Catalytic hydrogenation method for olefin
A technology for catalytic hydrogenation and olefins, which is applied in the fields of hydrogenation to hydrocarbons, organic chemistry, and refined hydrocarbon oils. It can solve the problems of inconvenient heat extraction and additional separation steps, and achieve the goals of reducing energy consumption, simplifying the process flow, and saving production costs. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0026] The preparation method of the catalyst used in the present invention is simple, and it can be prepared only after uniformly mixing the above-mentioned main catalyst, co-catalyst, regulator and solvent. Generally speaking, when preparing the catalyst, the main catalyst and the co-catalyst are prepared into solutions with the selected solvent respectively, then the two are mixed, and the regulator is added. The order in which the components are added has little effect on the performance of the final catalyst, but catalyst preparation generally needs to be carried out under the protection of an anhydrous and oxygen-free inert atmosphere. The specific preparation method and conditions are similar to those of Ziegler-Natta catalysts known to those skilled in the art.
[0027] The method provided by the present invention can be applied to the hydrogenation reaction of various olefins, for example, the olefins can be olefins with double bonds at the terminal positions. Since ...
Embodiment 1
[0034] This example is used to illustrate the olefin hydrogenation method provided by the present invention.
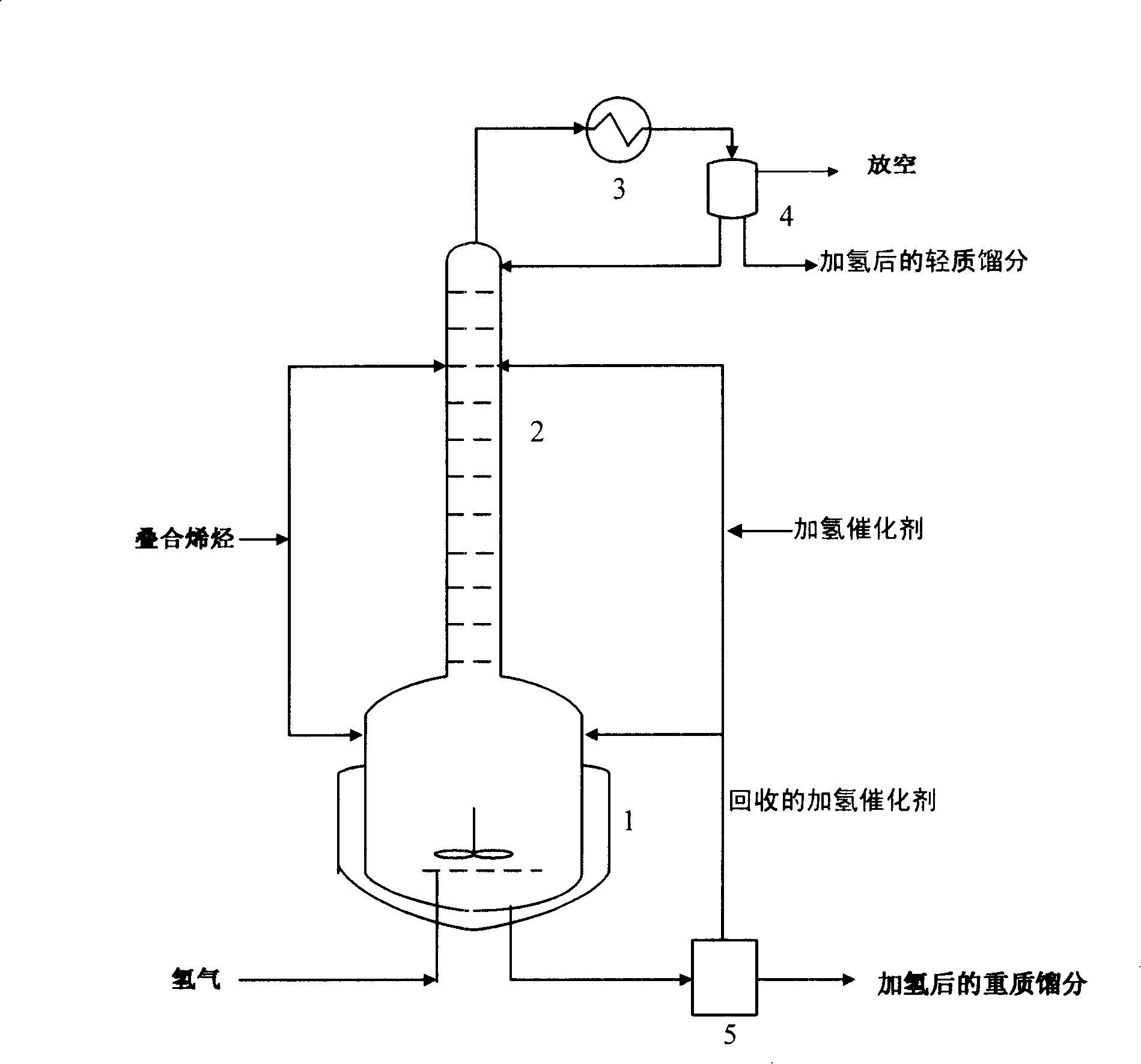
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the reactor is connected up and down by connecting a stainless steel reactor 1 with a volume of 2 liters and a diameter of Φ150 mm with a magnetically coupled stirring device with a stainless steel sieve tray tower 2 with a diameter of Φ50 mm and 28 plates. The top of the sieve tray column 2 is connected with a cooler 3 and a reflux tank 4 to obtain. The stainless steel reaction kettle 1 communicates with a settling separator 5 with a volume of 2 liters. C containing 150 μg / g Zigler-Natta-type nickel-based catalyst 4 Composite olefin enters the stainless steel sieve tray tower 2 from the 14th tray (with the first one near the cooler end as the first tray) at a speed of 2000 g / h, and is still separated from the 14th tray after separating the heavy product from the bottom of the tower. Each tray (with the uppermost one near the coole...
Embodiment 2
[0039] This example is used to illustrate the olefin hydrogenation method provided by the present invention.
[0040] Carry out C according to the method for embodiment 1 4 For the hydrogenation test of superimposed olefins, the difference is that 150 grams of amorphous nickel alloy catalyst (produced by Sinopec Jianchang Catalyst Branch Company, model SRNY-4) with a particle diameter of 50-150 microns is added to stainless steel reactor 1 middle. C after the stable operation of the reaction system 4 The flow rate and composition of superimposed olefin feedstock, hydrogenated light fraction and hydrogenated heavy fraction are shown in Table 2.
[0041] Table 2
[0042] C 4 Aligned Olefin Feedstock
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com