Patents
Literature
50 results about "Policy-based management" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Policy-based management is a technology that can simplify the complex task of managing networks and distributed systems. Under this paradigm, an administrator can manage different aspects of a network or distributed system in a flexible and simplified manner by deploying a set of policies that govern its behaviour. Policies are technology independent rules aiming to enhance the hard-coded functionality of managed devices by introducing interpreted logic that can be dynamically changed without modifying the underlying implementation. This allows for a certain degree of programmability without the need to interrupt the operation of either the managed system or of the management system itself. Policy-based management can increase significantly the self-managing aspects of any distributed system or network, leading to more autonomic behaviour demonstrated by Autonomic computing systems.
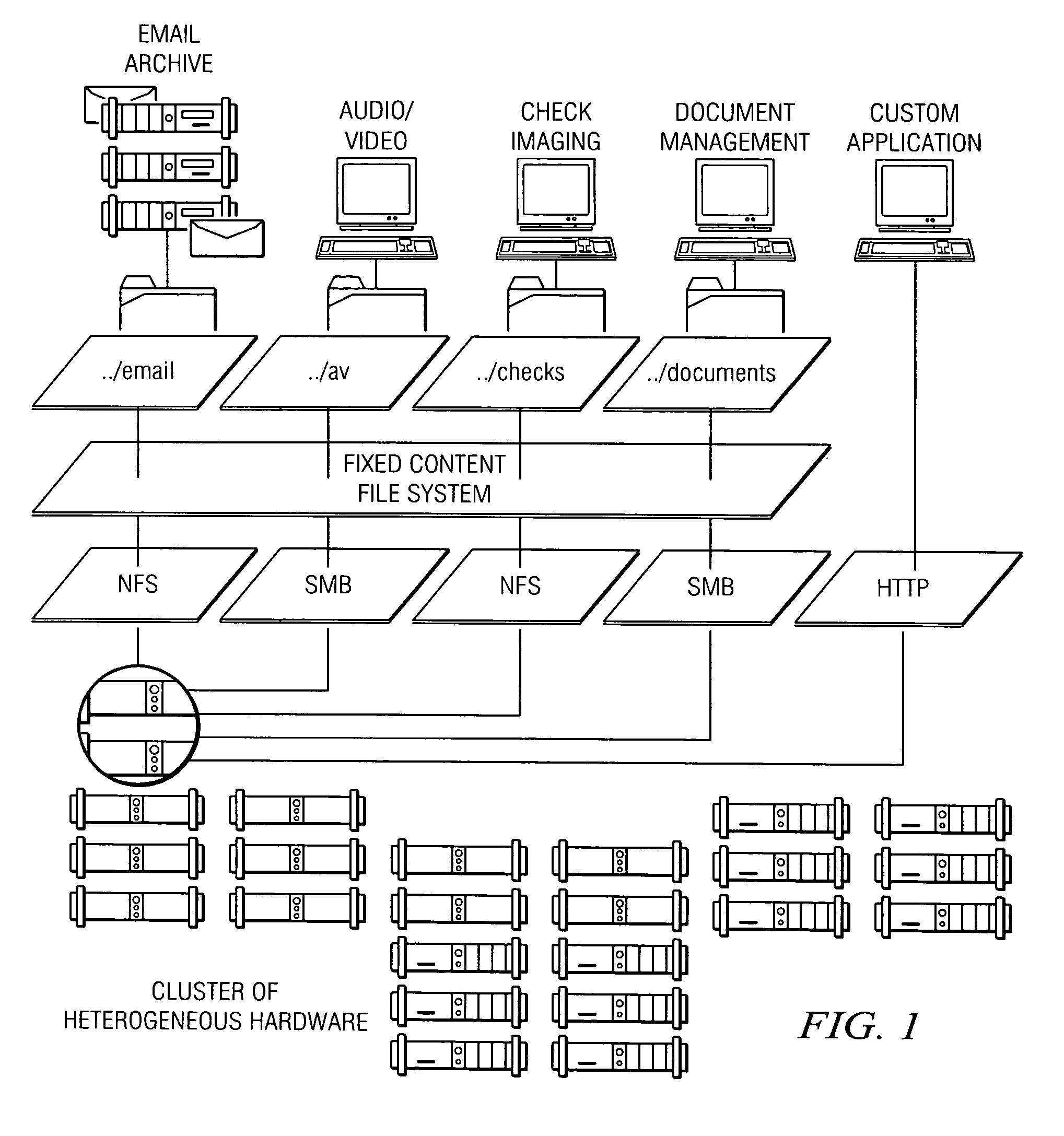
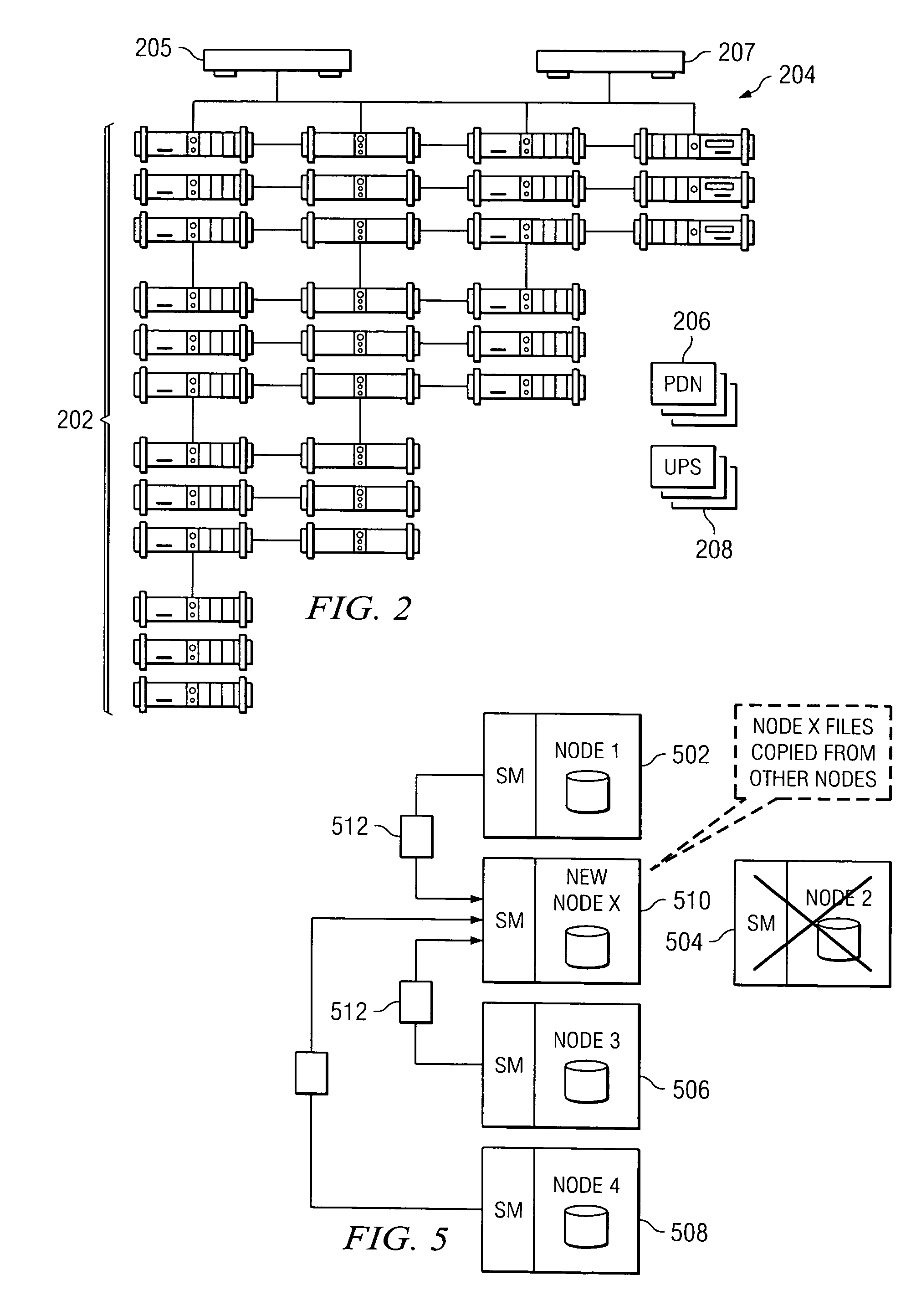
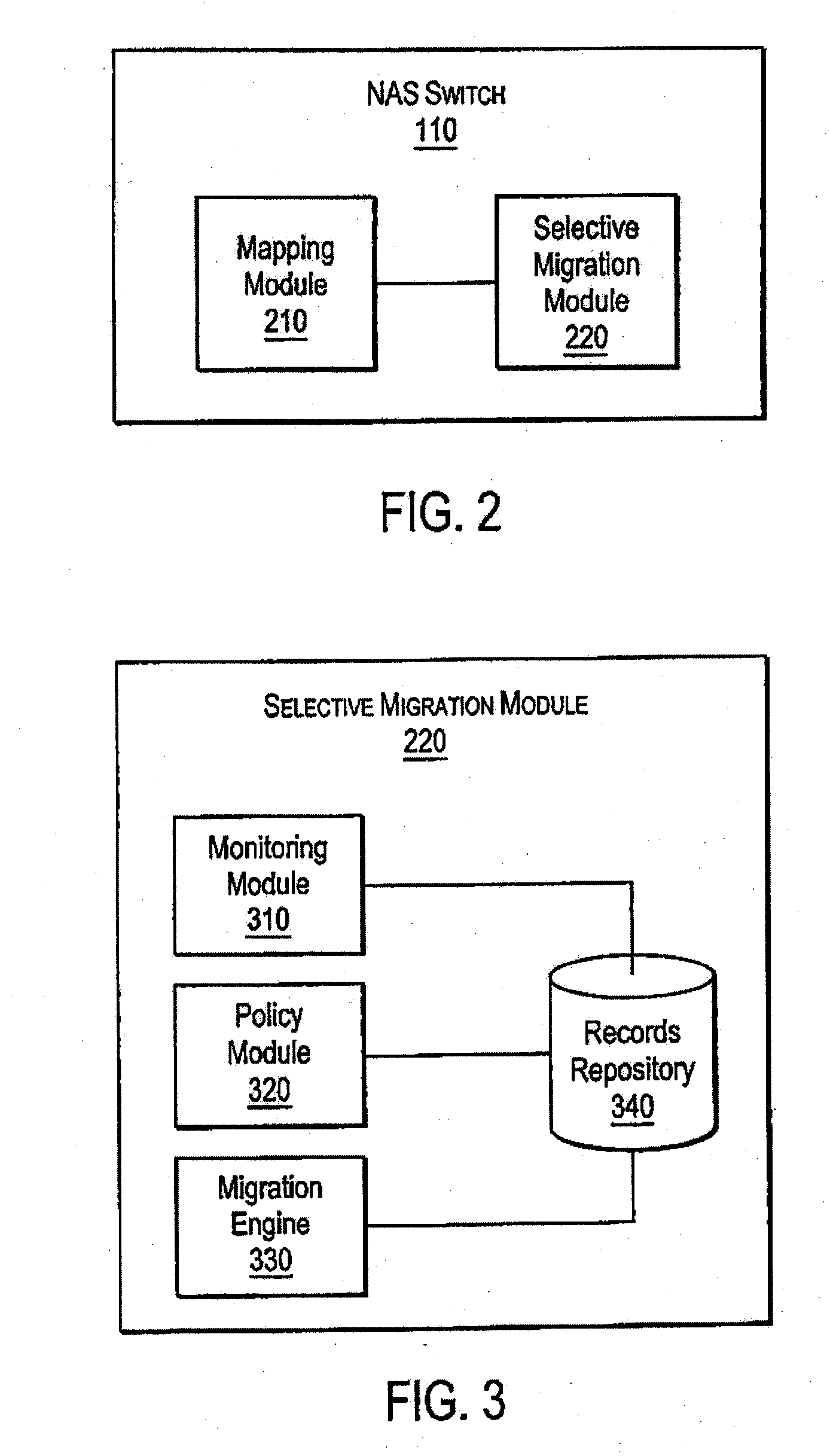
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS20050120025A1Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
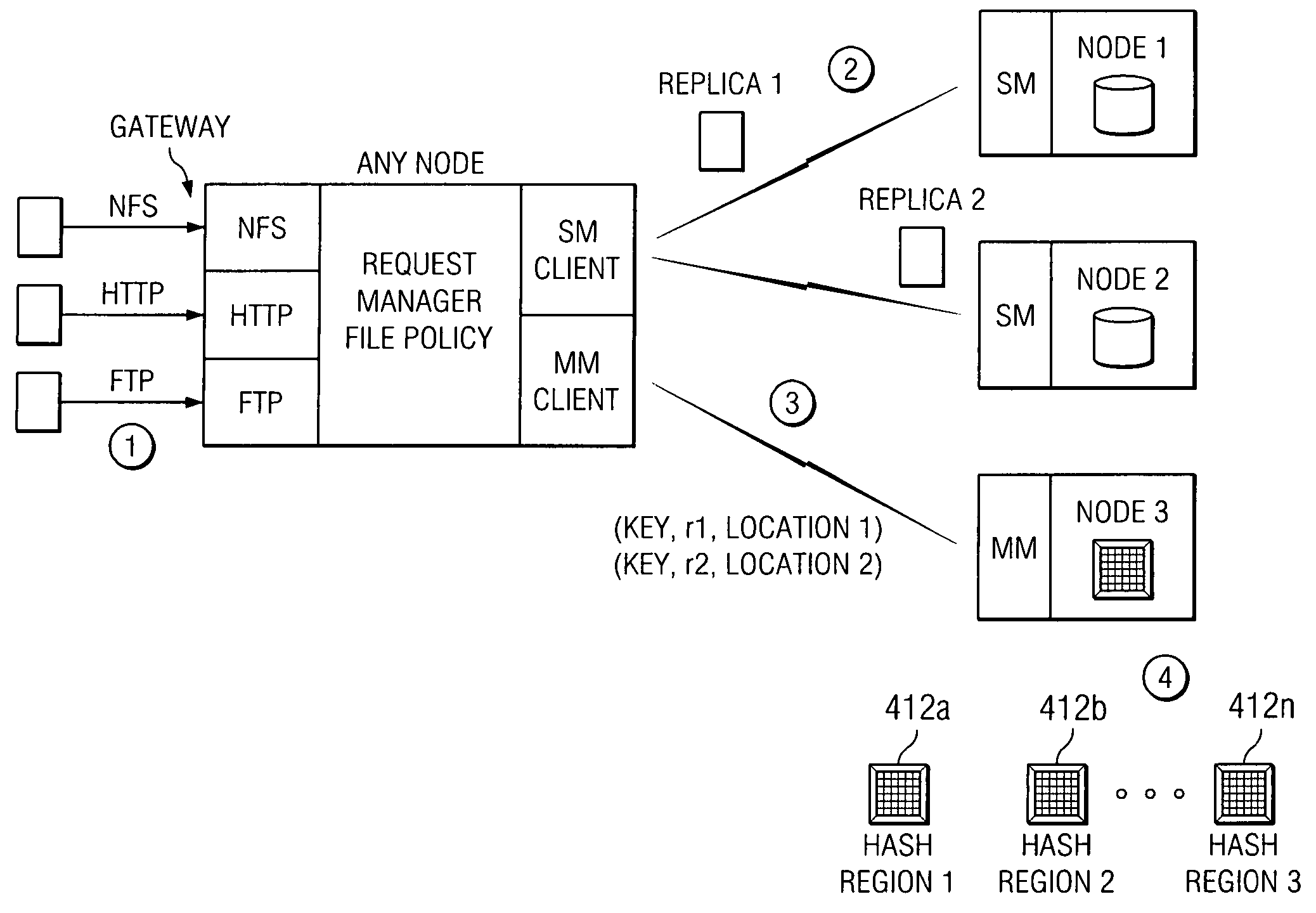
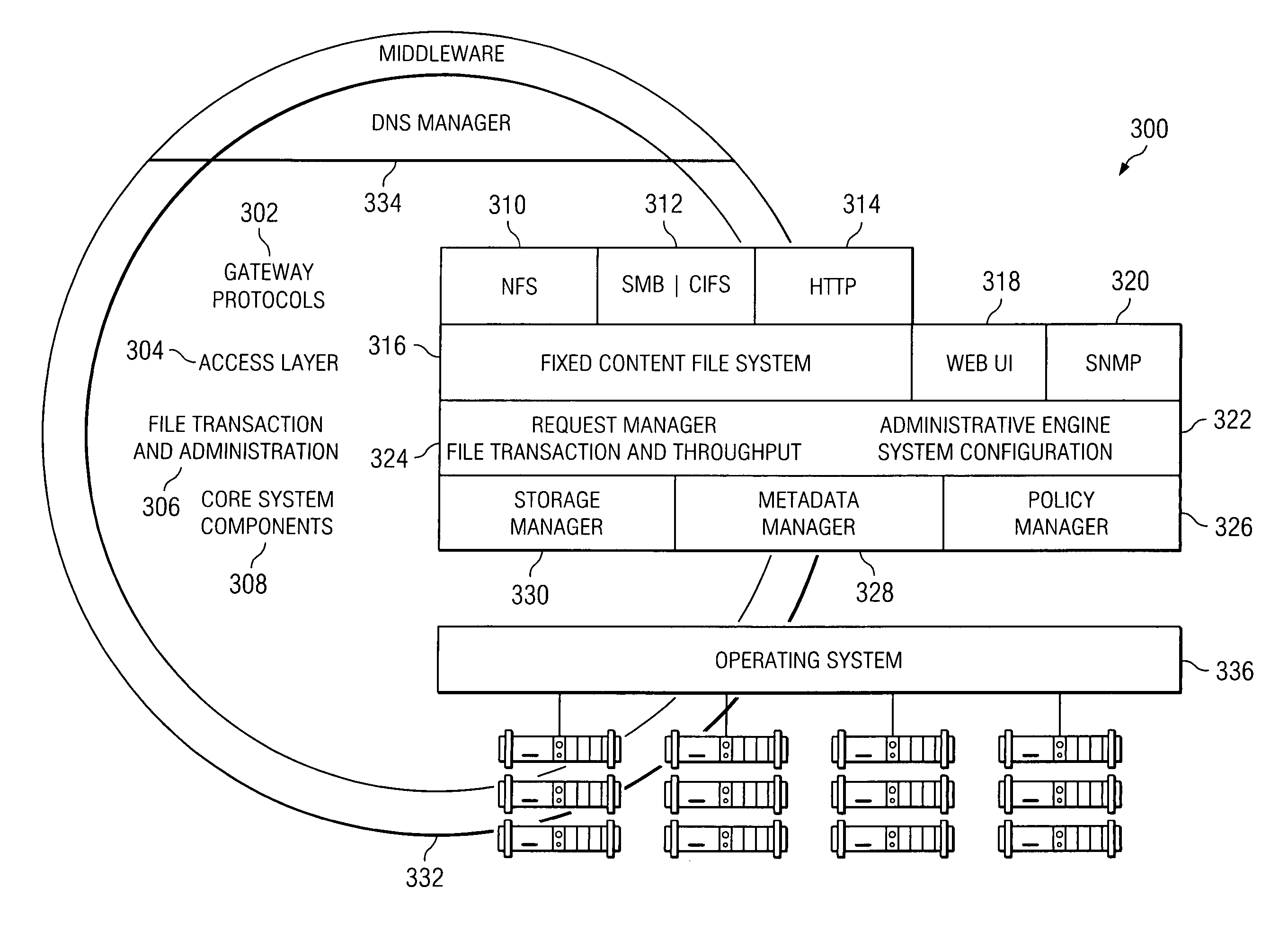
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
Policy-based management of a redundant array of independent nodes
ActiveUS7155466B2Reduce complexityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsObject basedMetadata management
An archive cluster application runs in a distributed manner across a redundant array of independent nodes. Each node preferably runs a complete archive cluster application instance. A given nodes provides a data repository, which stores up to a large amount (e.g., a terabyte) of data, while also acting as a portal that enables access to archive files. Each symmetric node has a set of software processes, e.g., a request manager, a storage manager, a metadata manager, and a policy manager. The request manager manages requests to the node for data (i.e., file data), the storage manager manages data read / write functions from a disk associated with the node, and the metadata manager facilitates metadata transactions and recovery across the distributed database. The policy manager implements one or more policies, which are operations that determine the behavior of an “archive object” within the cluster. The archive cluster application provides object-based storage. Preferably, the application permanently associates metadata and policies with the raw archived data, which together comprise an archive object. Object policies govern the object's behavior in the archive. As a result, the archive manages itself independently of client applications, acting automatically to ensure that all object policies are valid.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA LLC
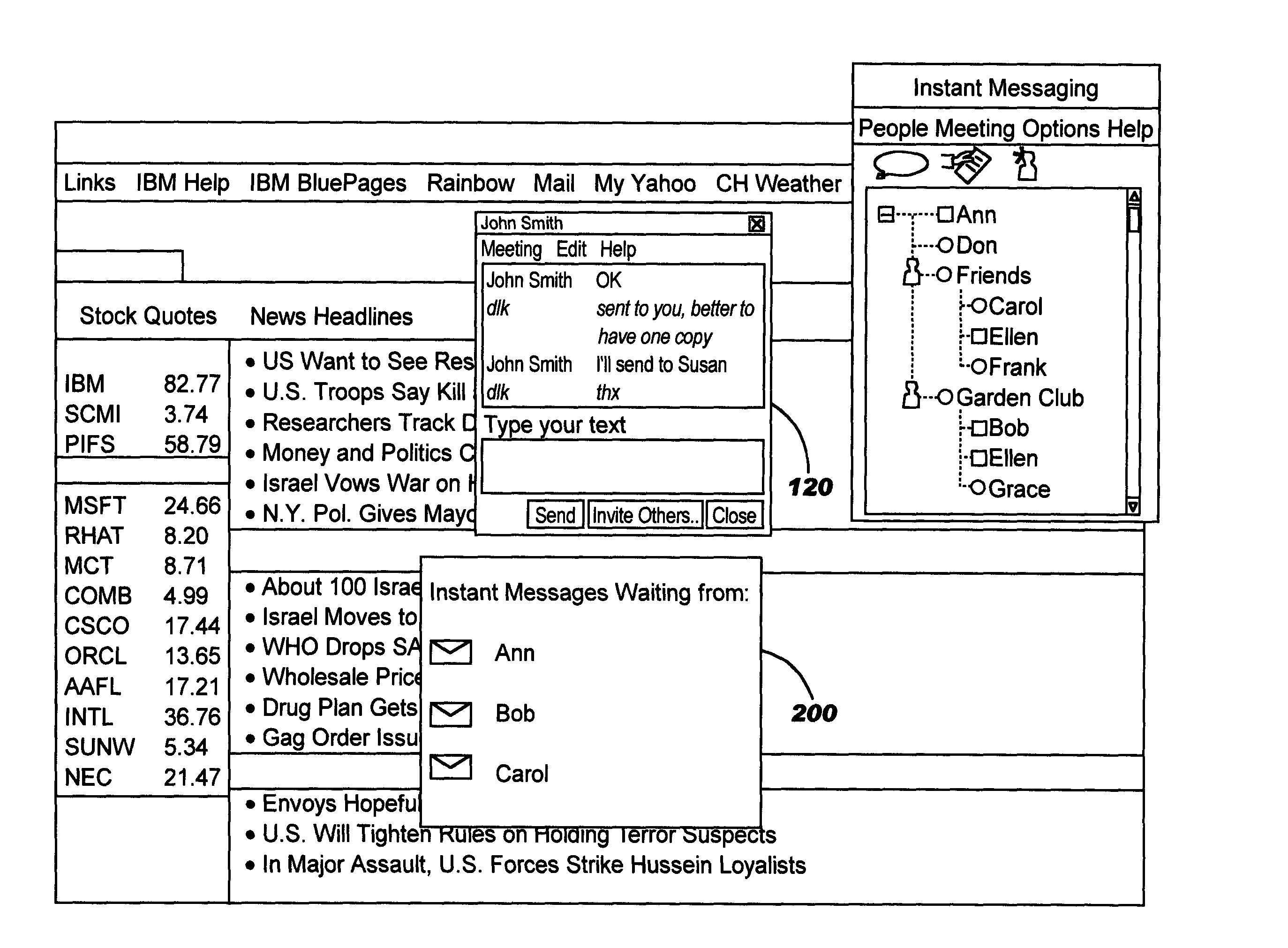
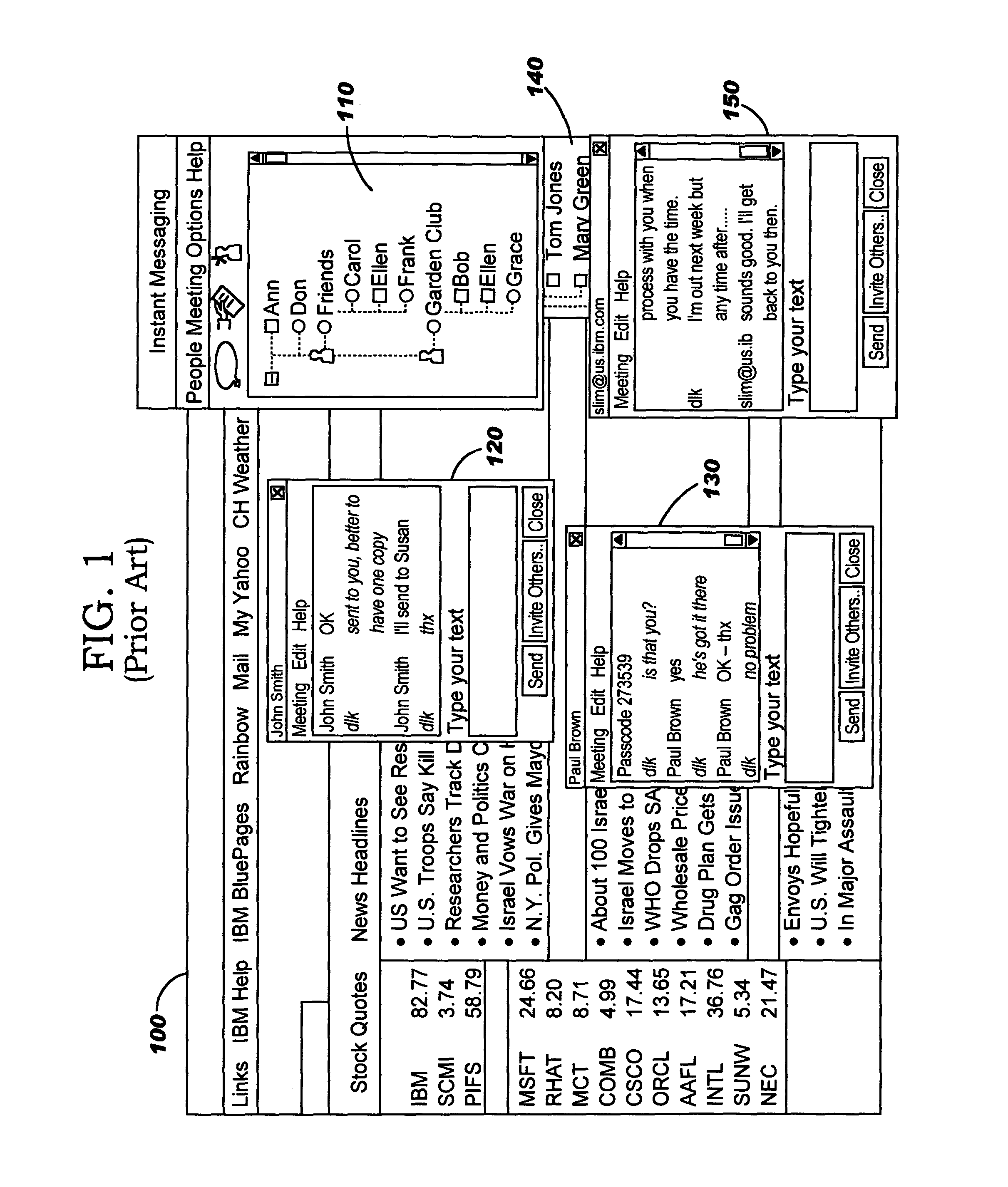
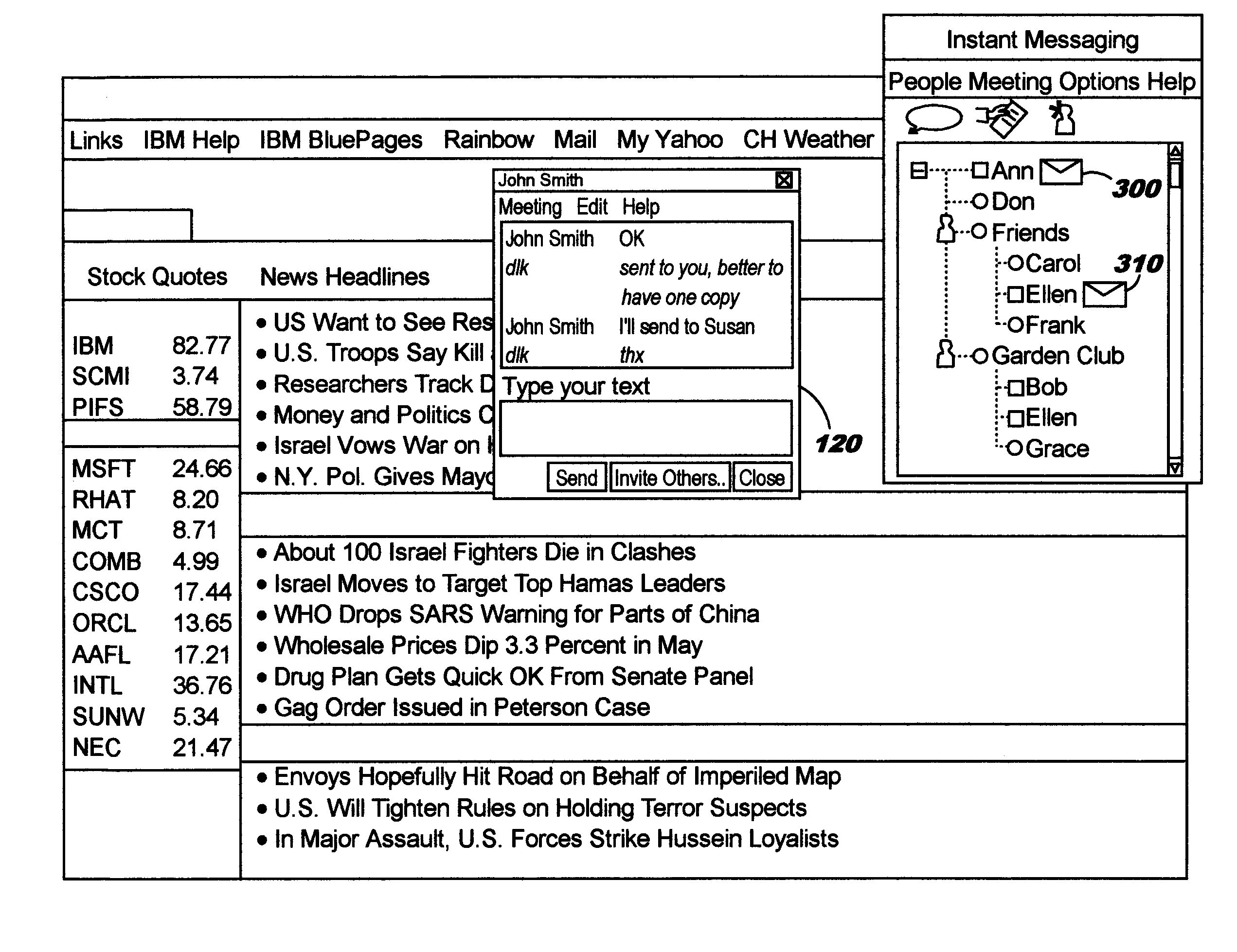
Policy-based management of instant message windows
InactiveUS20050055412A1Simple technologyPrevent proliferationMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksPolicy-based managementInstant messaging
Techniques are disclosed for managing instant messages, including the display of windows for incoming messages, as well as for managing status information for instant messaging users. In one aspect, an instant messaging user defines policy information to programmatically determine a response to an arriving instant message. As an example, the policy may control whether a new window will pop up for a newly-arriving message, and may specify other attributes of the window if desired. In another aspect, an instant messaging user defines attributes pertaining to how his instant messaging status will be presented to others.
