Digital type silicon optical waveguide switch based on narrow slit waveguide
A slit waveguide and waveguide switch technology, applied in the field of digital silicon optical waveguide switches, can solve the problems of limited application range, low extinction ratio, large absorption loss, etc., so as to improve modulation efficiency, shorten device structure, and increase branch spacing. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
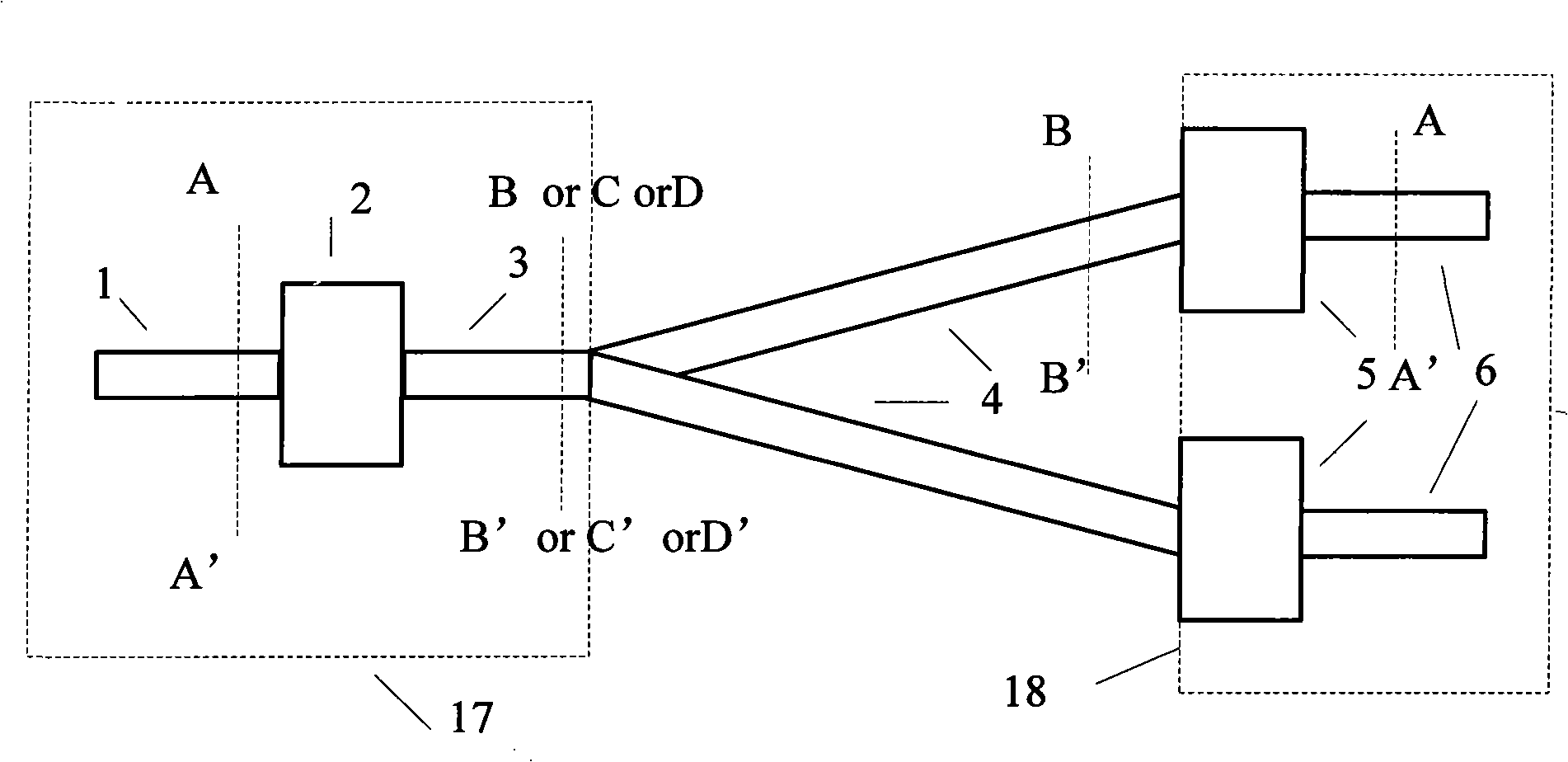
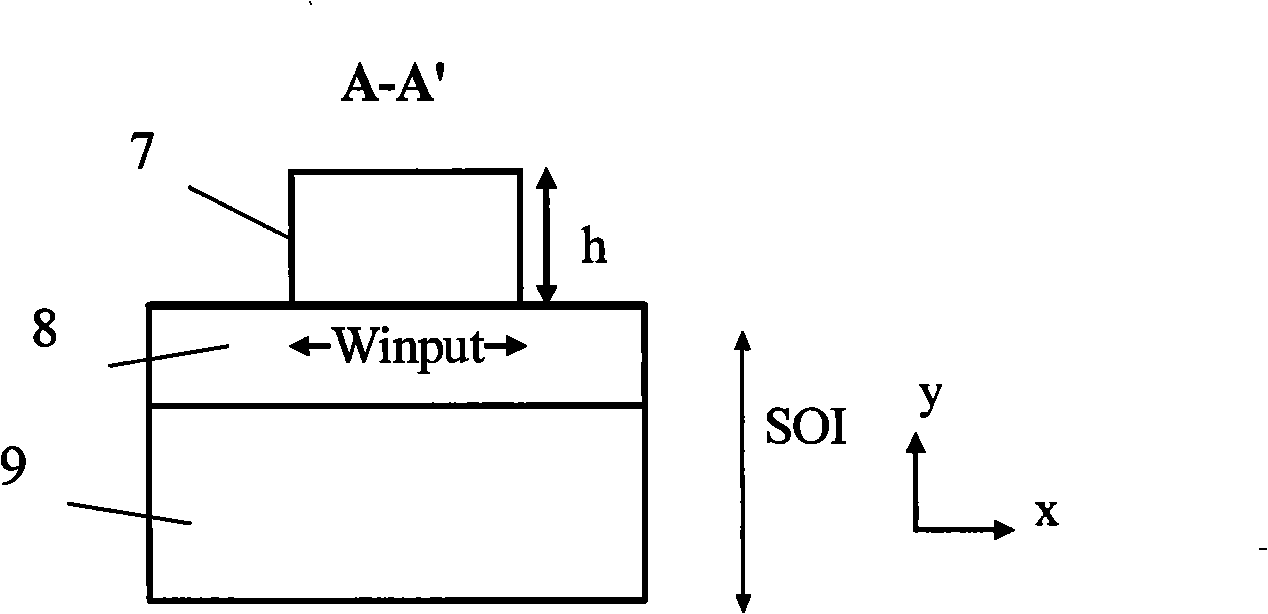
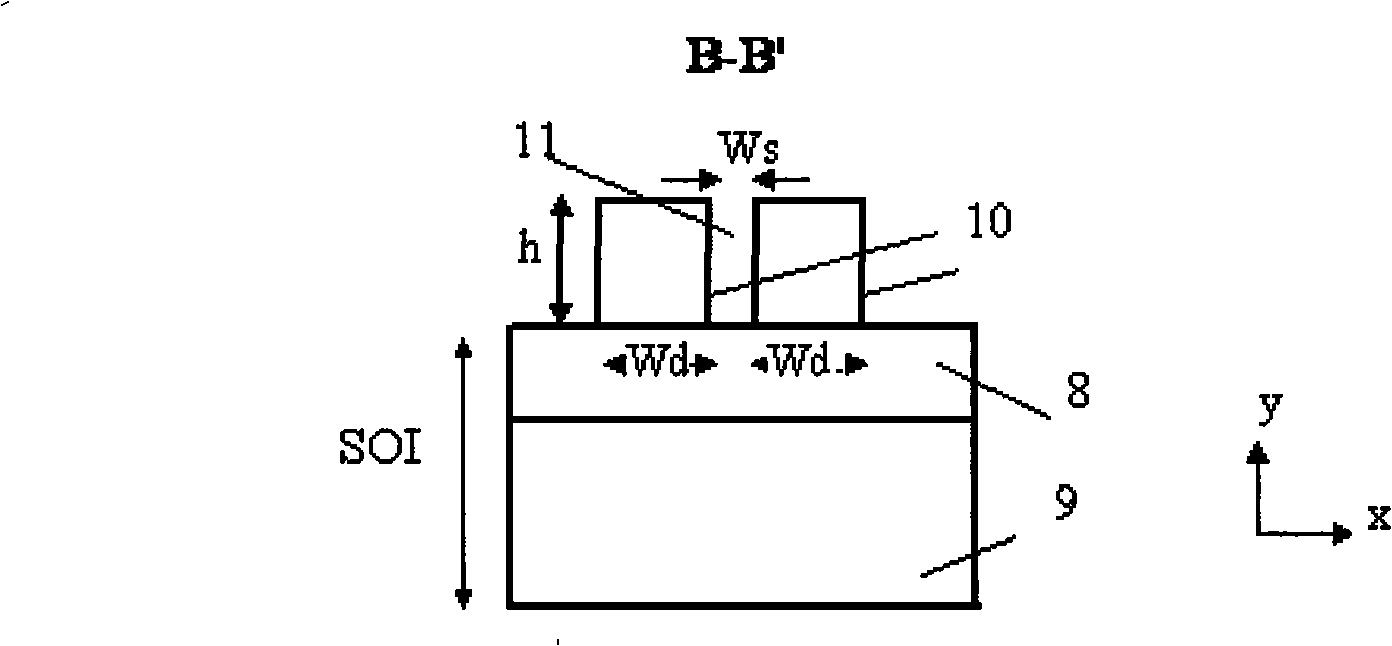
[0046] see Figure 10 As shown, a digital silicon optical waveguide switch with branch arms formed by symmetrical bifurcation of a single slit. Take an SOI sheet with a silicon thickness of 340 nm on the top layer and a silicon dioxide buffer layer 8 with a thickness of 1 micron, thermally oxidize a layer of silicon dioxide on the top layer as a mask, and use the E-beam direct writing method to etch the device structure . Including the input single-mode waveguide 1, introducing a single silicon waveguide to form a complementary tapered tapered waveguide pair 12 to form the first group of mode spot conversion structure 2, a section of