Connection fragment PCR detecting method for appraising unknown gene sequence
A technology for connecting fragments and detection methods, which is applied in the field of unknown DNA sequences, can solve the problems of obtaining coding sequences on functional genes, failing to obtain regulatory element sequences, consuming a lot of manpower and material resources, and achieving amplification specificity and amplification. Efficiency enhancement, simple and reliable result analysis, simplified labor effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
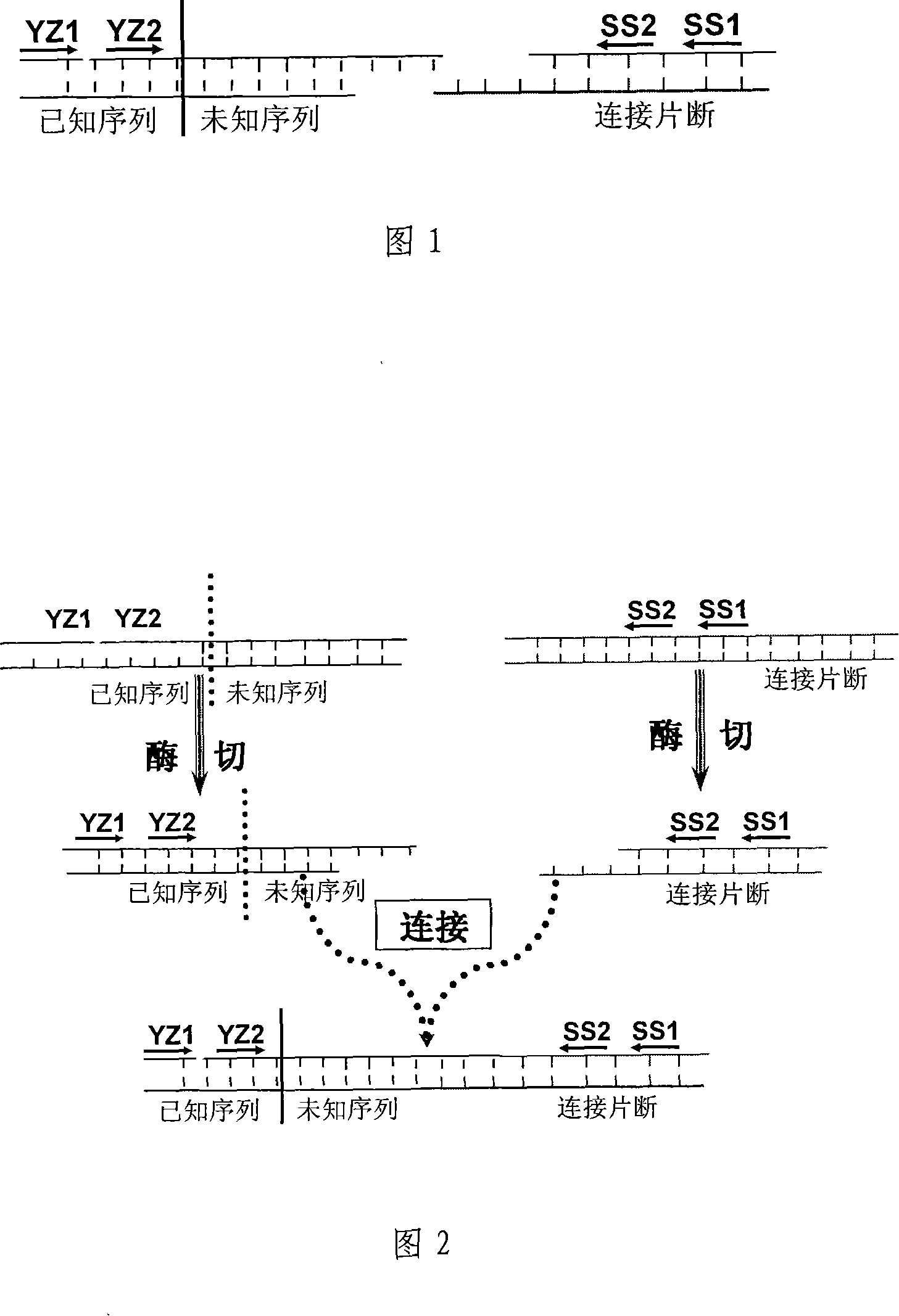
[0030] Amplification of the insertion site for transgenic crop GT73. In this experiment, the restriction endonuclease Hind III was selected to digest the rapeseed genome, and the digested DNA was ligated with a junction fragment with a Hind III restriction site sticky end under the action of ligase, and then the exogenous gene cp4- The nested forward primer of the epsps gene and the nested reverse primer on the connecting fragment were used for nested PCR amplification of the connected system. After two rounds of PCR amplification, a very bright electrophoresis band greater than 2000 bp was obtained. Collect the amplified product, connect the recovered fragment to the pGEM-T Easy vector, transform Escherichia coli competent cell DH5α, pick positive clones, digest and sequence to identify the obtained sequence. Some of the measured sequences are shown in Figure 3. According to DNAMAN and NCBI analysis, the sequence before 2372bp is derived from exogenously inserted DNA, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0032]Amplification of plant unknown sequences next to the insertion site in transgenic maize 59122. In this experiment, the restriction endonuclease Sac I was selected to digest the rapeseed genome, and the digested DNA was ligated with a junction fragment with a sticky end of the Sac I restriction site under the action of ligase, and then the exogenous gene promoter of transgenic crops was used The nested primers (UbiF1 / R1 / R2) of the gene and the nested primers (SS1 / SS2) on the connecting fragment were used to perform nested PCR amplification on the connected system. After two rounds of PCR amplification, a very bright Electrophoretic bands larger than 2000bp. The amplified product was recovered, and the recovered fragment was connected to the pGEM-T Easy vector, transformed into Escherichia coli competent cell DH5α, positive clones were picked, digested with restriction enzymes, and sequenced to identify the obtained sequence. . Align the known sequences with DNAMAN softw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com