino group (—NH—), or both, in total of 3 to 12.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
PH sensitive type liver-targeted compound nano drug delivery system based on sodium alginate and preparation method
InactiveCN102836435ARealize drug release at a fixed pointReduce leakageOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectDrug carrier
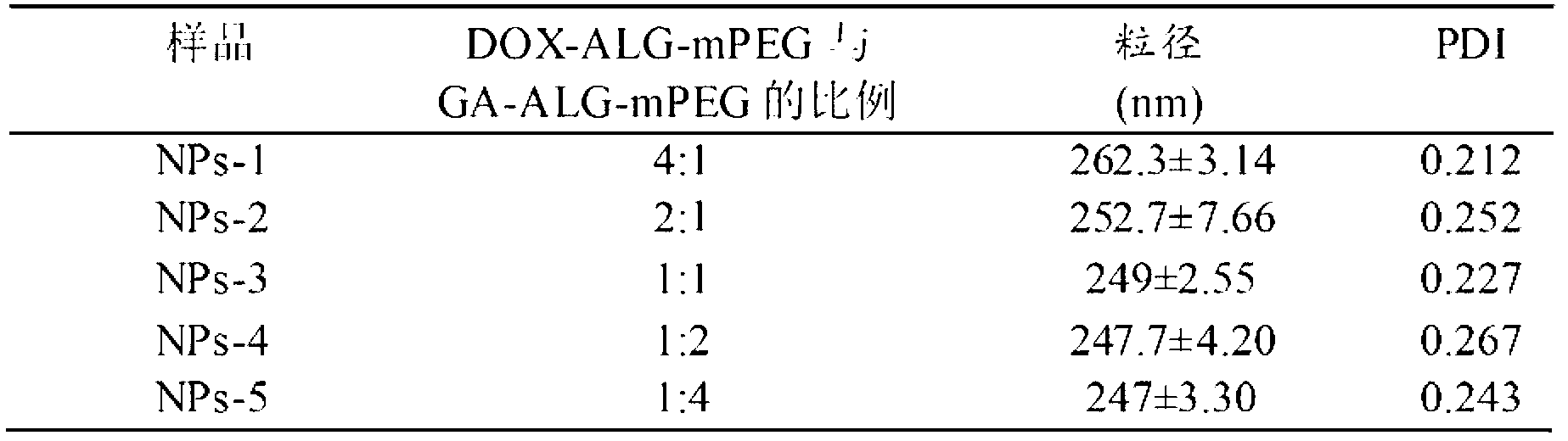
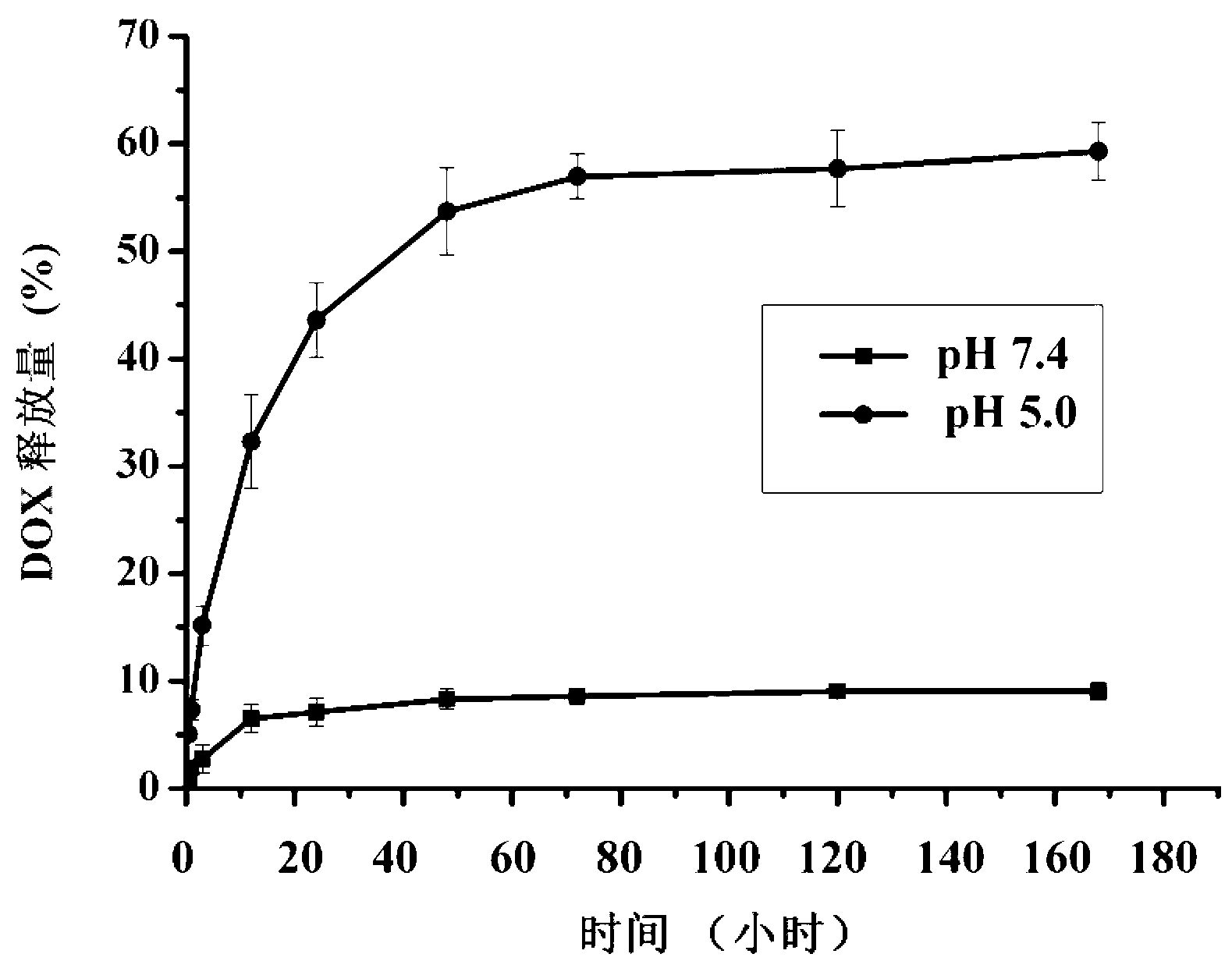
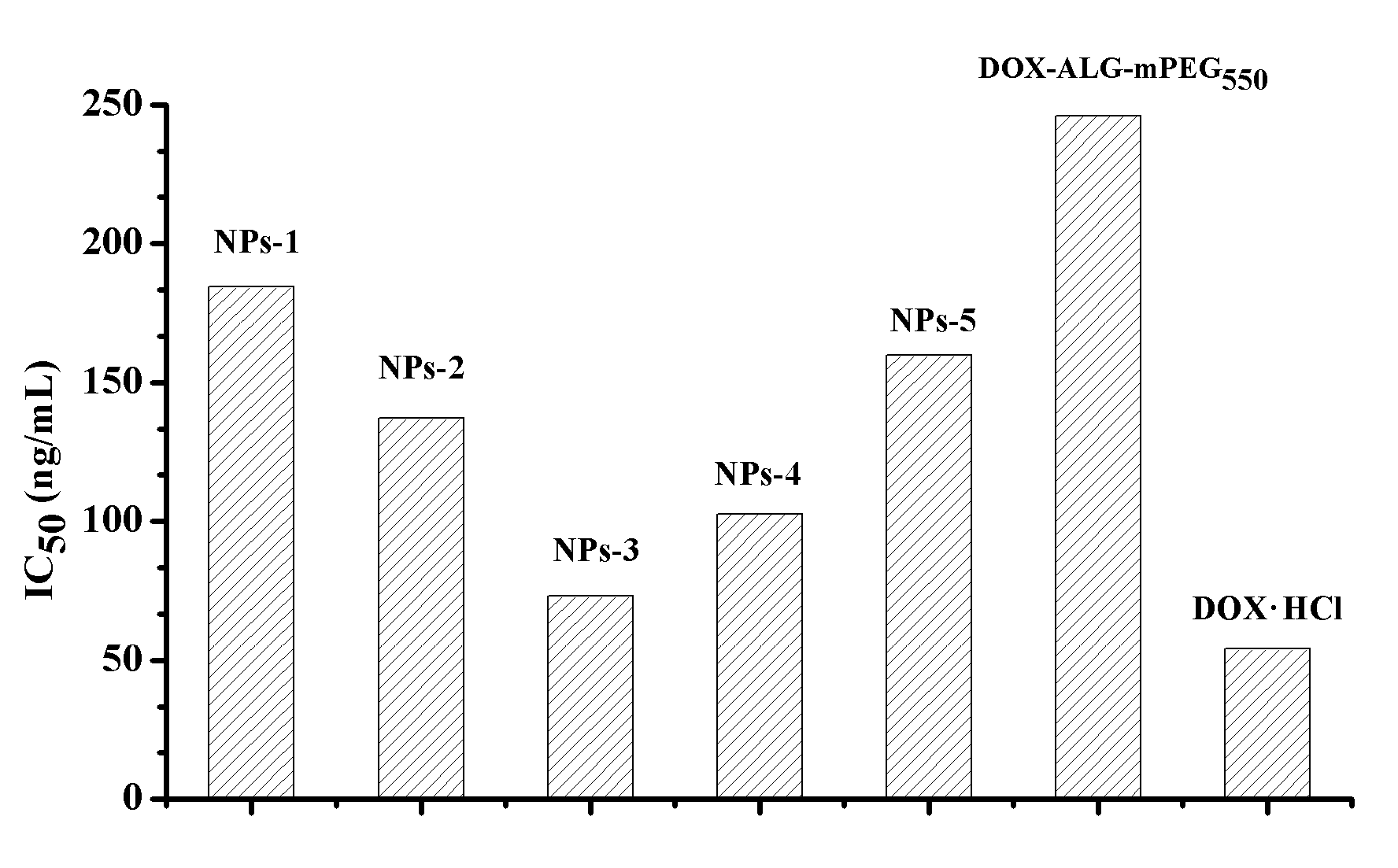
The invention relates to a pH sensitive type liver-targeted compound nano drug delivery system based on sodium alginate and a preparation method. The system is prepared by blending a liver-targeted carrier GA-ALG-mPEG or GA-ALG and a pH sensitive type drug carrier DOX-ALG-mPEG or DOX-ALG proportionally in a mode of dialysis through self assembly. The preparation of the material comprises a sodium alginate derivative (ALG-mPEG), the liver-targeted carrier and the pH sensitive type drug carrier. By the modification of the