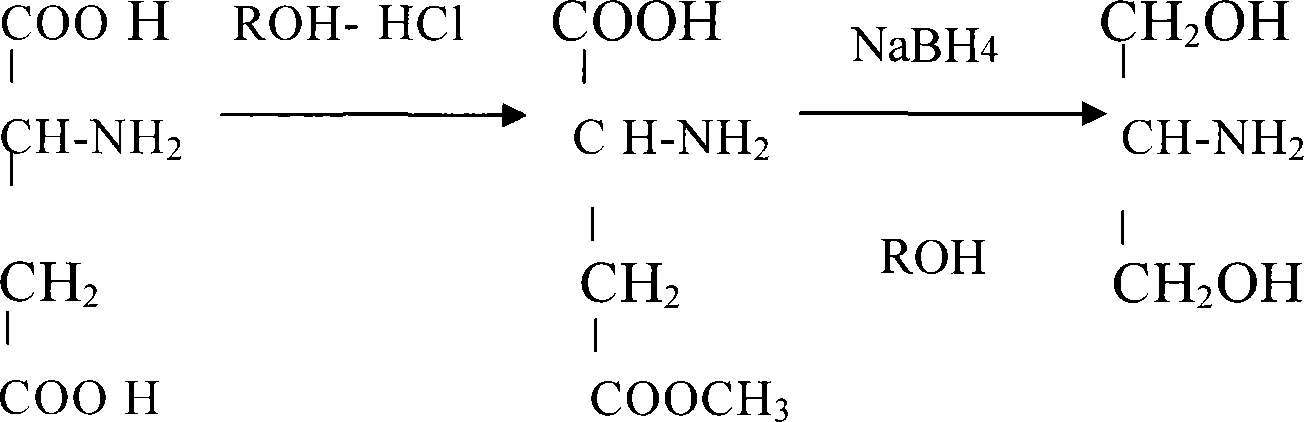Technique for preparing L-homoserine
A technology of homoserine and a new process, which is applied in the field of preparation of homoserine, can solve the problems of inflammability and explosion, technical level limitation, "three wastes" pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing product yield, reducing production cost, and simplifying process steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Step 1 Preparation of L-Aspartic Acid Methyl Ester
[0023] Add 133.1g of L-aspartic acid (1.0mol) and 1000ml of anhydrous methanol into a 2000ml three-neck flask, and feed 73g of HCl at below 5°C. After passing through, the temperature was slowly raised to reflux for 2 hours, and the organic solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain 165.2 g of white crystal L-aspartic acid methyl ester hydrochloride, with a purity of 98.5% and a yield of 90.0% (using L-tianmen aspartic acid meter).
[0024] Step 2 Preparation of L-homoserine by reduction of L-aspartic acid methyl ester
[0025] Take the above 73.5g of L-aspartic acid methyl ester hydrochloride (0.4mol), add 1100g of anhydrous methanol into a 2000mL three-necked flask and mix evenly, and adjust the pH to 5 with triethylamine, then slowly add 31g (0.8mol )NaBH 4 , The feeding temperature is controlled at 0-5°C, and the adding speed of the reducing agent is controlled to prevent the reaction from being to...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Step 1 Preparation of L-ethyl aspartate
[0028] Add 133.1g of L-aspartic acid (1.0mol) and 1000ml of absolute ethanol into a 2000ml three-necked flask, and feed 73g of HCl at below 5°C. After passing through, the temperature was slowly raised to reflux for 2 hours, and the organic solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain 180.0 g of white crystal L-aspartic acid ethyl ester hydrochloride with a purity of 98.6% and a yield of 91.1% (using L-tianmen aspartic acid meter).
[0029] Step 2 Preparation of L-homoserine by reduction of L-aspartic acid ethyl ester
[0030] Take the above 79.0g of L-aspartic acid ethyl ester hydrochloride (0.4mol), add 790g of absolute ethanol into a 1500mL three-necked flask and mix evenly, and adjust the pH to 5 with triethylamine, then slowly add 31g (0.8mol )NaBH 4 , The feeding temperature is controlled at 0-5°C, and the adding speed of the reducing agent is controlled to prevent the reaction from being too violent or the l...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Step 1 Preparation of L-Aspartic Acid Methyl Ester
[0033] Add 133.1g of L-aspartic acid (1.0mol) and 1000ml of anhydrous methanol into a 2000ml three-neck flask, and feed 73g of HCl at below 5°C. After passing through, the temperature was slowly raised to reflux for 2 hours, and the organic solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to obtain 165.2 g of white crystal L-aspartic acid methyl ester hydrochloride, with a purity of 98.5% and a yield of 90.0% (using L-tianmen aspartic acid meter).
[0034] Step 2 Preparation of L-homoserine by reduction of L-aspartic acid methyl ester
[0035] Take the above 73.5g L-aspartic acid methyl ester hydrochloride (0.4mol), add 750g of anhydrous methanol into a 1500mL three-necked flask and mix evenly, and adjust the pH to 5 with triethylamine, then slowly add 18.5g (0.48 mol)LiAlH 4 , The feeding temperature is controlled at 0-5°C, and the adding speed of the reducing agent is controlled to prevent the reaction from being to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com