Owner:IBM CORP
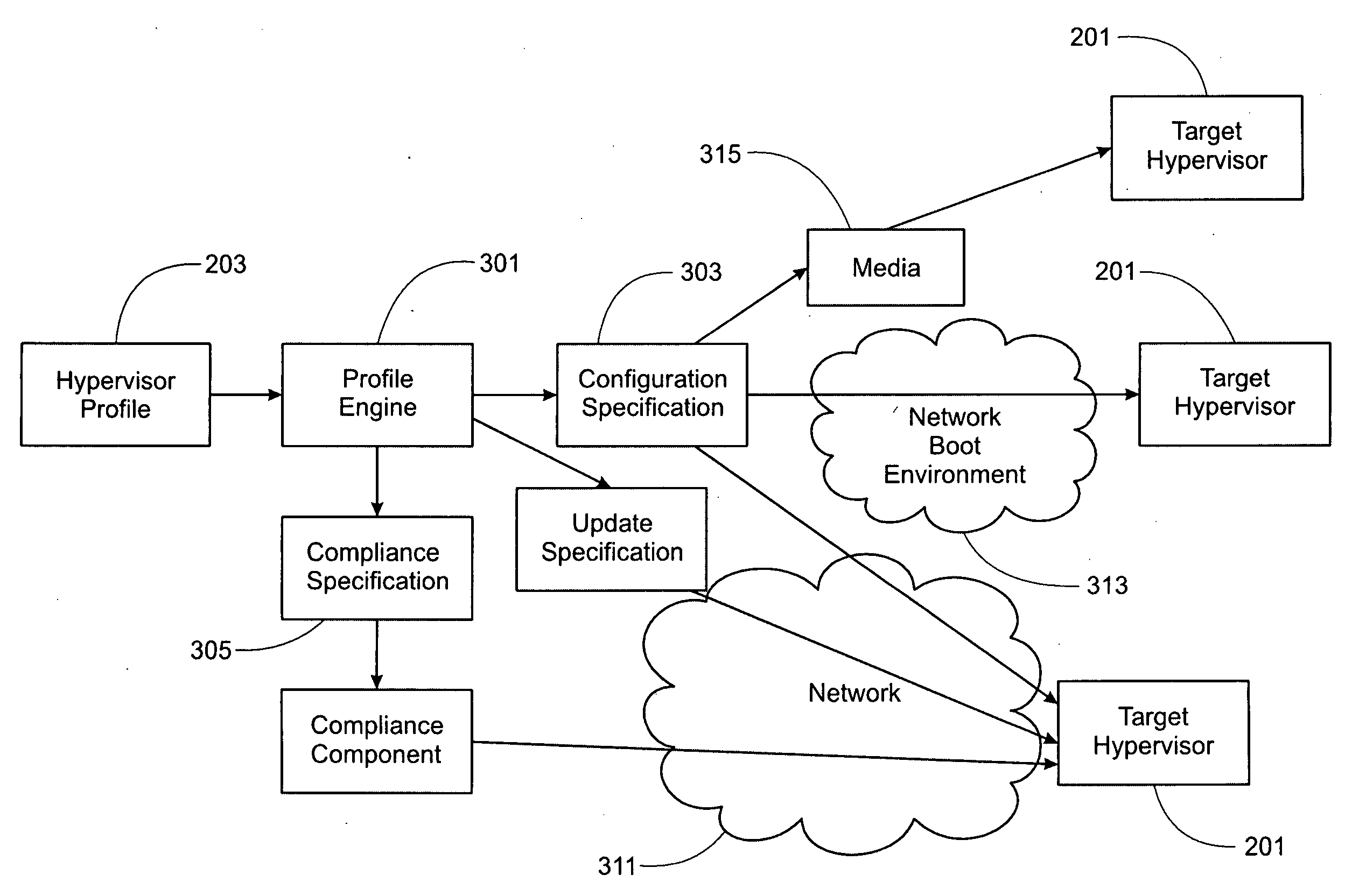
Policy-Based Hypervisor Configuration Management
ActiveUS20100070970A1Digital computer detailsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPolicy-based managementOperating system
At least one target configuration of a host at a virtualization software level is automatically assembled based on a source configuration. A policy based profile describing the source configuration is processed. A configuration specification describing the target configuration is automatically created, based on the policy based profile describing the source configuration. The configuration specification is automatically applied to target configurations, such that the target configuration(s) are compliant with the policy based profile.
Owner:VMWARE INC
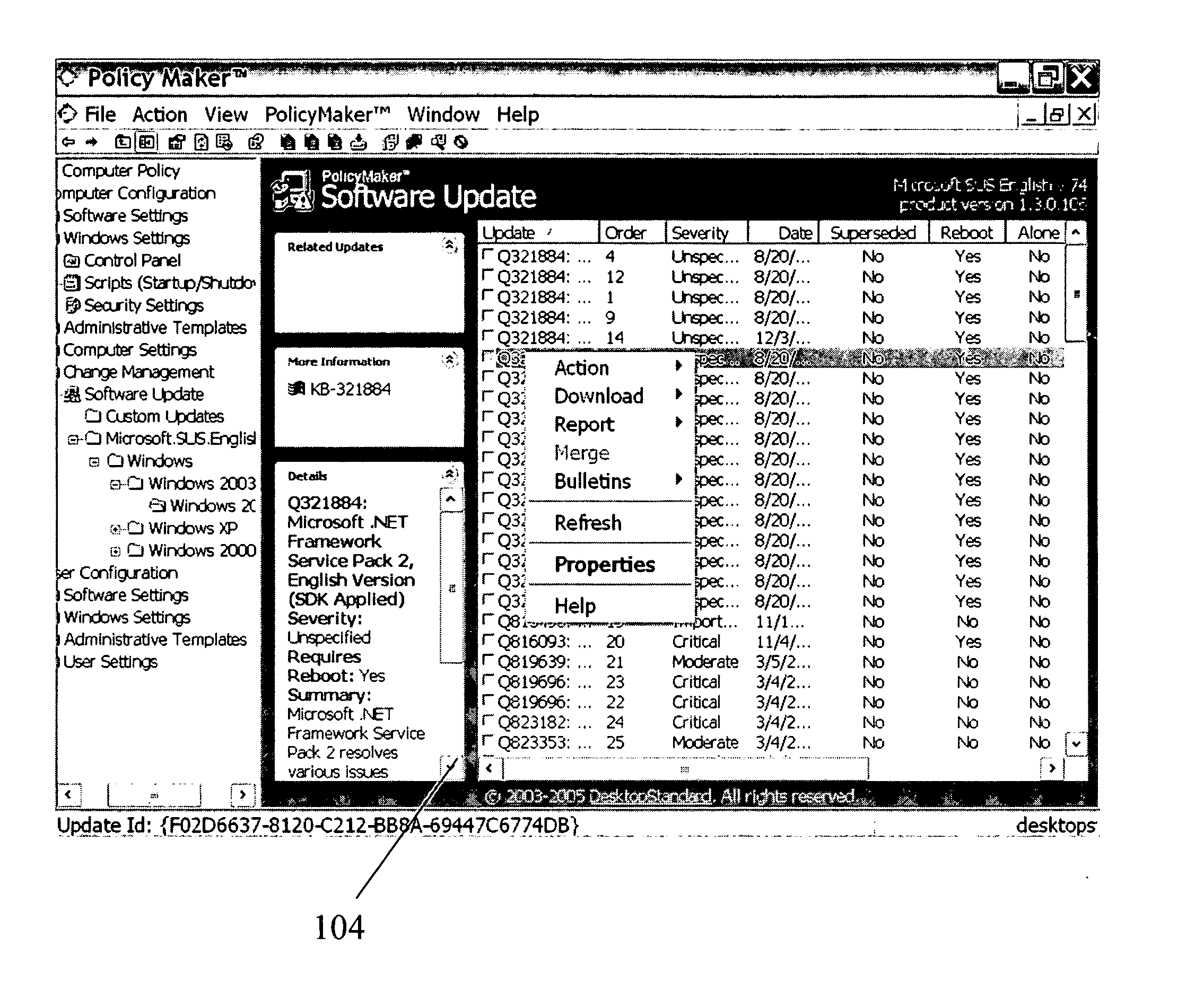
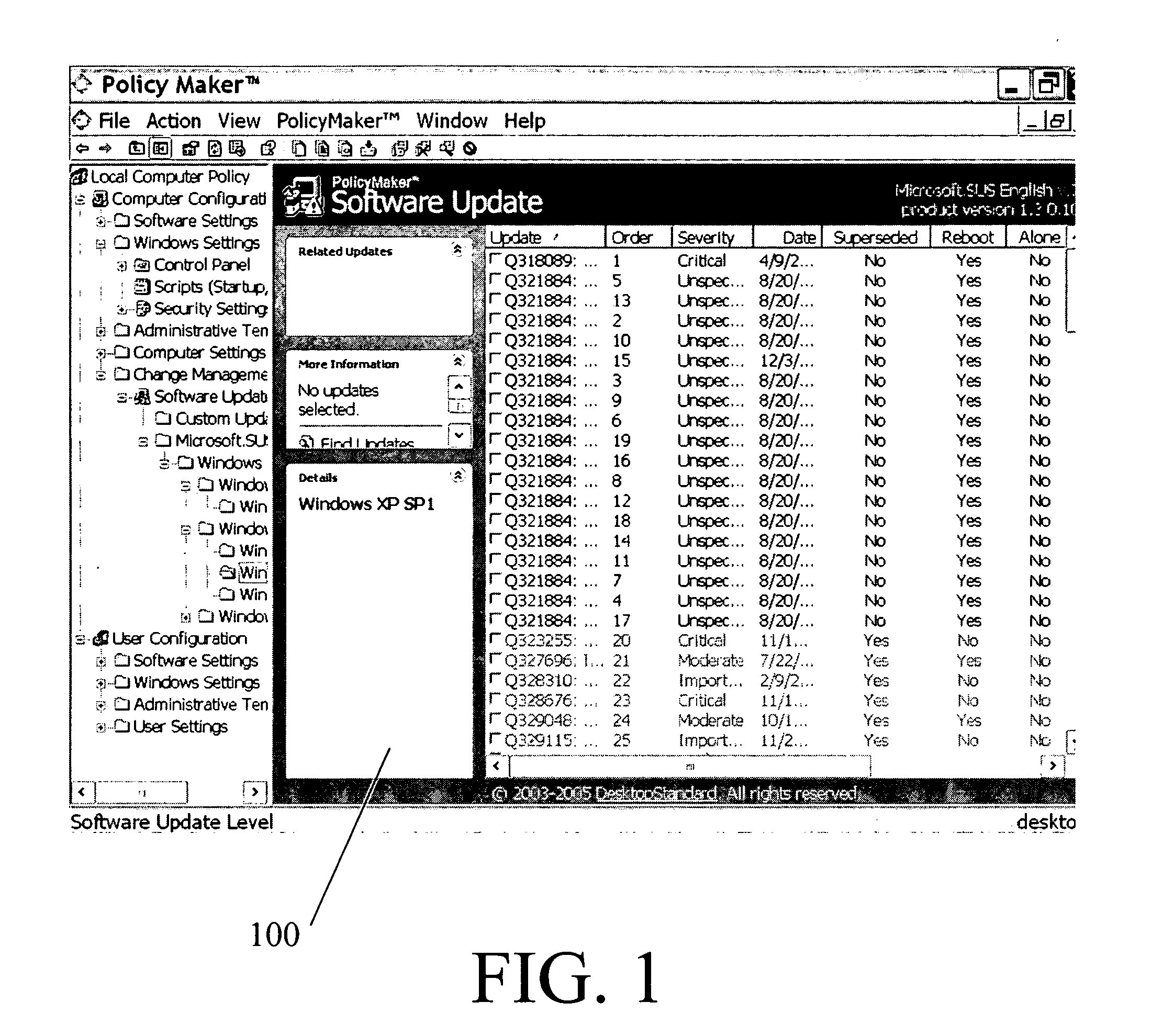
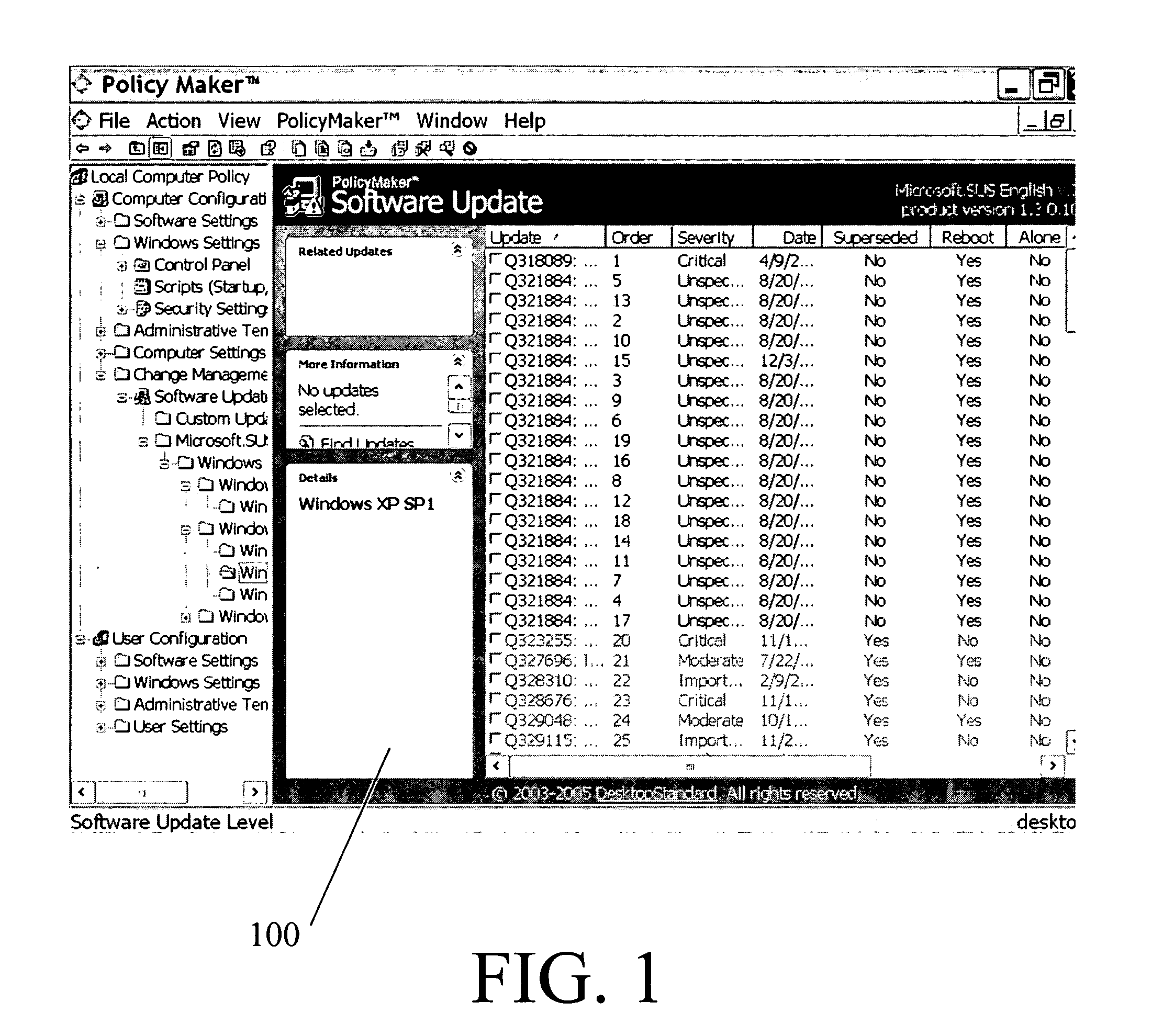
System for policy-based management of software updates
ActiveUS20050262076A1Program loading/initiatingSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware updateSystem maintenance
A computer system configured for policy-based management of software updates is disclosed. The system maintains group-policy objects, with which groups of computers are associated. The system obtains identities of software updates from a source of software updates. The system also obtains filter criteria for each update, for determining whether the update should be applied to a particular computer or not. The system assigns newly available updates to respective selected group-policy objects and adds the obtained filter criteria to each such group-policy object. The system performs necessary installations of updates by, for each group-policy object, determining whether, for each combination of a computer belonging to a group associated with that policy object and an update assigned to that policy object, the computer satisfies the filter criteria for the update, and if so, applying the update to that computer, but if not, refraining from applying the update.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
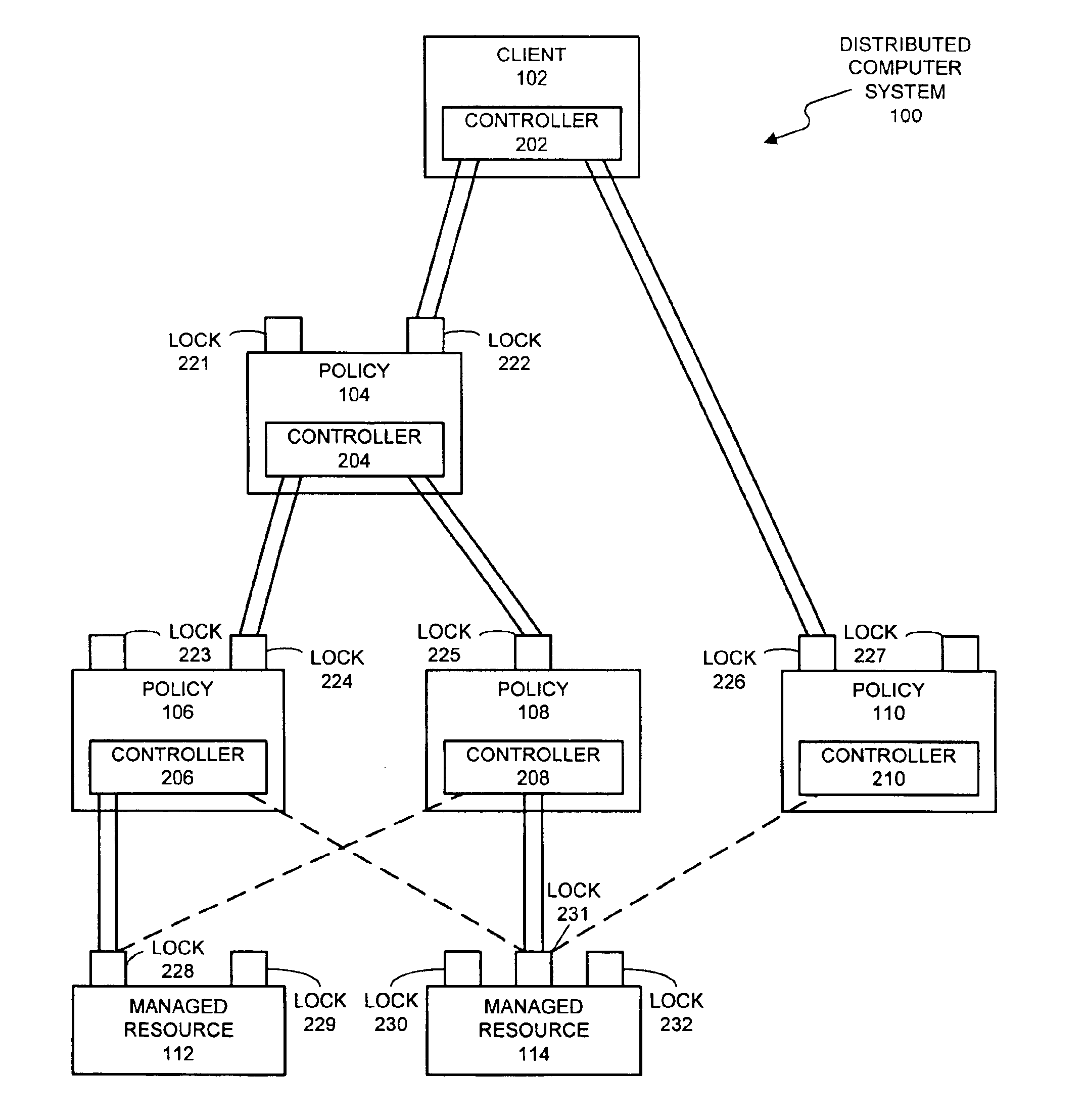
Method and apparatus for concurrency control in a policy-based management system
InactiveUS6865549B1Facilitates concurrency controlData processing applicationsProgram synchronisationConcurrency controlPolicy-based management
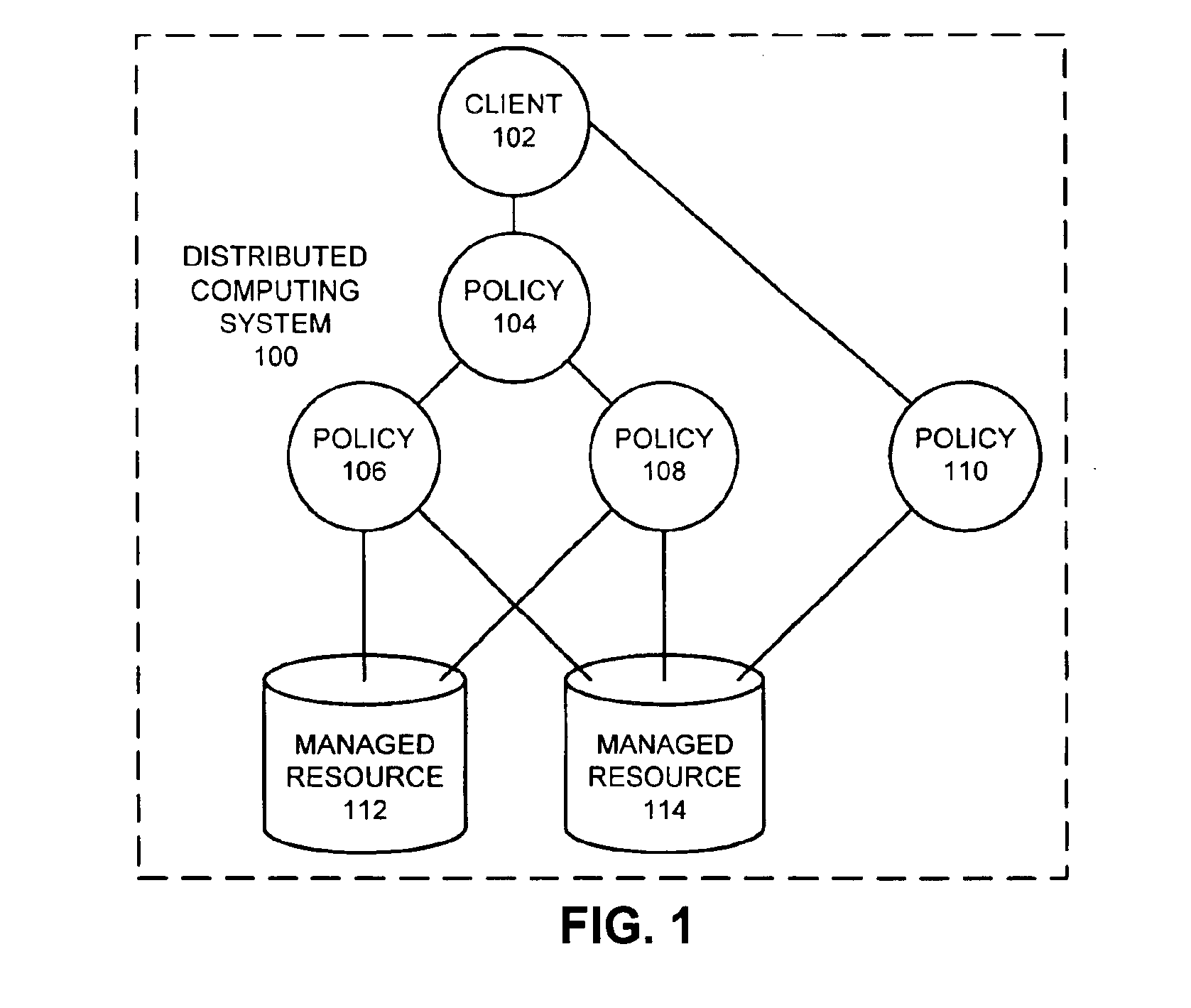
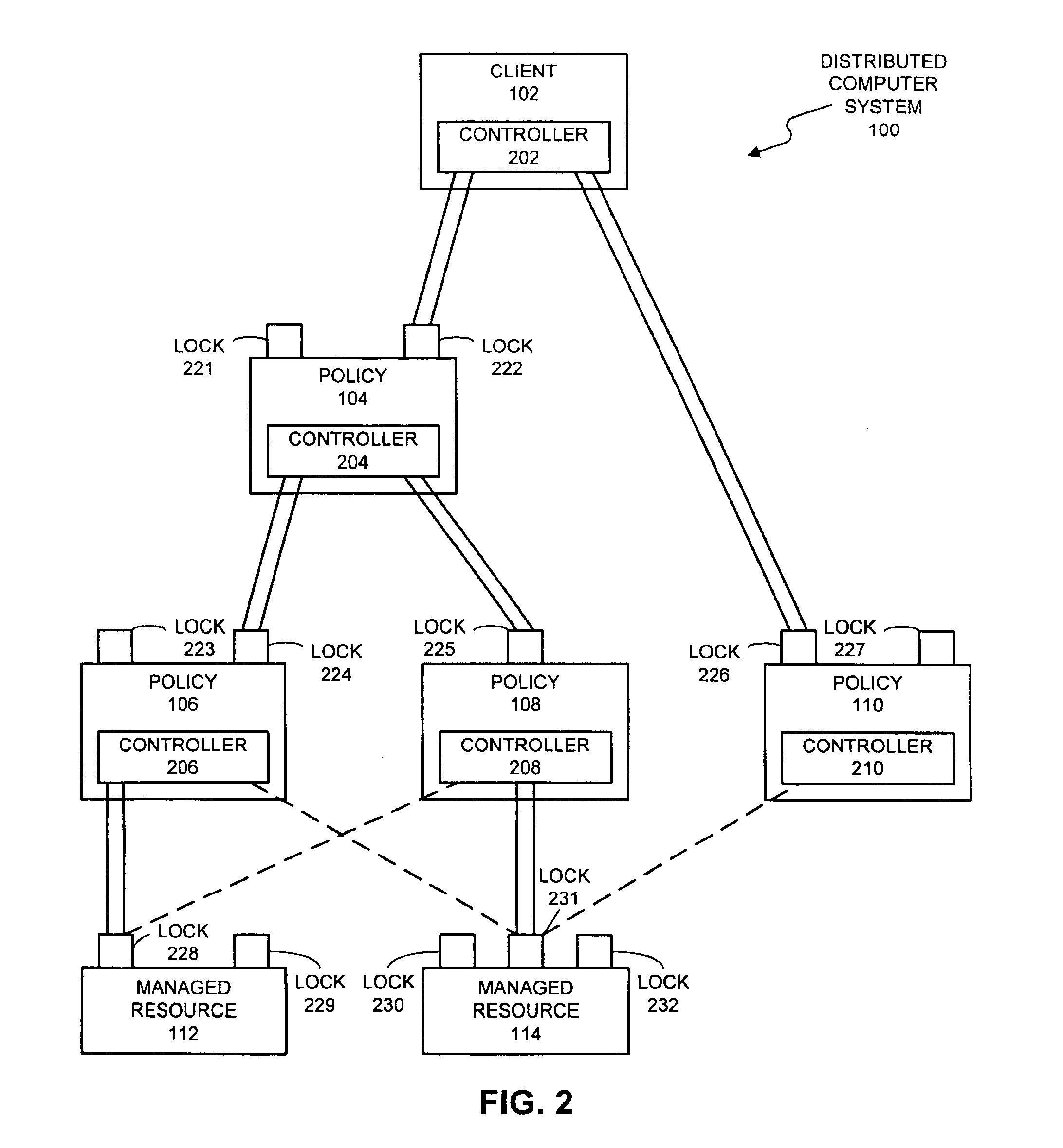
A system that facilitates concurrency control for a policy-based management system that controls resources in a distributed computing system. The system operates by receiving a request to perform an operation on a lockable resource from a controller in the distributed computing system. This controller sends the request in order to enforce a first policy for controlling resources in the distributed computing system. In response the request, the system determines whether the controller holds a lock on the lockable resource. If so, the system allows the controller to execute the operation on the lockable resource. If not, the system allows the controller an opportunity to acquire the lock. If the controller is able to acquire the lock, the system allows the controller to execute the operation on the lockable resource.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