hydrophilic mPEG according to the compound nano drug delivery system, the non-specific adsorption with cells and protein can be effectively avoided. Meanwhile, the capabilities of drug loading and ligand targeting of the material are enhanced. The pH sensitive type liver-targeted compound nano drug delivery system based on the sodium alginate has the function of liver targeting. Meanwhile, the drug release of a fixed point at the part of a tumor can also be realized according to the difference of pH at normal tissues and the part of the tumor so as to enhance the curative effect and lower the side effect of drugs. The preparation method is simple, is easy to amplified production and has favorable application prospect.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Binding protein molecule
InactiveUS20090130776A1Take advantage ofImprove accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansNin one binding proteinBinding site
A binding protein molecule, characterized in that it has a first domain having a binding site to an inhibitor of non-specific adsorption in which the domain comprises a part of the variable region of an antibody as the binding site and a second domain having a binding site to a target substance in which the domain comprises a part of the variable region of an antibody as the binding site, wherein the first and second domains are bound via a linker.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for detecting DNA by stacking hybridization fluorescent amplify magnetic separation
InactiveCN101082583AUltra sensitive detectionEnsure ultra-low detection limit analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMagnetite Nanoparticles
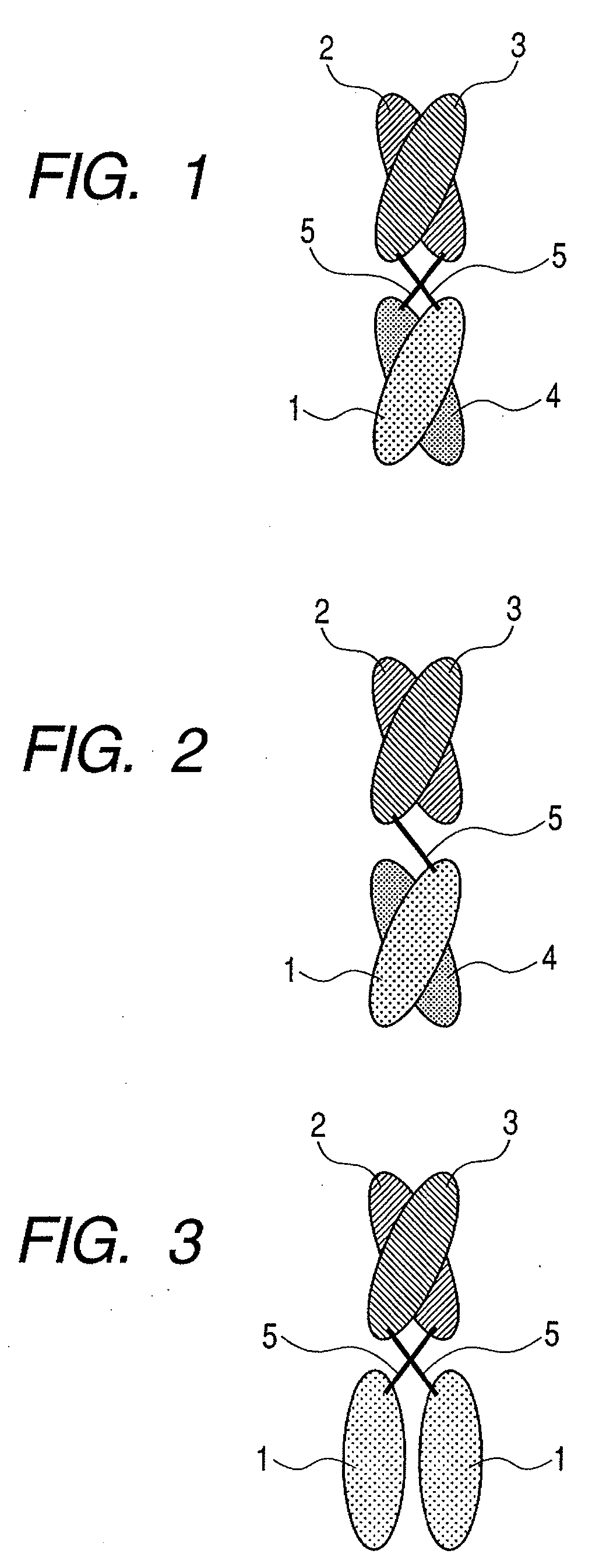
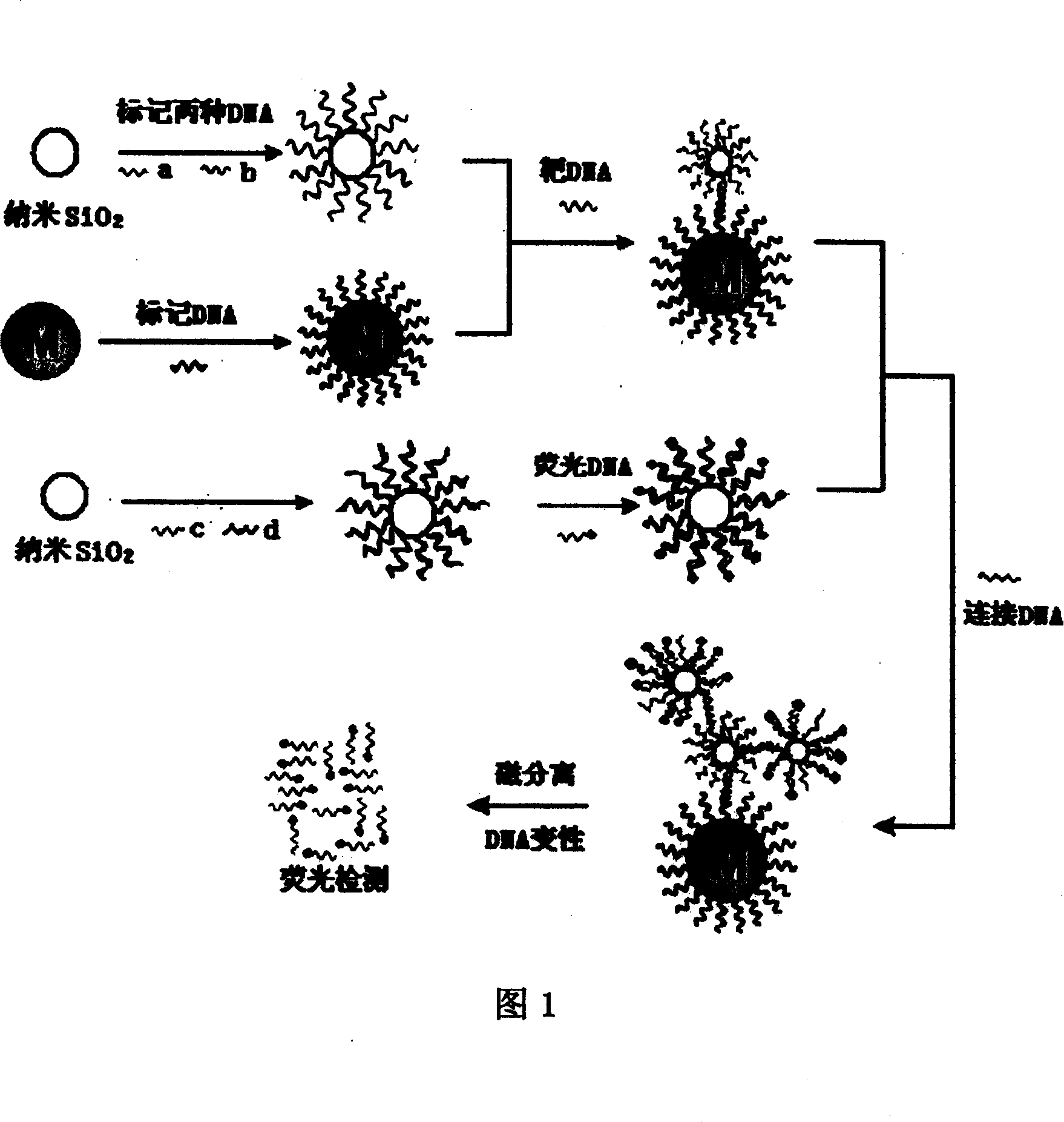
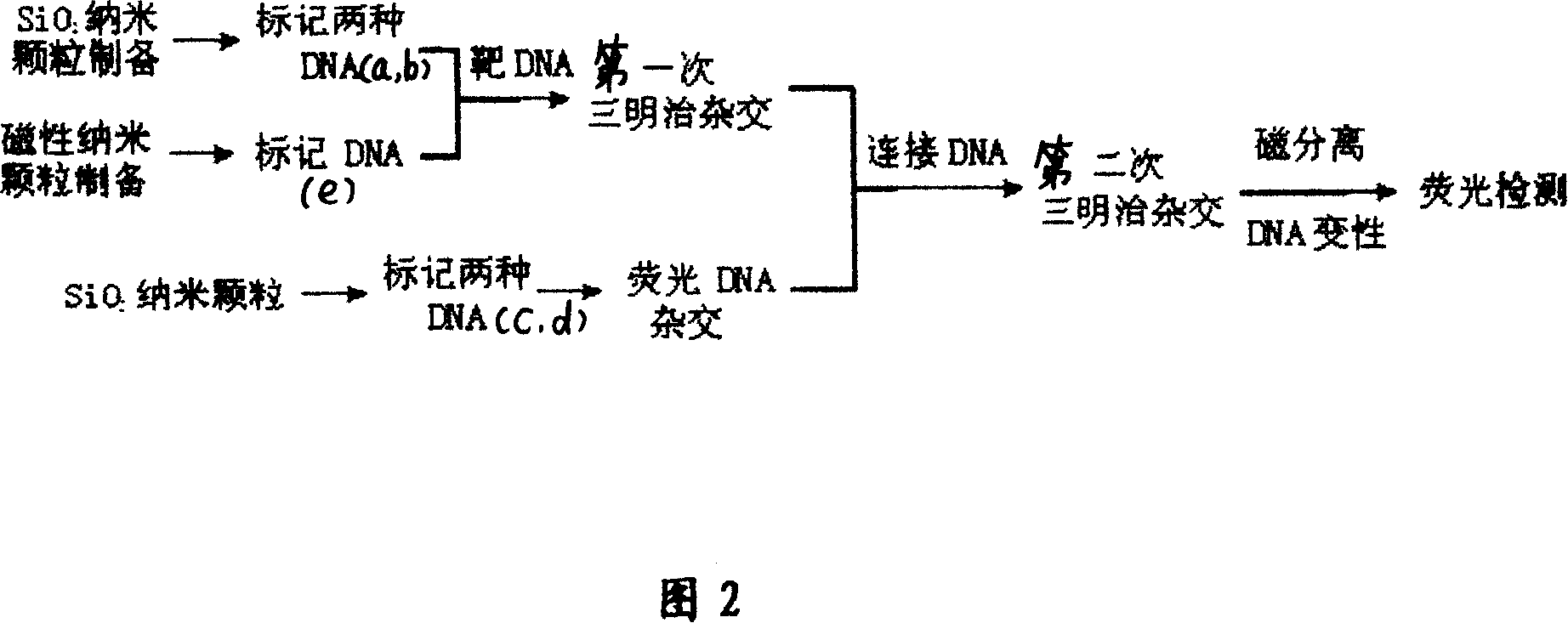
The invention discloses a laminated crossed fluorescent amplified magnetic separating and detecting method of DNA, which comprises the following steps: marking DNA of two different sequences a and b on the SiO2 nanometer particle simultaneously; marking DNA on the magnetic nanometer particle surface of sequence e; crossing one end of target DNA and the DNA of the sequence b on the SiO2 nanometer particle; crossing the other end of target DNA and DNA of sequence e on the magnetic nanometer particle; marking the DNA of two different sequences c and d on the SiO2 nanometer particle simultaneously; crossing DNA of SiO2 nanometer particle on the sequence c and fluorescent DNA; finishing the first sandwich crossing; crossing the DNA of first sandwich crossed SiO2 nanometer particle on the sequence a and one end of connected DNA; crossing the other end of DNA and the DNA on the nanometer particle on the sequence d after fluorescent cross; cleaning the product after the second sandwich cross through magnetic separation; removing residual fluorescent molecule and non-specific adsorption; denaturizing the DNA after the second sandwich cross; proceeding fluorescent detection for the unlinked fluorescent DNA.