waveguide 3 before the branch using a single slit, and two slit waveguide structures The branch arm 4 also introduces a single silicon waveguide to form a second group of mode speckle conversion structures 5 composed of complementary tapered tapered waveguide pairs 12 and two output single-mode waveguides 6 . The inner silicon waveguides 16 of t...
Embodiment 2
[0049] see Figure 11 As shown, the digital silicon optical waveguide switch is formed by double slit symmetrical bifurcation. Take an SOI sheet with a silicon thickness of 340 nm on the top layer and a silicon dioxide buffer layer 8 with a thickness of 1 micron, thermally oxidize a layer of silicon dioxide on the top layer as a mask, and use the E-beam direct writing method to etch the device structure . Including the input single-mode waveguide 1, the first group of mode spot conversion structures 2 formed by introducing two silicon waveguides to form a complementary tapered tapered waveguide pair 14 or the second mode spot conversion structure 15 of a hollow waveguide formed by a direct bifurcation gradient, using A section of waveguide 3 before the branch of the double slit, two branch arms 4 of the slit waveguide structure, introduce a single silicon waveguide to form a complementary tapered tapered waveguide pair 12 to form the second group of mode spot conversion struc...
Embodiment 3
[0052] see Figure 12 As shown, the digital silicon optical waveguide switch with branch arms formed by symmetrical bifurcation of multiple slits is illustrated by taking three slits as an example. Take an SOI sheet with a silicon thickness of 340 nm on the top layer and a silicon dioxide buffer layer 8 with a thickness of 1 micron, thermally oxidize a layer of silicon dioxide on the top layer as a mask, and use the E-beam direct writing method to etch the device structure . Including the input single-mode waveguide 1, the first group of mode spot conversion structures 2 composed of the first mode spot conversion structure 13 of the hollow waveguide formed by direct bifurcation and gradual change, a section of waveguide 3 before the branch using three slits, and two slits The branch arm 4 of the slot waveguide structure introduces a single silicon waveguide to form a second group of mode-spot conversion structures 5 composed of complementary tapered tapered waveguide pairs 12...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com