Drug eluting vascular closure devices and methods
A blood vessel and blood vessel wall technology, applied in the field of drug-eluting blood vessel closure devices for hemostasis at blood vessel puncture points, can solve problems such as serious complications, substances entering the bloodstream, dependence, etc., and achieve the effects of complete hemostasis and reduction of bleeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
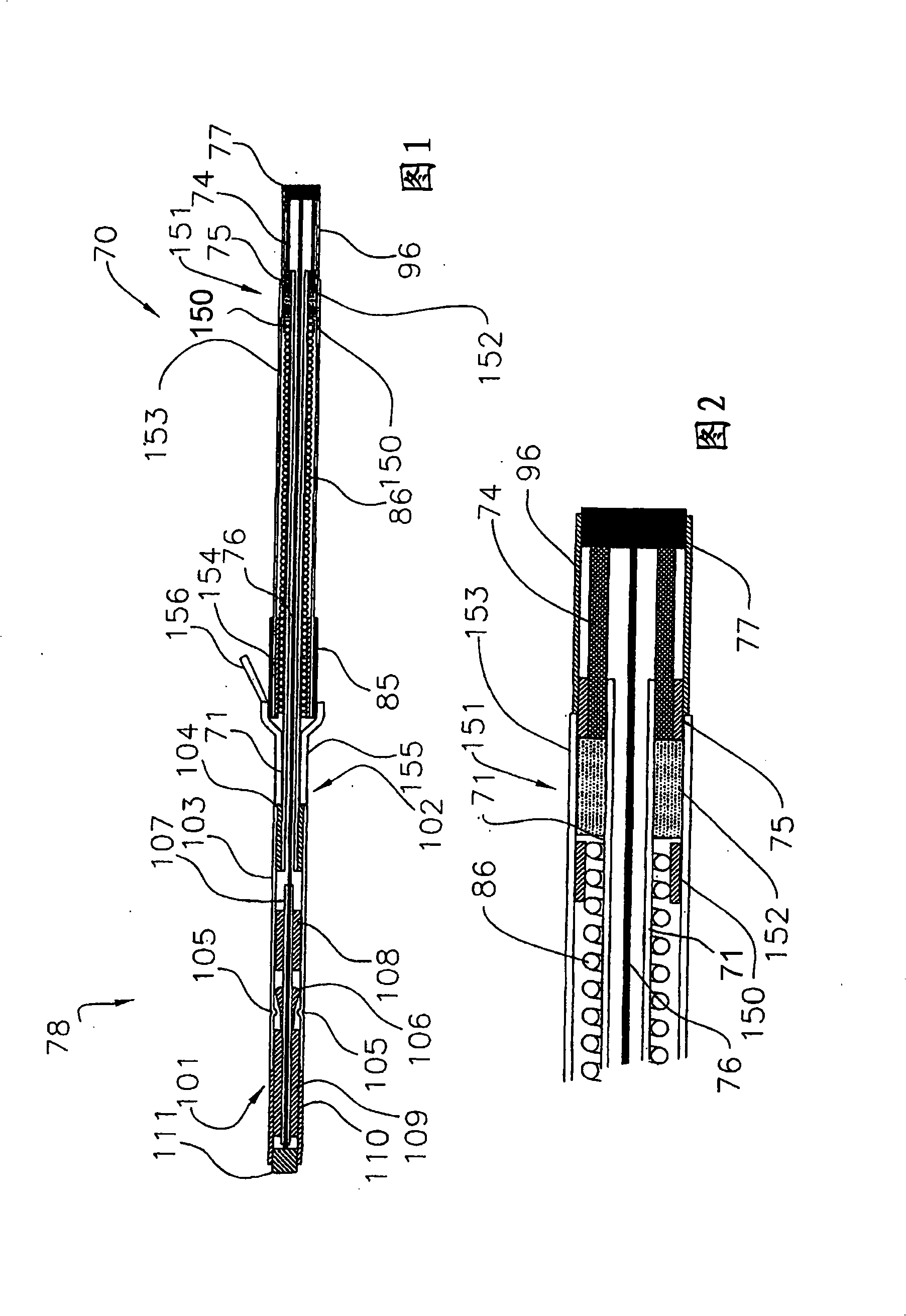
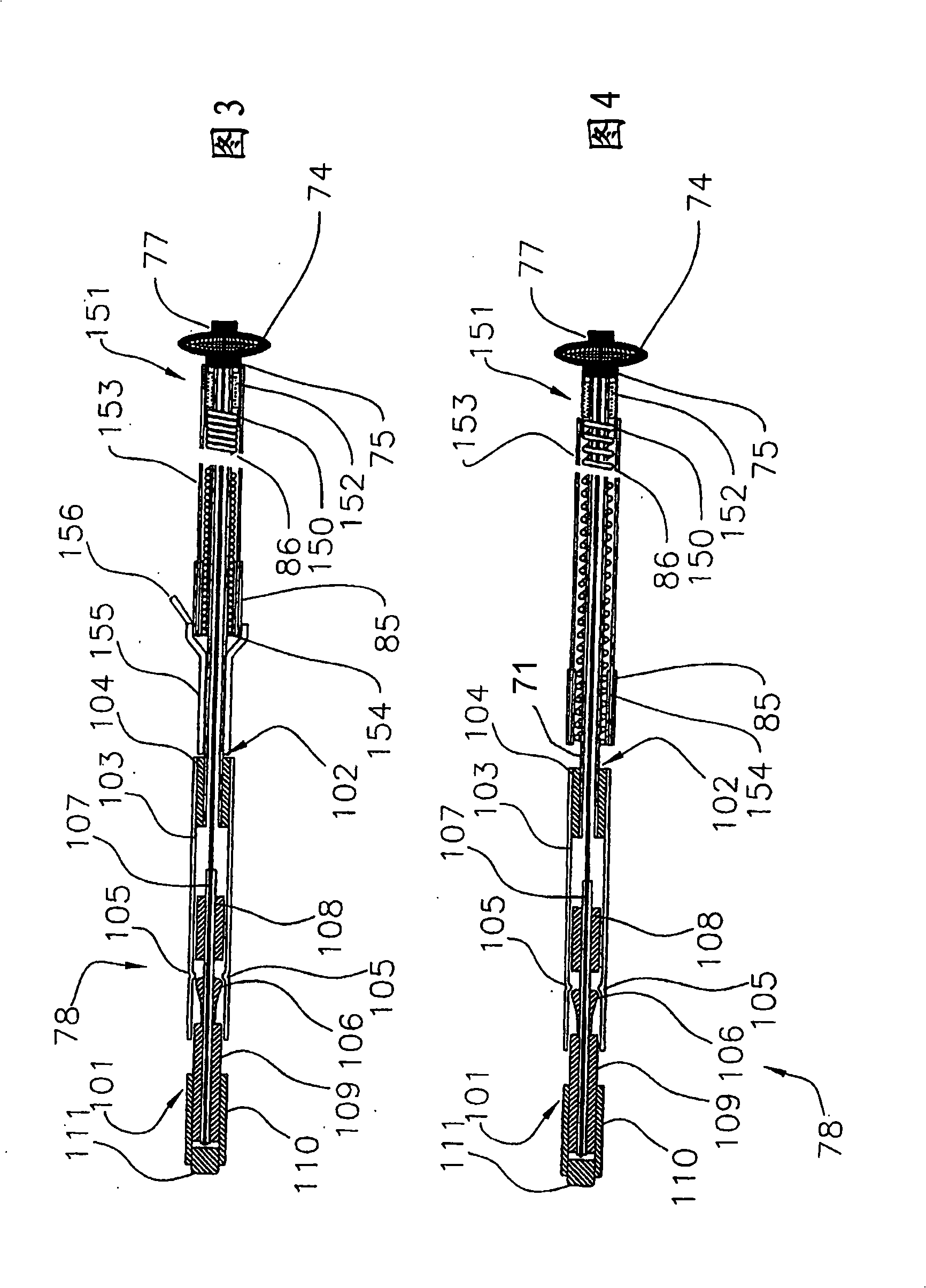
