Method for preparing designable layered polymer base conductive composite material
A conductive composite material and polymer technology, which is applied in the field of polymer processing, can solve the problems that the electrical conductivity is difficult to be designed, and the conductive composite material is difficult to obtain a repeatable and controllable ideal shape structure, etc., to achieve simple and easy equipment high yield, low production cost, and improved elongation at break
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
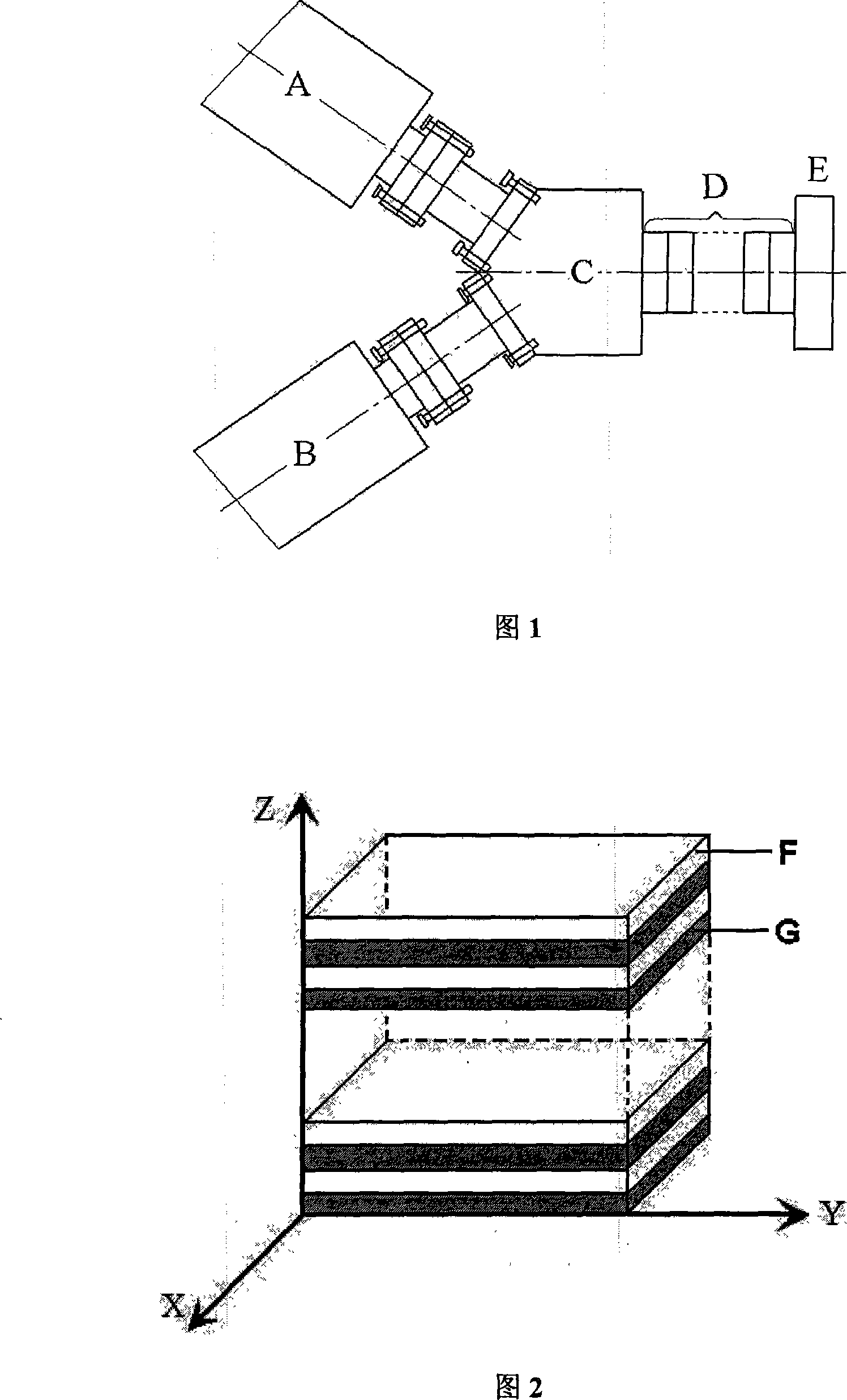
[0027] The raw materials are polypropylene and carbon black, the insulating layer and the conductive layer are pure polypropylene and carbon black filled polypropylene respectively. Firstly, common carbon black-filled polypropylene was prepared, with a carbon black content of 11%. After the polypropylene and carbon black were dried, they were melt-mixed and granulated in a twin-screw extruder. The conductive layer and insulating layer pellets are put into the two extruders of the layered co-extrusion device respectively. The extruder speed ratio is 1:1. The temperature of each section of the extruder is controlled between 170-200 °C. The temperature of the stacking unit and the exit mold are both 200°C. Using two stacking units, the melt of the conductive composite product flows out of the exit mold under the traction of the traction device, and after being cooled by the cooling device, an 8-layer layer is prepared Polypropylene-based conductive composites. The resistivity of...
Embodiment 2
[0029]The raw materials are polyethylene and carbon black, and the insulating layer and conductive layer are respectively pure polyethylene and carbon black filled polyethylene. First, ordinary carbon black-filled polyethylene was prepared, with a carbon black content of 11%. After the polyethylene and carbon black were dried, they were melt-mixed and granulated in a twin-screw extruder. The conductive layer and insulating layer pellets are put into the two extruders of the micro-layer co-extrusion device respectively. The extruder speed ratio is 2:1. The temperatures of the lamination unit and the outlet die were both 200°C, and a 4-layer layered polyethylene-based conductive composite was prepared using one lamination unit. The resistivity of the material is 5.02×10 3 Ω·cm, PTC strength is 3.26, elongation at break is 316%. As a comparison, the resistivity and elongation at break of the traditional polyethylene-based conductive composite with the same carbon black content ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] The raw materials are polypropylene and carbon black, the insulating layer and the conductive layer are pure polypropylene and carbon black filled polypropylene respectively. First prepare ordinary carbon black-filled polypropylene with carbon black content of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 18, 22, 30% respectively: after drying polypropylene and carbon black, extrude Melt mixing and granulation in the machine. The conductive layer and insulating layer pellets are put into the two extruders of the micro-layer co-extrusion device respectively. The extruder speed ratio is 1:1. The temperatures of the lamination unit and the outlet die were both 200°C, and a 4-layer layered polypropylene-based conductive composite was prepared using one lamination unit. The percolation value for this material is approximately 5.0 wt%. For comparison, the percolation value of conventional polypropylene-based conductive composites is about 7.0 wt%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com