Owner:东莞市才智坊新材料有限公司
Highly cross-linked monodisperse epoxy-group-containing polymeric microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104788609AGood dispersionGood spherical shapeMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationEpoxyCross-link
The invention relates to a highly cross-linked monodisperse epoxy-group-containing polymer microsphere and a preparation method thereof. The microsphere contains an epoxy group, methacrylic acid glycidyl ester is used as a monomer, divinyl benzene (DVB) is used as a cross-linking agent, and the microsphere is obtained through polymerization; the particle size of the microsphere is 2 to 10 [mu]m, and the polydispersity index is 1.04 to 1.07. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1), methacrylic acid glycidyl ester, the DVB and an initiating agent are together added into a solvent for uniform mixing, after nitrogen is introduced, sealing is performed, the reaction temperature is controlled to be 82 to 90 DEG C, and the reaction time lasts for 3 to 5 hours; (2), a reaction product obtained in the step (1) is washed and dried, so that the polymer microsphere is obtained. The polymer microsphere prepared by the invention contains the epoxy group, the epoxy group is an active group, derivative reaction is facilitated, and the problems of high hydrophobicity, high probability of non-specific adsorption can be solved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Labeled particle obtained by immobilizing a fragmented antibody to a labeling substance
InactiveUS20090203155A1Improve responseReduced nonspecific adsorptionImmunoglobulinsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesAntigenAntibody