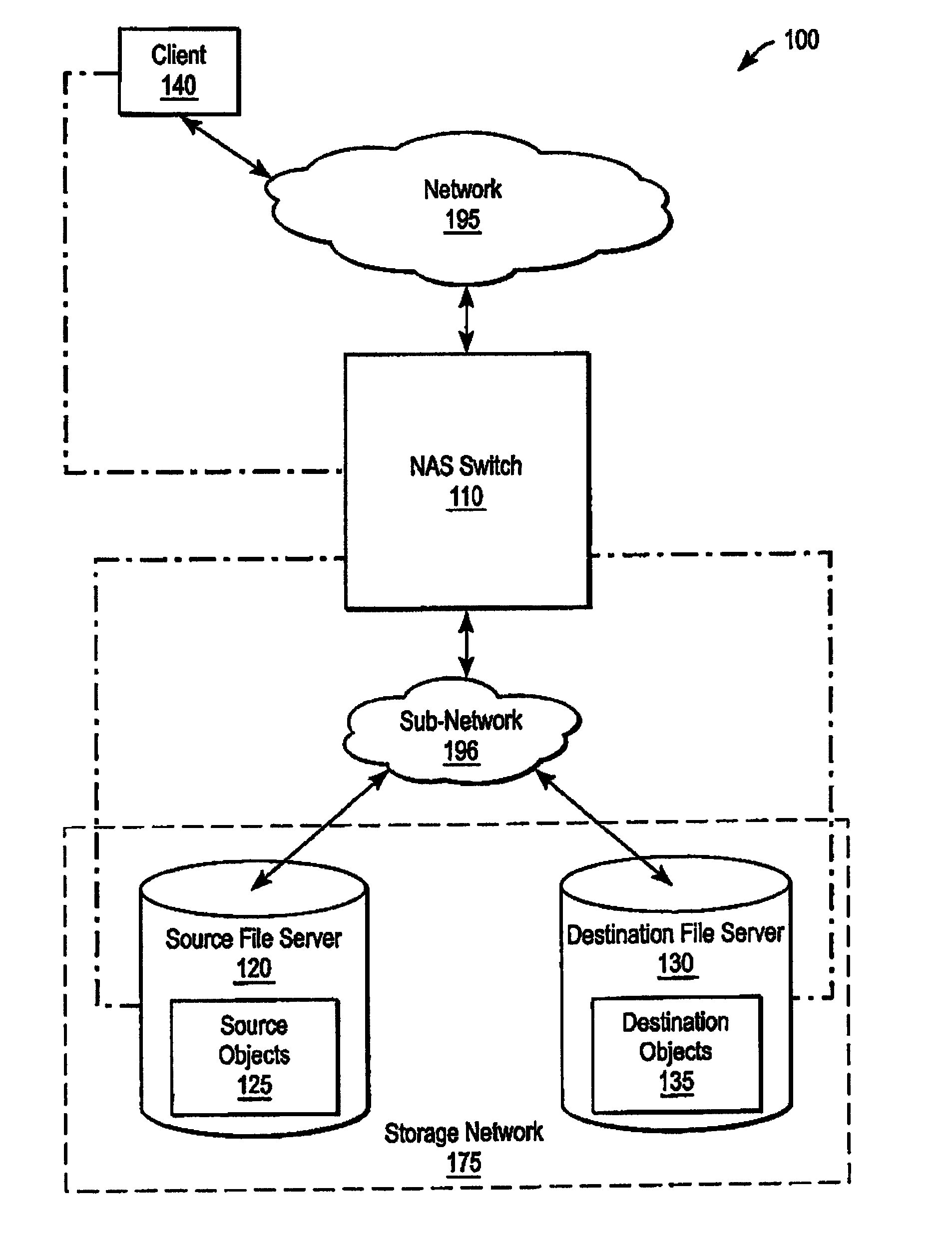
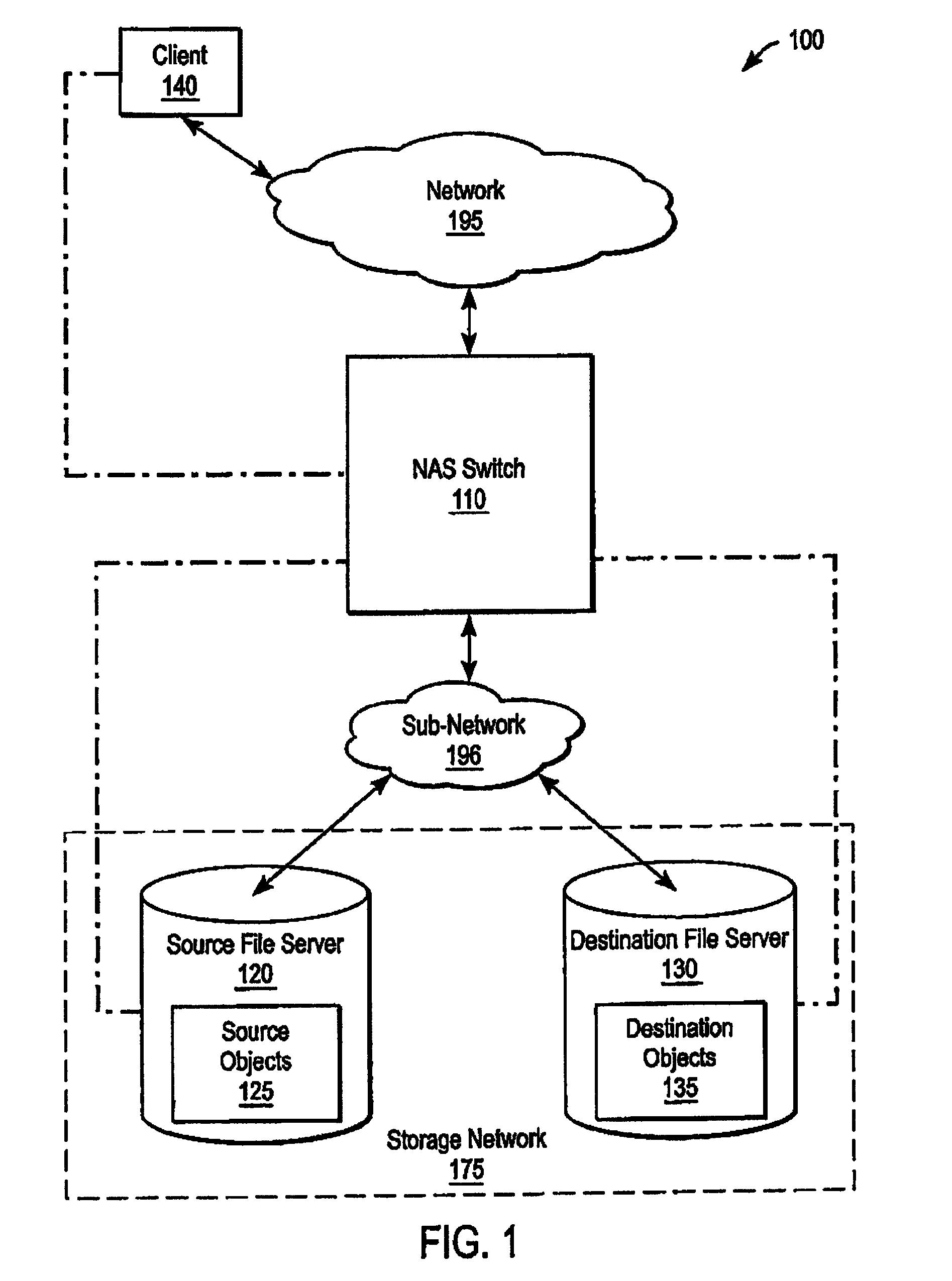
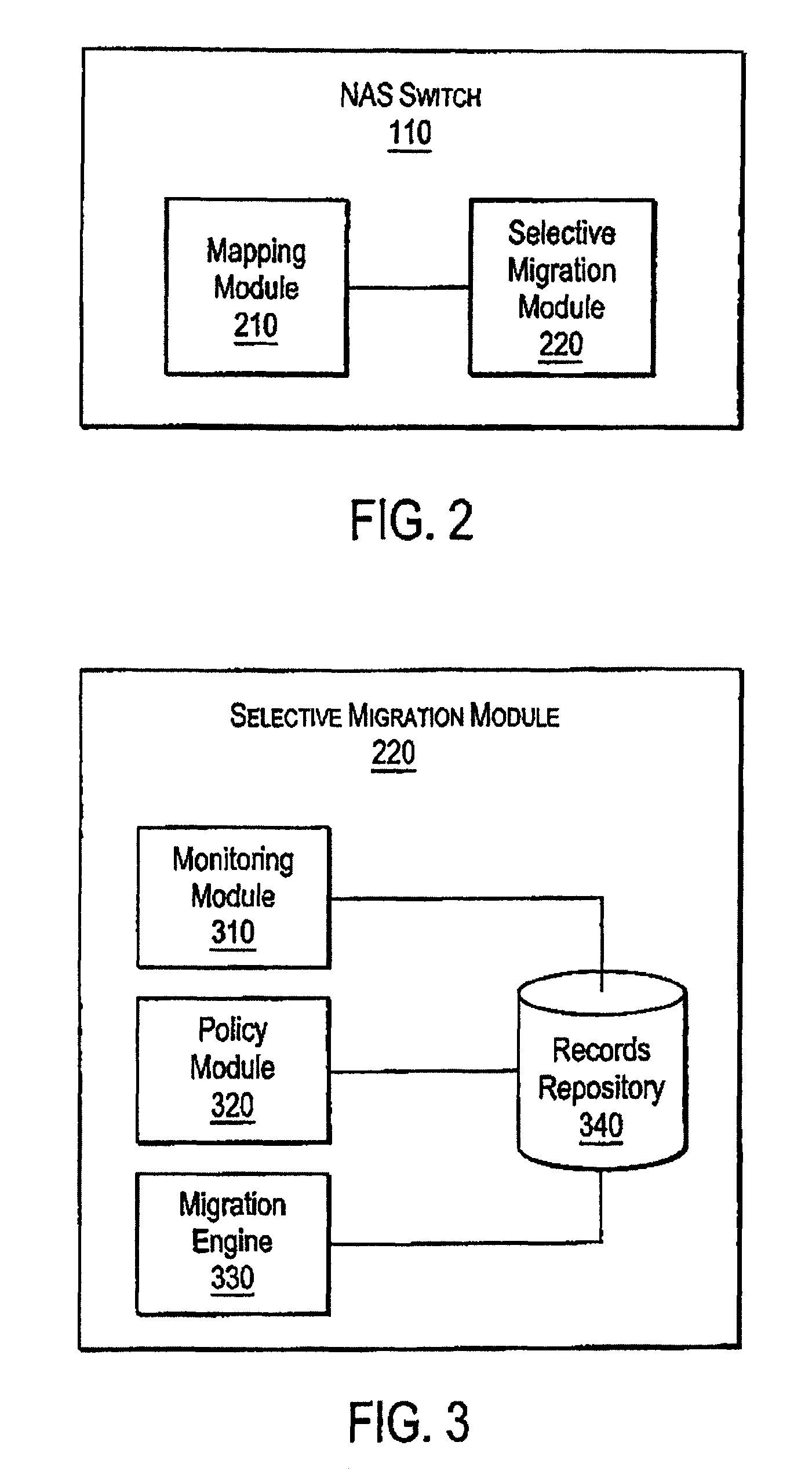
Accumulating access frequency and file attributes for supporting policy based storage management
ActiveUS20070136308A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsAccess frequencyStorage management
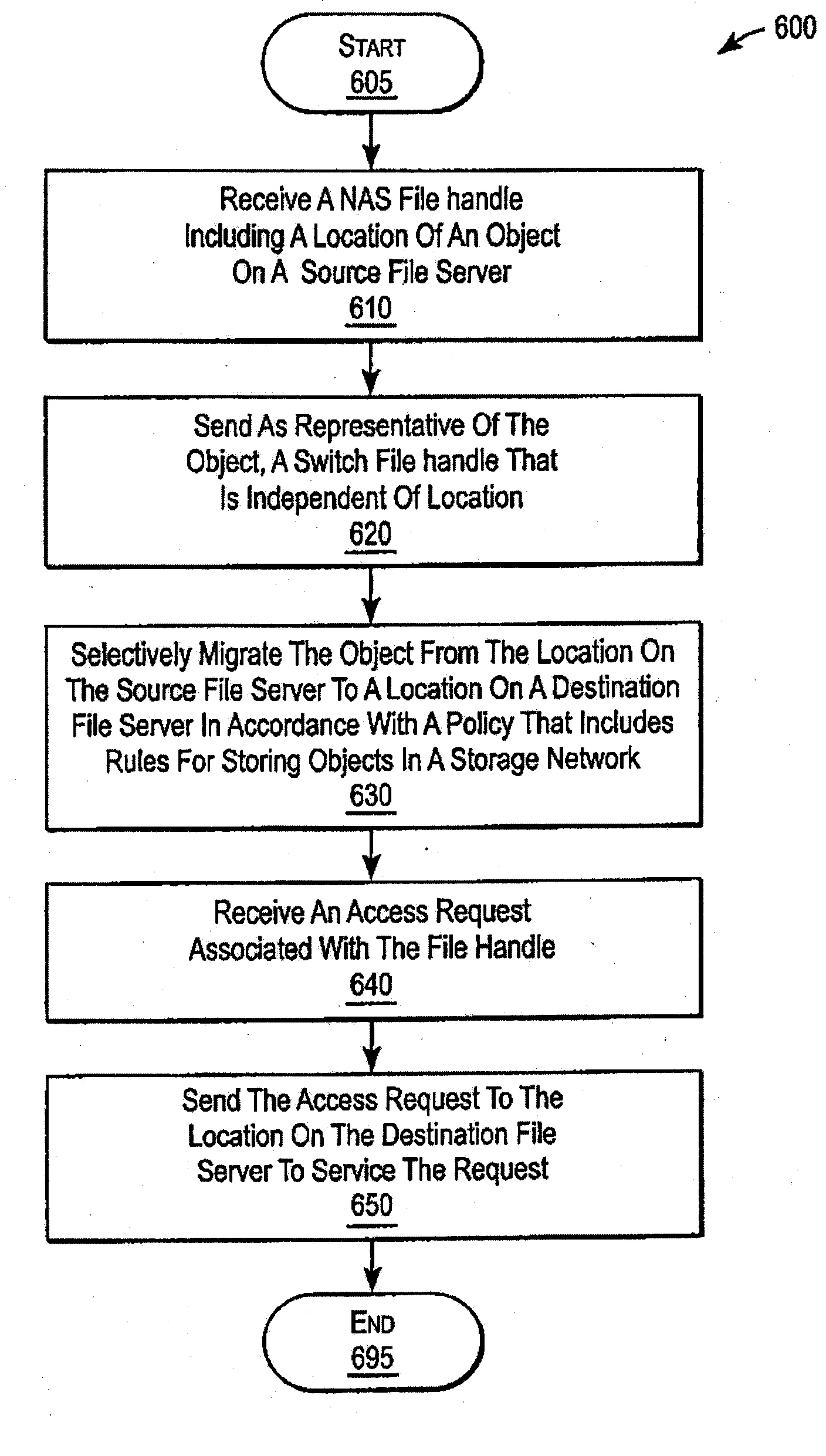
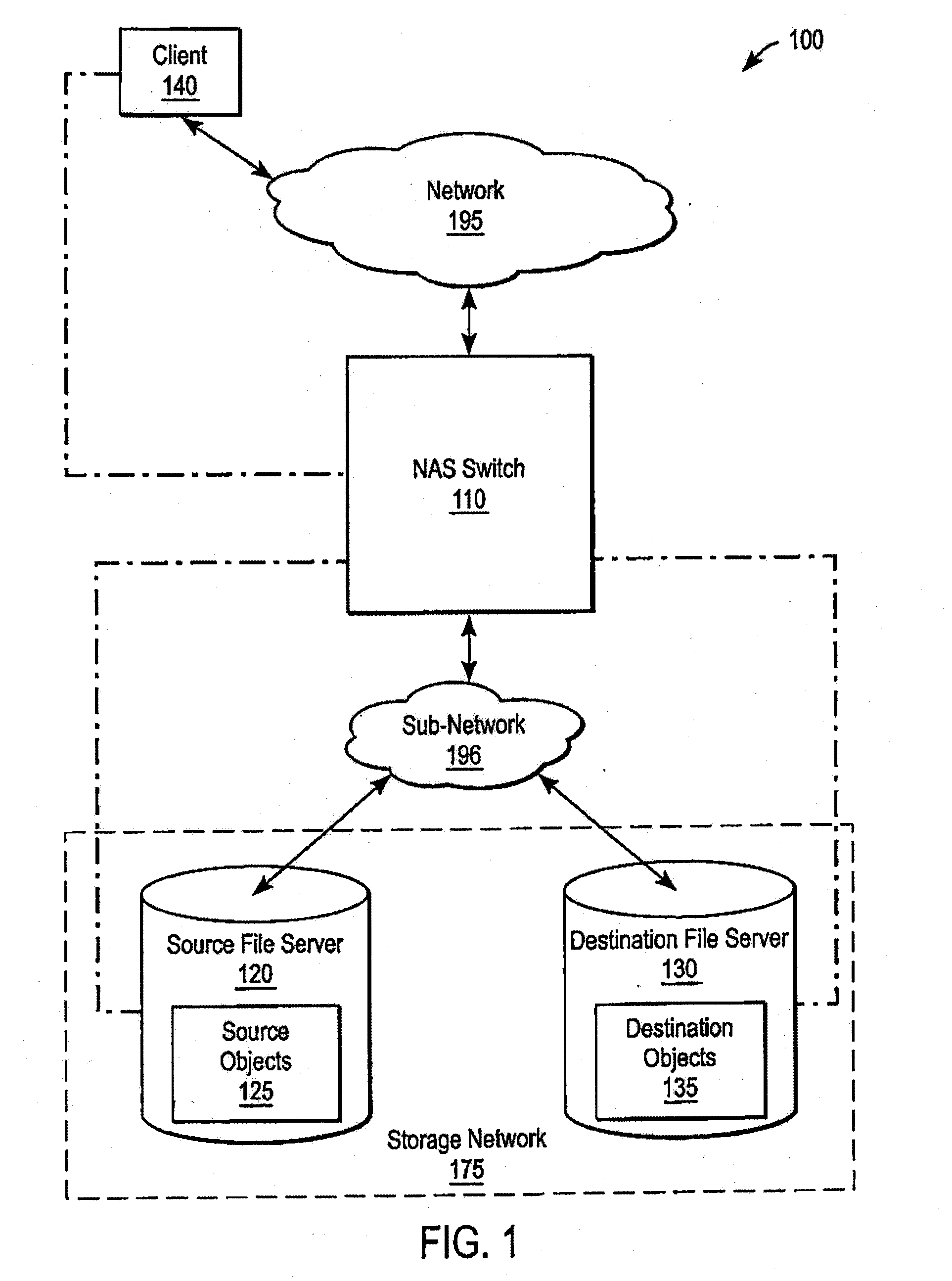
A system and method for performing policy-based storage management using data related to access frequency and file attribute accumulation. A switch device provides transparency for transactions between a client and a storage network. The transparency allows objects (e.g., files or directories) to be moved (e.g., migrated) on the storage network without affecting a reference to the object used by the client (e.g., a file handle). A monitoring module generates accumulation data associated with the transactions for use in policy-based management. The accumulation data can describe uses of the file such as how often certain files are accessed, modifications to files such as creations of new directories or files, and other uses.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
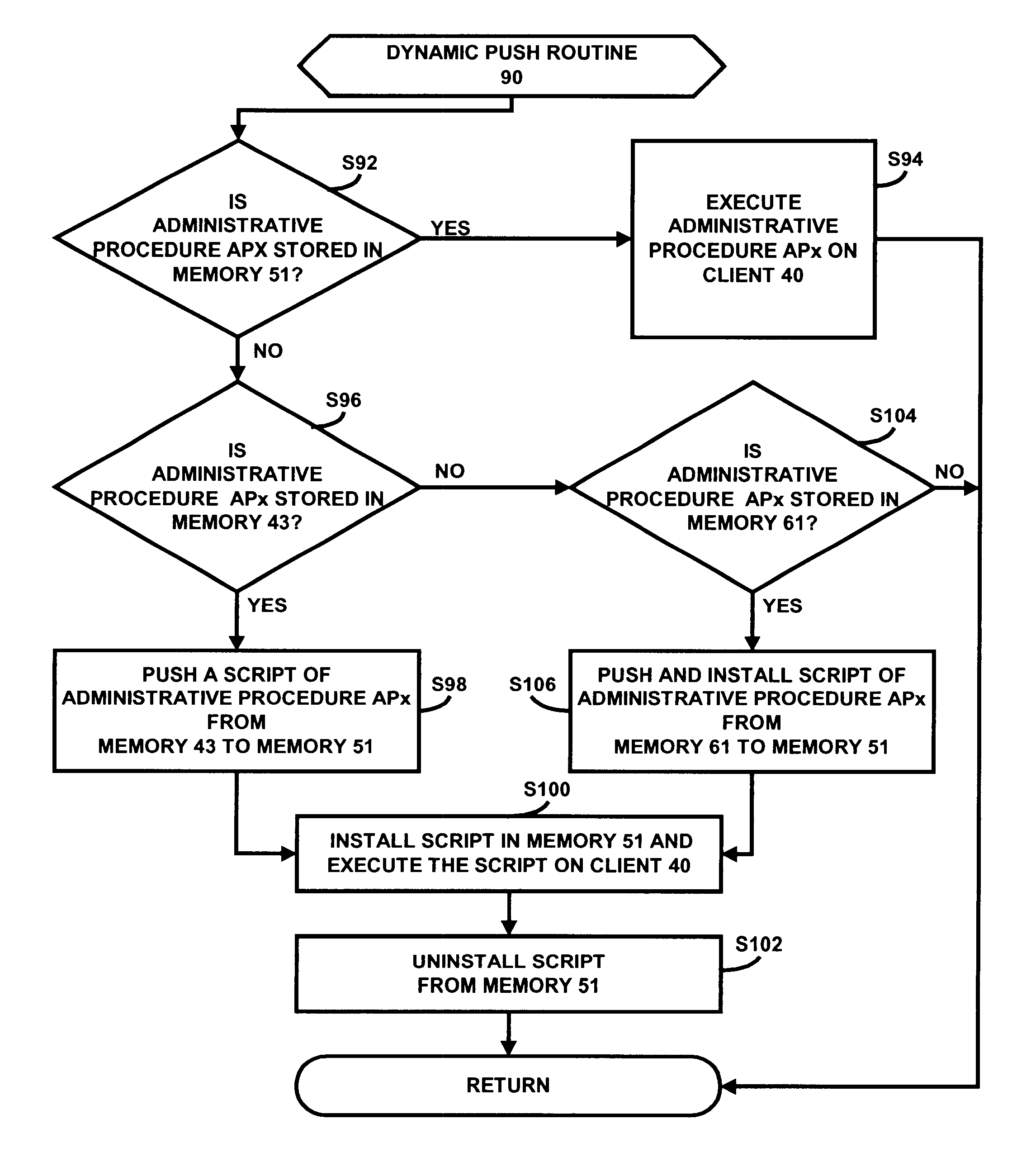
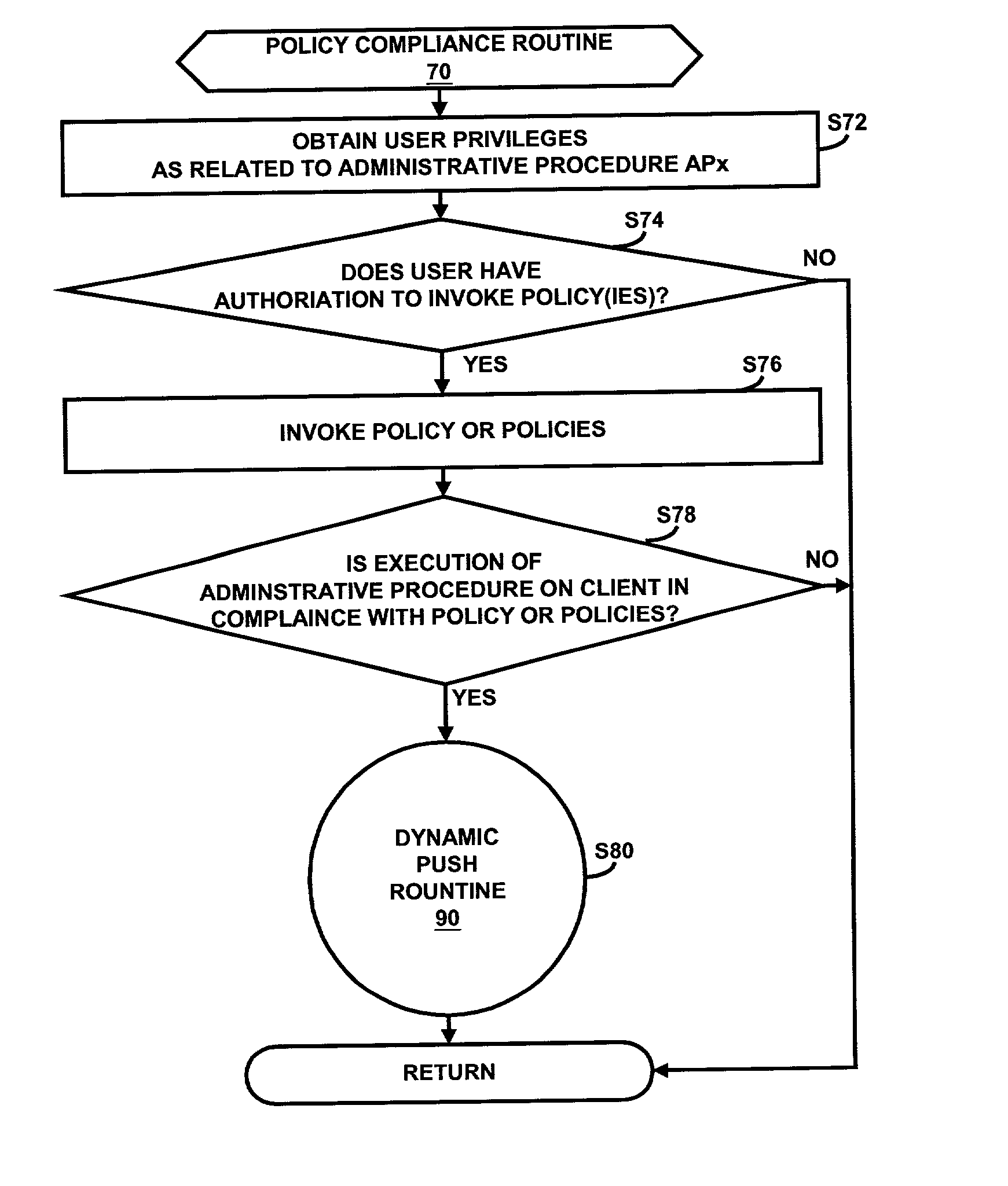
Dynamic, policy based management of administrative procedures within a distributed computing environment
InactiveUS6769118B2Specific access rightsUser identity/authority verificationDistributed Computing EnvironmentAdministrative management
An administrative management system comprising an administrative server and a client is disclosed. In response to a selection of an administrative procedure to be executed on the client, the administrative server determines if an execution of the administrative procedure on the client is in compliance with one or more corresponding policies. If the execution is in compliance with the corresponding policy or policies, the administrative server determines the storage location of the administrative procedure. If the selected administrative procedure is stored on the client, the administrative server executes the administrative procedure on the client. If the selected administrative procedure is stored on the administrative server, the administrative server pushes a corresponding script of the administrative procedure from the administrative server to the client and then installs and executes the script on the client. If the selected administrative procedure is stored at a remote location, the administrative server pushes a corresponding script of the administrative procedure from the remote location to the client and then installs and executes the script on the client.
