Capacitance single mass three-shaft acceleration transducer and preparation method
A shaft acceleration and single-mass technology, applied in piezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devices, televisions, generators/motors, etc., can solve problems such as high packaging complexity, increased process difficulty, and large chip area , to achieve the effect of avoiding quadrature mismatch error, good off-axis sensitivity characteristics, and reducing sensor area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
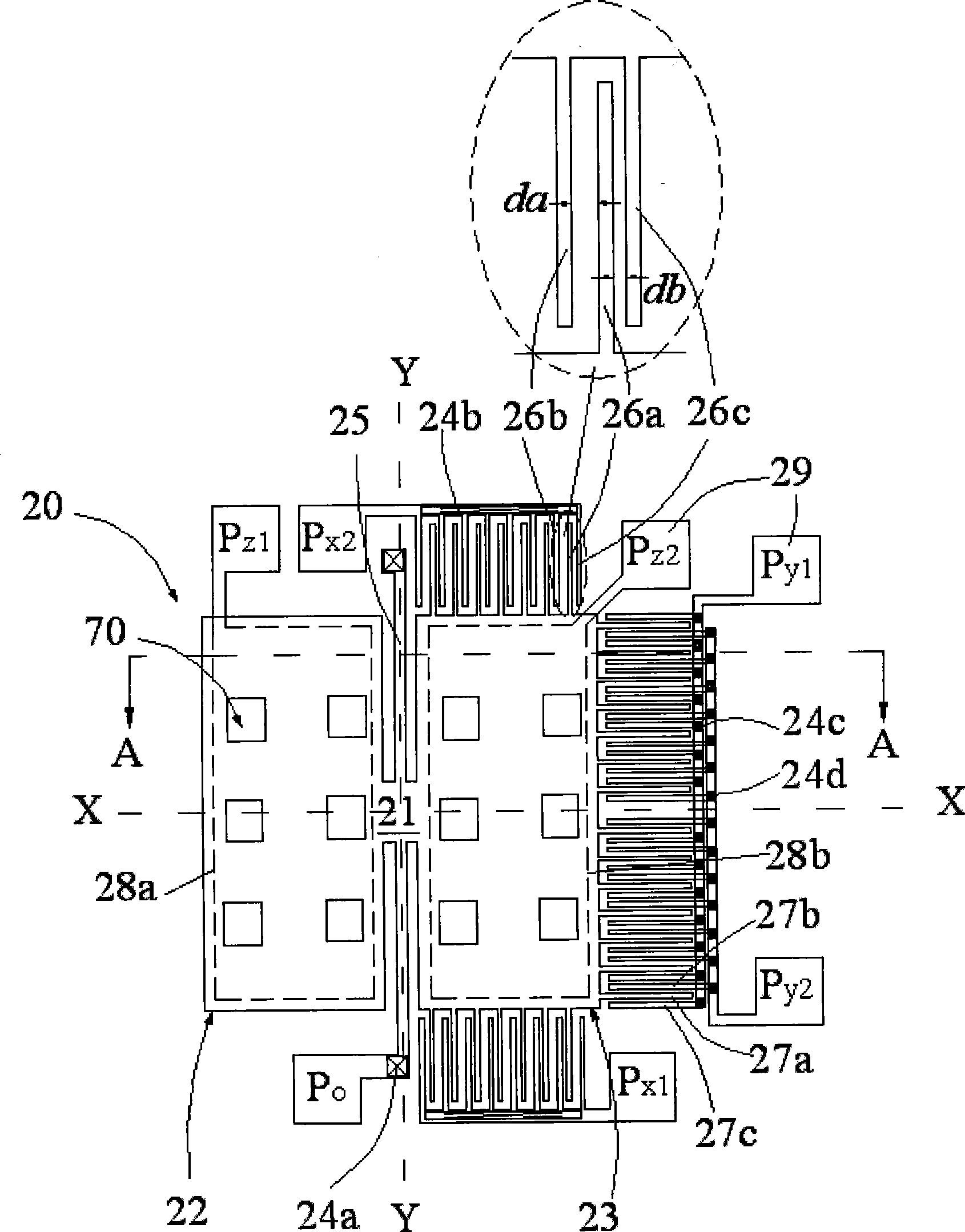
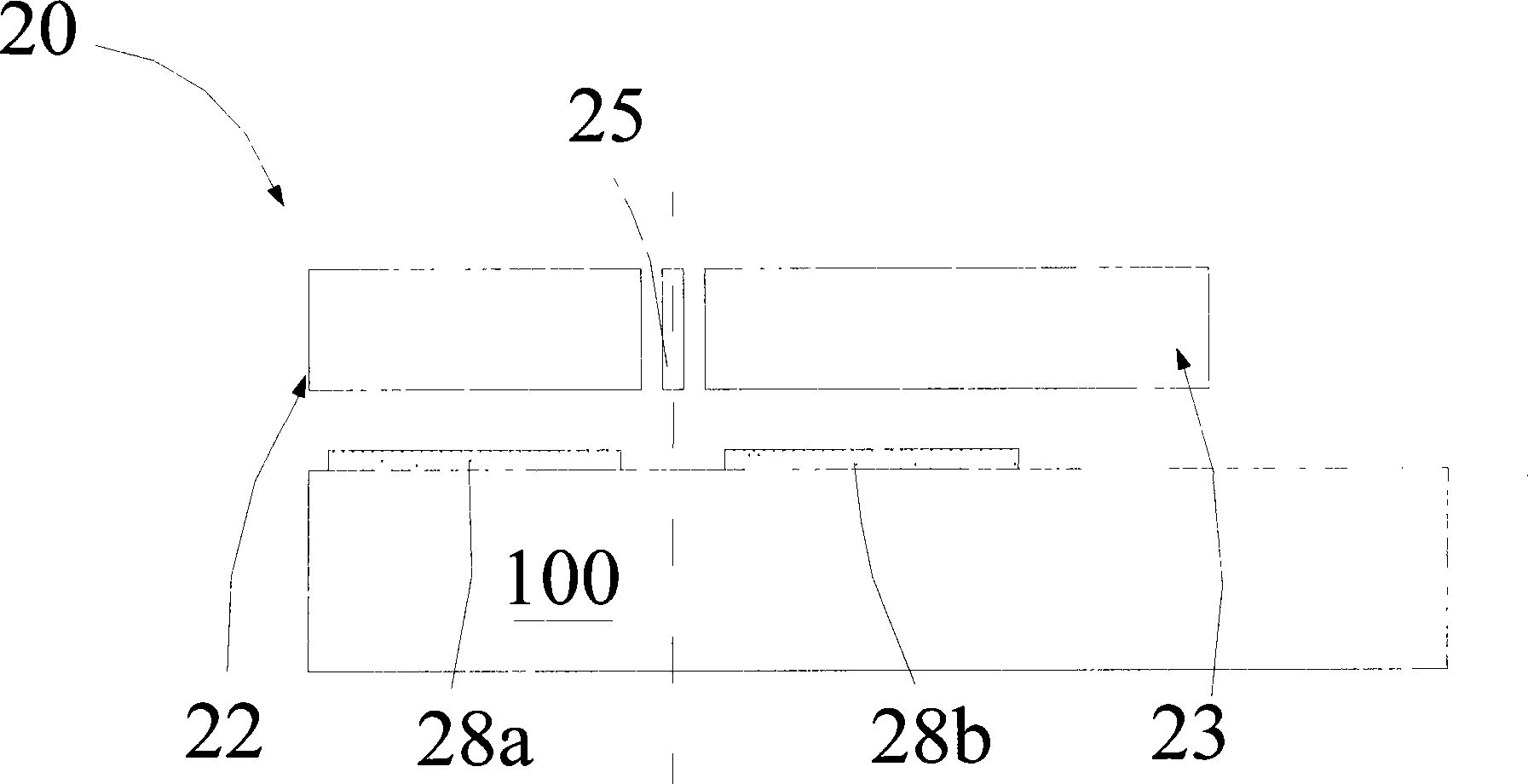
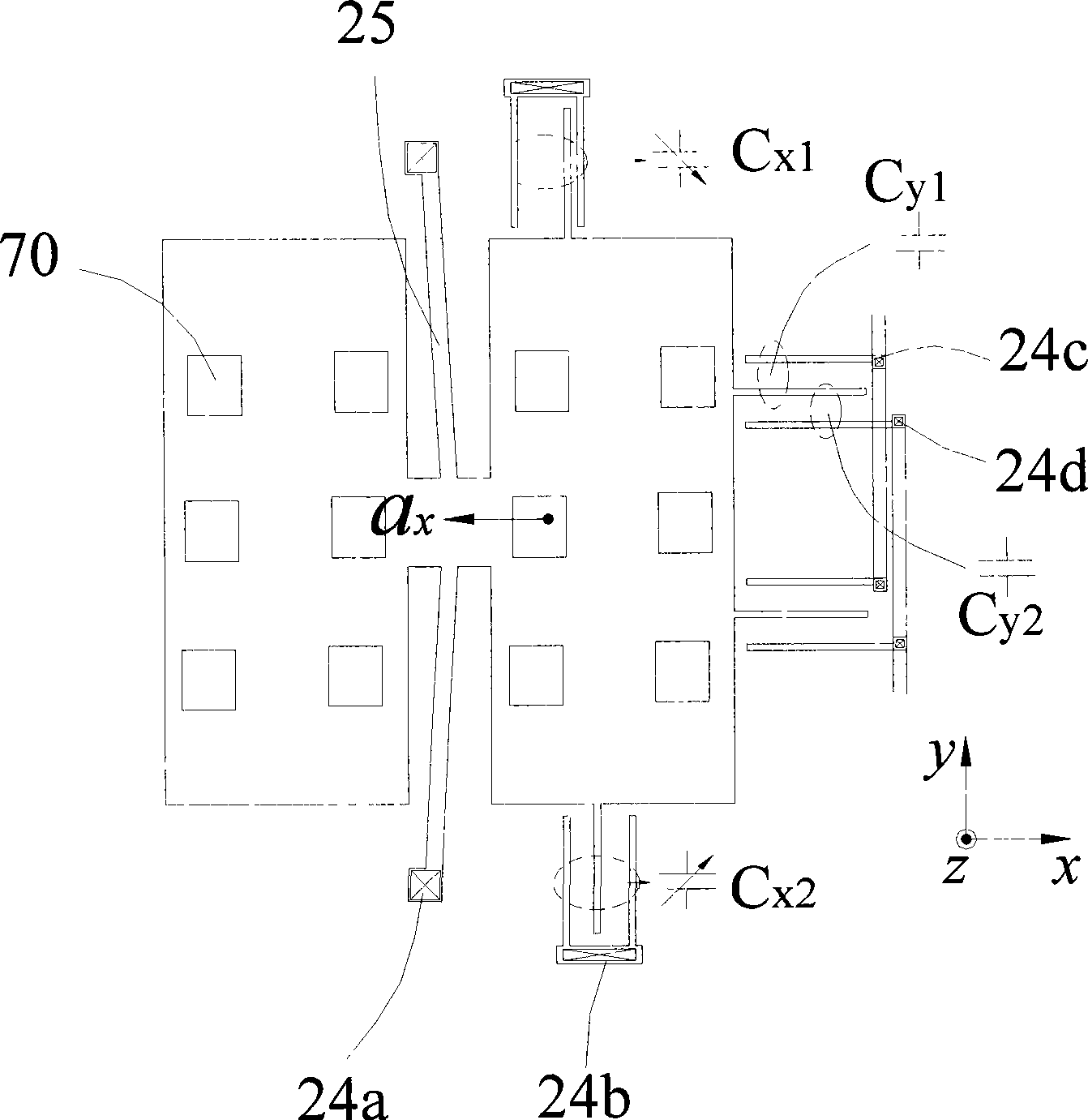
[0025] see Figure 1A and 1B , the capacitive single-mass triaxial acceleration sensor 20 of the present invention at least includes: a substrate 100, a mass area 21, a comb-tooth structure area and a signal output area.
[0026] The substrate 100 includes a substrate and a dielectric insulating layer formed on the substrate. The dielectric insulating layer may be a single-layer structure or a multi-layer structure, such as a composite composed of silicon oxide and silicon nitride. Floor.