An object of the present invention is to provide a labeled particle having a high reactivity with an antigen and a suppressed non-specific adsorption, and an immunochromatographic method using the labeled particle. The present invention provides a labeled particle, wherein a fragmented antibody is immobilized to a labeling substance via a chemical bond.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
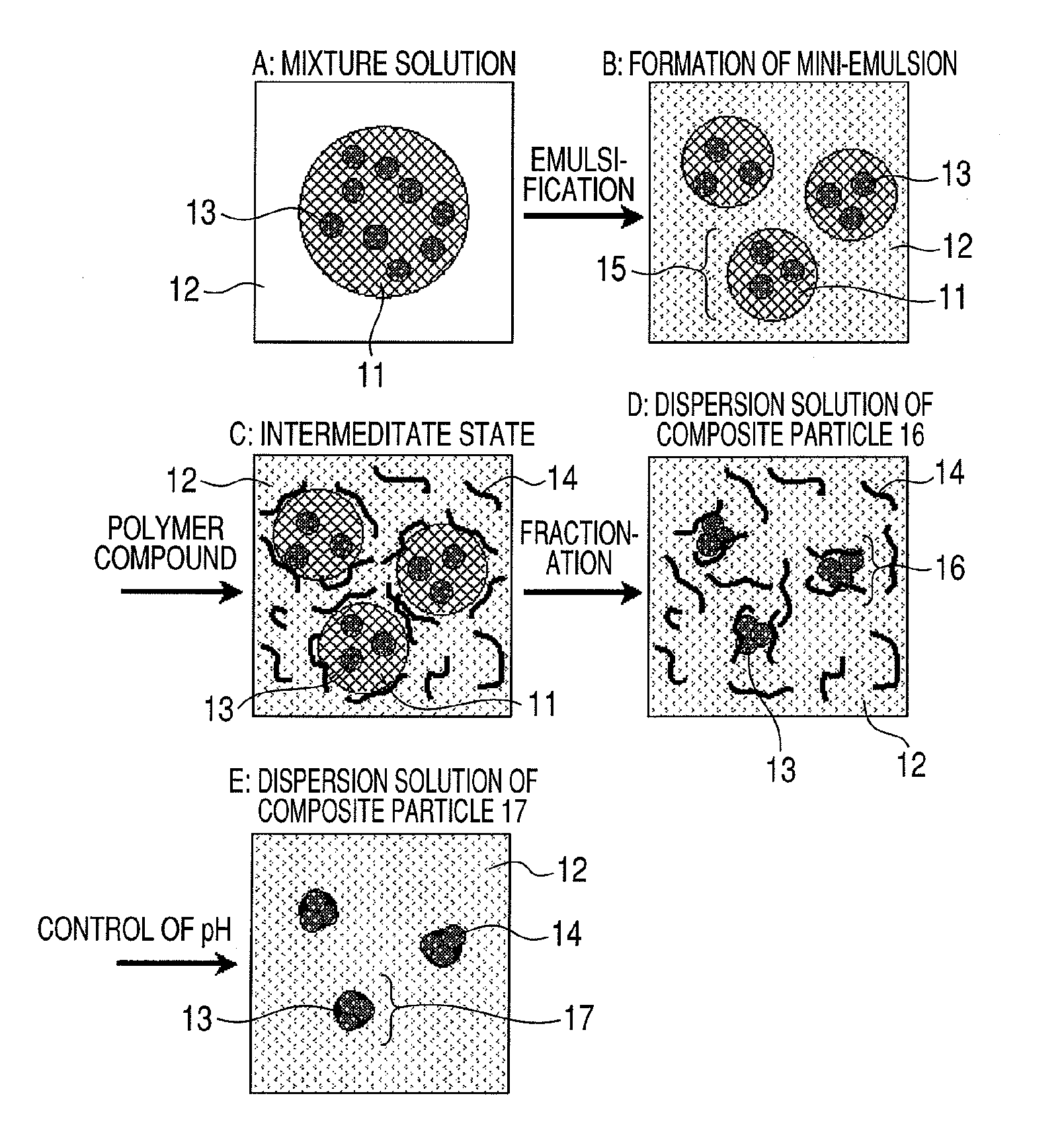
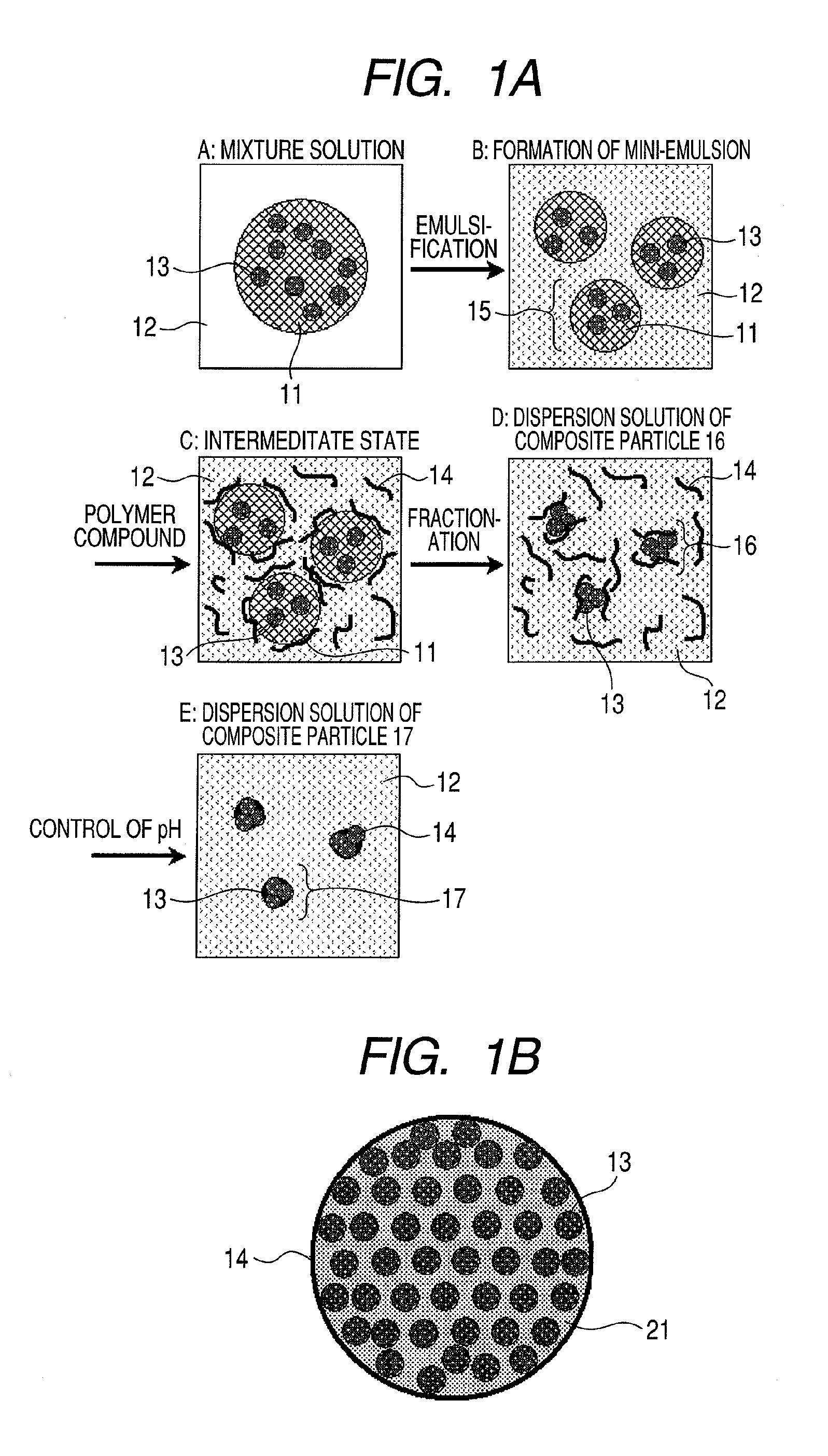
Composite particle, method for producing the same, dispersion solution, magnetic biosensing apparatus and magnetic biosensing method
InactiveUS20100330704A1Good monodispersityIncrease contentNanomagnetismComponent separationDispersityDispersion stability
To provide a method for producing composite particles small in particle size, excellent in mono-dispersibility, high in magnetic-substance content per particle, large in saturation magnetization, excellent in dispersion stability and having non-specific adsorption suppressibility.The method includes (1) mixing a first liquid and particles to prepare a mixture solution;(2) mixing the mixture solution and a second liquid to prepare an emulsion containing a dispersoid formed of the first liquid and the particles; (3) mixing a polymer compound with the emulsion; and (4) fractionating the emulsion to extract the first liquid from the dispersoid to produce the composite particles each containing the particles and the polymer compound, characterized in that the dispersoid has a single-peak particle size distribution and a dispersity index (Dhw / Dhn) calculated from a number-average hydrodynamic particle size (Dhn) and a weight-average hydrodynamic particle size (Dhw) is 1.5 or less.
