Method for recovering and processing discarded fluorescent lamp
A technology for recycling and processing fluorescent lamps, which is applied in glass recycling, recycling technology, electronic waste recycling, etc. It can solve the problems of different forms, waste of resources, and inability to completely remove pollution sources, so as to avoid treatment, simplify processes, and process methods. and economical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
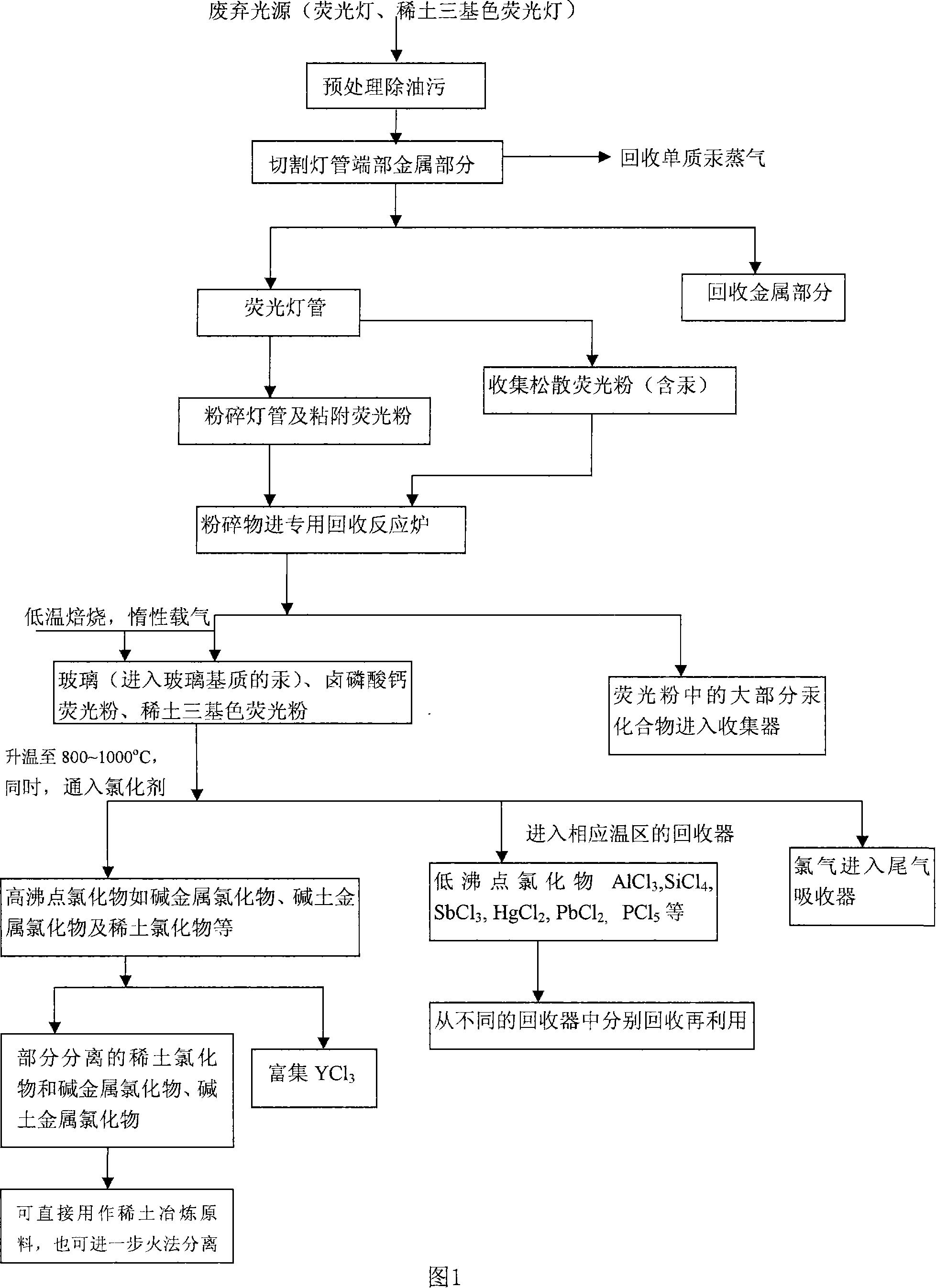
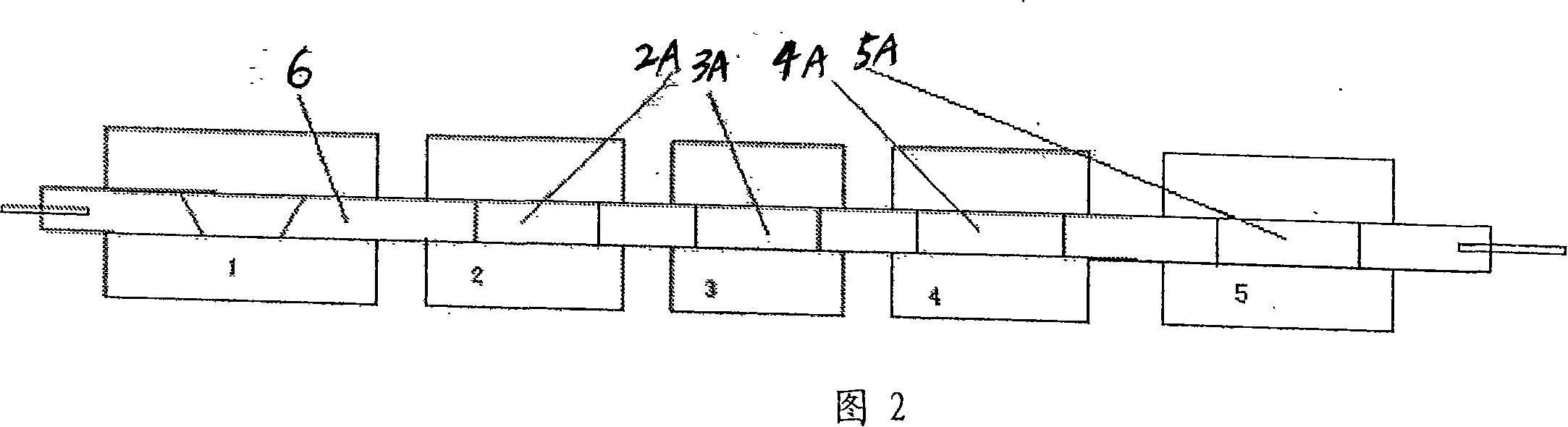
[0034] A recovery example of the present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with the flow process of accompanying drawing 1, and the waste fluorescent lamps processed are all 40W T12 straight-tube household lighting fluorescent lamps, each lamp tube contains 20-40mg of mercury, and 4.5g of three primary color phosphors , whose basic composition is 60% Y 2 o 3 :Eu 3+ , 30% Ce 0.67 Mg 0.33 Al 11 o 19 :Tb 3+ , 10% BaMgAl 16 o 27 :Eu 2+ . The glass tube is mainly made of Na 2 SiO 3 , CaSiO 3 , SiO 2 And a small amount of PbO; the end metal part: generally composed of Al cap, brass plug, Cu-Ni alloy wire and polyacrylate insulator; the filament is usually tungsten wire.
[0035] 1) Clean the surface of the collected waste fluorescent lamps with detergent powder, sodium hydroxide solution (2-3 mol / L), nitric acid solution (2 mol / L), and tap water to remove oil stains. After drying, cut off the non-glass part at the end of the lamp tube with a cuttin...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Other content and operation are the same as Example 1, the difference is: the recovery of gaseous mercury in the cutting process in step 1 is completed in 25% acetone solution; in step 4), the starting chlorination temperature is 350 ° C, but the chlorination The time is slightly longer, and each component is also recovered; in the mixed recovery of glass and fluorescent powder in step 5), the roasting temperature is controlled at 950°C, the reaction time is 90min, and the control temperatures of corresponding recovery furnaces 2, 3, 4, and 5 are respectively reduced. It is about 800°C, 700°C, 600°C, and 400°C. Adopt these conditions, also can reach the recycling treatment effect as example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com