Owner:IBM CORP
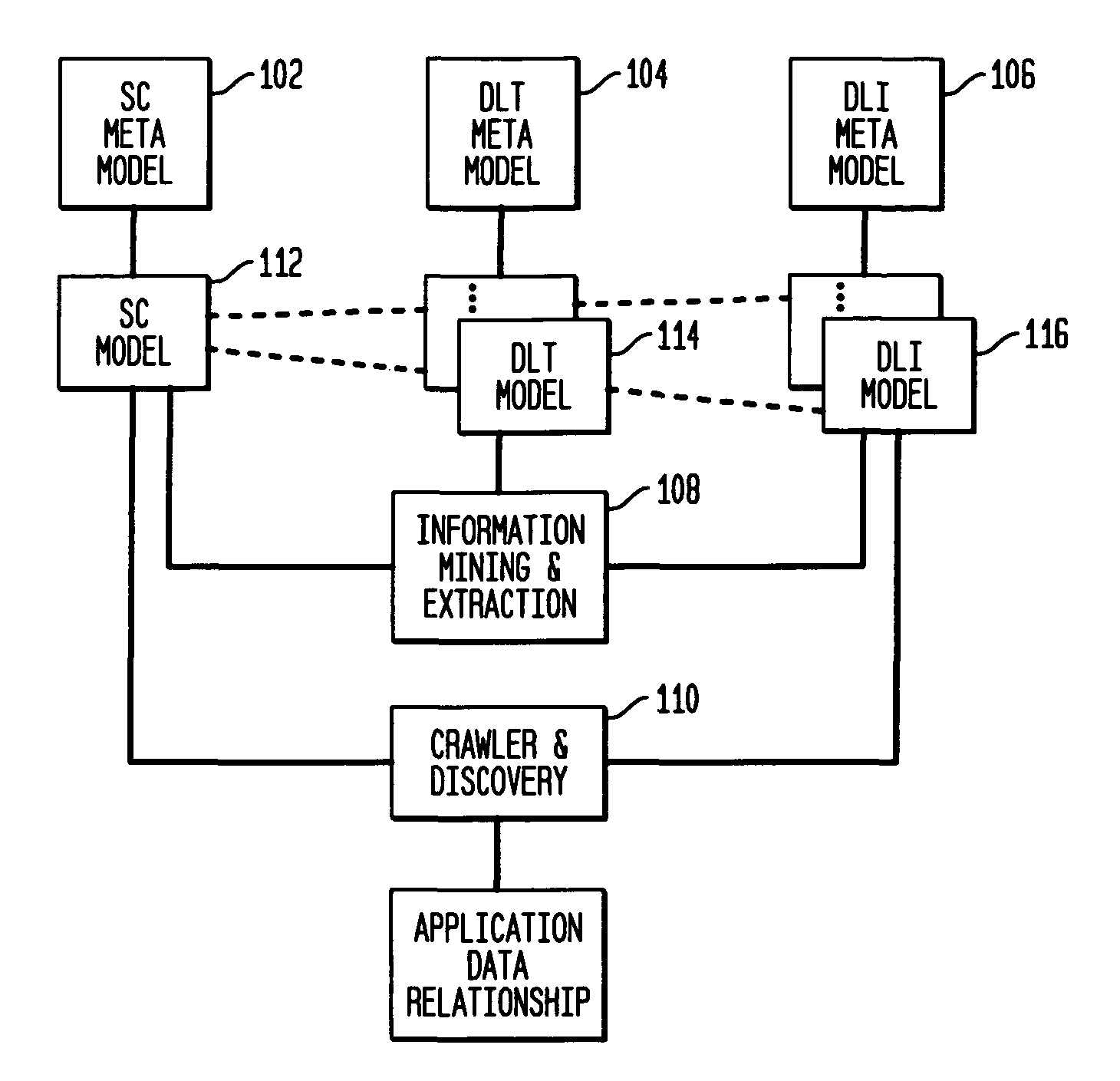
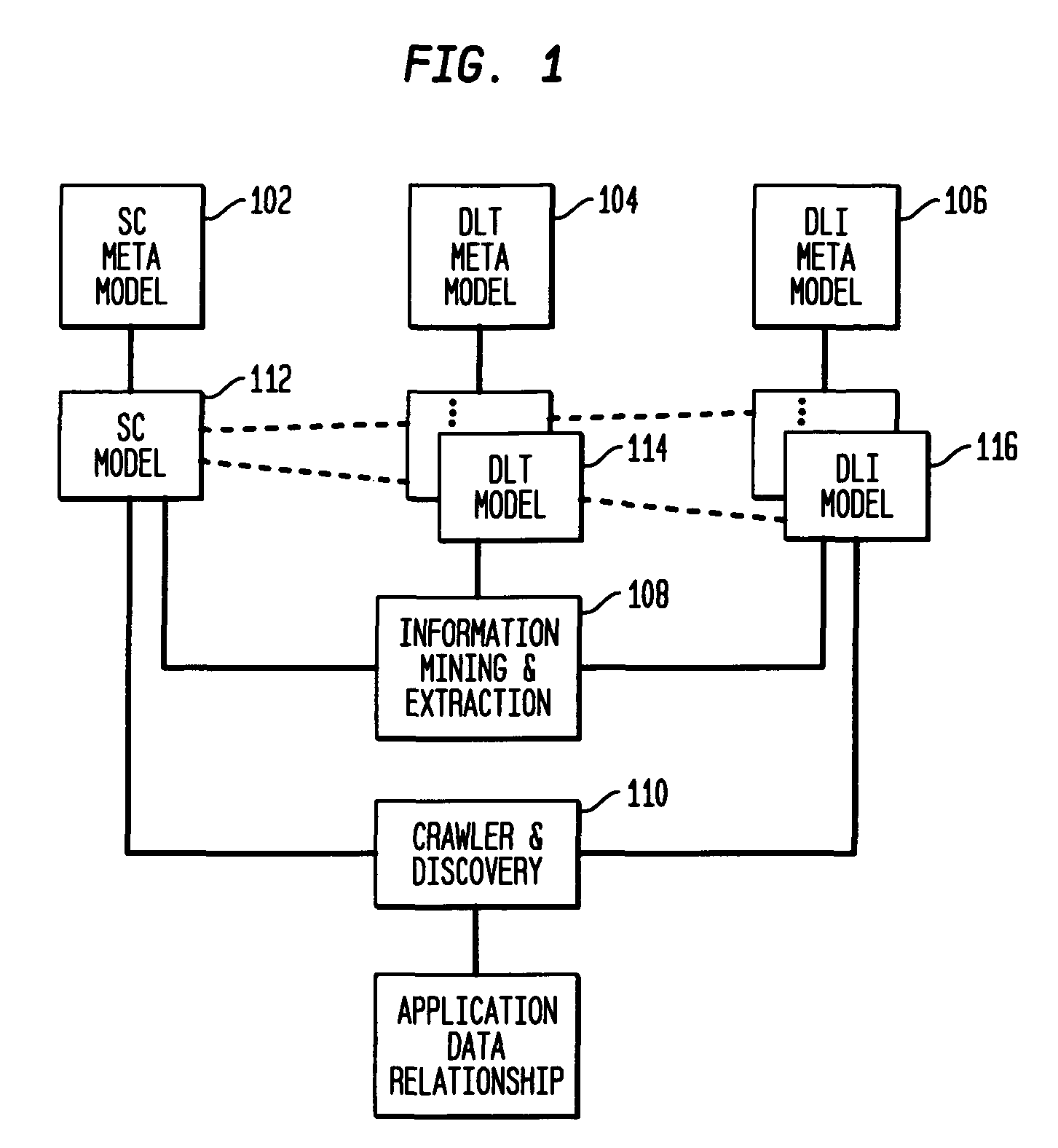
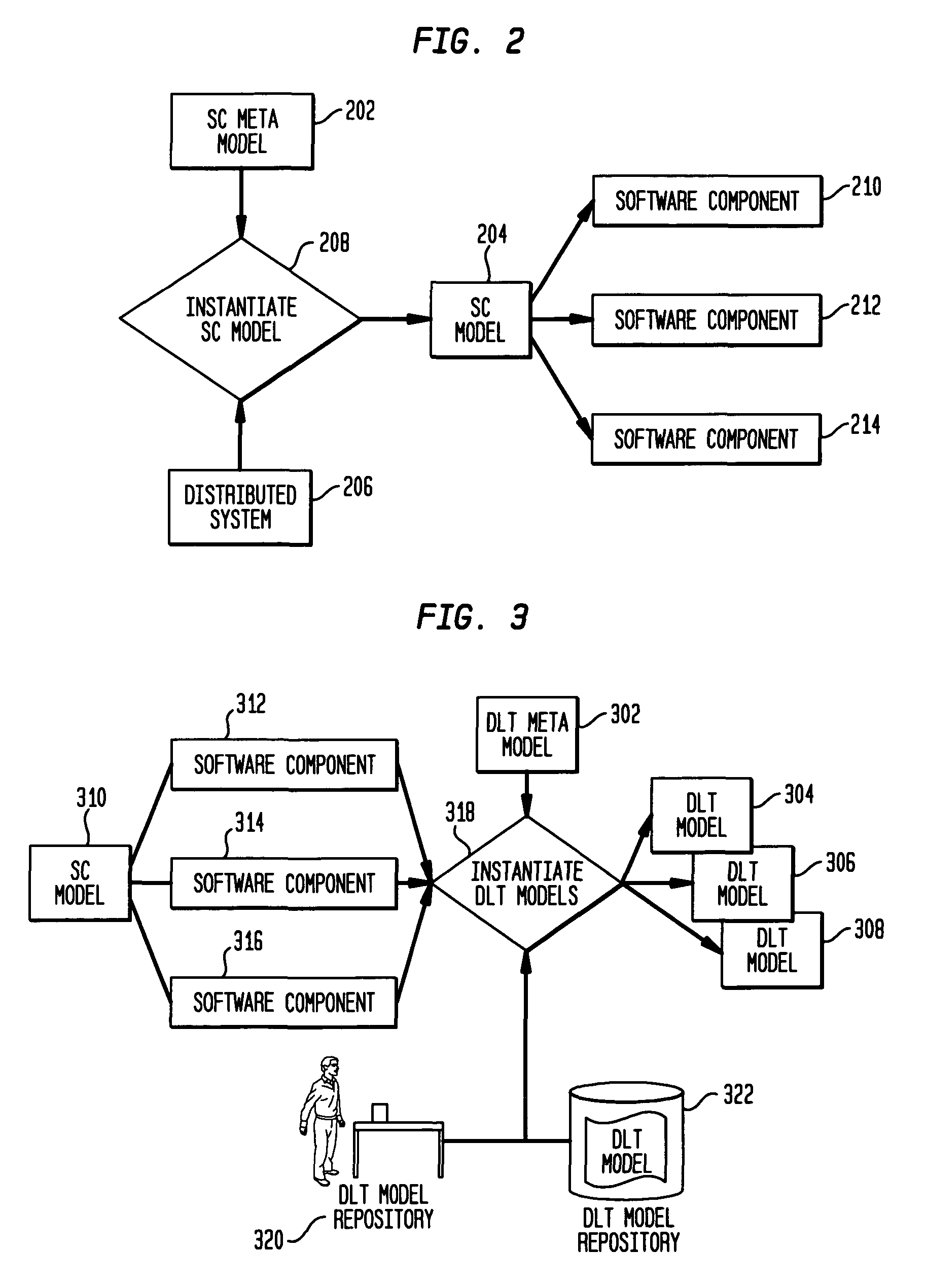
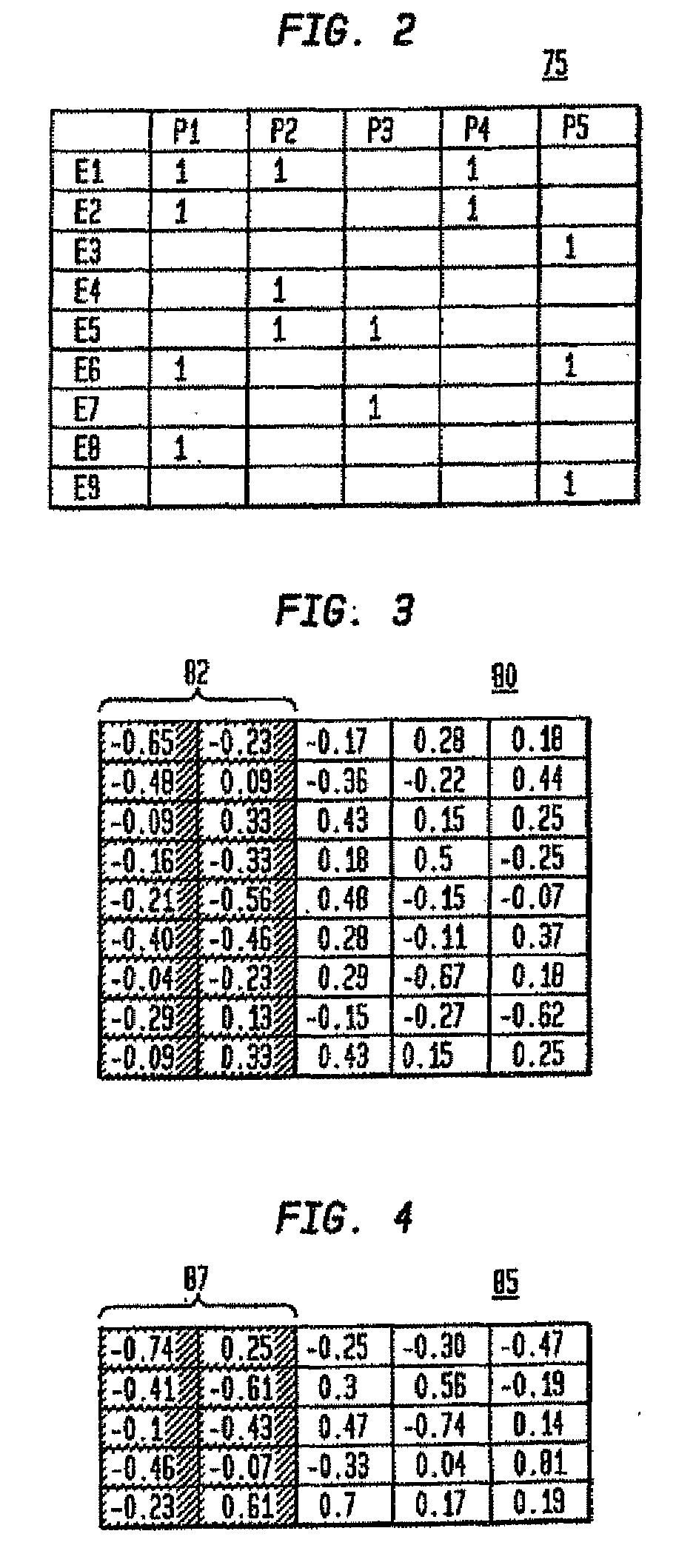
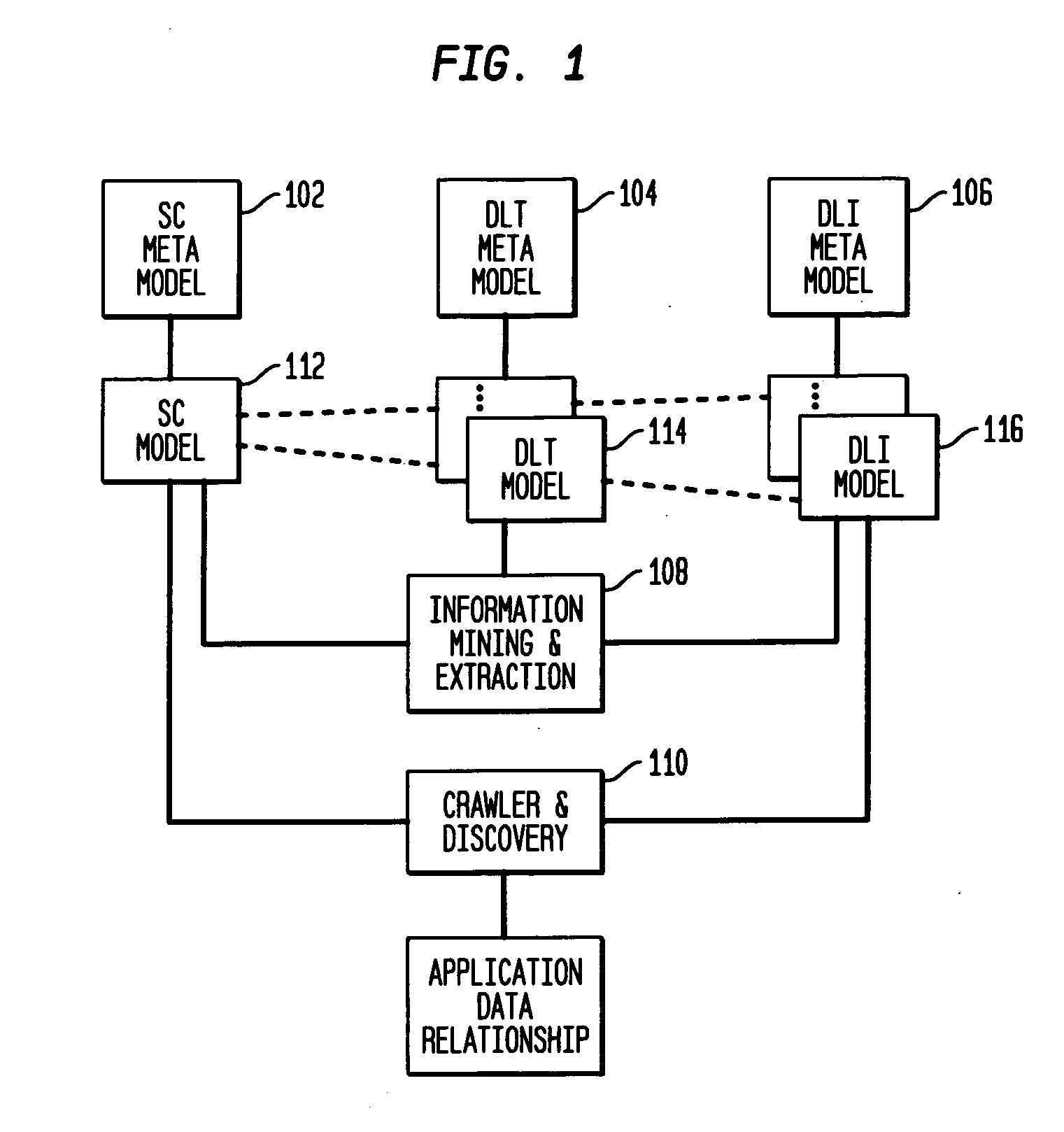
Data locations template based application-data association and its use for policy based management
Method and system are disclosed for automatically discovering associations between applications and data in multi-tiered distributed systems. The method in one aspect uses a machine-readable specification of a model or template that describes use and transformation of data by software components. The method additionally utilizes a model of system configuration and appropriate runtime support to mine information available from systems management software present in enterprise systems. The application-data association discovery process performs a traversal of the distributed system configuration graph with actions taken during this traversal driven by the contents of the templates for the software components present in the system. The results of the application-data association discovery process are stored in a database and may be used to specify application-specific information lifecycle management (ILM) policy or as input to impact analysis tools in access control and antivirus systems.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
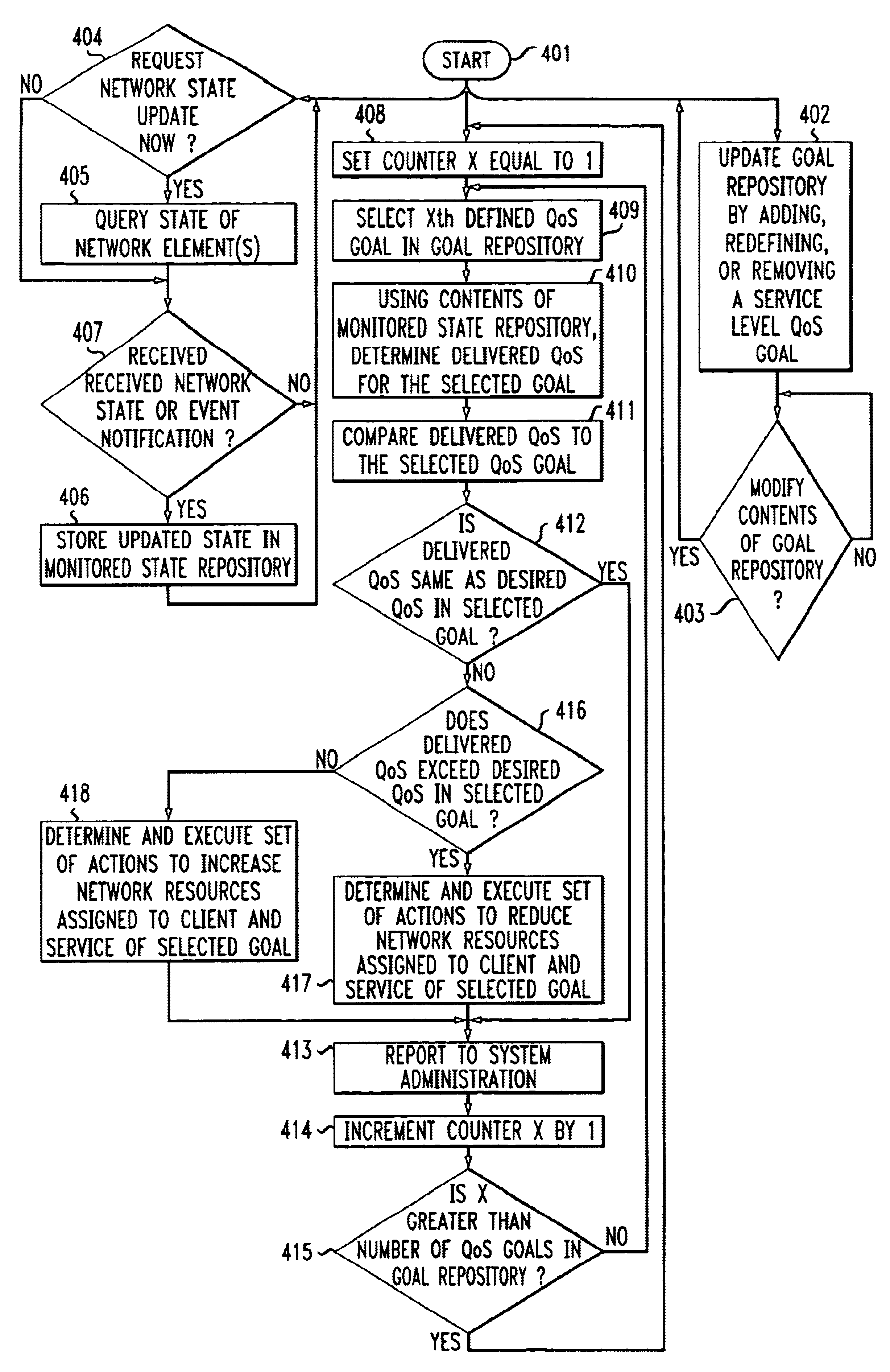
Method and apparatus for use in specifying and insuring service-level quality of service in computer networks
InactiveUS6871233B1Easily specify parameterNetwork resource is reducedMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksQuality of serviceClient-side
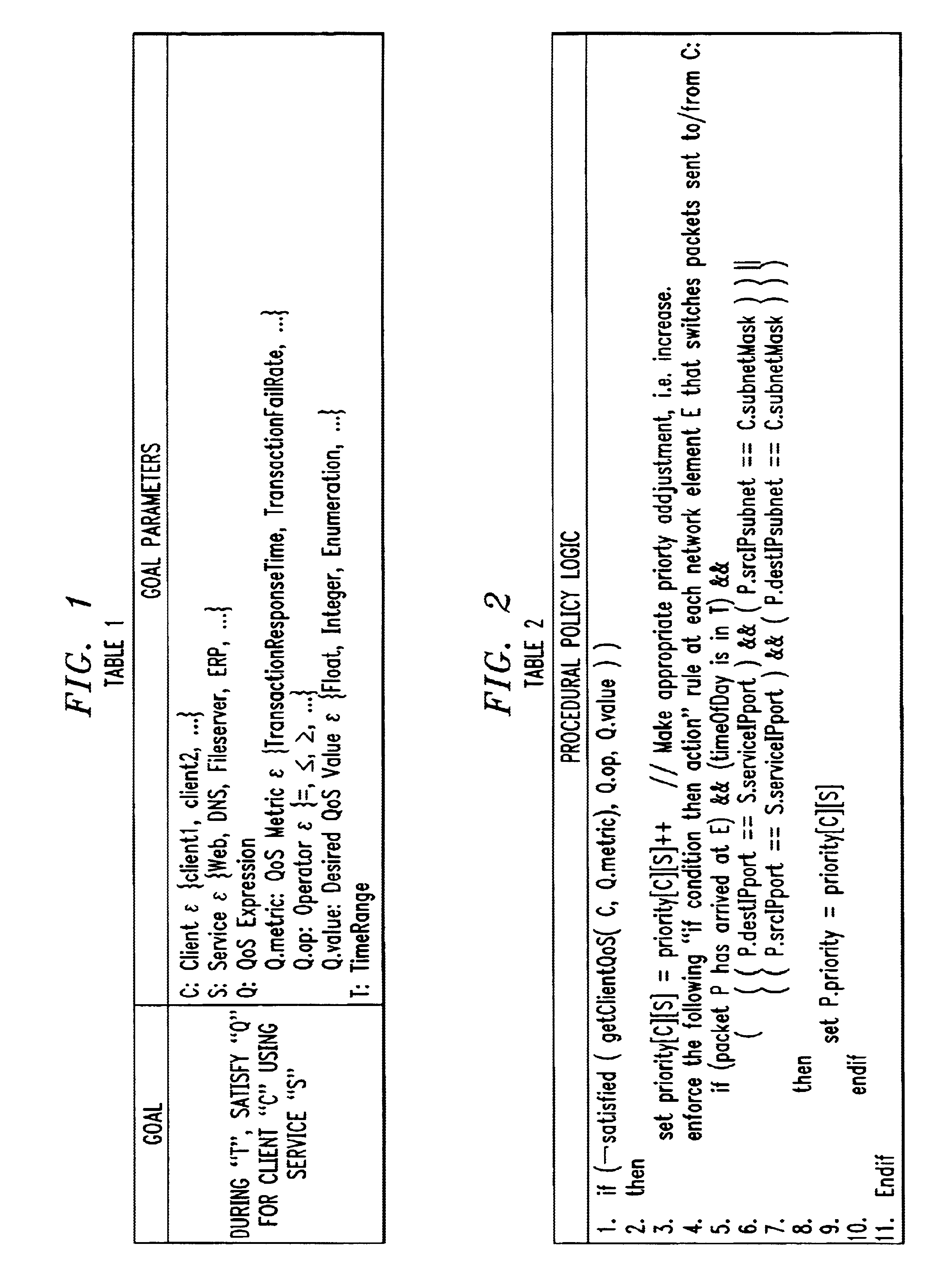
The “what” and “how” of policy-based management is integrated in a single framework that enables a system administrator to specify service-level quality of service (QoS) goals for automatic enforcement. Automatic enforcement of the specified “high-level” QoS goals is realized through the execution of “low-level” rule-based or procedural logic, without the client having to specify the low level logic. Specifically, one embodiment of the invention employs a management server including a graphical interface that allows a user, e.g. a system administrator, to easily specify parameters for service-level QoS goals. A QoS goal is defined by the administrator selecting a client, a service and a QoS expression that specifies the desired service-level QoS. The state of the network is monitored and one or more defined QoS goals are selected for evaluation in a continuous process. The QoS delivered for the selected goal is determined and compared to the desired QoS for the selected QoS goal. Then, prescribed actions are taken or not depending whether the delivered QoS is equal to the selected QoS goal. If not, and the delivered QoS exceeds the selected QoS goal, a set of actions is determined and executed to reduce network resources assigned to the client and service of the selected goal. Similarly, if the delivered QoS is worse than the selected QoS goal, a set of actions is determined and executed to increase network resources assigned to the client and service of the selected goal.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
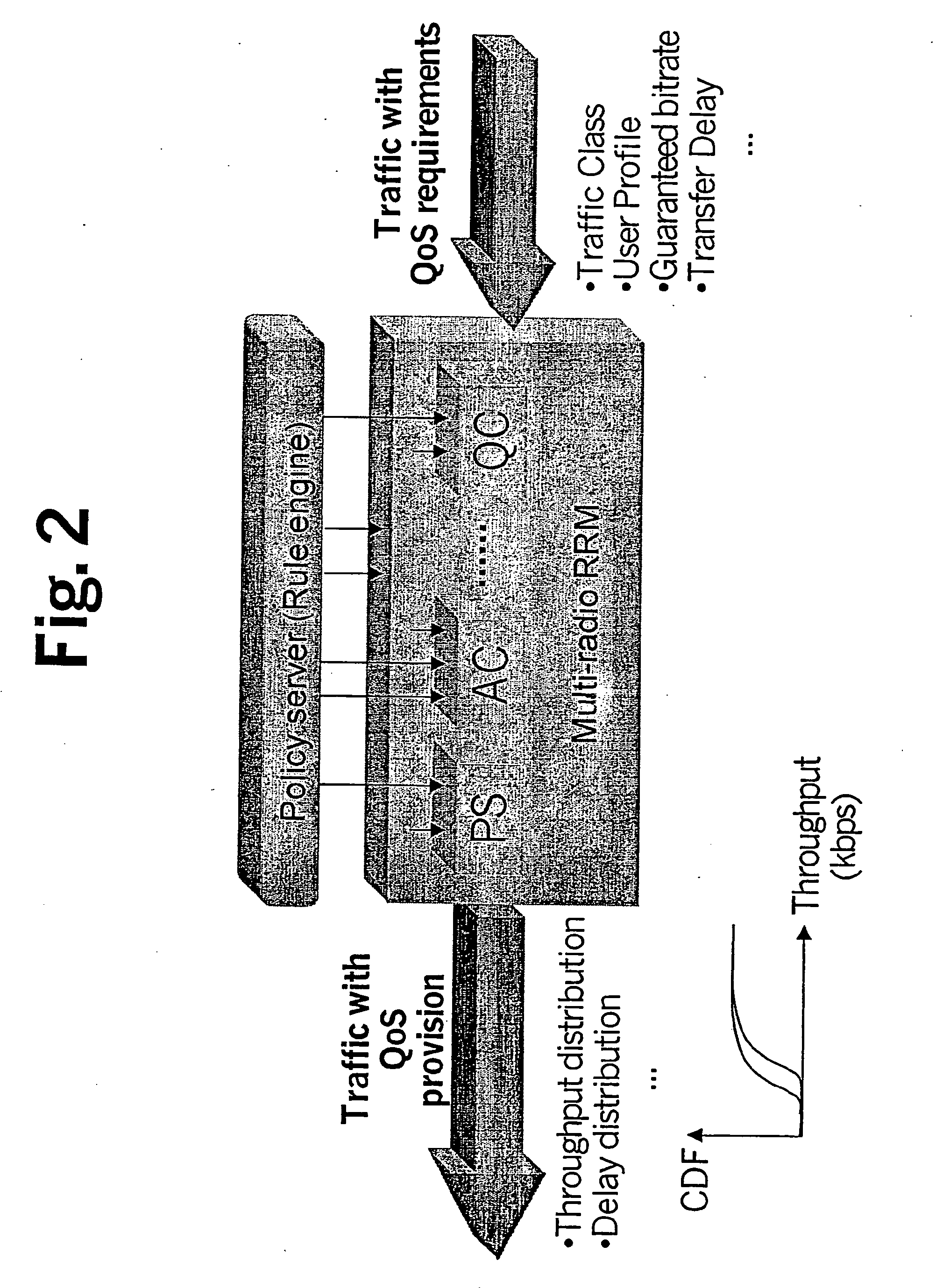
Policy-based qos management in multi-radio access networks
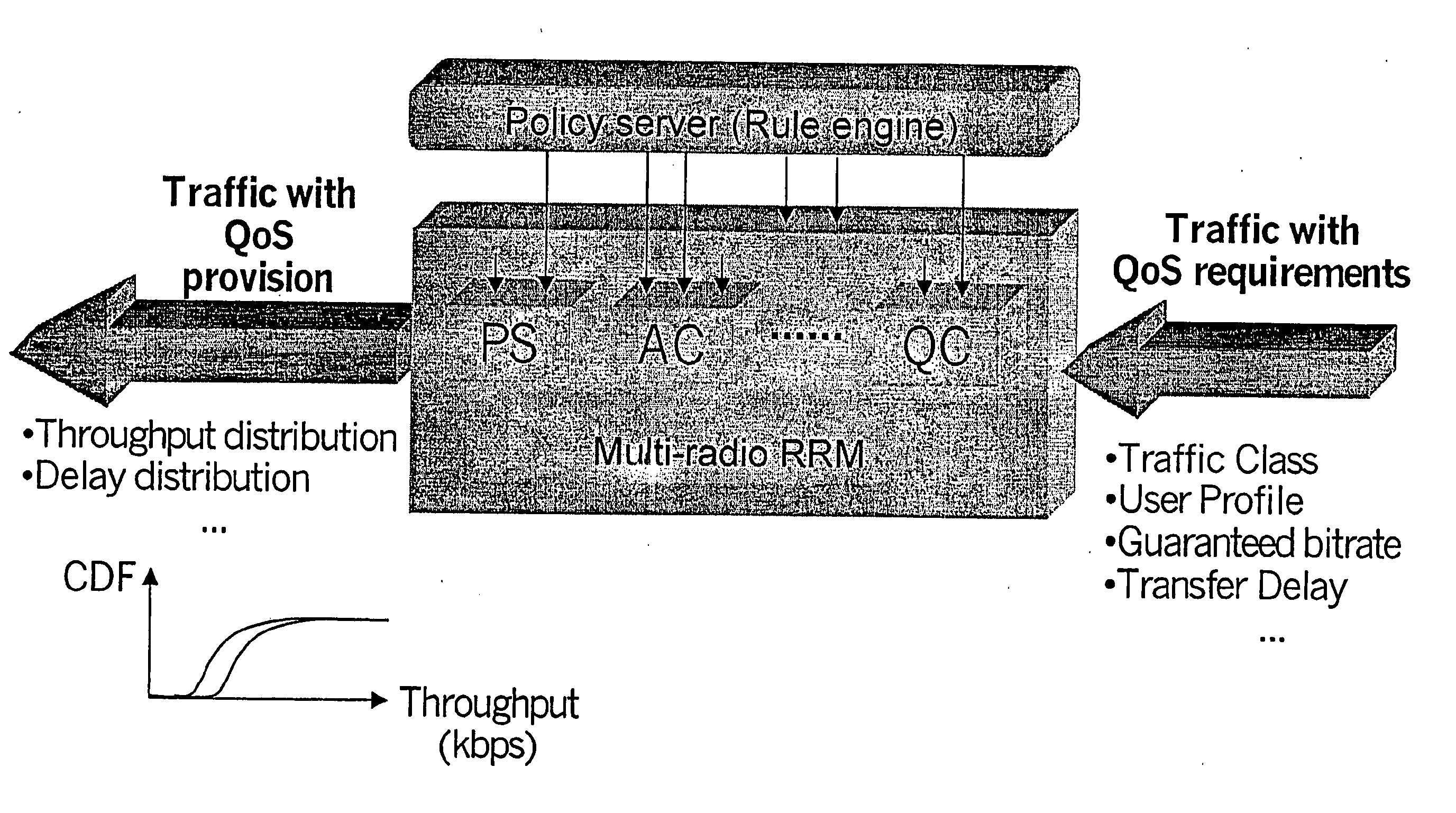
A system for providing a policy based Quality-of-Service management in multi-radio access mobile networks, comprising: control center means for administrating said radio access networks, thereby controlling the behavior thereof, wherein information model is implemented in said control center means which describes different Quality-of-Service mechanisms including attributes which are involved in each function under policy thus representing the manageable parameters of specific network implementations, and wherein said information model forms the basis of a set of policy rules defining actions to be executed in dependency of the occurrence of conditions; and a policy based management device adapted to receive said set of rules for the implementation thereof, said device having a plurality of policy based radio resource management means each adapted for managing said parameters of specific network implementations, and a translation function means adapted to translate said rules in a form executable by said plurality of policy based radio resource management means.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Policy-Based Management of Instant Message Windows
InactiveUS20070288580A1Simple technologyPrevent proliferationMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksState dependentPolicy-based management
Techniques are disclosed for managing instant messages, including the display of windows for incoming messages, as well as for managing status information for instant messaging users. In one aspect, an instant messaging user defines policy information to programmatically determine a response to an arriving instant message. As an example, the policy may control whether a new window will pop up for a newly-arriving message, and may specify other attributes of the window if desired. In another aspect, an instant messaging user defines attributes pertaining to how his instant messaging status will be presented to others.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System, method and program for distributed policy integration