Owner:CANON KK
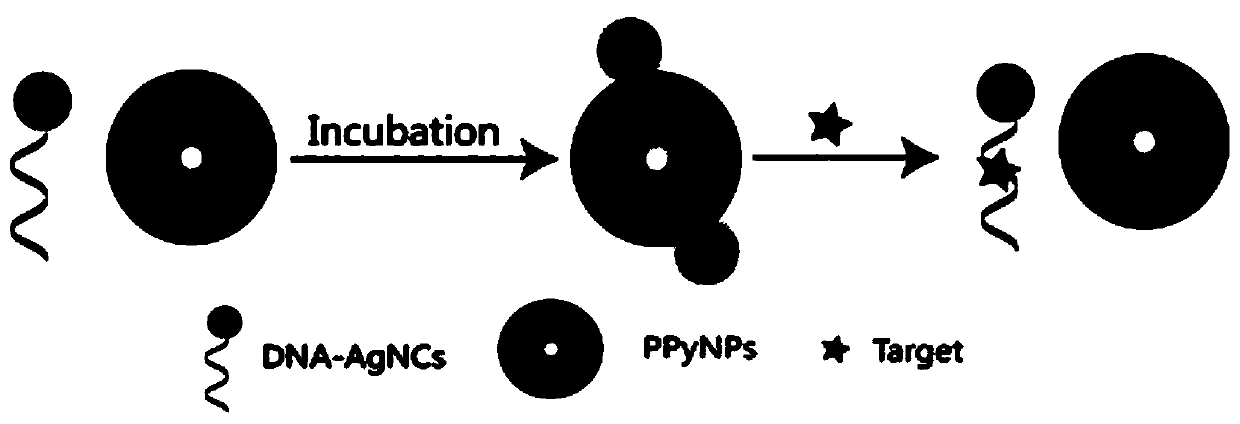
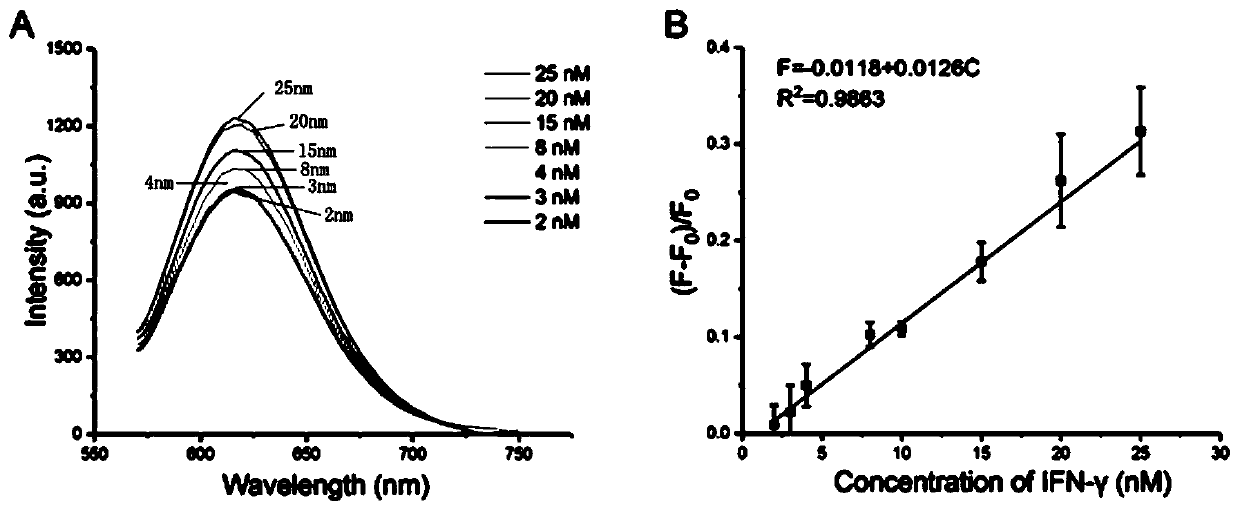
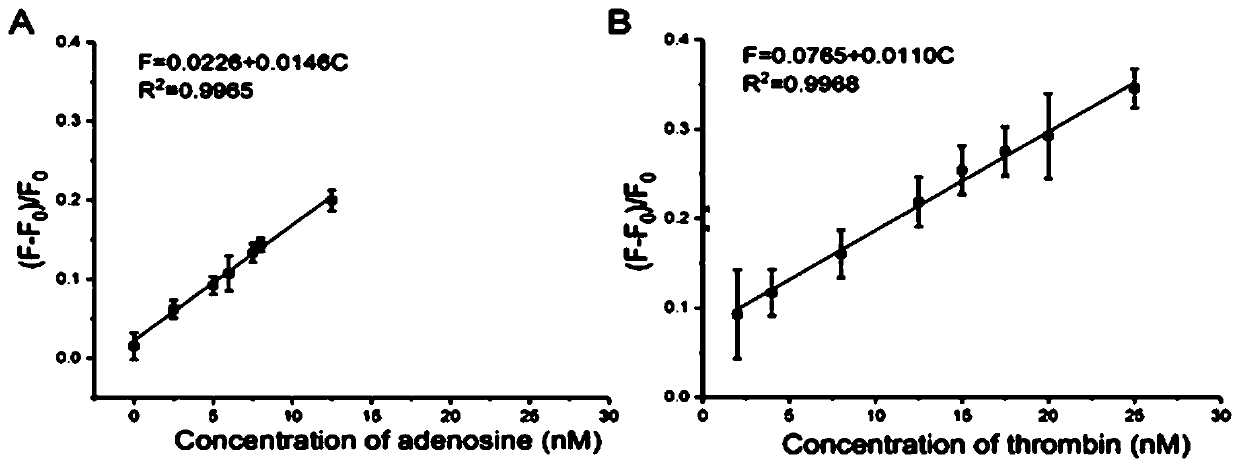
Method for detecting multiple targets based on nucleic acid aptamer fluorescence sensor
The invention discloses a method for detecting multiple targets based on nucleic acid aptamer fluorescence sensor, which applies polypyrrole nanoparticles and DNA silver nanoclusters for the first time and establishes an aptamer sensing platform based on a steric hindrance effect.In addition, the invention obtains a good detection result based on the low non-specific adsorption characteristic ofthe polypyrrole nanoparticles, and realizes the detection of multiple targets based on the specific recognition characteristic of the aptamer sequence, improving the universal performance of the invention.The method for detecting multiple targets based on nucleic acid aptamer fluorescence sensor, provided by the invention, has the advantages of label-free property, no enzyme and high sensitivity,and can realize high-efficiency detection in biological samples.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Reduction of non-specific adsorption of biological agents on surfaces
InactiveUS20060134656A1Reduced non-specific adsorptionReduce non-specific bindingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlycol synthesisBiochip
The present invention relates to surface-modified substrates that demonstrate reduced non-specific adsorption of biological agents. The substrates are silicon or carbon substrates having ethylene glycol oligomers covalently bound to at least one substrate surface. The substrates may be used in sensor devices, such as biochips, and in implantable medical devices in order to reduce the non-specific binding of biological agents.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
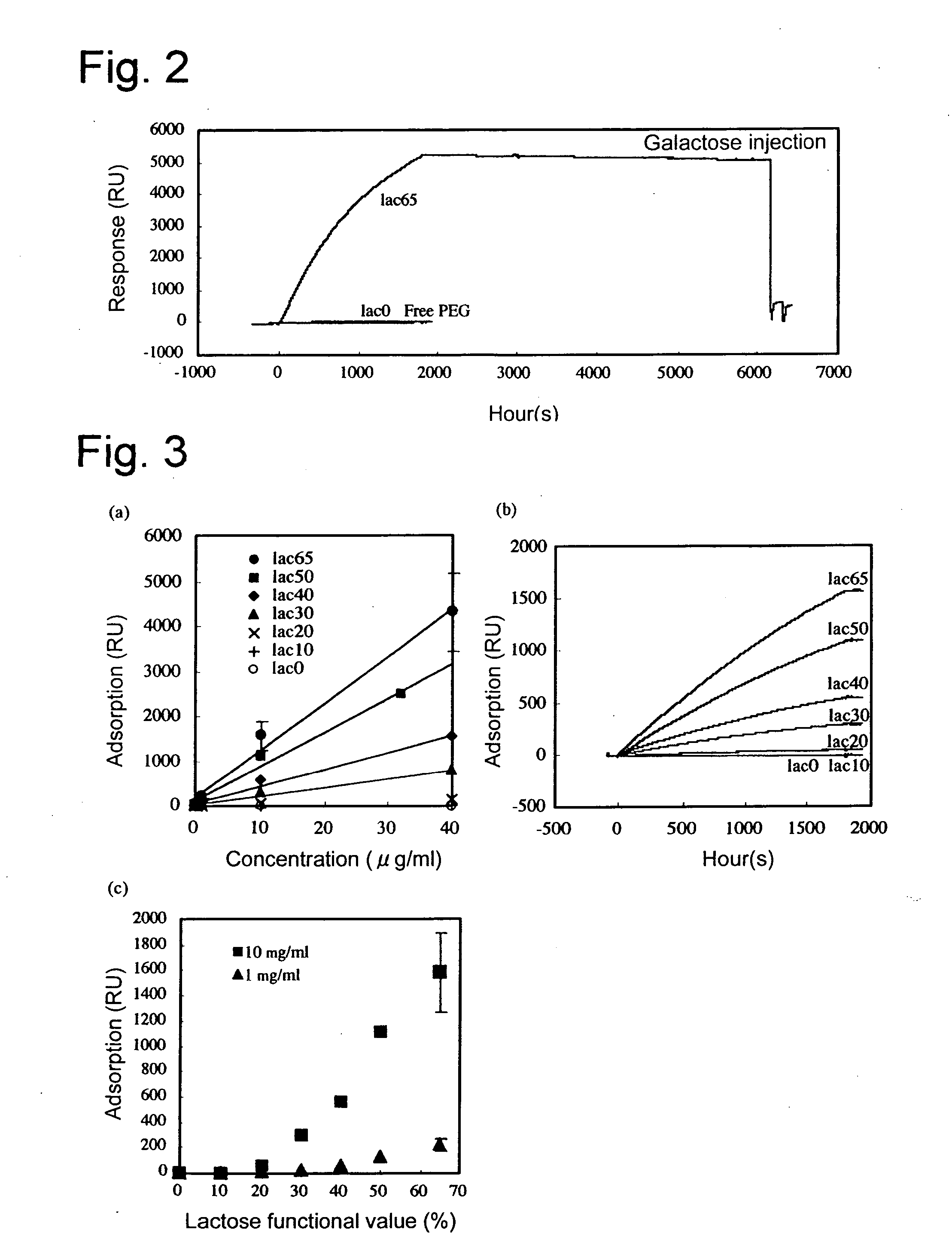
Temperature response type beta-cyclodextrin silica gel stationary phase and preparation method thereof
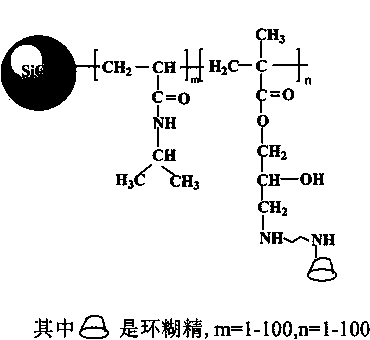
InactiveCN104028254ANovel structureUnique Behavior CapabilitiesOther chemical processesTemperature responseDouble bond
