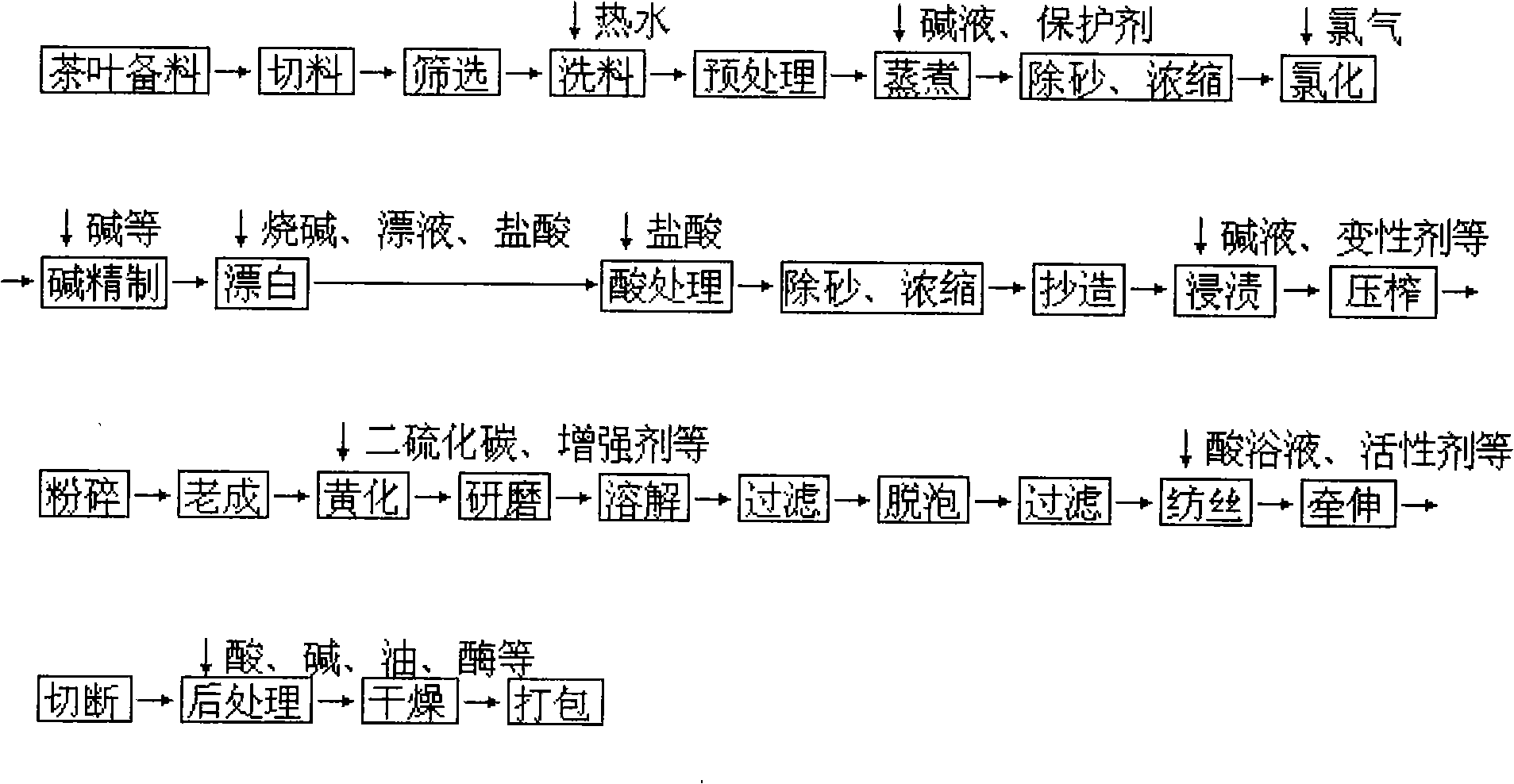
Production process for tea viscose fiber
A viscose fiber and production process technology, applied in fiber treatment, biochemical fiber treatment, fiber raw material treatment, etc., can solve the problems of drug allergic reaction, failure to achieve health care purposes, loss, etc., and achieve abundant storage and long-lasting radiation resistance The effect of sexual growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] (1) Pretreatment: liquid ratio: 1:2.5; temperature 160°C; time 180 minutes.