InactiveUS20060136437A1Increase independenceImprove reusabilityDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsSystems approachesPolicy-based management
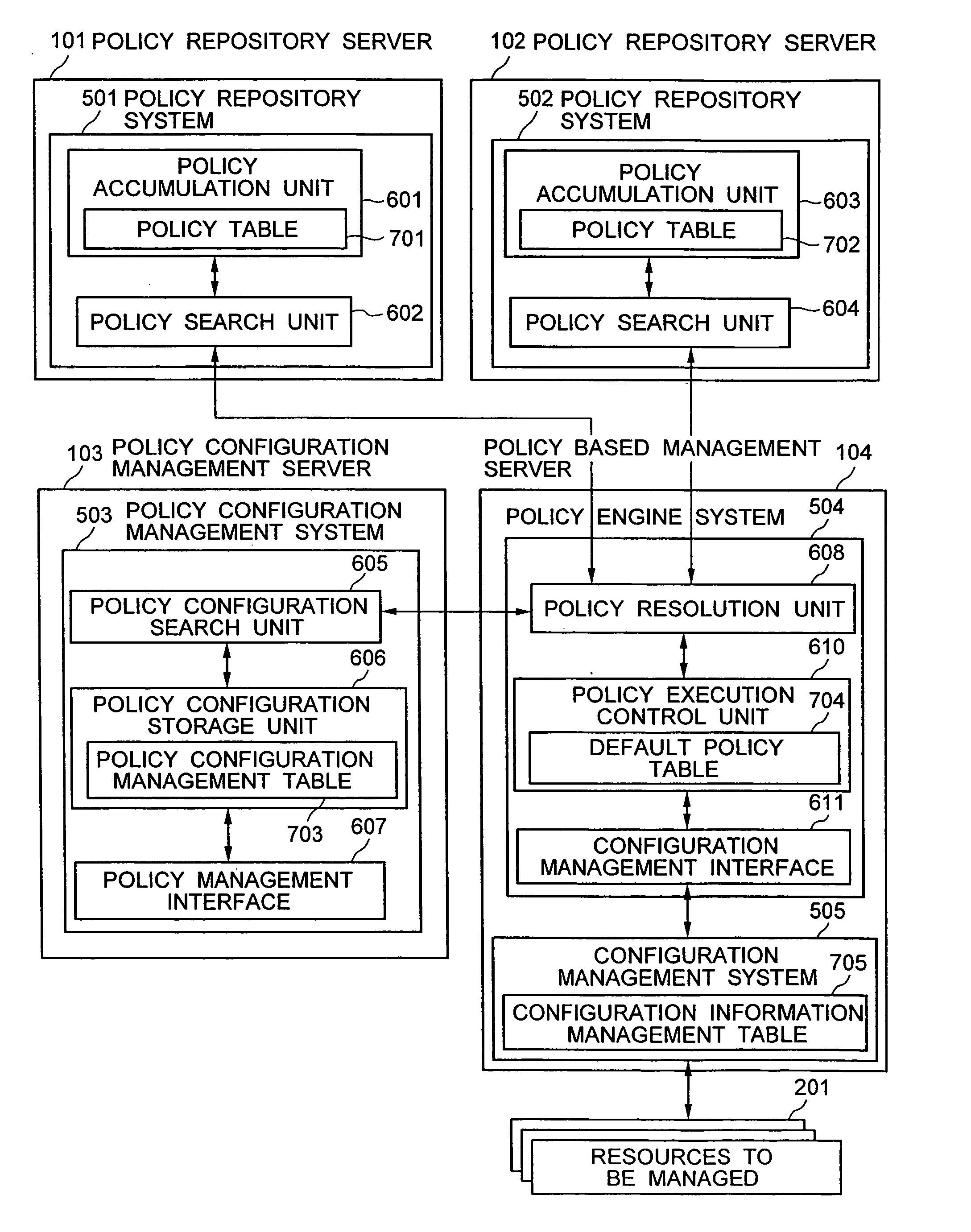
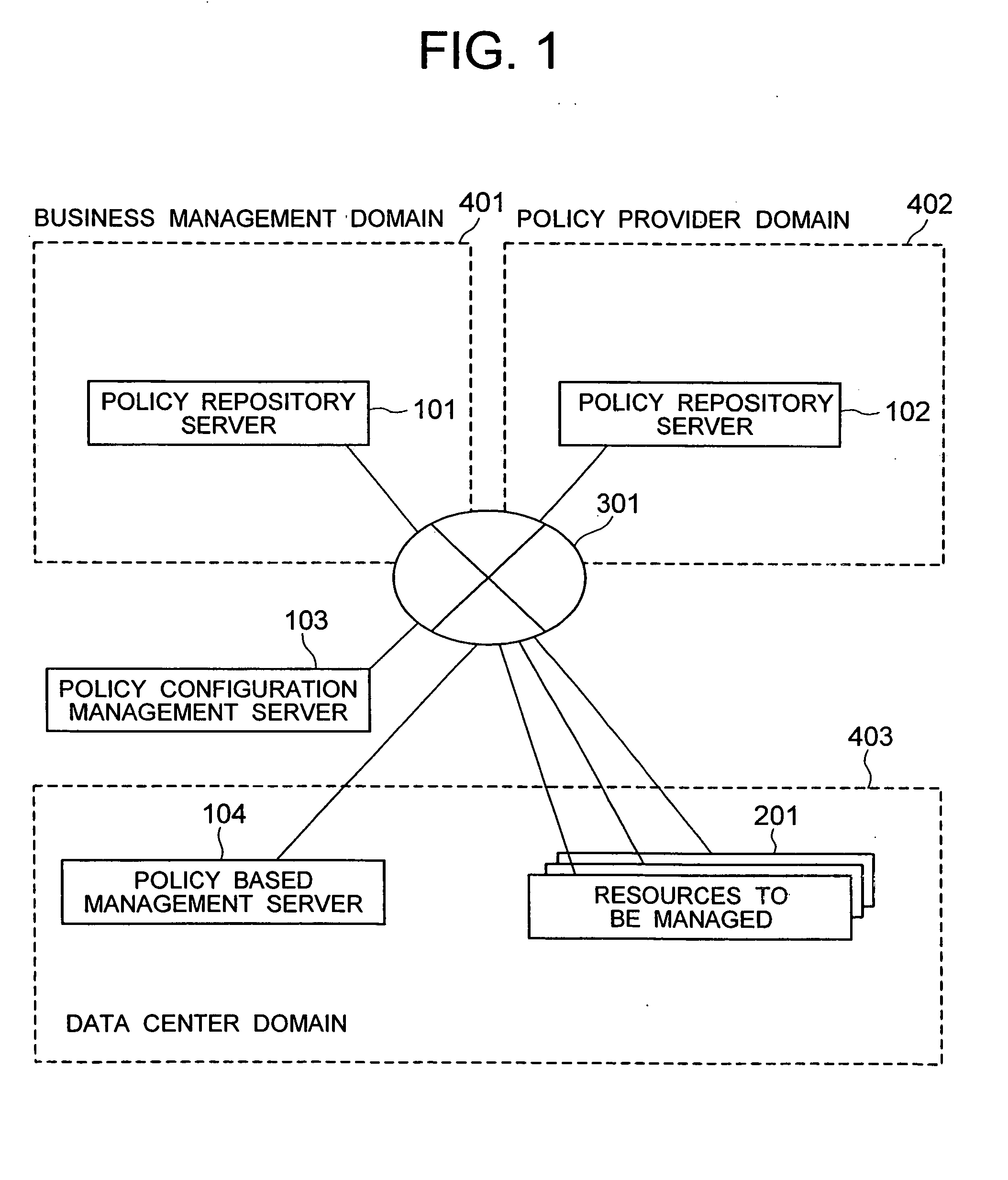
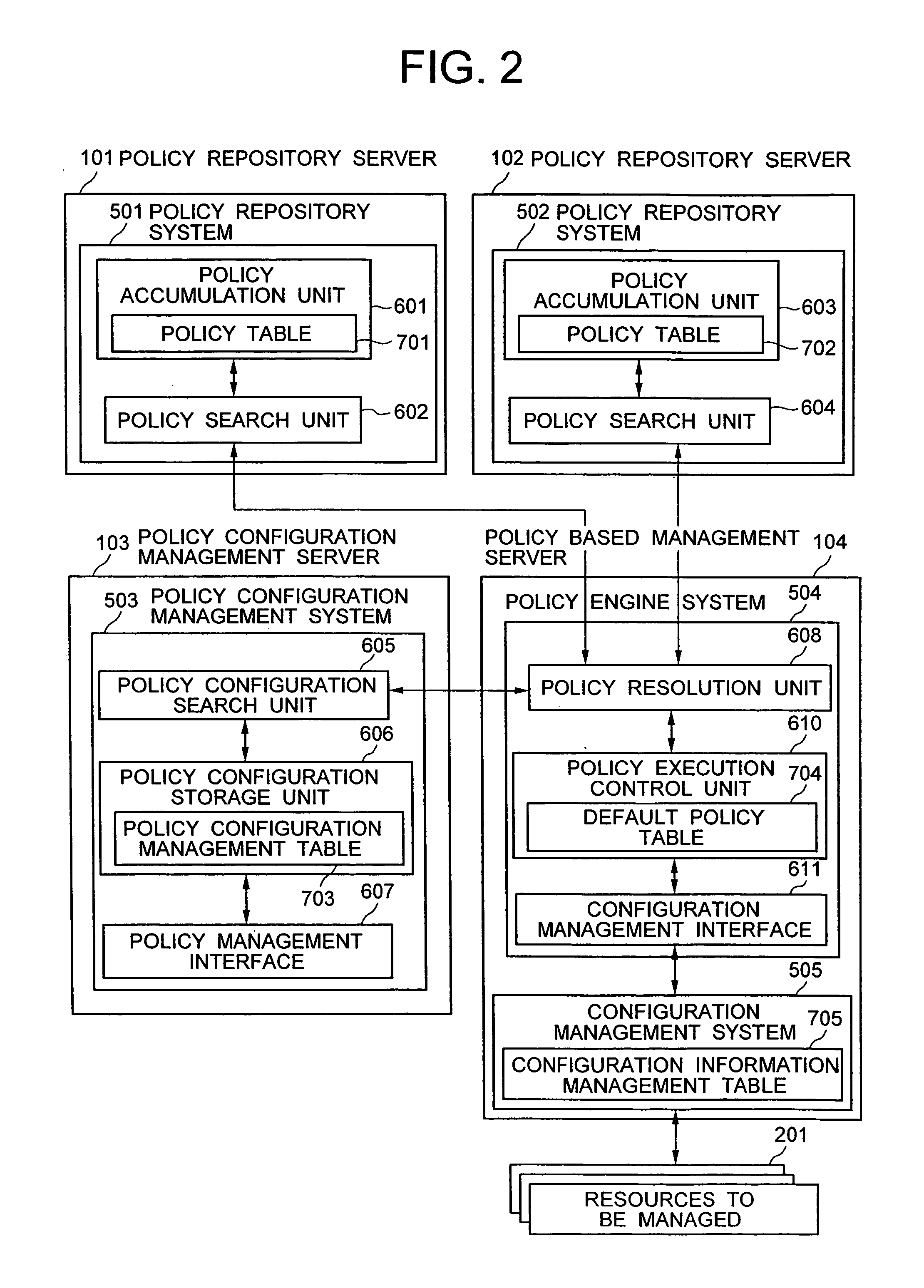
A distributed policy linking method is provided which performs a policy based management according to a plurality of pieces of policy information distributed in a plurality of domains. A policy configuration management system is installed which manages a set of an identifier and a policy repository for each piece of policy information stored in a plurality of policy repositories. The policy information corresponding to an event issued from a resource being managed is searched from the first policy repository. If the policy information retrieved includes an identifier representing a reference to a second policy repository, an access unit to the second policy repository is retrieved from the policy configuration management system according to the identifier. Policy information is then retrieved from the second policy repository and, based on the policy information obtained, a configuration modification operation is executed on the resource being managed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System for policy-based management of software updates
ActiveUS7496910B2Program loading/initiatingSpecial data processing applicationsSoftware updateComputerized system
A computer system configured for policy-based management of software updates is disclosed. The system maintains group-policy objects, with which groups of computers are associated. The system obtains identities of software updates from a source of software updates. The system also obtains filter criteria for each update, for determining whether the update should be applied to a particular computer or not. The system assigns newly available updates to respective selected group-policy objects and adds the obtained filter criteria to each such group-policy object. The system performs necessary installations of updates by, for each group-policy object, determining whether, for each combination of a computer belonging to a group associated with that policy object and an update assigned to that policy object, the computer satisfies the filter criteria for the update, and if so, applying the update to that computer, but if not, refraining from applying the update.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Conflict detection in rule sets
InactiveUS20060010439A1Improves operation of systemOvercome excessive storage spaceDigital data protectionKnowledge representationPolicy-based managementRule sets
The invention provides a method and system for detecting conflicts in policy-based management rule sets. This is achieved by expanding a set of input rules such that each rule relates only to one subject performing one action on a single object, and is known as a singleton rule. Then, data defining the semantic relationships between the different actions is received, and this is used to further expand the singleton rules to give a complete rule set defining every possible rule according to the semantic relationships between rules. This complete set can the be processed to detect conflicts between two or more rules, and any conflicting rules are identified and displayed to a user. Additionally, the invention also provides that the rule sets may be reduced to a canonical form for compact representation thereof.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
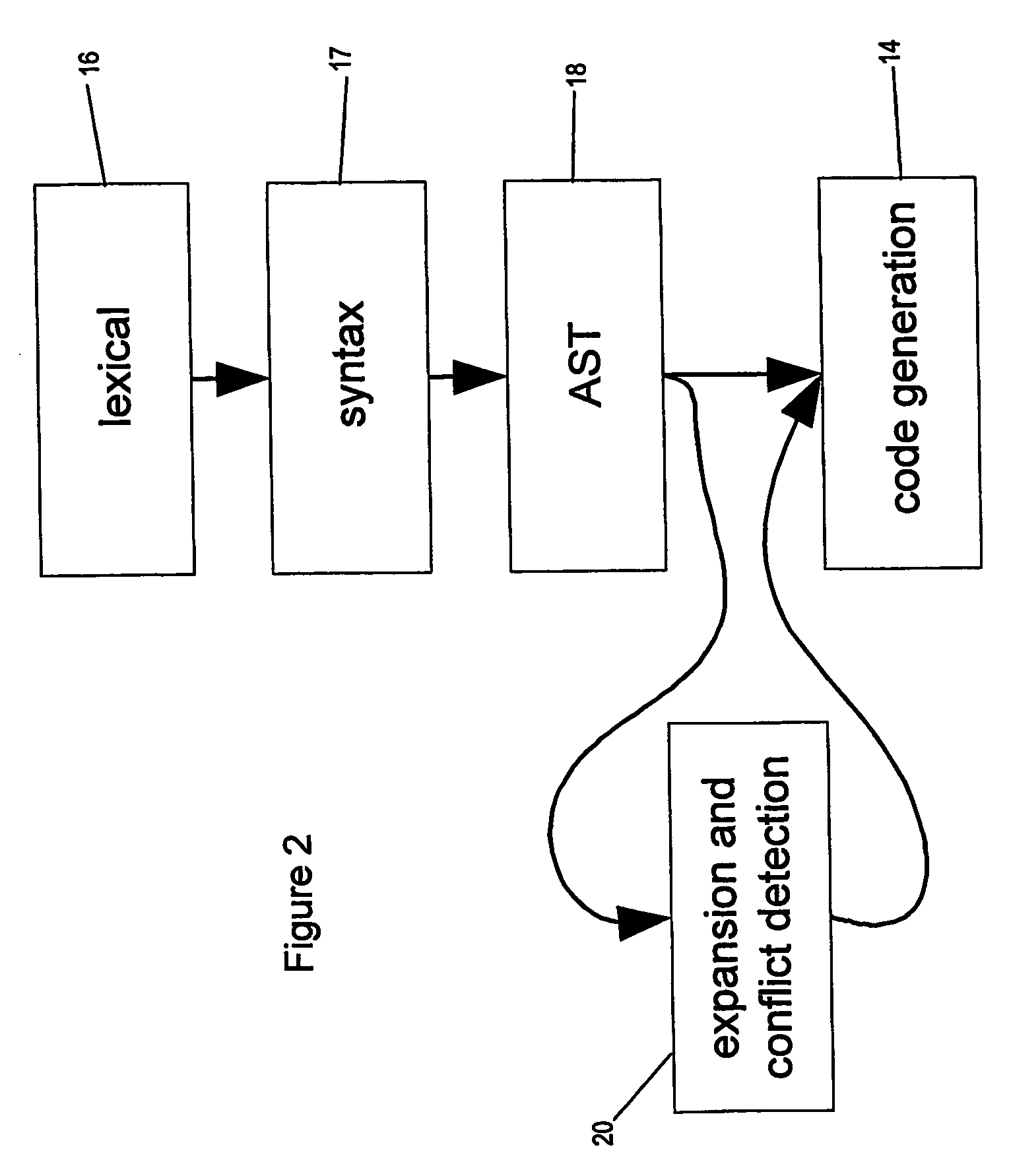
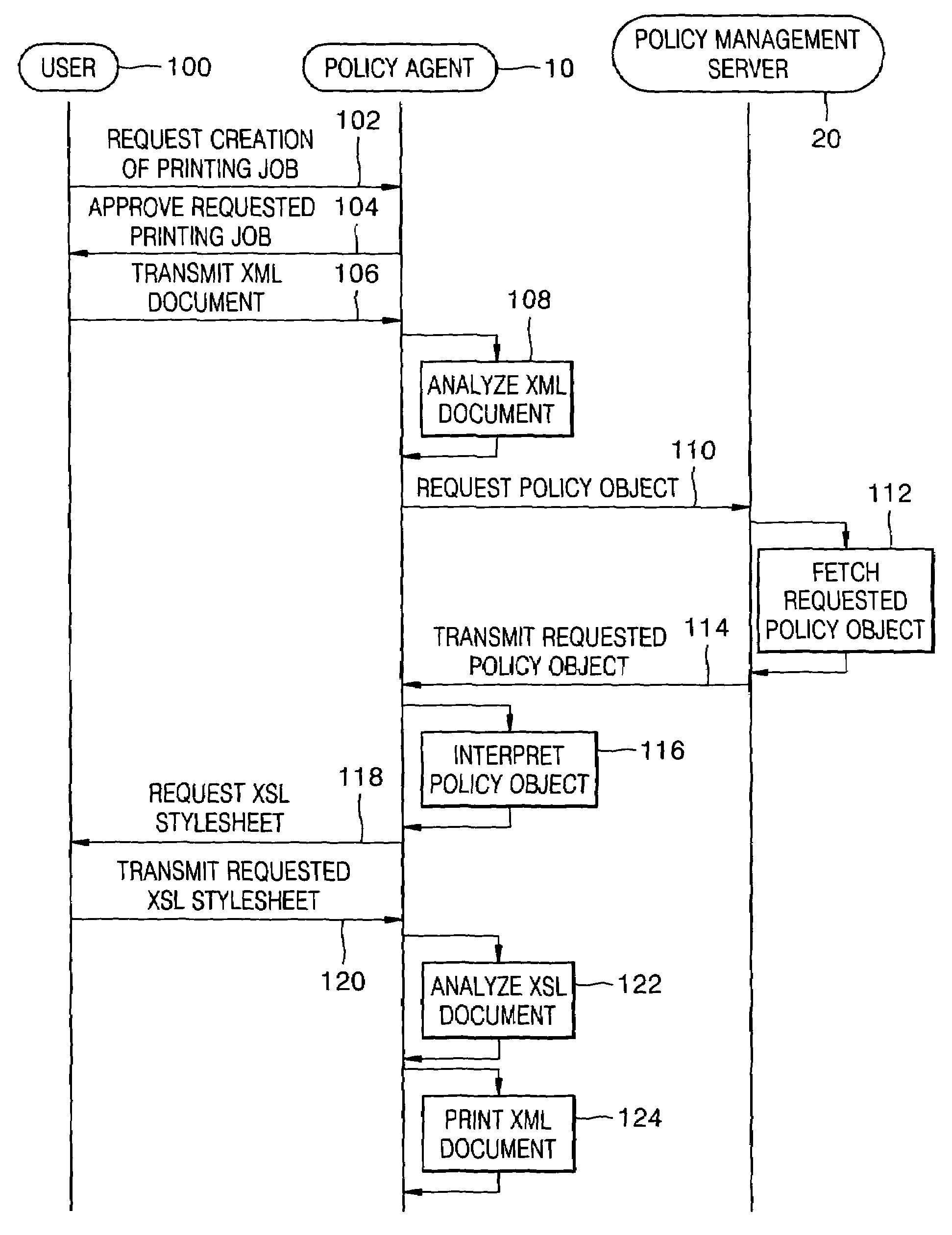
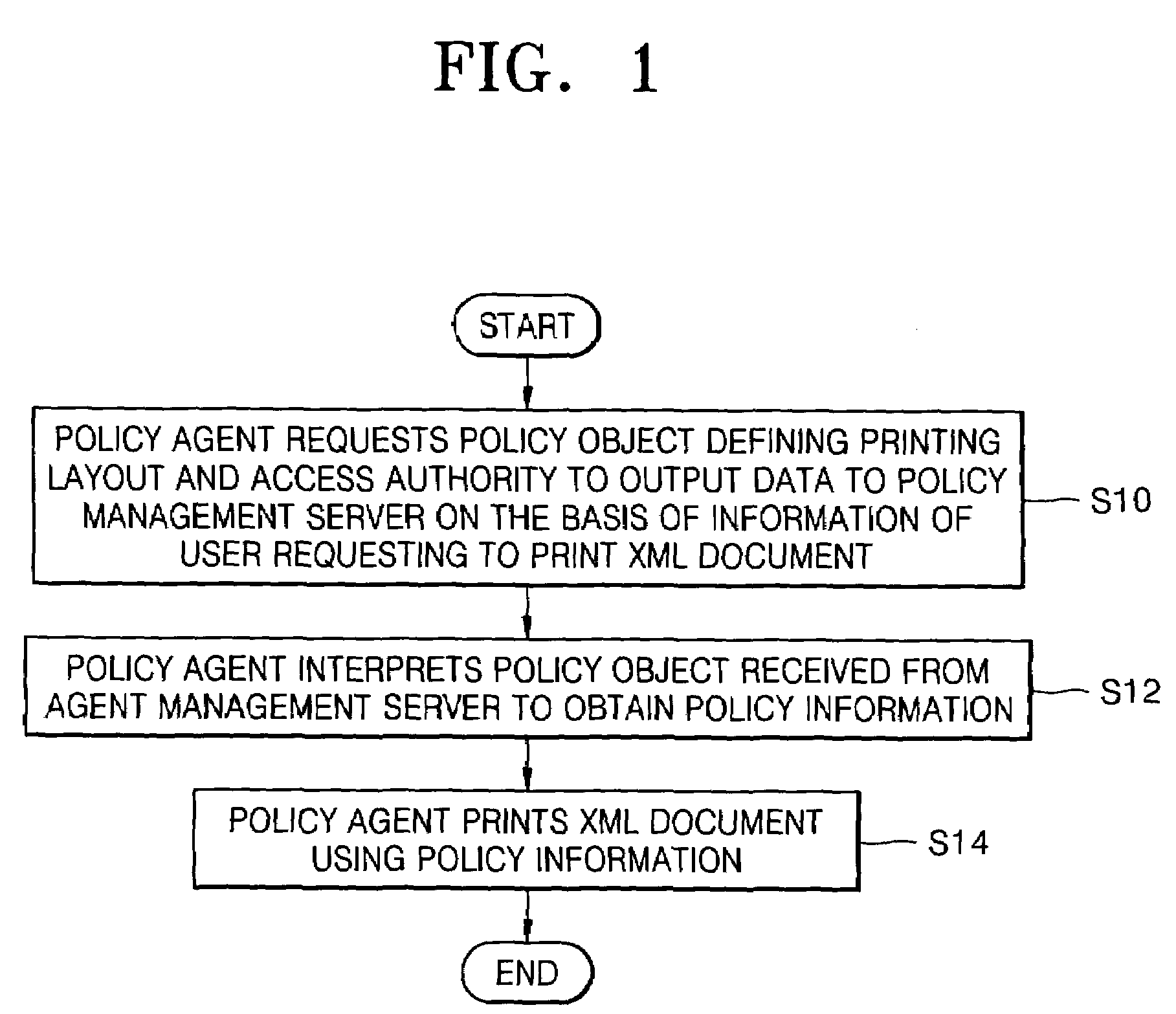
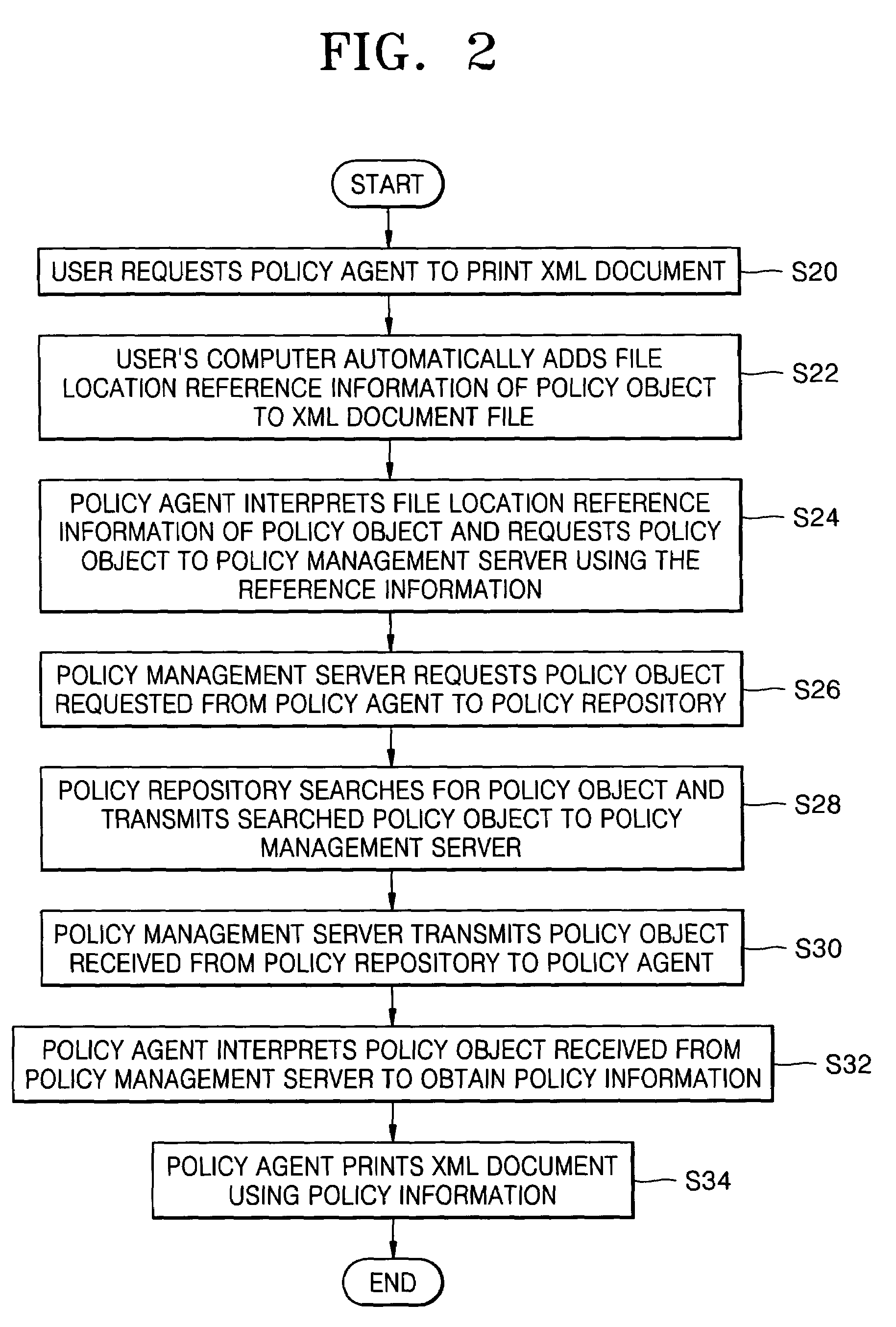
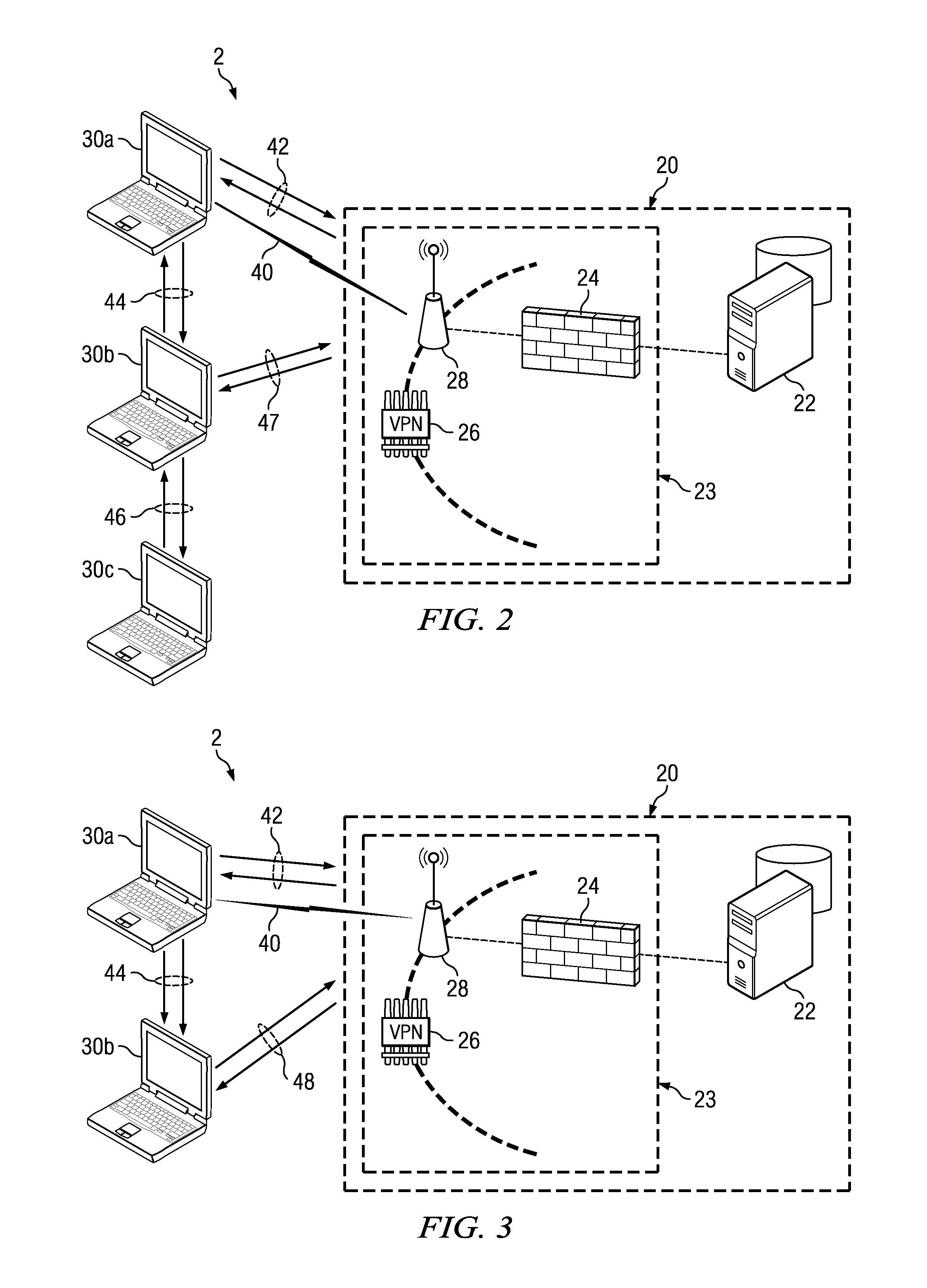
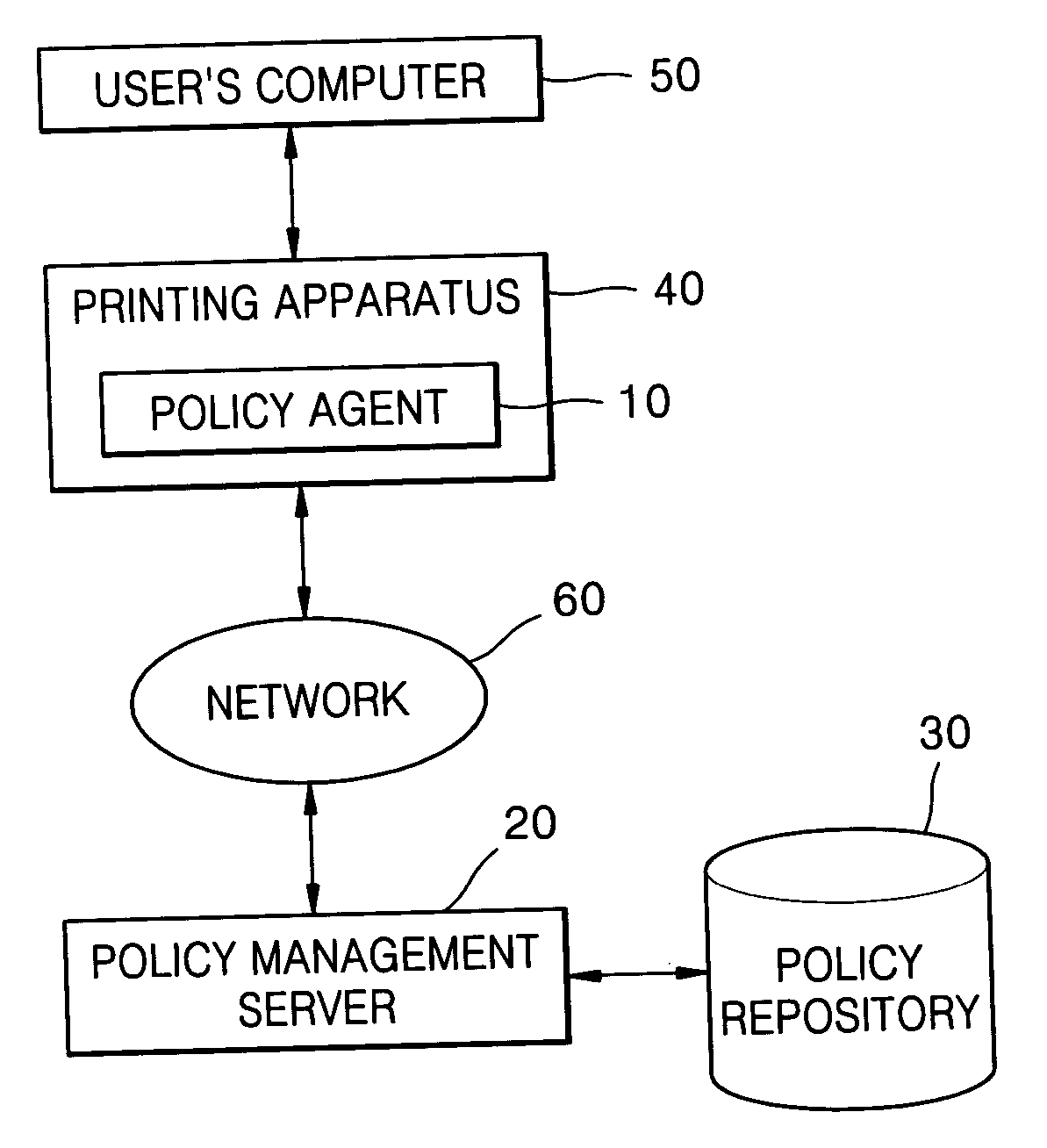
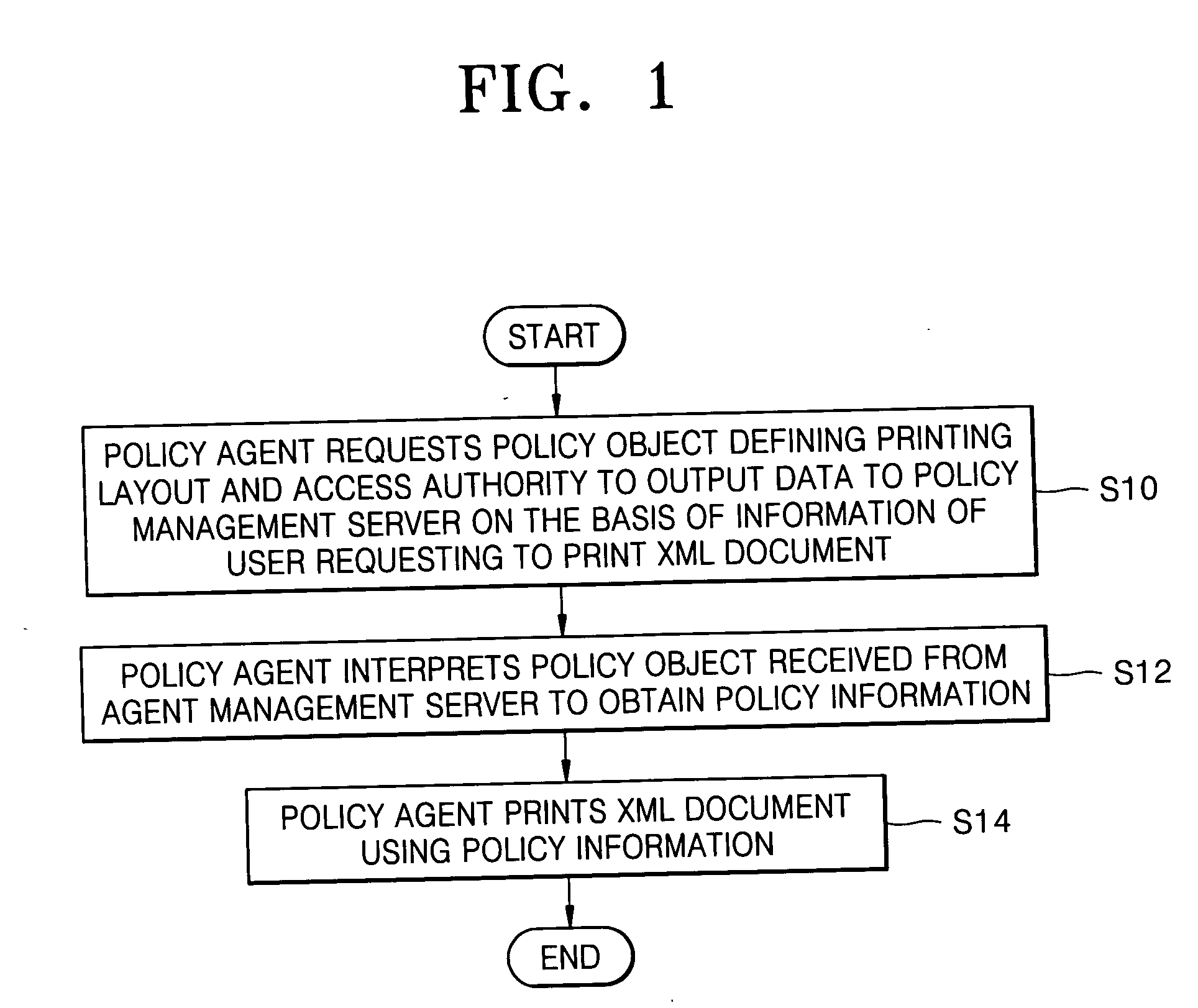
Policy-based management method and system for printing of extensible markup language (XML) documents
InactiveUS7660803B2Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsExtensible markupDocumentation
There are provided a policy-based extensible markup language (XML) document print management method and system, using a policy object defining a print layout and an access authority to output data, on the basis of the information of a user requesting to print the XML document. The policy-based XML document print management method includes (a) requesting a policy object defining a printing layout and an access authority to output data to a policy management server, on the basis of information of a user requesting to print the XML document, in a policy agent; (b) receiving the policy object from the policy management server, interpreting the policy object, and obtaining policy information, in the policy agent; and (c) printing the XML document using the policy information, in the policy agent. Therefore, it is possible to determine a printing layout of an XML document and print the XML document, according to policy information. Also, by determining whether a user requesting to print the XML document has an access authority to the XML document on the basis of the policy information, it is possible to allow the printing job only to the user having the access authority.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
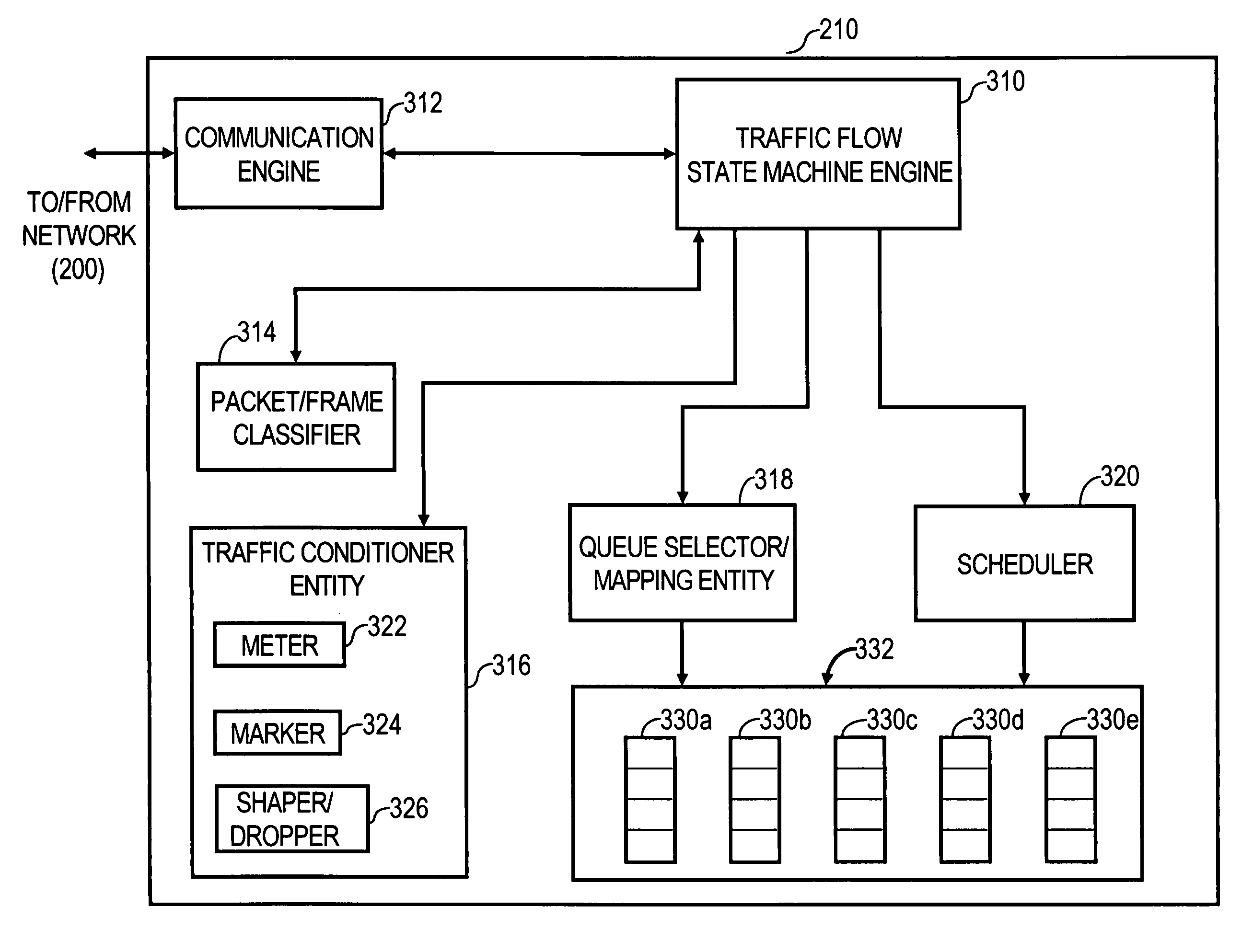
Method and apparatus for creating policies for policy-based management of quality of service treatments of network data traffic flows
