Patents
Literature
259results about How to "Improve modulation efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
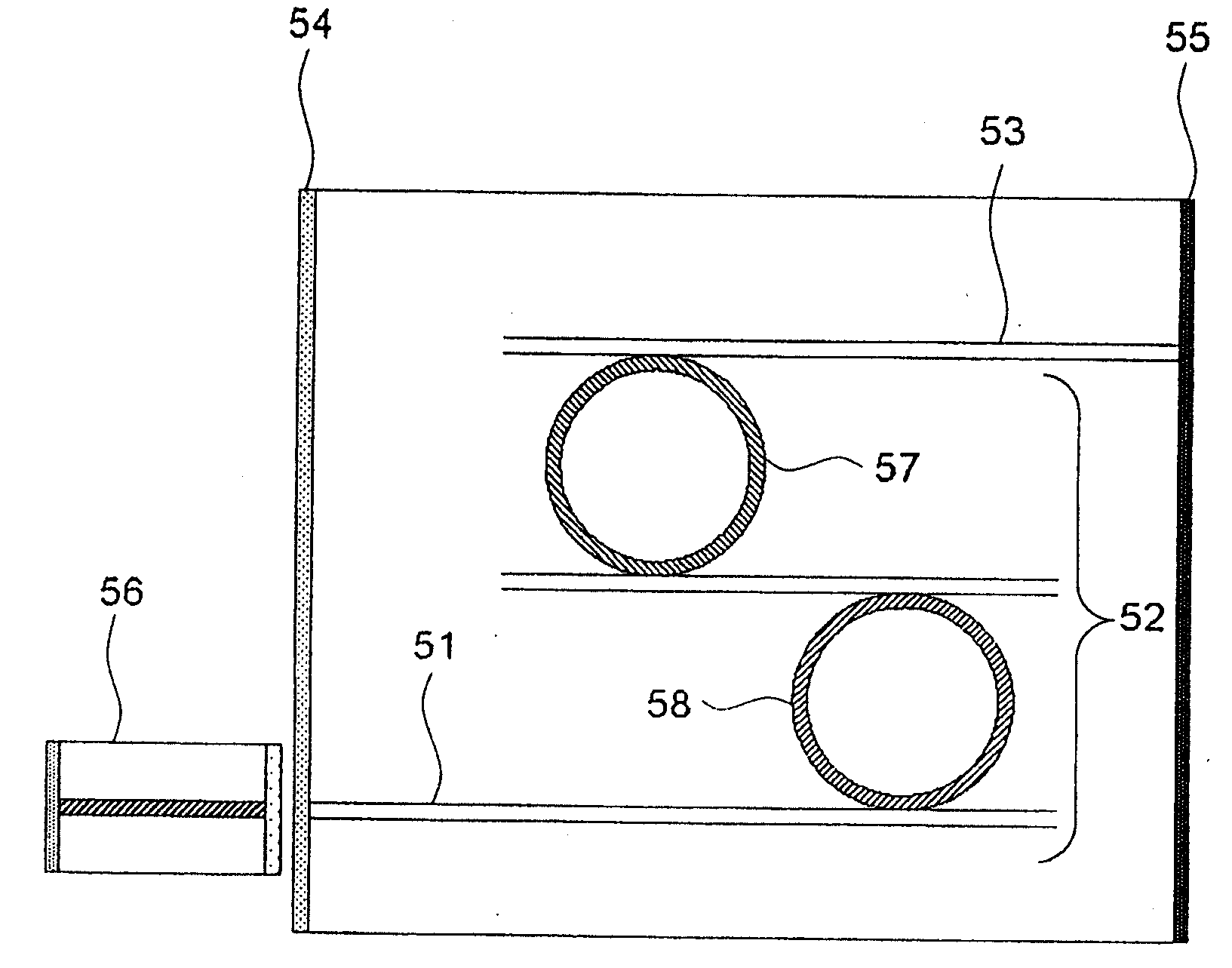