The invention relates to a temperature response type beta-cyclodextrin silica gel stationary phase. The structural formula of the temperature response type beta-cyclodextrin silica gel stationary phase is as shown in the specification. The preparation method comprises the steps of deriving beta-cyclodextrin to obtain a beta-cyclodextrin derivative with a reaction group and a functional group, then performing silylation reaction, modifying a silica gel surface with a silylation reagent with two bonds, performing polymerization reaction on acrylamide and a glycidyl ether monomer to form a meshed temperature-sensitive polymer layer on the silica gel surface through azodiisobutyronitrile serving as an initiator, and finally implanting the beta-cyclodextrin derivative into a polymer chain to obtain the temperature response type beta-cyclodextrin silica gel stationary phase. The preparation process is simple, and the property is stable; the prepared temperature response type beta-cyclodextrin silica gel stationary phase can overcome the shortcomings that silica gel cannot resist water and alkali and undergoes non-specific adsorption; a prepared separation material is novel in structure and flexible in application; effective separation of compounds can be realized by controlling the column temperature; furthermore, the beta-cyclodextrin derivative in the polymer chain can improve the hydrophilicity and the chiral recognition capacity of the stationary phase, and is suitable for separation and chiral separation of polar and hydrophilic compounds and chemical molecules.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Non-specific adsorption inhibitor
InactiveUS20100204424A1Prevent non-specific adsorptionLower critical solution temperatureWater soluble
A non-specific adsorption inhibitor includes a water-soluble polymer obtained by polymerizing a monomer unit that includes a monomer (A) that forms a polymer that has a lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of 80° C. or less in an aqueous solution under normal pressure when subjected to homopolymerization, and a monomer (B) that forms a polymer that does not have the LCST in an aqueous solution under normal pressure when subjected to homopolymerization.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com