InactiveUS7346677B1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
A method and apparatus for creating policies for use in policy-based management of quality of service treatments of network data traffic flows are described. The policies are defined based on information about types of network traffic flows generated by an application program, and information about quality of service functions that are available in devices of the network. In one embodiment, application information is received that defines one or more traffic flows generated by an application program, including information identifying one or more points at which an application generates the traffic flows, from a first individual having responsibility for managing enterprise applications in the network. Further, QoS information is received that defines one of more quality of service treatments that the network device may apply to data processed by the network device, from a second individual having responsibility for managing the network. Based on the device QoS information and the application information, one or more processing policies that associate the traffic flows with the quality of service treatments are determined. Mappings of the application information to the quality of service treatments, which may be used to generate the quality of service value when the application program generates traffic flows, are created and stored. As a result, the policies are informed both by application program expertise and network expertise. Methods and mechanisms of integrating the policies into a directory are described.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
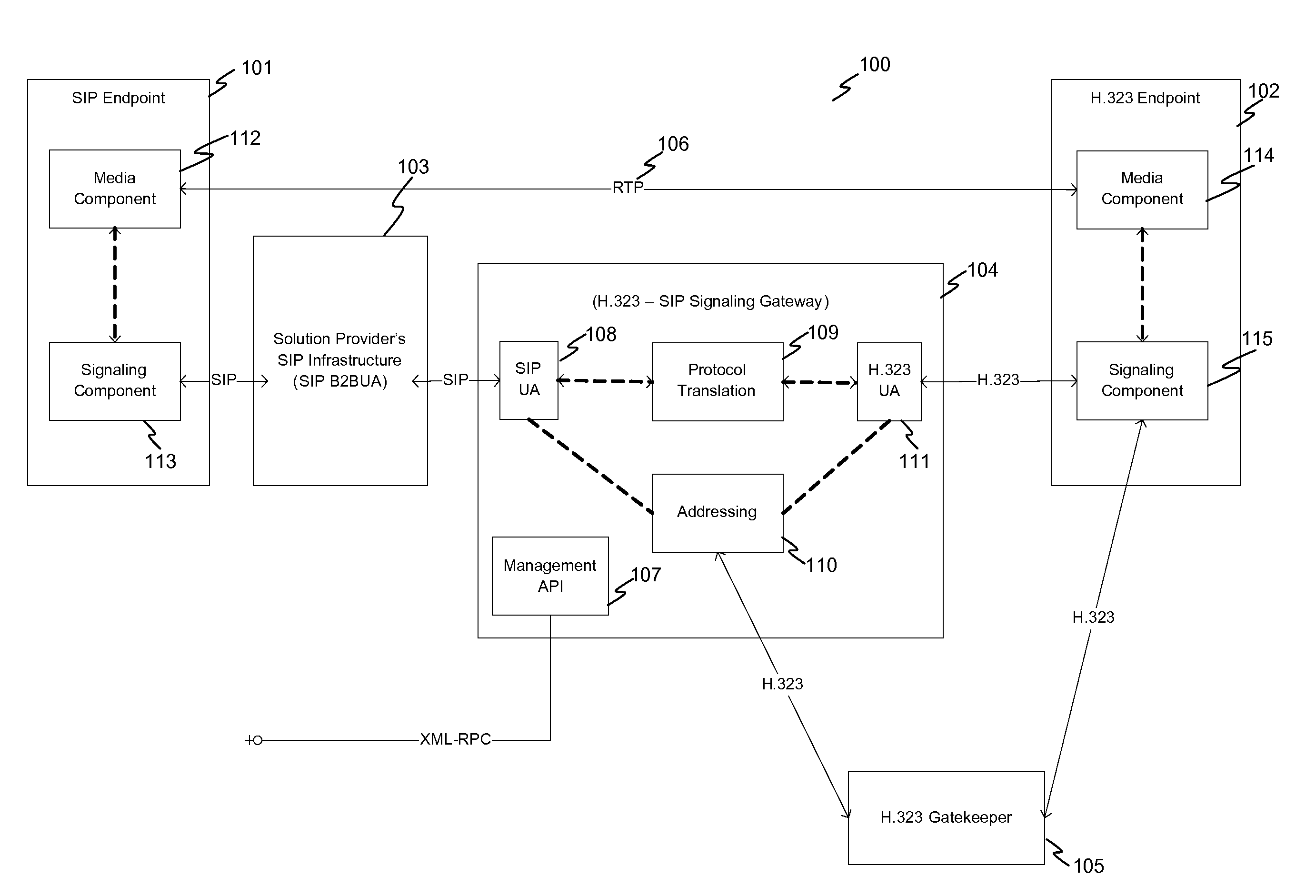
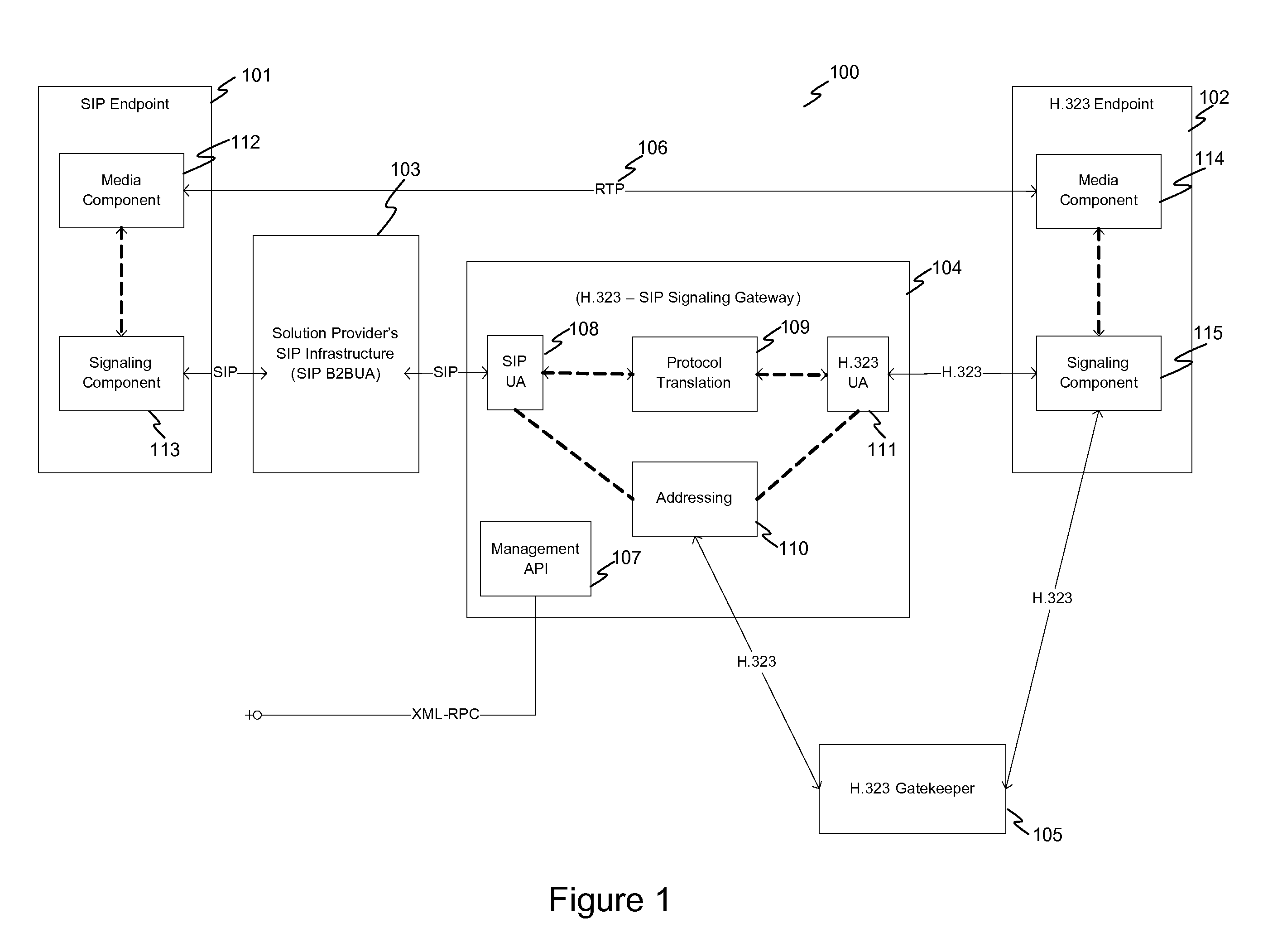
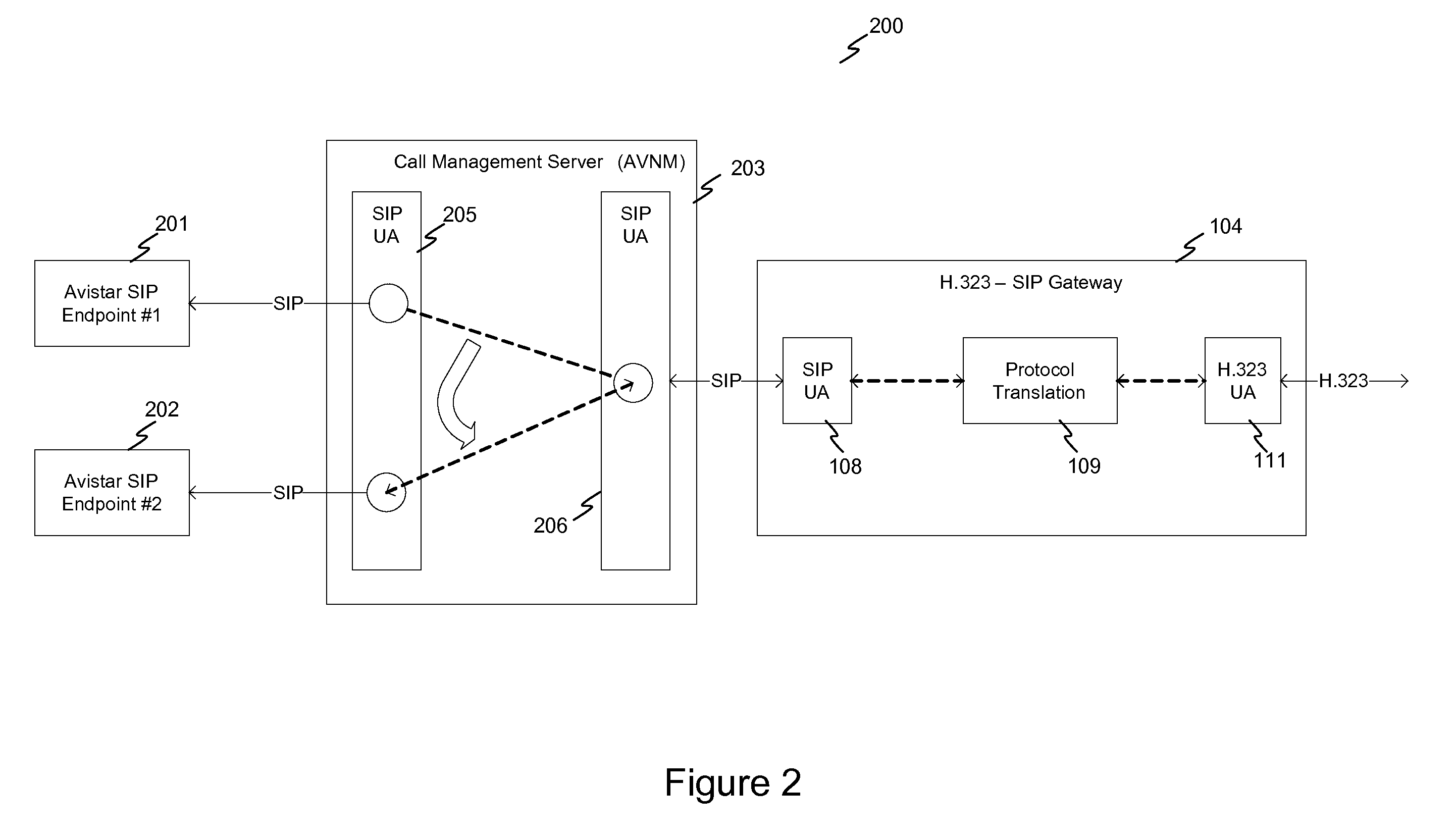
System and method for achieving interoperability between endpoints operating under different protocols
InactiveUS20100085959A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetwork connectionsTeleconferencePolicy-based management
A teleconferencing system for achieving interoperability between a multiple endpoints including a first endpoint following SIP protocol, a second endpoint following H.323 protocol and a third endpoint following a proprietary protocol. The teleconferencing system incorporates a signaling gateway and a call control server. In the teleconferencing system, the signaling gateway and a call control server are configured to perform policy-based management of calls between the first endpoint, the second endpoint and the third endpoint.
Owner:AVISTAR COMM
Dynamic, policy based management of administrative procedures within a distributed computing environment
InactiveUS20020091939A1Specific access rightsUser identity/authority verificationDistributed Computing EnvironmentAdministrative management
An administrative management system comprising an administrative server and a client is disclosed. In response to a selection of an administrative procedure to be executed on the client, the administrative server determines if an execution of the administrative procedure on the client is in compliance with one or more corresponding policies. If the execution is in compliance with the corresponding policy or policies, the administrative server determines the storage location of the administrative procedure. If the selected administrative procedure is stored on the client, the administrative server executes the administrative procedure on the client. If the selected administrative procedure is stored on the administrative server, the administrative server pushes a corresponding script of the administrative procedure from the administrative server to the client and then installs and executes the script on the client. If the selected administrative procedure is stored at a remote location, the administrative server pushes a corresponding script of the administrative procedure from the remote location to the client and then installs and executes the script on the client.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transparent proxy architecture for multi-path data connections
ActiveUS9253015B2Performance maximizationHigh bandwidthAssess restrictionDigital computer detailsData connectionNetwork conditions
A method for forming an optimized communication connection providing enhanced performance of at least one application utilizing the communication connection is provided, the communication connection including a plurality of individual communication networks. The method includes the steps of: obtaining a set of performance requirements corresponding to the application utilizing the communication connection; obtaining real-time capacity information for each of a plurality of available channels associated with the respective individual communication networks; applying at least one policy-based management criteria to the available channels for controlling, in real-time, one or more aspects of the available channels; dynamically aggregating the individual communication networks to form the optimized communication connection, the communication connection leveraging one or more features and capabilities of at least a subset of the communication networks; and controlling real-time traffic scheduling across at least a subset of the available channels so as to adapt the communication connection to changes in network conditions and / or policy-based management criteria.
Owner:ATTILA TECH
Method for heterogeneous network policy based management
