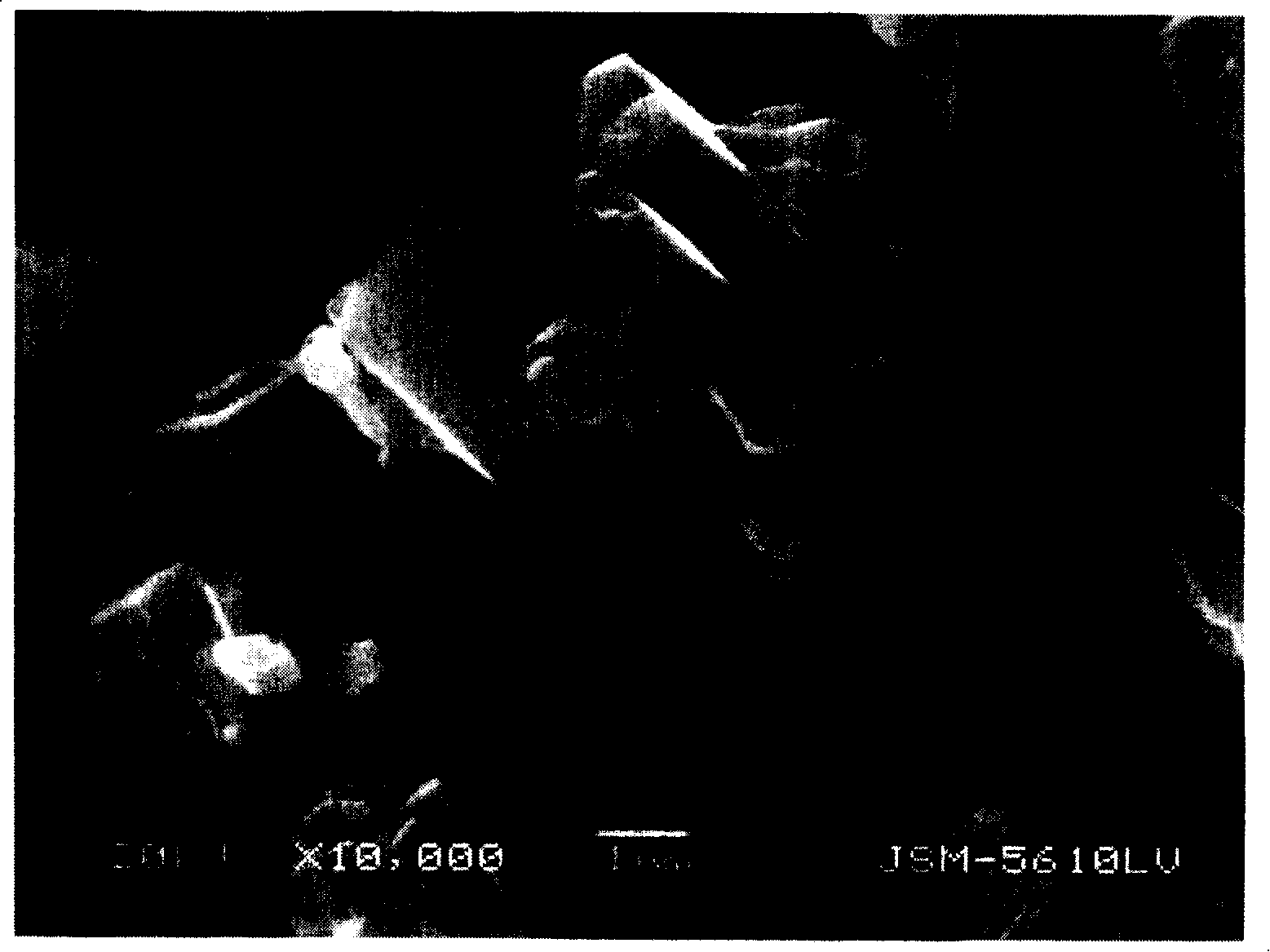
Method for preparing ferrous oxalate hydrated salt crystal
A technology of ferrous oxalate and oxalate, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, can solve the problems of large particle size and poor reactivity, and achieve the effect of good reactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0019] The method for preparing ferrous oxalate hydrate salt crystals provided by the present invention includes contacting and reacting an aqueous solution of oxalate with an aqueous solution of divalent iron salt, wherein the contact reaction between the oxalate solution and the solution of divalent iron salt is carried out in an organic solvent and It is carried out in the presence of a mixed solvent of water, and the organic solvent is completely miscible with water.
[0020] According to the preparation method provided by the present invention, the contact reaction of the oxalate aqueous solution and the divalent iron salt aqueous solution is to add the oxalate aqueous solution and the divalent iron salt aqueous solution to a mixed solvent of an organic solvent and water, respectively.
[0021] According to the preparation method provided by the present invention, the pH value at the end of the reaction between the oxalate aqueous solution and the divalent iron salt aqueous s...
Embodiment 1
[0037] Add 1.0 liter of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH) is miscible with 0.2 liters of water to make a mixed solvent (temperature 25°C). Dissolve 556 grams (2 moles) of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O), and add a small amount of sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 1.8. In addition, dissolve 368 grams (2 moles) of potassium oxalate monohydrate (K 2 C 2 O 4 ·H 2 O), and add a small amount of potassium hydroxide (KOH) aqueous solution to adjust the pH of the solution to 8.6. At a dropping rate of 50 ml / min, 2000 ml of potassium oxalate solution was dropped onto the ethanol mixed solvent over 40 minutes, and 2000 ml of ferrous sulfate solution was dropped onto the mixed solvent at the same rate over 40 minutes. With the dropping of potassium oxalate solution and ferrous sulfate solution, ferrous oxalate precipitated (temperature 25°C, pH 2.8).
[0038] Next, filtration is performed to recover ferrous oxalate, and the recovered ferrous oxalate is washed with 10 liters o...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Put 335 ml of ethanol (C 2 H 5 OH) is miscible with 65 ml of water to make a mixed solvent (temperature 25°C). Dissolve 556 grams (2 moles) of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O), and adding a small amount of sulfuric acid to adjust the pH of the solution to 2.0. In addition, dissolve 368 grams (2 moles) of potassium oxalate monohydrate (K 2 C 2 O 4 ·H 2 O), and add a small amount of potassium hydroxide (KOH) aqueous solution to adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0. At a dropping rate of 100 ml / min, 2000 ml of potassium oxalate solution was dropped into the ethanol mixed solvent over 20 minutes, and 2500 ml of ferrous sulfate solution was dropped into the mixed solvent at the same rate over 25 minutes. With the dropping of potassium oxalate solution and ferrous sulfate solution, ferrous oxalate was precipitated (temperature 25°C, pH 2.5).
[0043] Next, filtration is performed to recover ferrous oxalate, and the recovered ferrous oxalate is washed with 10 liters o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com