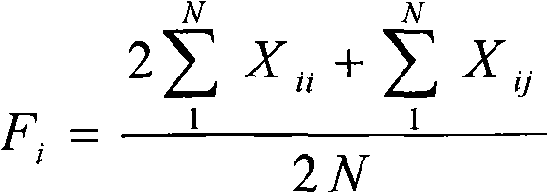Method for identifying indica rice and japonica rice by inserting or deleting molecular marker in rice DNA
A technology of molecular markers and DNA sequences, applied in the field of identification of indica and japonica rice, can solve the problems that affect the efficiency of indica and japonica rice identification, time-consuming, inaccurate detection results, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
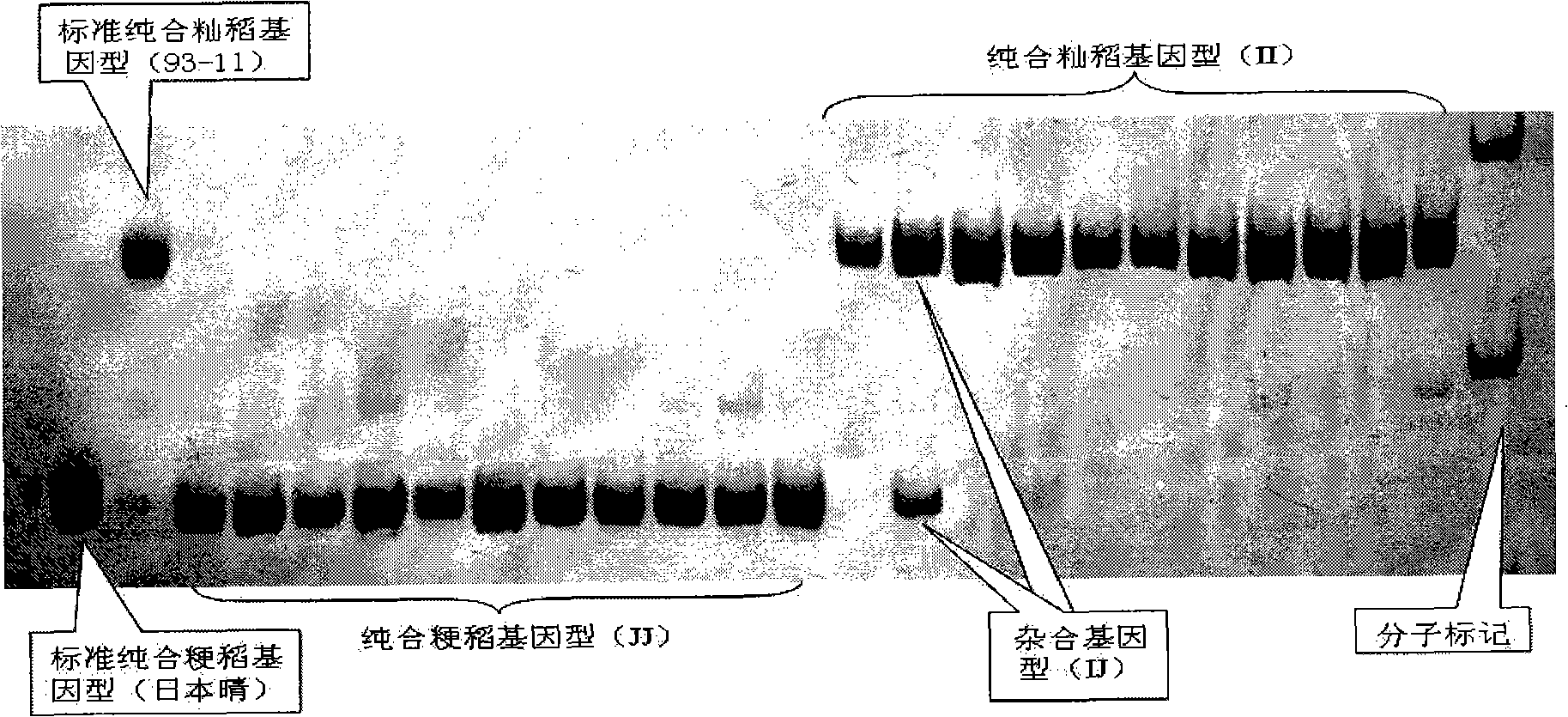
[0043] InDel molecular markers were used to identify 10 typical indica and 10 typical japonica rice varieties determined by "Cheng's index method".
[0044] Table 1. Embodiment 1 identification experimental material:
[0045]
[0046]
[0047] The reaction system used is as follows:
[0048] The PCR reaction conditions and procedures are as follows: (20 μl system):
[0049] 1) 10×PCR buffer (containing 25mM MgCl 2 ) 2μl
[0050] 2) 2.5mM dNTP Mixture 1.6μl
[0051] 3) 1μl of 10μM PCR primers
[0052] 4) 1U Taq DNA Polymerase 0.2μl
[0053] 5) DNA template 20ng
[0054] 6)ddH 2 O (double distilled water) to make up to 20μl
[0055] PCR reaction program:
[0056] 1) Pre-denaturation at 94°C for 4 minutes
[0057] 2) Denaturation at 94°C for 40 seconds
[0058] 3) Annealing temperature: 52-58°C, annealing time: 30-45 seconds
[0059] 4) Extend at 72°C for 40 seconds
[0060] 5) The cycle steps are 2) 3) 4), 36 cycles
[0061] 6) Extend at 72°C for 10 minutes
...