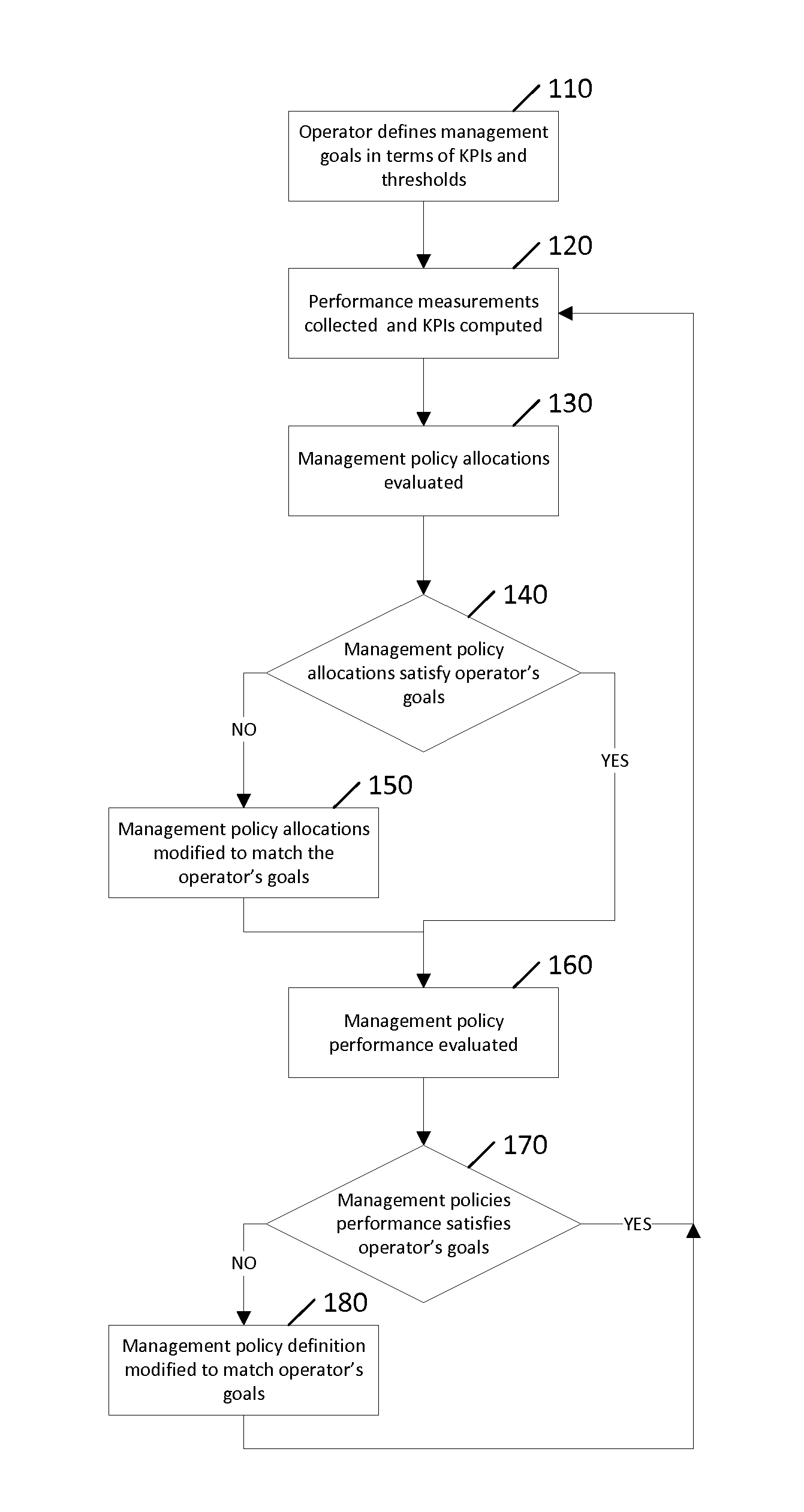
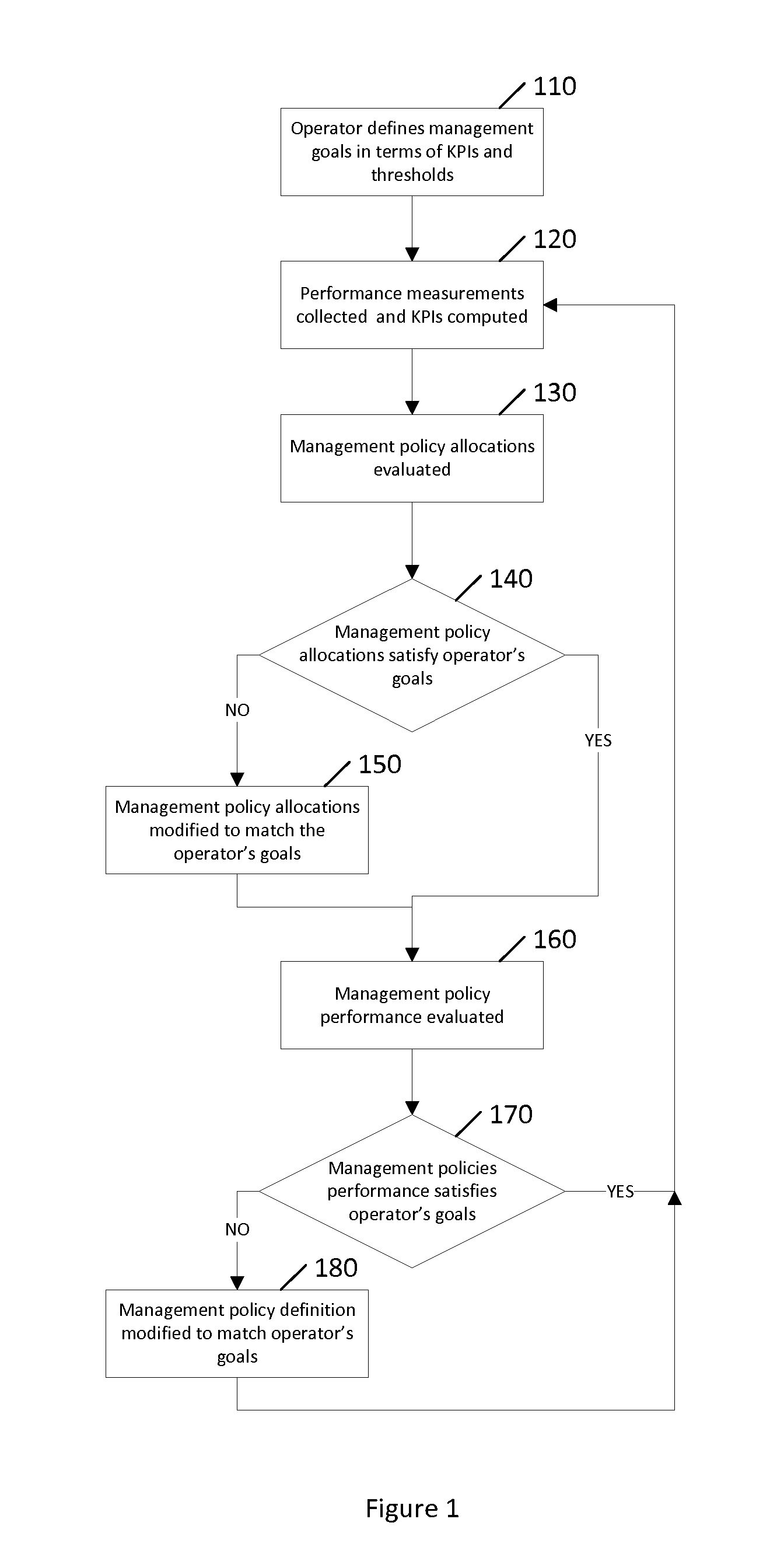
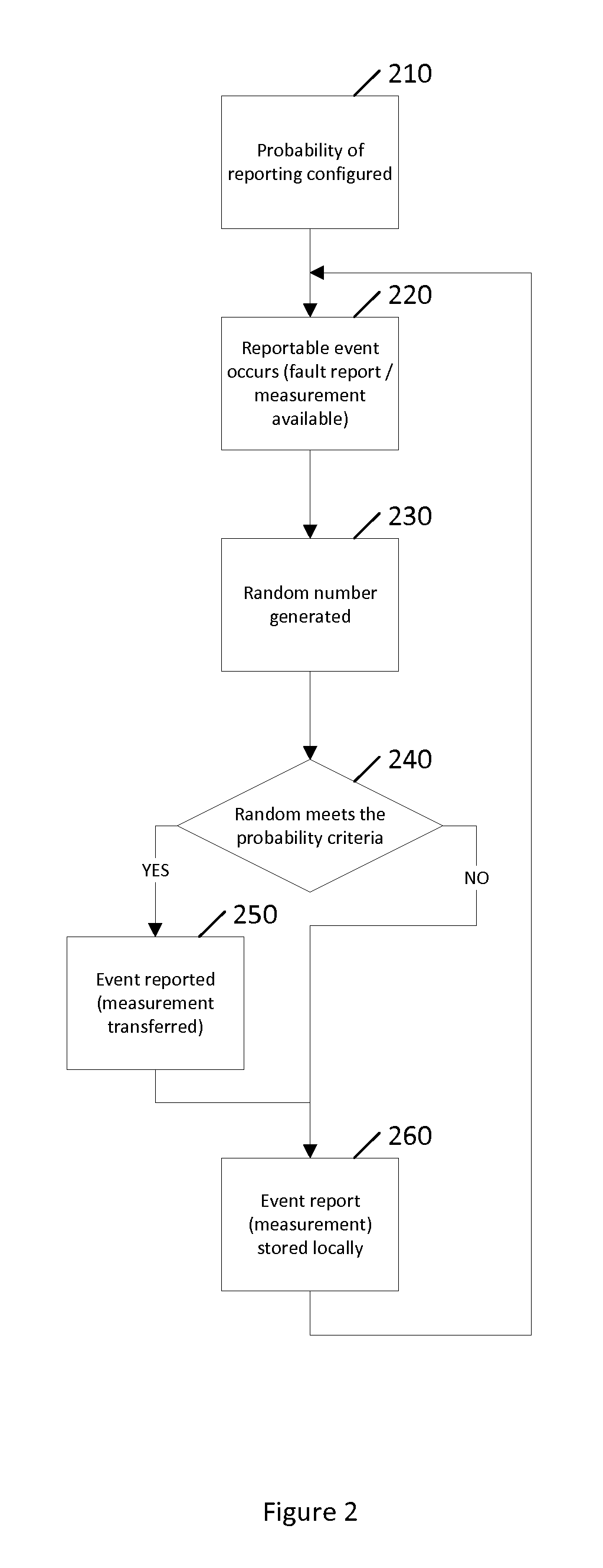
ActiveUS20130290230A1Digital computer detailsKnowledge representationHeterogeneous networkData mining
Communication networks in general may benefit from appropriate policy based management. More particularly, heterogeneous networks or HetNets may benefit from methods for policy based management. A method according to certain embodiments includes detecting a reportable event. The method also includes determining whether or how to report the event based on a probability criterion. The method further includes taking an action with respect to reporting the event based on whether the probability criterion is met.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Accumulating access frequency and file attributes for supporting policy based storage management
ActiveUS8131689B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsComputer moduleAccess frequency
A system and method for performing policy-based storage management using data related to access frequency and file attribute accumulation. A switch device provides transparency for transactions between a client and a storage network. The transparency allows objects (e.g., files or directories) to be moved (e.g., migrated) on the storage network without affecting a reference to the object used by the client (e.g., a file handle). A monitoring module generates accumulation data associated with the transactions for use in policy-based management. The accumulation data can describe uses of the file such as how often certain files are accessed, modifications to files such as creations of new directories or files, and other uses.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
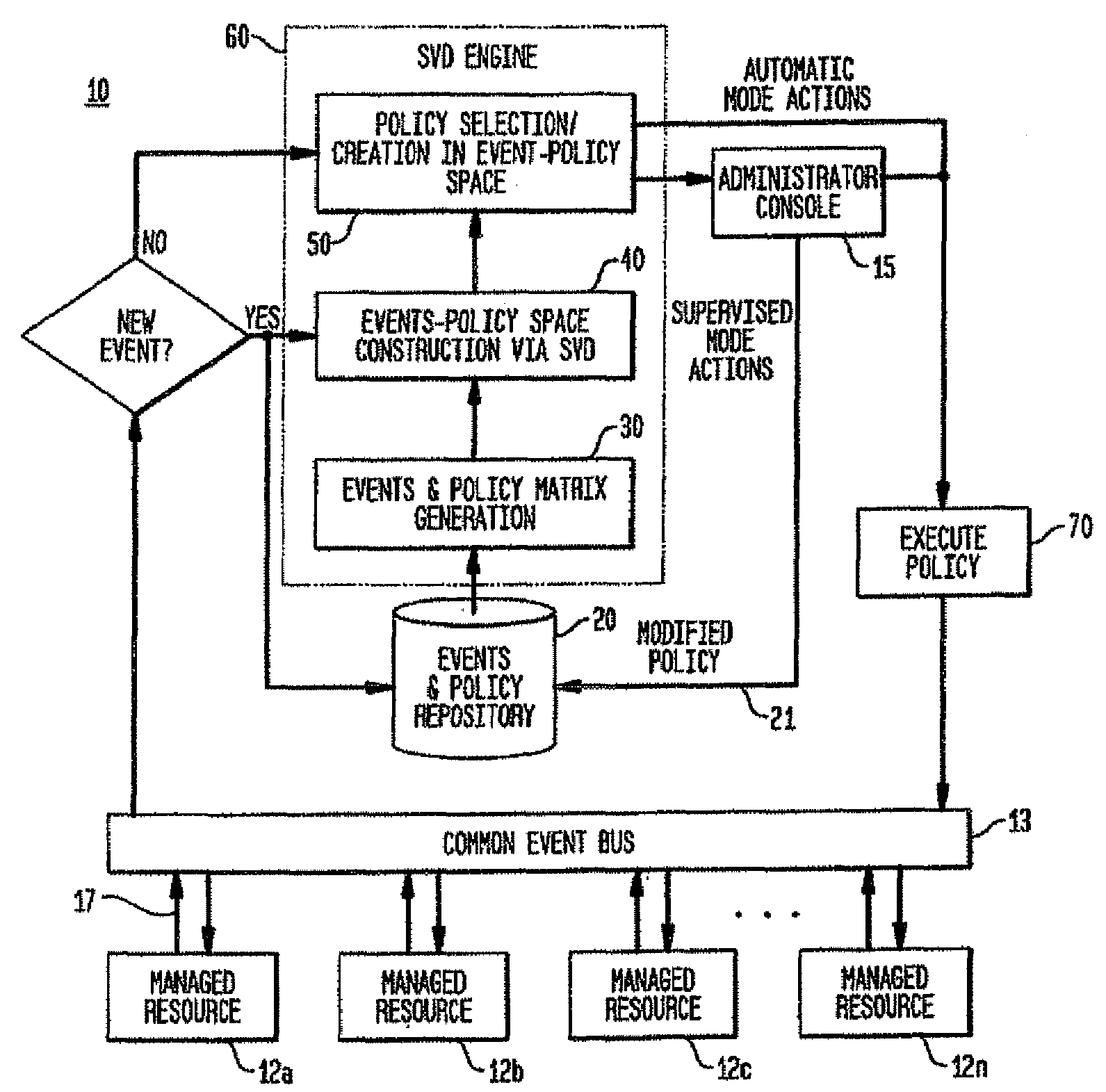
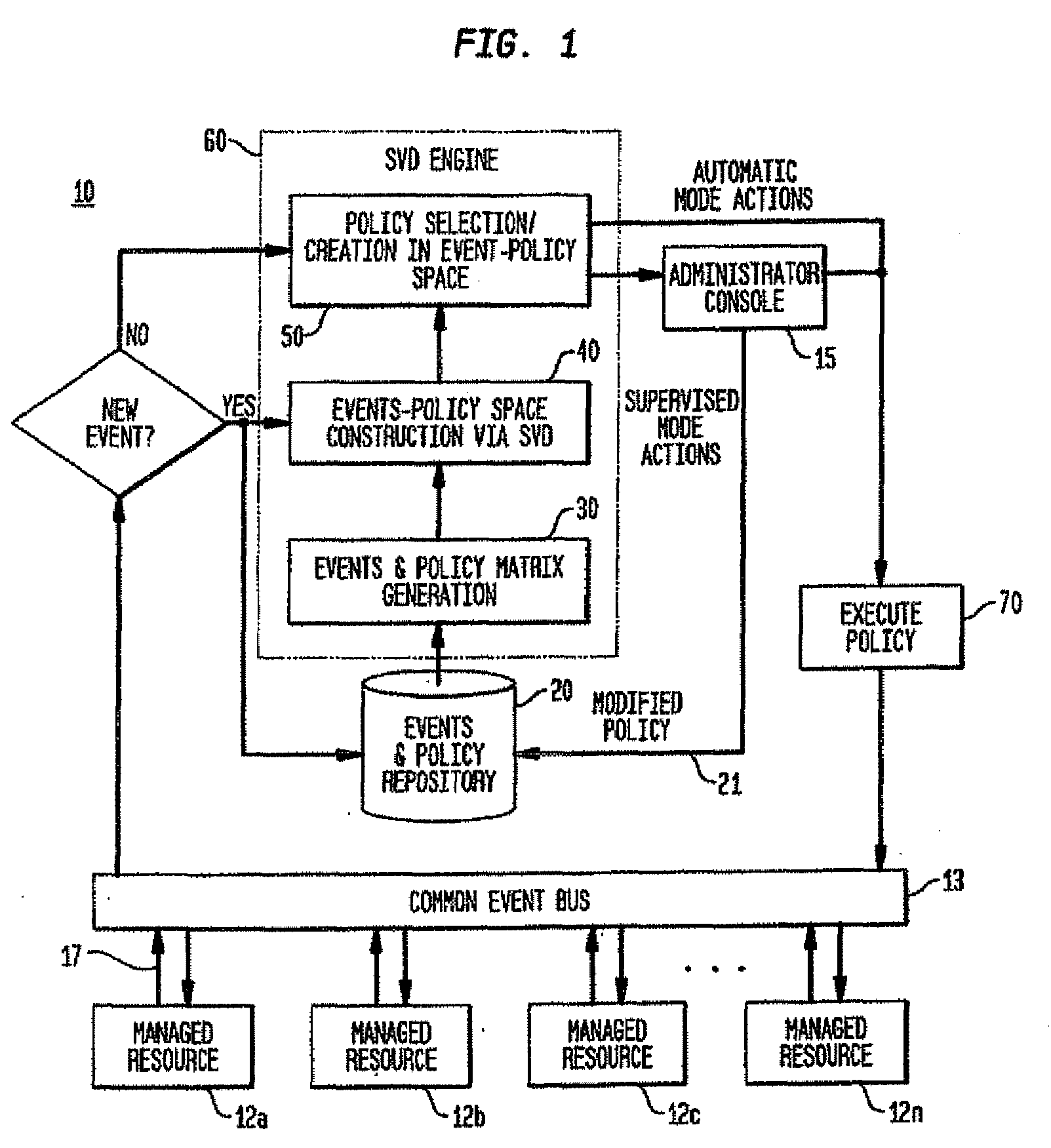
Policy-based management system with automatic policy selection and creation capabilities by using singular value decomposition technique
InactiveUS20080235168A1Improve accuracyDigital computer detailsKnowledge representationSingular value decompositionExact match
A statistical approach implementing Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to a policy-based management system for autonomic and on-demand computing applications. The statistical approach empowers a class of applications that require policies to handle ambiguous conditions and allow the system to “evolve” in response to changing operation and environment conditions. In the system and method providing the statistical approach, observed event-policy associated data, which is represented by an event-policy matrix, is treated as a statistical problem with the assumption that there are some underlying or implicit higher order correlations among events and policies. The SVD approach enables such correlations to be modeled, extracted and modified. From these correlations, recommended policies can be selected or created without exact match of policy conditions. With a feedback mechanism, new knowledge can be acquired as new situations occur and the corresponding policies to manage them are recorded and used to generate new event and policy correlations. Consequently, based on these new correlations, new recommended policies can be derived.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data locations template based application-data association and its use for policy based management
Method and system are disclosed for automatically discovering associations between applications and data in multi-tiered distributed systems. The method in one aspect uses a machine-readable specification of a model or template that describes use and transformation of data by software components. The method additionally utilizes a model of system configuration and appropriate runtime support to mine information available from systems management software present in enterprise systems. The application-data association discovery process performs a traversal of the distributed system configuration graph with actions taken during this traversal driven by the contents of the templates for the software components present in the system. The results of the application-data association discovery process are stored in a database and may be used to specify application-specific information lifecycle management (ILM) policy or as input to impact analysis tools in access control and antivirus systems.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for policy based management for a high security MANET
ActiveUS8769068B2Network topologiesMultiple digital computer combinationsPolicy decisionPolicy-based management
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Data locations template based application-data association and its use for policy based management
Method and system are disclosed for automatically discovering associations between applications and data in multi-tiered distributed systems. The method in one aspect uses a machine-readable specification of a model or template that describes use and transformation of data by software components. The method additionally utilizes a model of system configuration and appropriate runtime support to mine information available from systems management software present in enterprise systems. The application-data association discovery process performs a traversal of the distributed system configuration graph with actions taken during this traversal driven by the contents of the templates for the software components present in the system. The results of the application-data association discovery process are stored in a database and may be used to specify application-specific information lifecycle management (ILM) policy or as input to impact analysis tools in access control and antivirus systems.
