Quantum point-trap infrared detector structure and method for producing the same
A technology of infrared detectors and quantum dots, applied in semiconductor devices, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve problems such as low quantum efficiency of devices, large dark current, and increased costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
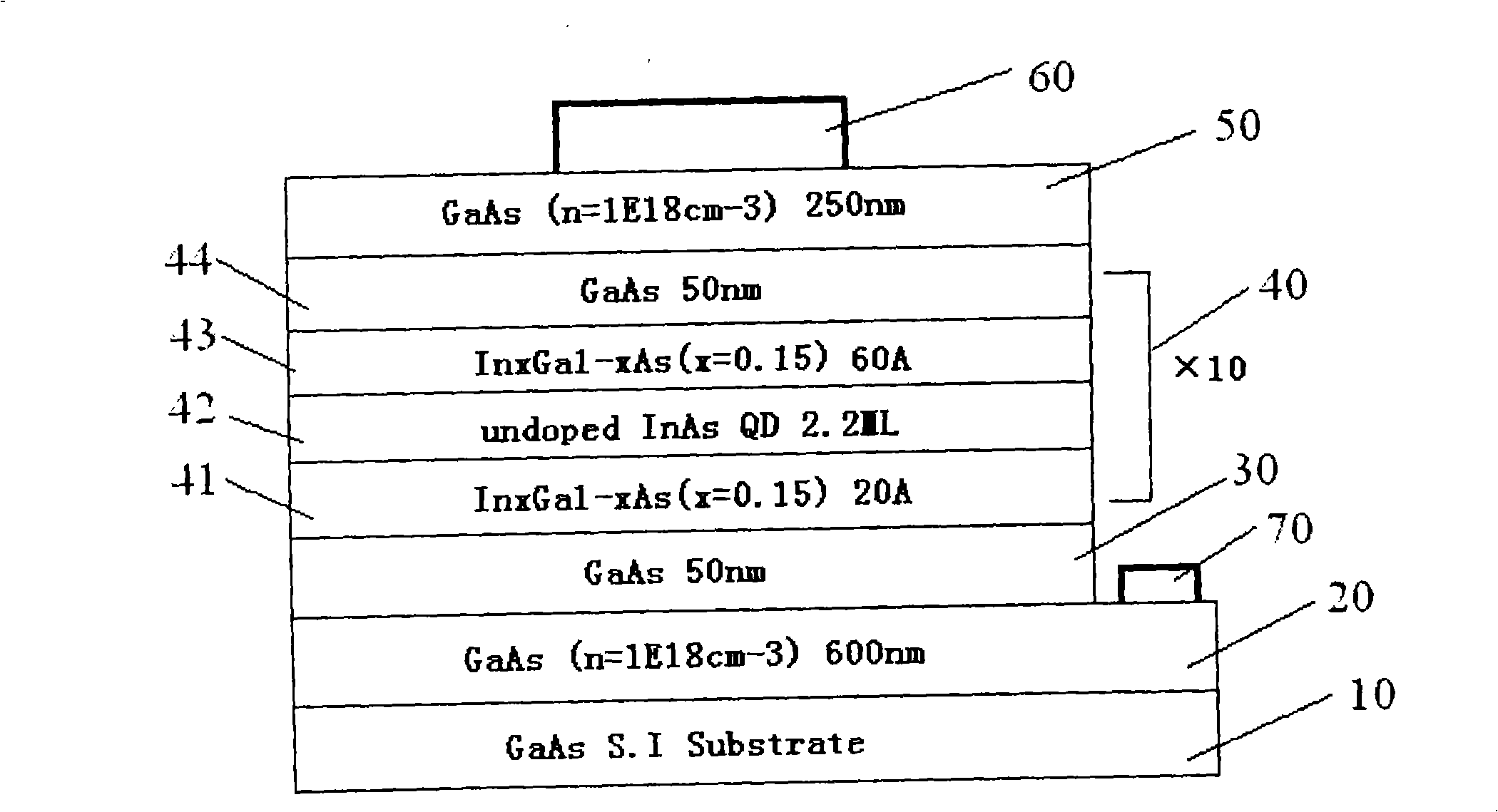
[0045] figure 1 It is the core idea of the present invention, that is, it is used in the growth process of the quantum dot-well structure infrared detector.
[0046] (1) First grow a highly doped GaAs bottom contact layer 20 on a semi-insulating GaAs substrate 10; the doping element is Si, and the doping concentration is 1×1018 / cm 3, the growth temperature is 580°C, and the thickness is 600nm. The purpose of doping the GaAs bottom contact layer 20 with a high concentration is to form a good ohmic contact with the electrode material AuGe / Ni / Au instead of a Schottky contact when the lower electrode 70 is fabricated later. The relatively thick 600nm growth is to facilitate the etching operation in the subsequent device manufacturing process;
[0047] (2) Then grow an undoped lower GaAs spacer layer 30 on the highly doped GaAs bottom contact layer 20 at a growth temperature of 580° C. and a thickness of 50 nm. The purpose of growing the undoped lower GaAs isolation layer 30 i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com