Embodiment 2
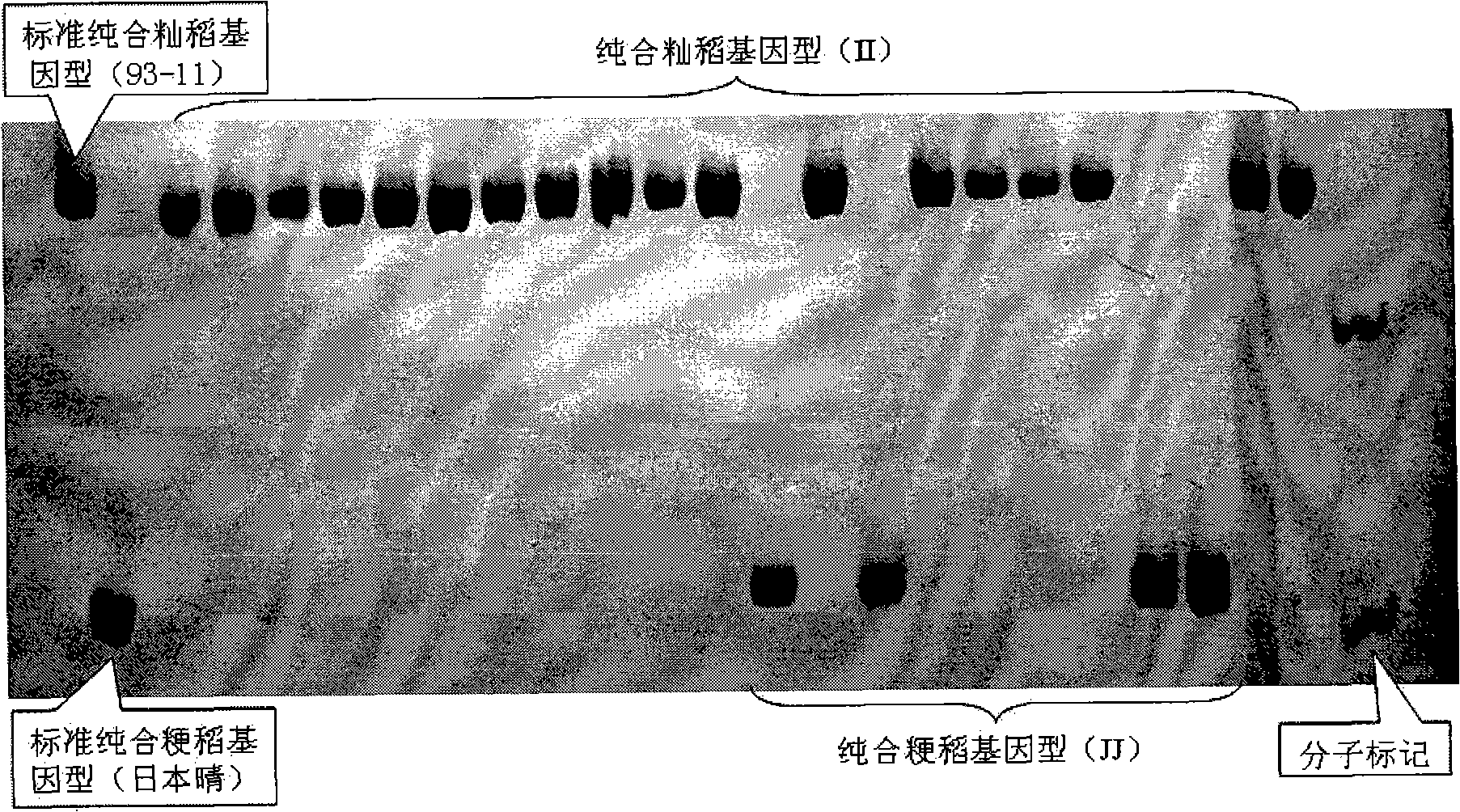
[0068] Identification of rice varieties with unknown indica and japonica characteristics using InDel molecular markers. Twenty samples were randomly selected from China, Bangladesh, India, Japan, Laos, Thailand and Malaysia for identification of indica or japonica rice.
[0069] Table 2. Embodiment 2 identification experimental materials:
[0070]
[0071]
[0072] The reaction system used is as follows:
[0073] The PCR reaction conditions and procedures are as follows: (20 μl system):
[0074] 1) 10×PCR buffer (containing 25mM MgCl 2 ) 2μl
[0075] 2) 2.5mM dNTP Mixture 1.6μl
[0076] 3) 10μM PCR primer 1μl
[0077] 4) 1U Taq DNA Polymerase 0.2μl
[0078] 5) DNA template 20ng
[0079] 6)ddH 2 O (double distilled water) to make up to 20μl
[0080] PCR reaction program:
[0081] 1) Pre-denaturation at 94°C for 4 minutes
[0082] 2) Denaturation at 94°C for 40 seconds
[0083] 3) Annealing temperature: 52-58°C, annealing time: 30-45 seconds
[0084] 4) Extend...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com