Owner:IBM CORP
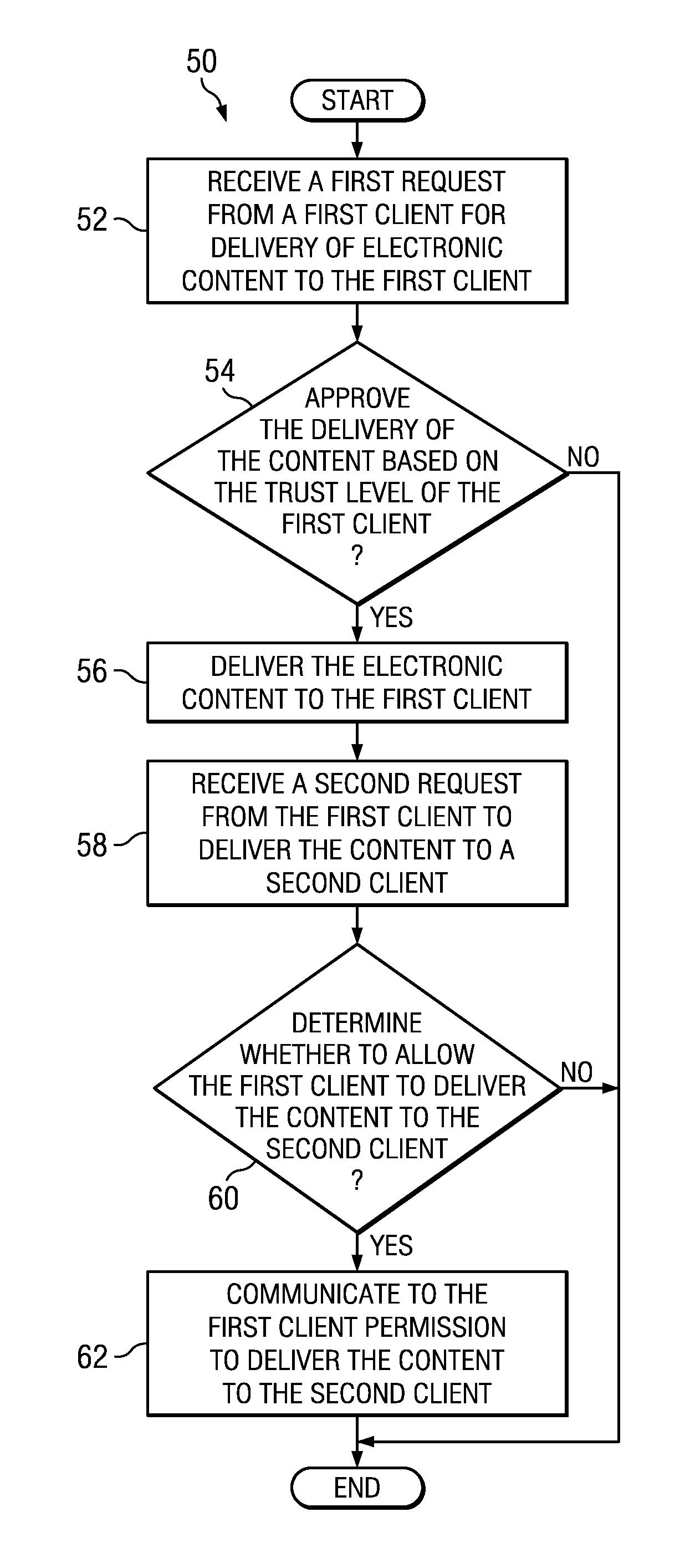
Consigning Authentication Method
InactiveUS20110321134A1Eliminates and reduces of disadvantageEliminates and reduces of and problemDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsTrust levelClient-side
A method for sharing content between clients at a common trust level in a trust hierarchy associated with a network implementing policy-based management includes receiving integrity information from a first client at a first trust level in the trust hierarchy at a second client at the first trust level, requesting permission to receive electronic content from the first client, receiving a determination regarding the requested permission, and communicating the determination to the first client. The first client obtained content from a policy enforcement point in the network. The request for permission is made to the policy enforcement point and the request includes the integrity information. The determination is received from the policy enforcement point and is based in part on the integrity information about the first client. The second client communicates to the first client the determination of whether the second client receives the content from the first client.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
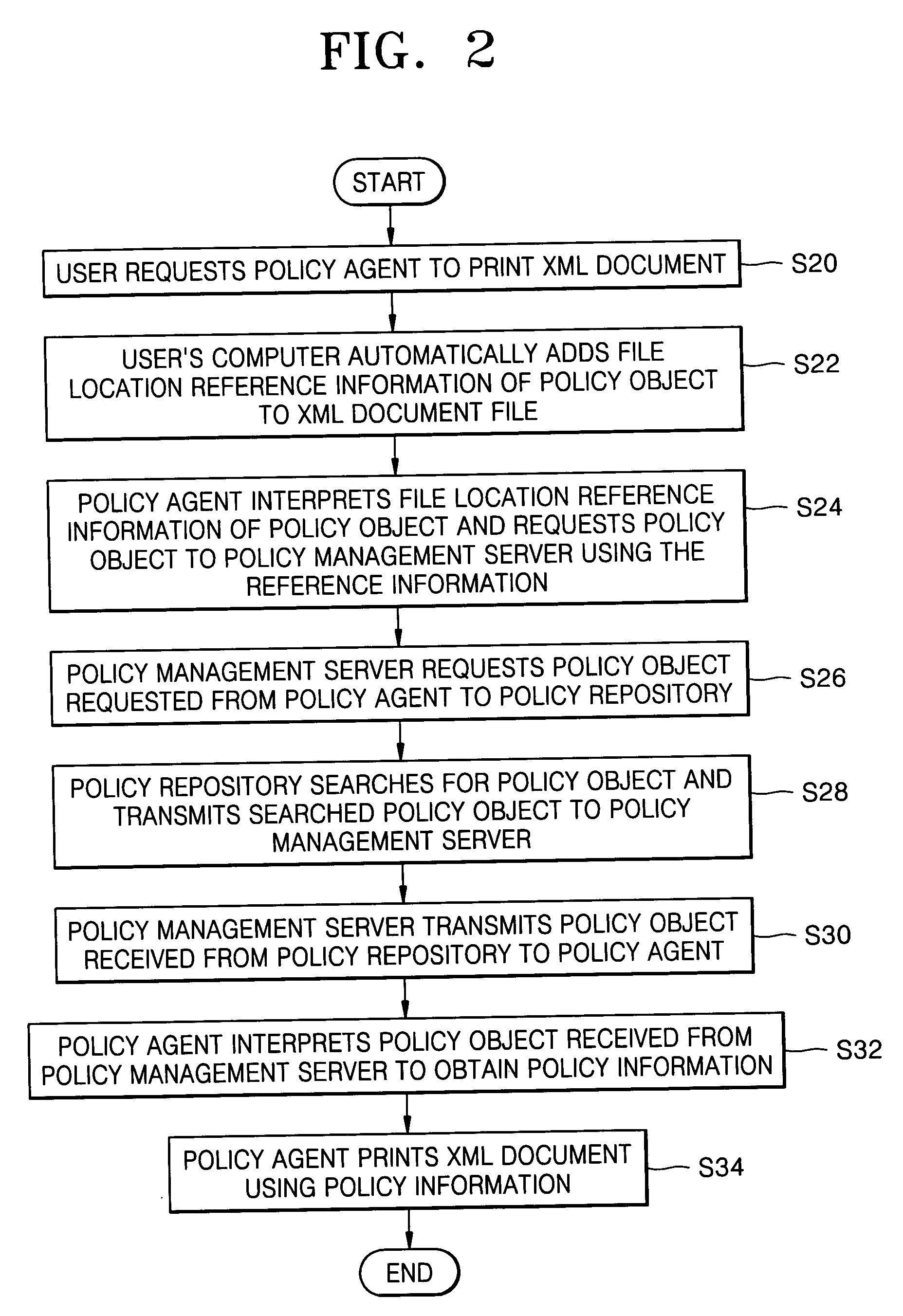
Policy-based management method and system for printing of extensible markup language (XML) documents
InactiveUS20060064420A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsExtensible markupDocumentation
There are provided a policy-based extensible markup language (XML) document print management method and system, using a policy object defining a print layout and an access authority to output data, on the basis of the information of a user requesting to print the XML document. The policy-based XML document print management method includes (a) requesting a policy object defining a printing layout and an access authority to output data to a policy management server, on the basis of information of a user requesting to print the XML document, in a policy agent; (b) receiving the policy object from the policy management server, interpreting the policy object, and obtaining policy information, in the policy agent; and (c) printing the XML document using the policy information, in the policy agent. Therefore, it is possible to determine a printing layout of an XML document and print the XML document, according to policy information. Also, by determining whether a user requesting to print the XML document has an access authority to the XML document on the basis of the policy information, it is possible to allow the printing job only to the user having the access authority.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
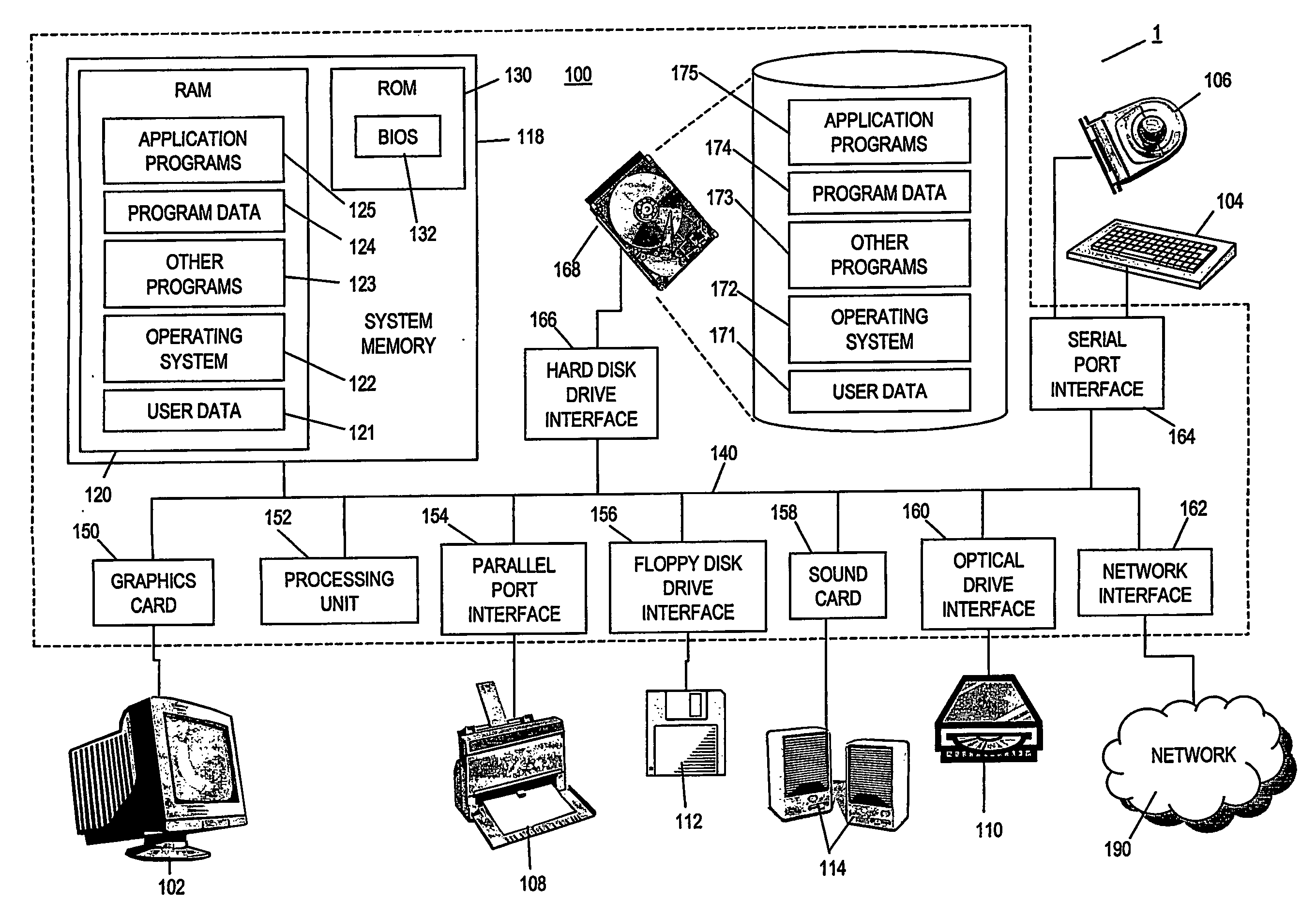
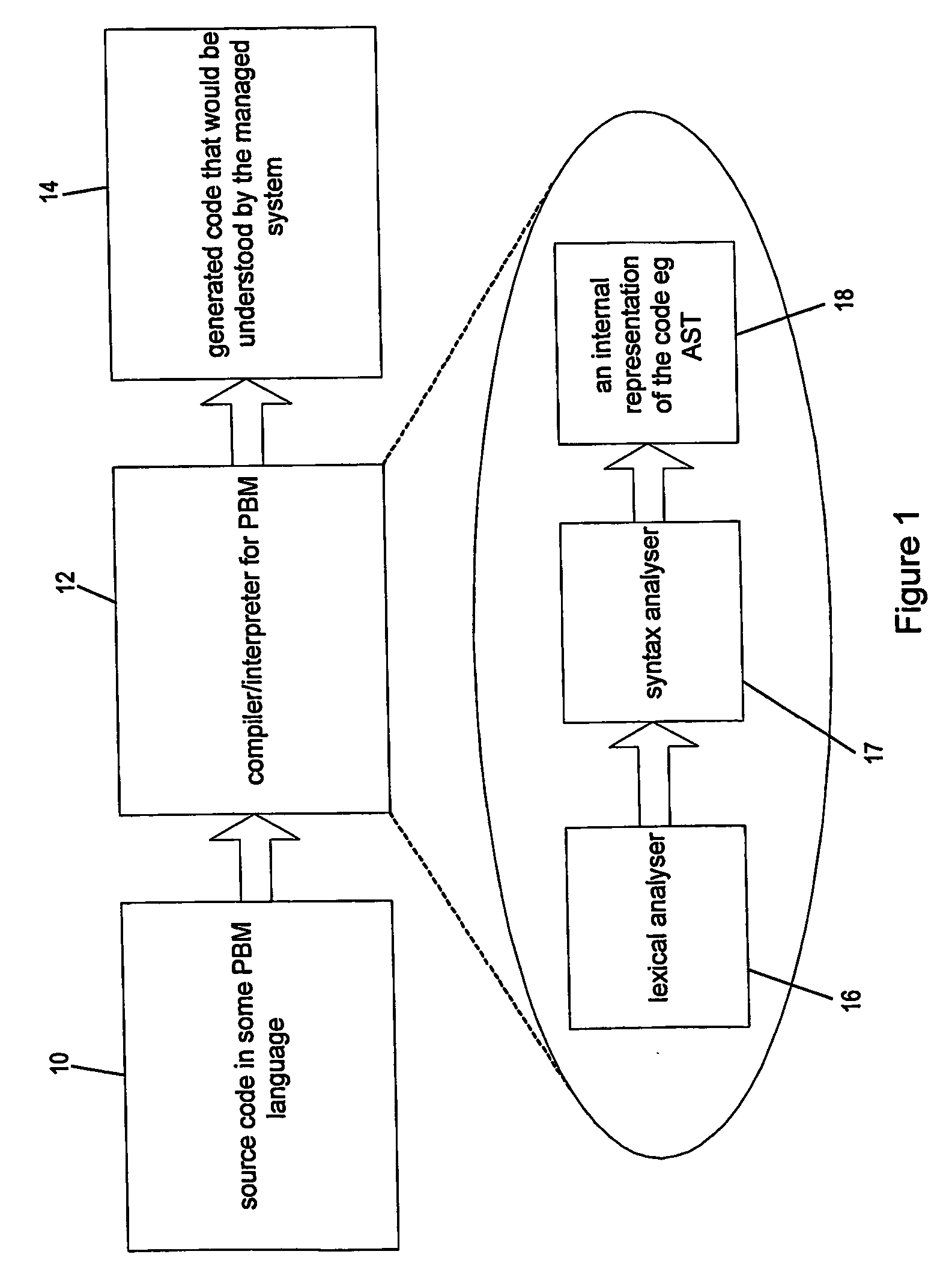
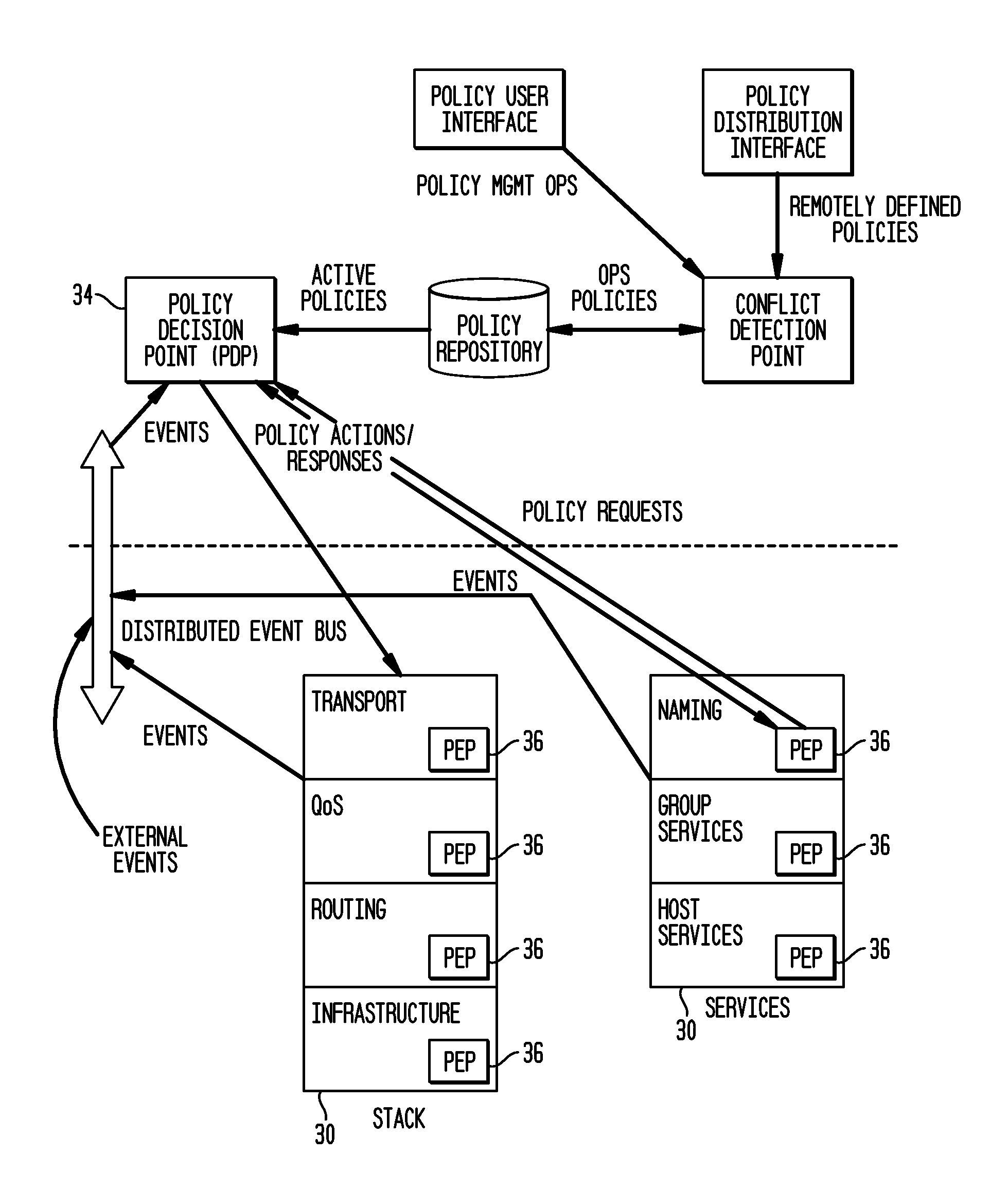
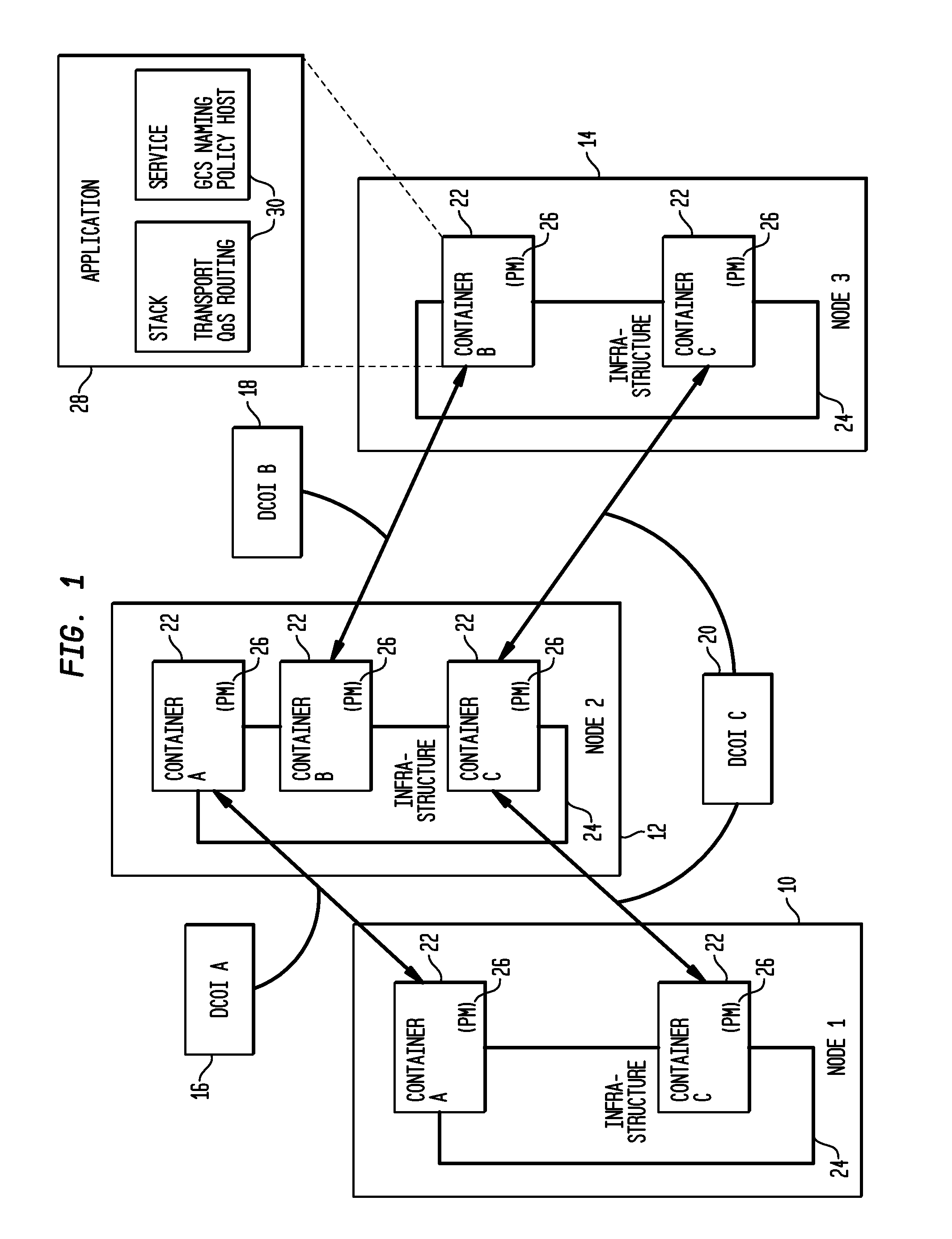
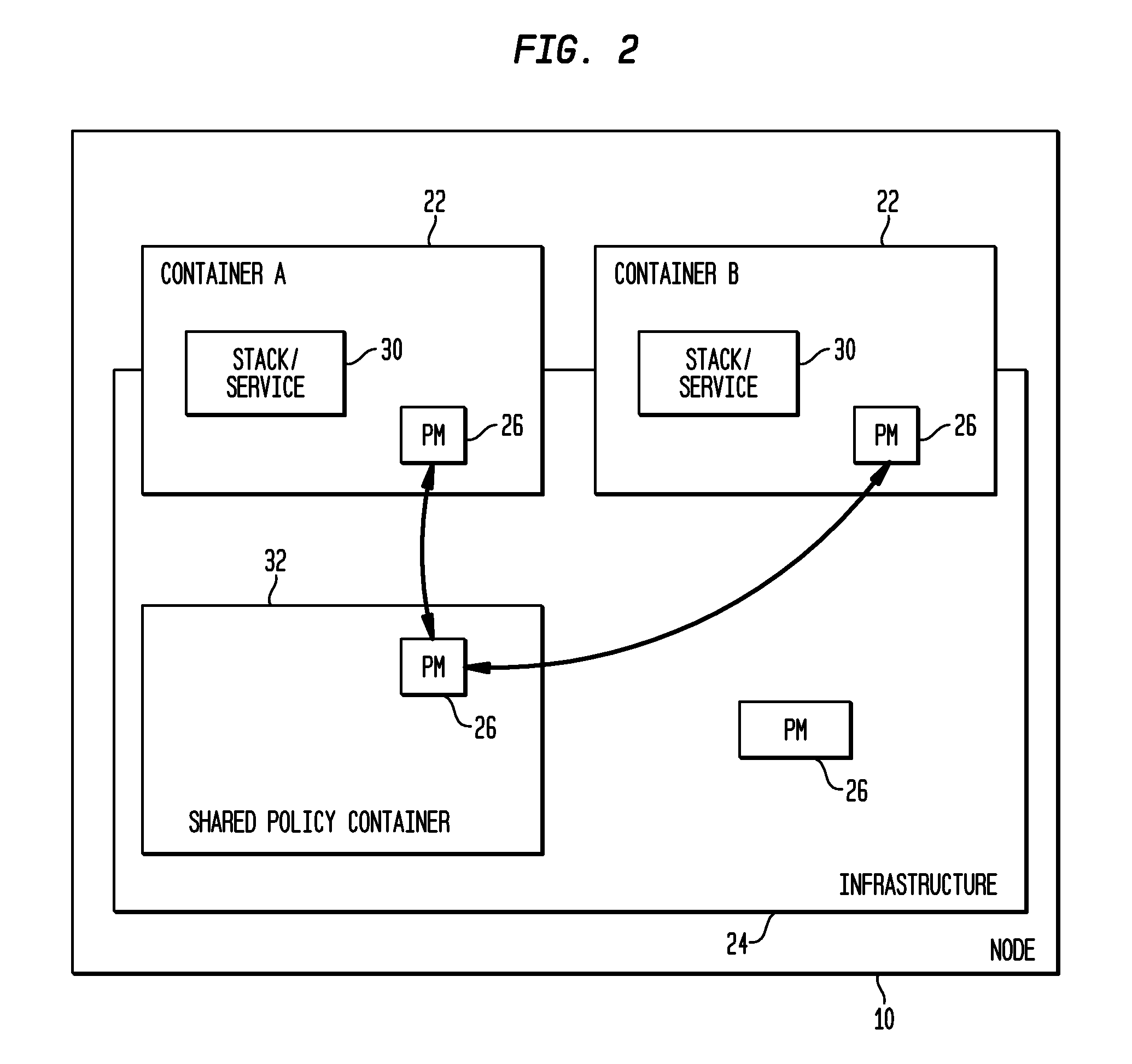
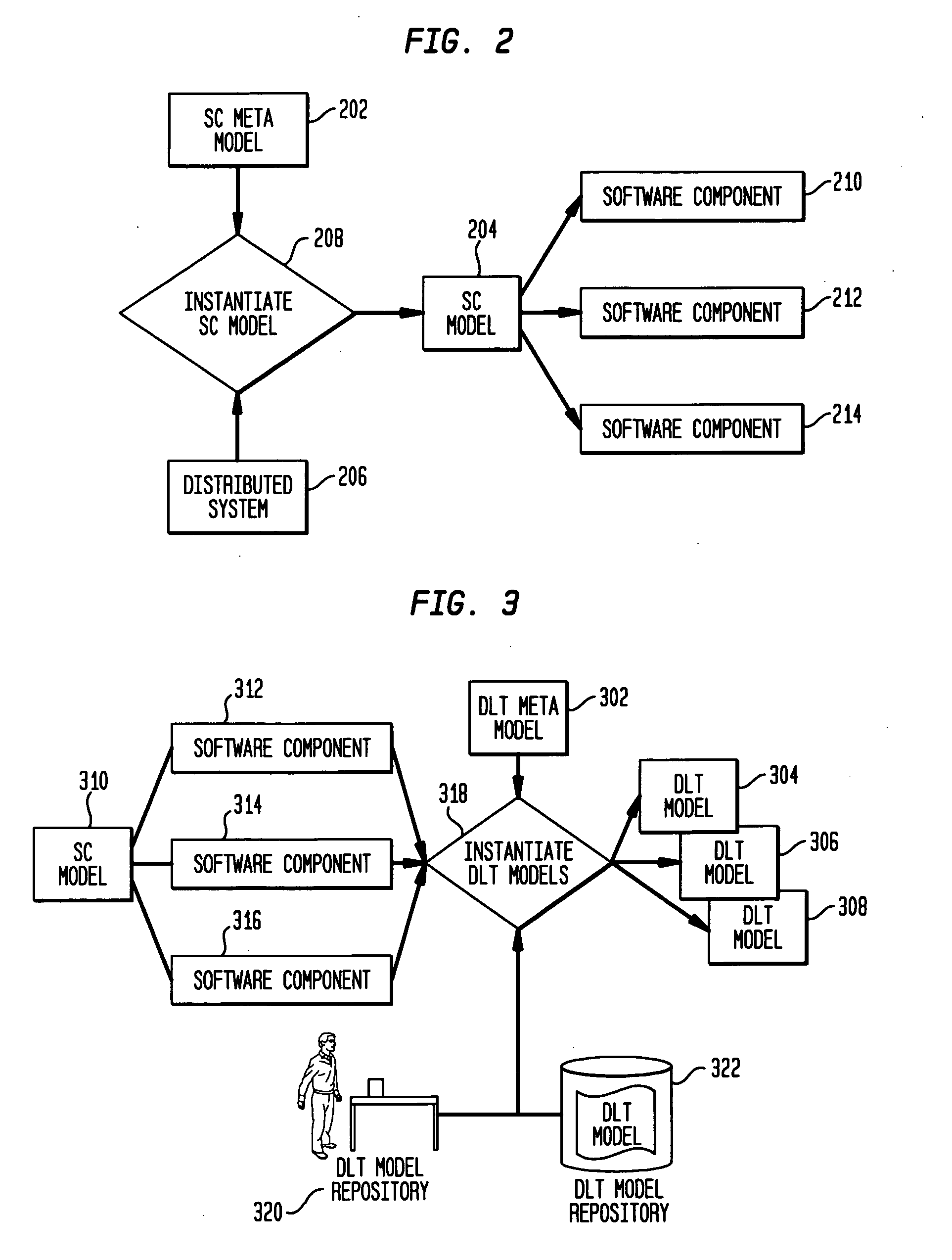
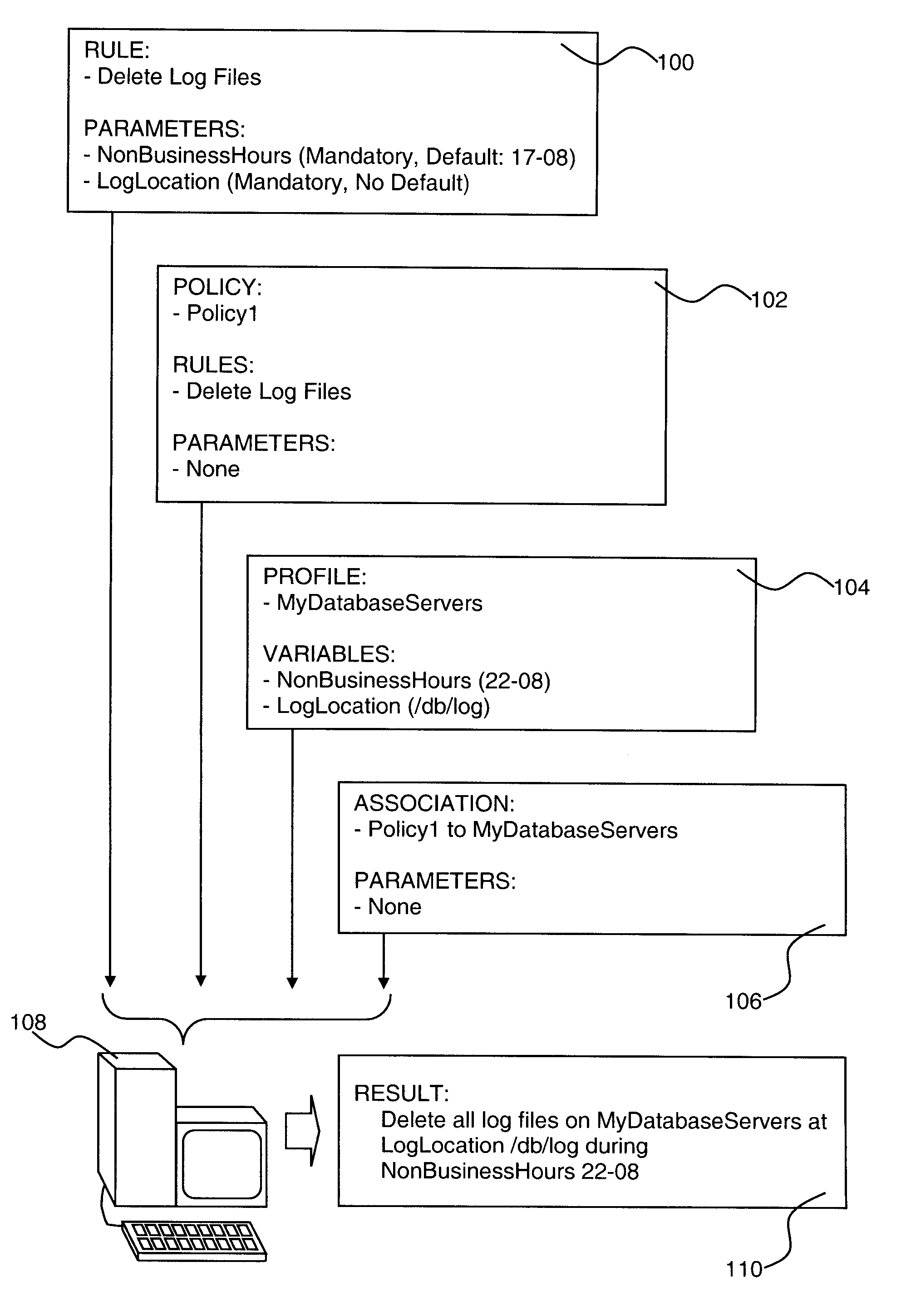
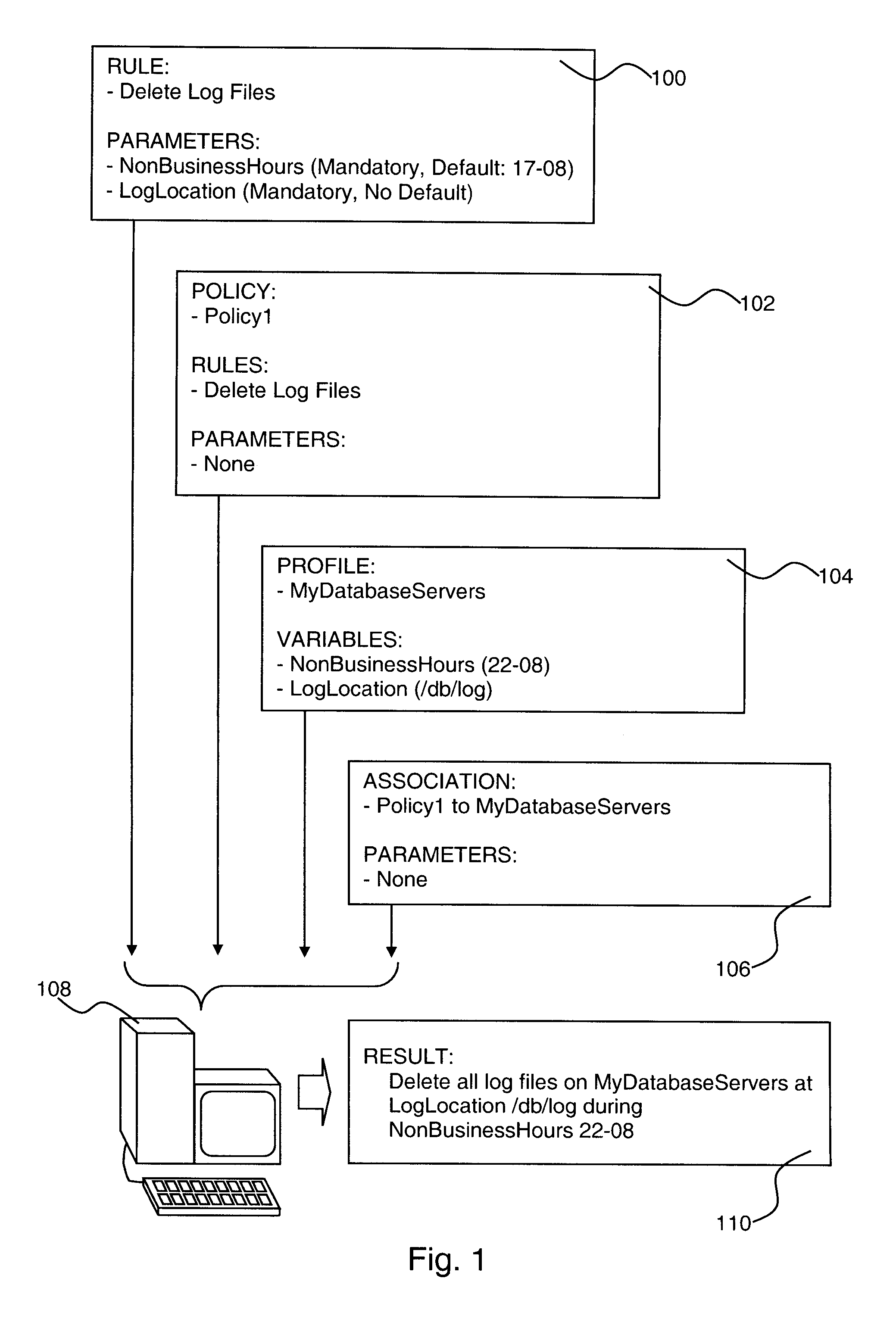
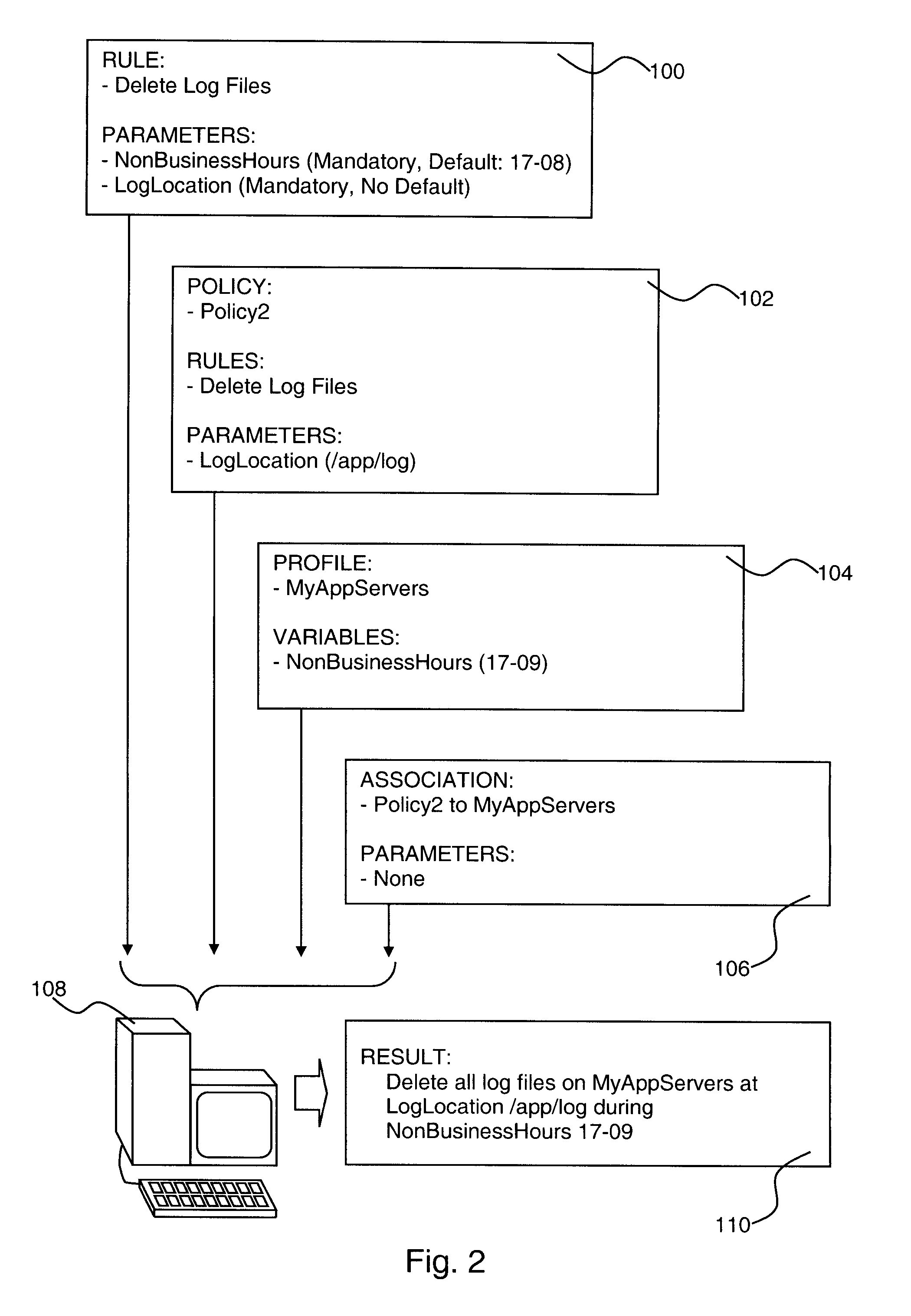
Policy-Based Management in a Computer Environment
A system for policy-based management in a computer environment, the system including at least one rule configured to be applied to an element of a computer environment, at least one policy including at least one of the rules, at least one profile including at least one element of the computer environment, at least one association defining a relationship between one of the policies and one of the profiles, and a computer configured to instaniate any of the associations, thereby invoking any of the rules included in the related policy for application to any of the elements in the related profile.
Owner:IBM CORP
Policy-based management of storage functions in data replication environments
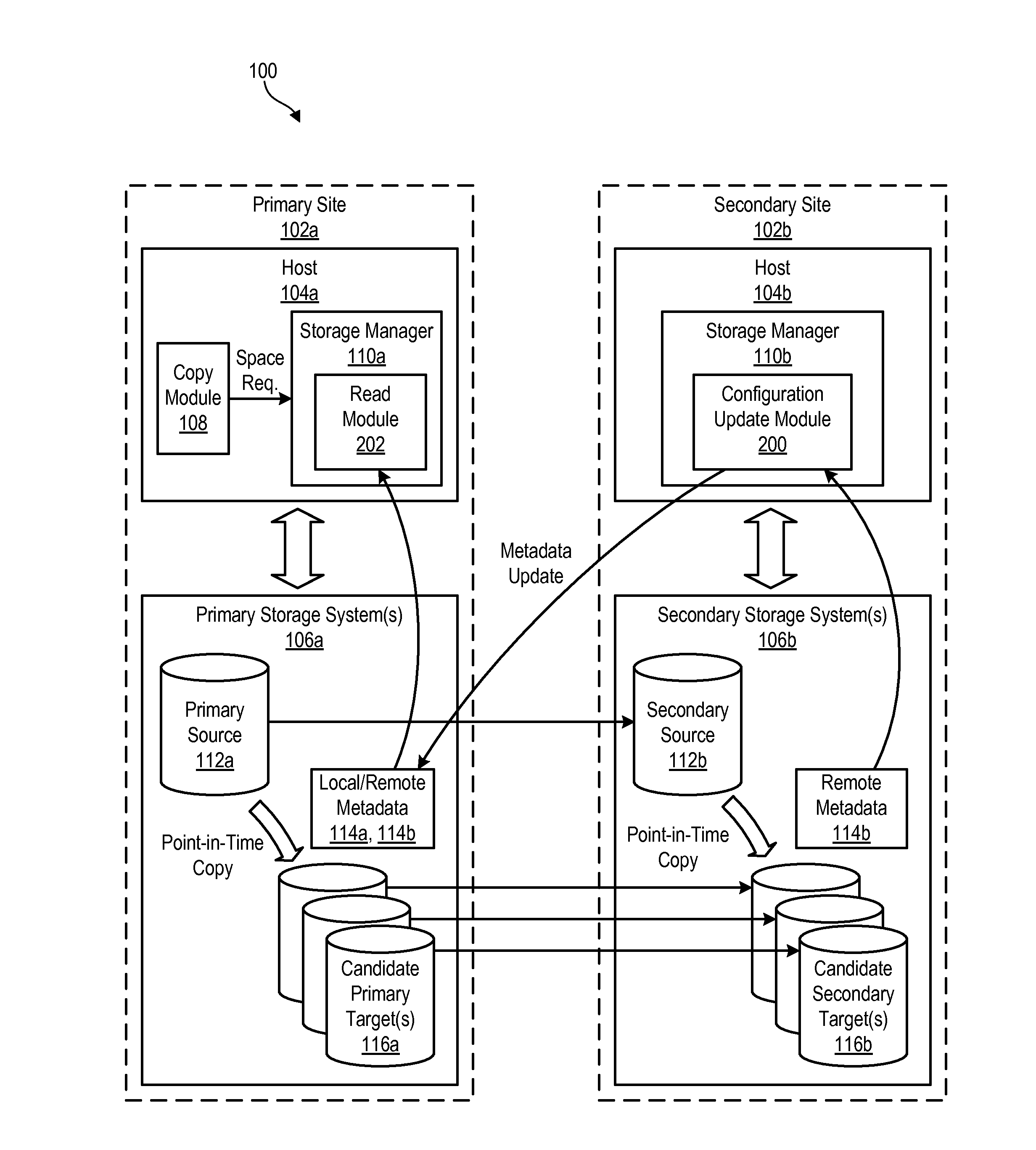
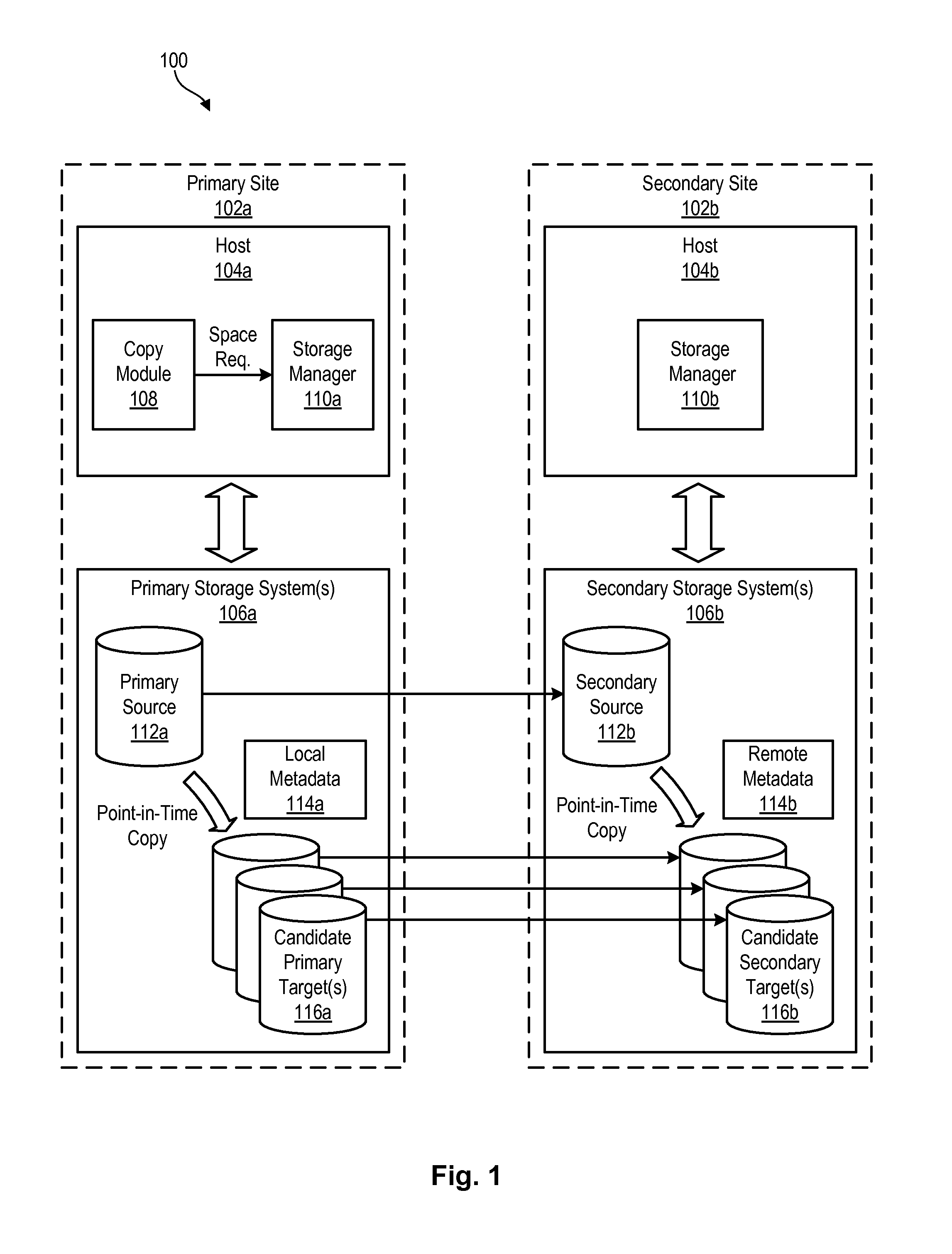
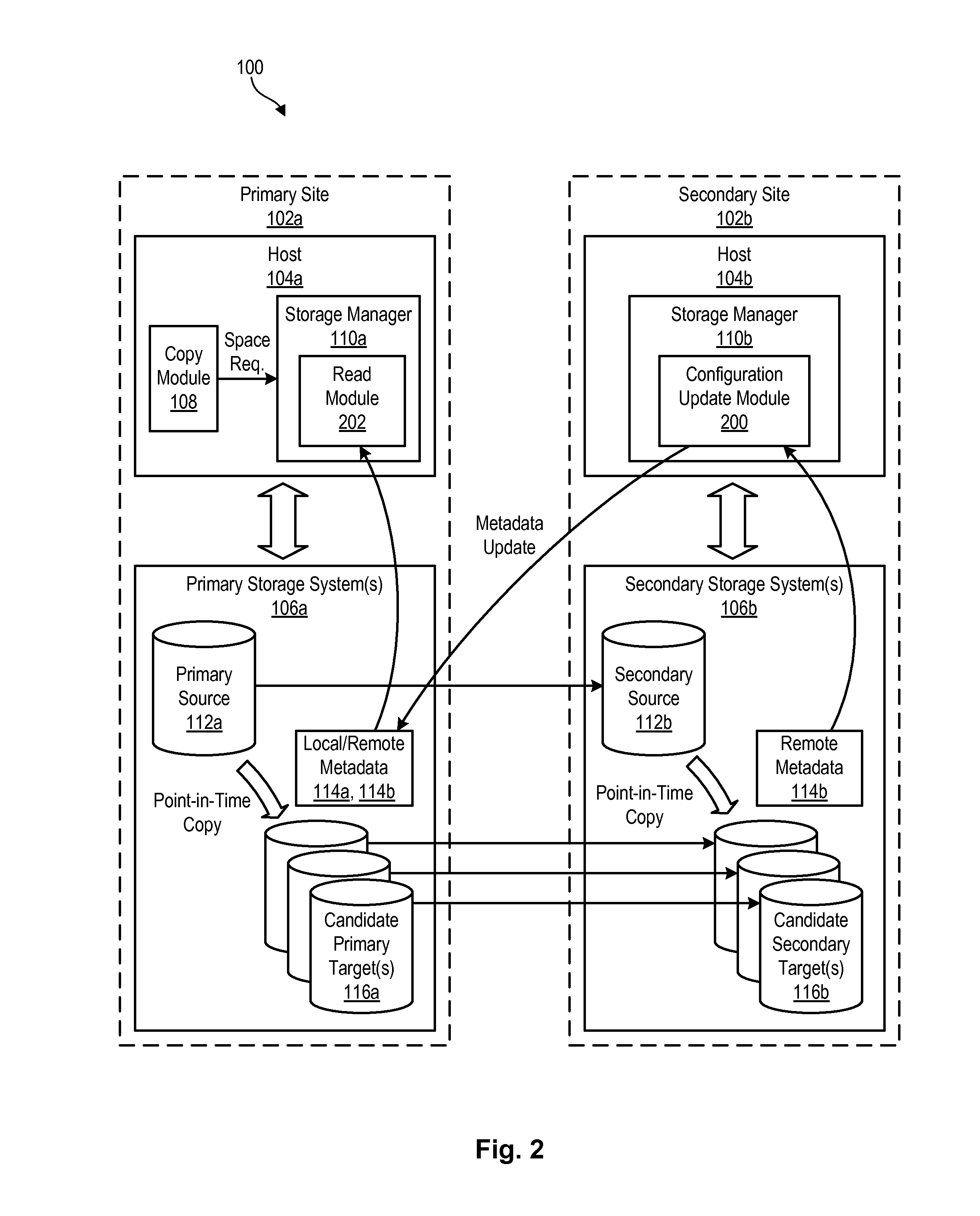
InactiveUS20130246367A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsCapability managementPrimary sites
A method for managing storage functions in a data replication environment is disclosed. In one embodiment, such a method includes continually monitoring for changes to a storage configuration at a secondary site. Upon detecting changes to the storage configuration at the secondary site, the method transmits remote metadata describing the changes to the primary site and stores the remote metadata at the primary site. The method then initiates a storage management function at the primary site which is mirrored to the secondary site. In order to perform the storage management function, the method reads the remote metadata at the primary site to determine the storage configuration at the secondary site. The method then performs the storage management function at the primary site in a way that takes into account the storage configuration at the secondary site. A corresponding apparatus, system, and computer-readable medium are also disclosed and claimed herein.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com