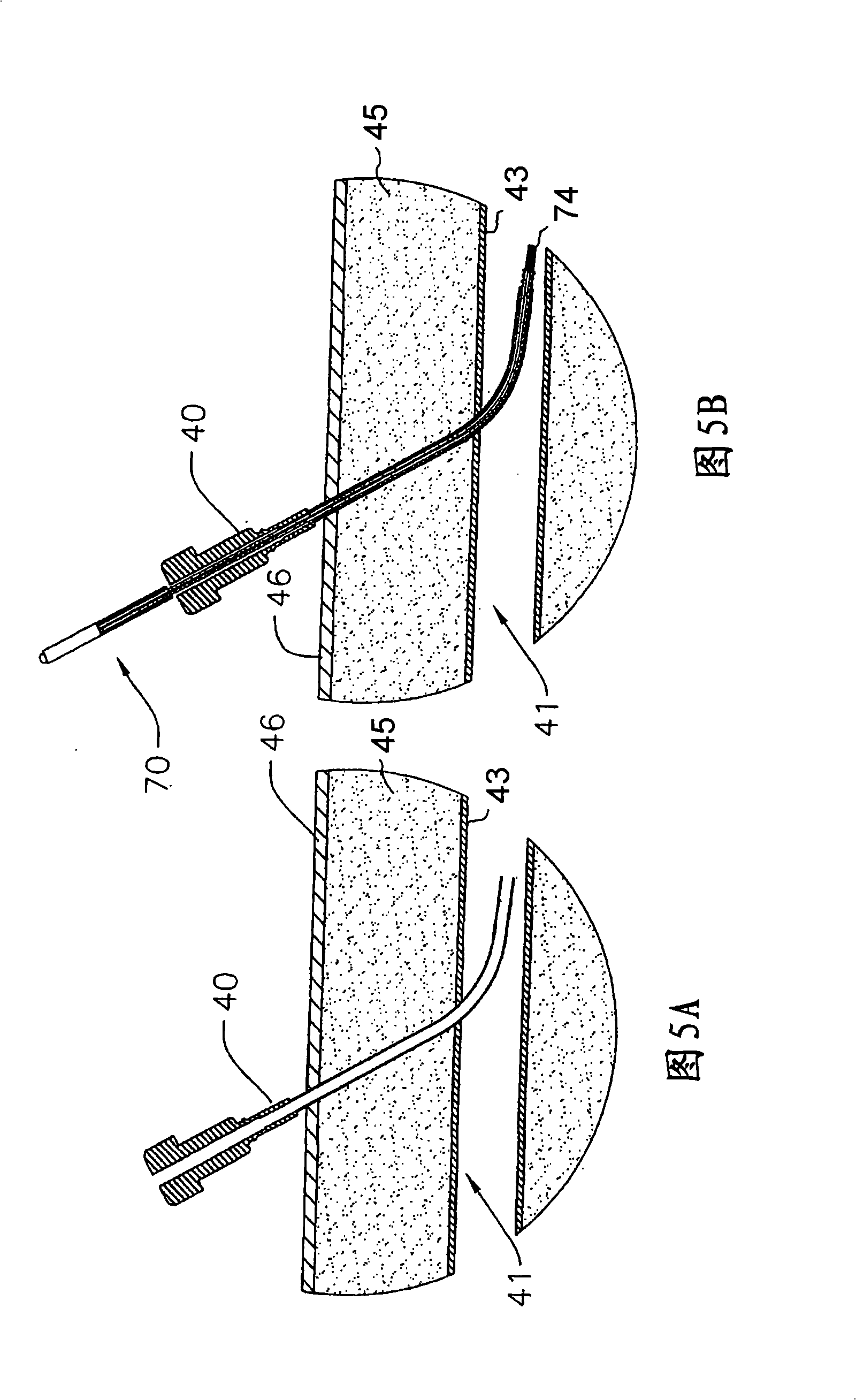
[0037] Referring now to FIG. 1 , there is shown a first embodiment of a drug-eluting, self-tensioning vaso-occlusive device 70 for hemostasis at a vascular puncture site, wherein at least one biochemical agent 152 is in a biochemical region or chamber 151 in combination with device as a whole. The device 70 typically consists of stainless steel coiled tubing or, for example, nylon, polyurethane, polyimide, PEEK 、PEBAX A first flexible elongated tubular element 71 formed of a polymer material such as the like. Tubular member 71 may have a length ranging from about 5 cm to about 50 cm, typically from about 10 cm to about 30 cm, and a diameter ranging from about 0.25 mm to about 5 mm, typically from about 0.5 mm to about 2 mm. An expandable occlusive element 74 is placed on the distal end of the tubular element 71 . Biochemical sealing element 153 is slidably positioned over tubular element 71 and adjacent expandable element 74 . A biochemical region 151 containing a bioche...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com