[0027]The mass region 21 includes a first conductive layer formed on the dielectric insulating layer, a cantilever beam 25 located on the first conductive layer and connected to the dielectric insulating layer at a fulcrum, and connected to the cantilever beam One side of 25 and the first conductive layer form a first movable block 22 as a first bifurcated capacitor, connected to the other side of the cantilever beam 25 and at the same level as the first movable block 22 and at the same t...
Embodiment 2
[0034] See figure 2 , which is the top view of the second embodiment of the capacitive single-mass three-axis acceleration sensor of the present invention. like figure 2 As shown, the capacitive single-mass triaxial acceleration sensor 30 includes a mass region 31 and a comb-tooth structure region formed by three sets of interdigital capacitors and disposed outside the mass-block region 51 , wherein the mass The area 31 is composed of a first movable block 32, a second movable block 33 and a cantilever beam 35 for supporting, and both ends of the cantilever beam 35 are fixed on the substrate through fulcrums 34a. The only difference from the first embodiment is that the second group of comb structures for measuring the X-axis acceleration is connected to the first movable block 32 , and the second movable block 33 has a larger mass than the second movable block 23 in the first embodiment. Since the combined region formed by the mass region 31 and the comb-tooth structure r...
Embodiment 3
[0037] See image 3 , which is the top view of the third embodiment of the capacitive single-mass three-axis acceleration sensor of the present invention. The capacitive single-mass triaxial acceleration sensor 40 includes a mass region 41 and three sets of interdigital capacitances formed by comb-tooth structure regions disposed outside the mass region 51 , wherein the mass region 41 is formed by a first movable block. 42. The second movable block 43 and the supporting cantilever beam 45 are composed. The difference from the first embodiment is that the first movable block 42 and the second movable block 43 are formed by the cantilever beam 45 at the outer ring of the two. For support, the cantilever beam 45 is fixed to the substrate through a fulcrum 44a located in the middle portion of the proof-mass region 41 . Because the combined region formed by the mass region 41 and the comb-tooth structure region has two asymmetrical left and right parts. The design that the fulcru...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com