[0082] (2) Cooking: amount of alkali used: 8% of absolute dry pulp in terms of NaOH; liquid ratio: 1:4; H 2 o 2 : 1% for absolute dry pulp; oxygen pressure: 0.70Mpa; protective agent HHT: 0.2‰ for absolute dry pulp; total heating time: 150 minutes; holding temperature: 125°C; holding time: 11 hours.
[0083] (3) Chlorination: amount of chlorine used for chlorination: 1% of absolute dry pulp; chlorination pulp concentration: 3.2%; chlorination time: 60 minutes; chlorination temperature: normal temperature.
[0084] (4) Alkali refining: pulp concentration: 5%; NaOH dosage: 2% of absolute dry pulp amount; refining temperature: 90°C; H 2 o 2 : 0.5% of absolute dry pulp; oxygen flow rate: 0.4% of absolute dry pulp; time: 100 minutes.
[0085] (5) Bleaching:
[0086] The pH of the first section is 9; chlorine consumption: 1% relative to absolute dry pulp; temperature: 38°C; time: 180 minutes. ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] (1) Pretreatment: liquid ratio: 1:3; temperature 170°C; time 150 minutes.
[0113] (2) Cooking: amount of alkali used: 13% of absolute dry pulp in terms of NaOH; liquid ratio: 1:5; H 2 o 2 : 2% for absolute dry pulp; oxygen pressure: 0.80Mpa; protective agent HHT: 0.8‰ for absolute dry pulp; total heating time: 200 minutes; holding temperature: 128°C; holding time: 8.5 hours.
[0114] (3) Chlorination: Chlorine amount for chlorination: 2.5% to absolute dry pulp volume; Chlorination pulp concentration: 3.0%; Chlorination time: 50 minutes; Chlorination temperature: normal temperature.
[0115] (4) Alkali refining: pulp concentration: 8%; NaOH dosage: 4% of absolute dry pulp amount; refining temperature: 80°C; H 2 o 2 : 1% of absolute dry pulp; oxygen flow rate: 0.5% of absolute dry pulp; time: 80 minutes.
[0116] (5) Bleaching:
[0117] The pH of the first section is 10; the amount of chlorine used: 2% relative to the absolute dry pulp; temperature: 37°C; time: 130 ...
Embodiment 3
[0143] (1) Pretreatment: liquid ratio: 1:3.5; temperature 180°C; time 100 minutes.
[0144] (2) Cooking: amount of alkali used: 16% of absolute dry pulp in terms of NaOH; liquid ratio: 1:6; H 2 o 2 : 3% for absolute dry pulp; oxygen pressure: 0.90Mpa; protective agent HHT: 1.5‰ for absolute dry pulp; total heating time: 240 minutes; holding temperature: 132°C; holding time: 6 hours.
[0145] (3) Chlorination: Chlorine amount for chlorination: 4% to absolute dry pulp volume; Chlorination pulp concentration: 2.8%; Chlorination time: 40 minutes; Chlorination temperature: normal temperature.
[0146] (4) Alkali refining: pulp concentration: 10%; NaOH dosage: 6% of absolute dry pulp amount; refining temperature: 70°C; H 2 o 2 : 1.5% of absolute dry pulp; oxygen flow rate: 0.6% of absolute dry pulp; time: 60 minutes.
[0147] (5) Bleaching:
[0148] The pH of the first section is 11; the amount of chlorine used: 3% relative to the absolute dry pulp; temperature: 35°C; time: 180...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| dry strength coefficient of variation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com