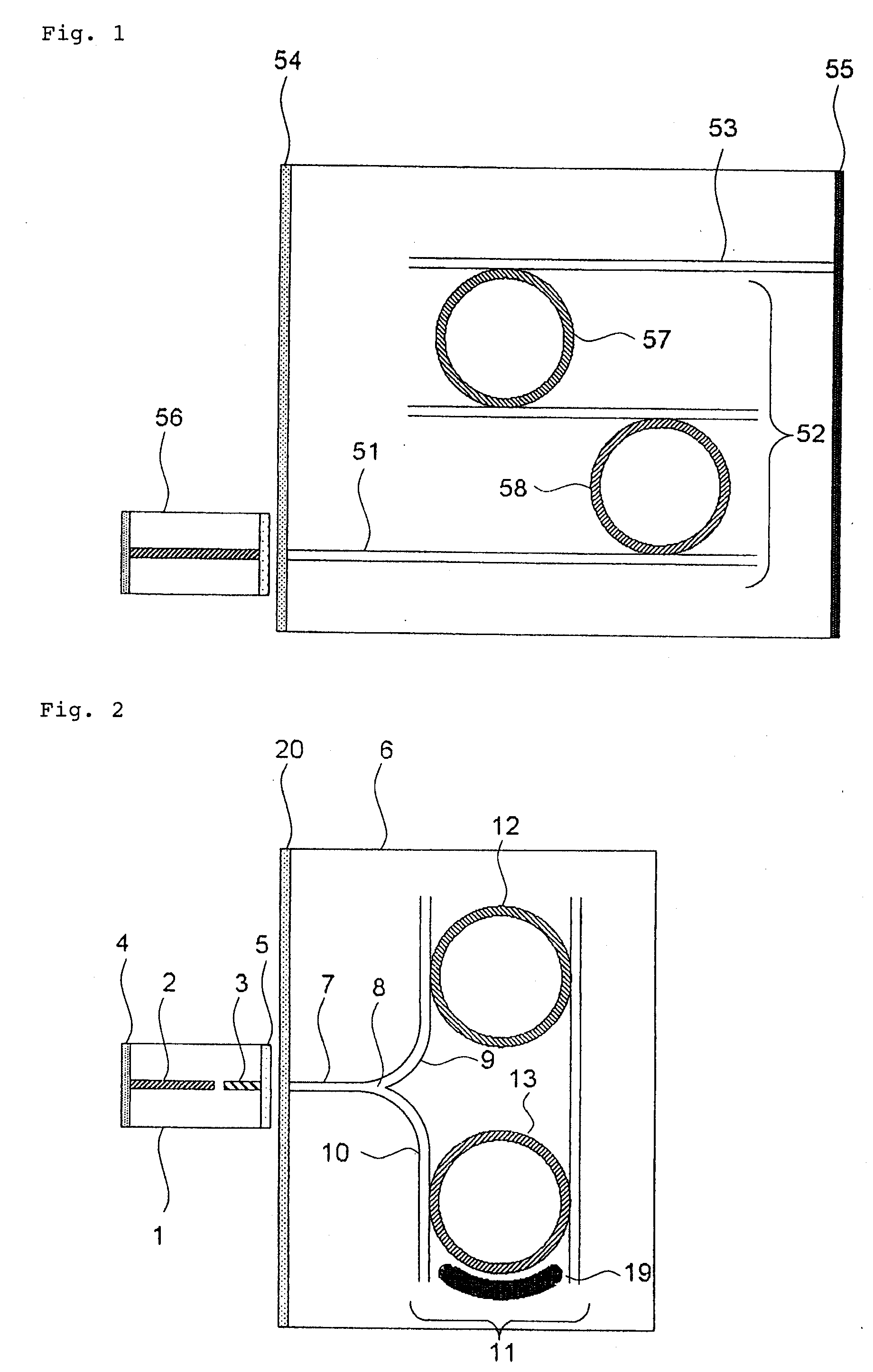
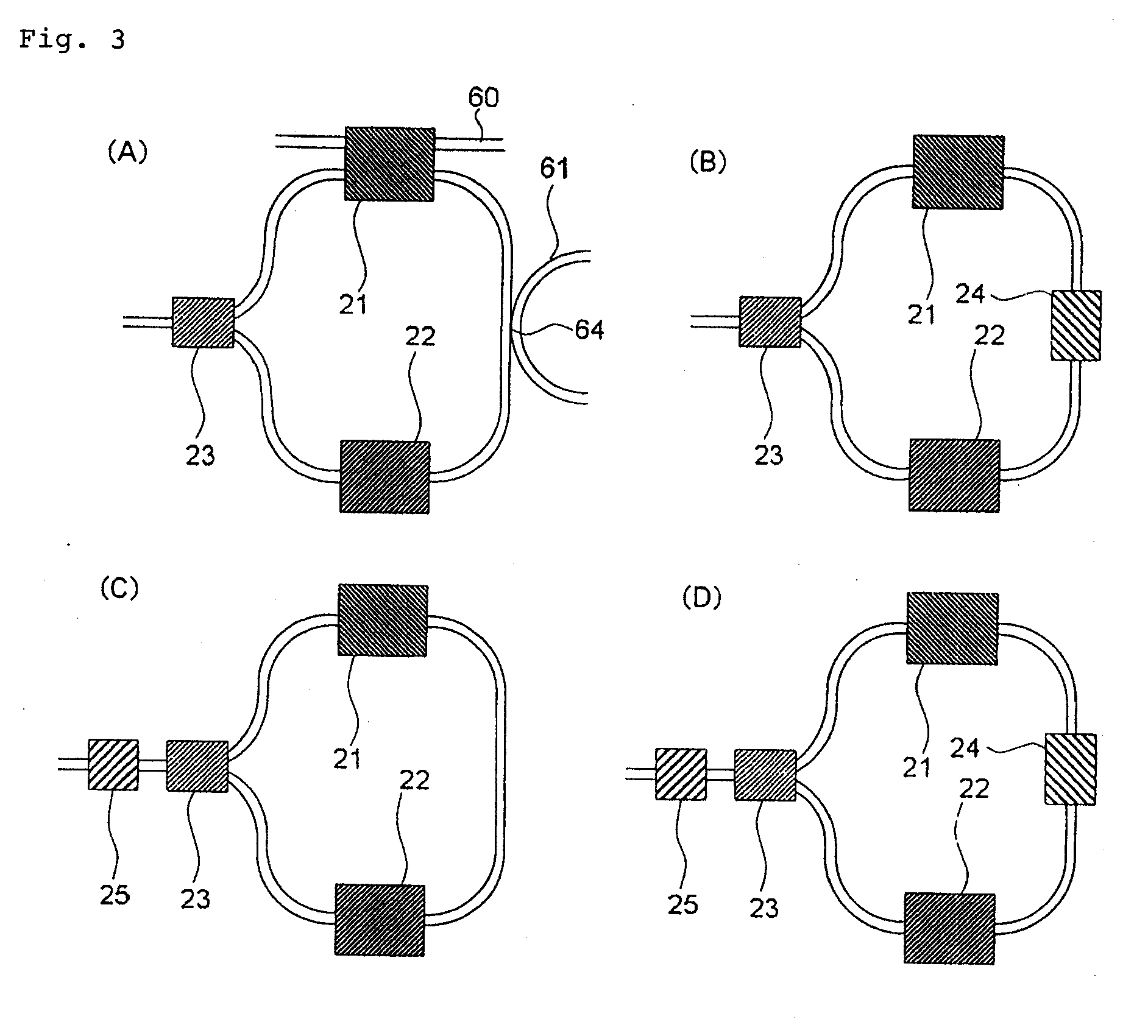
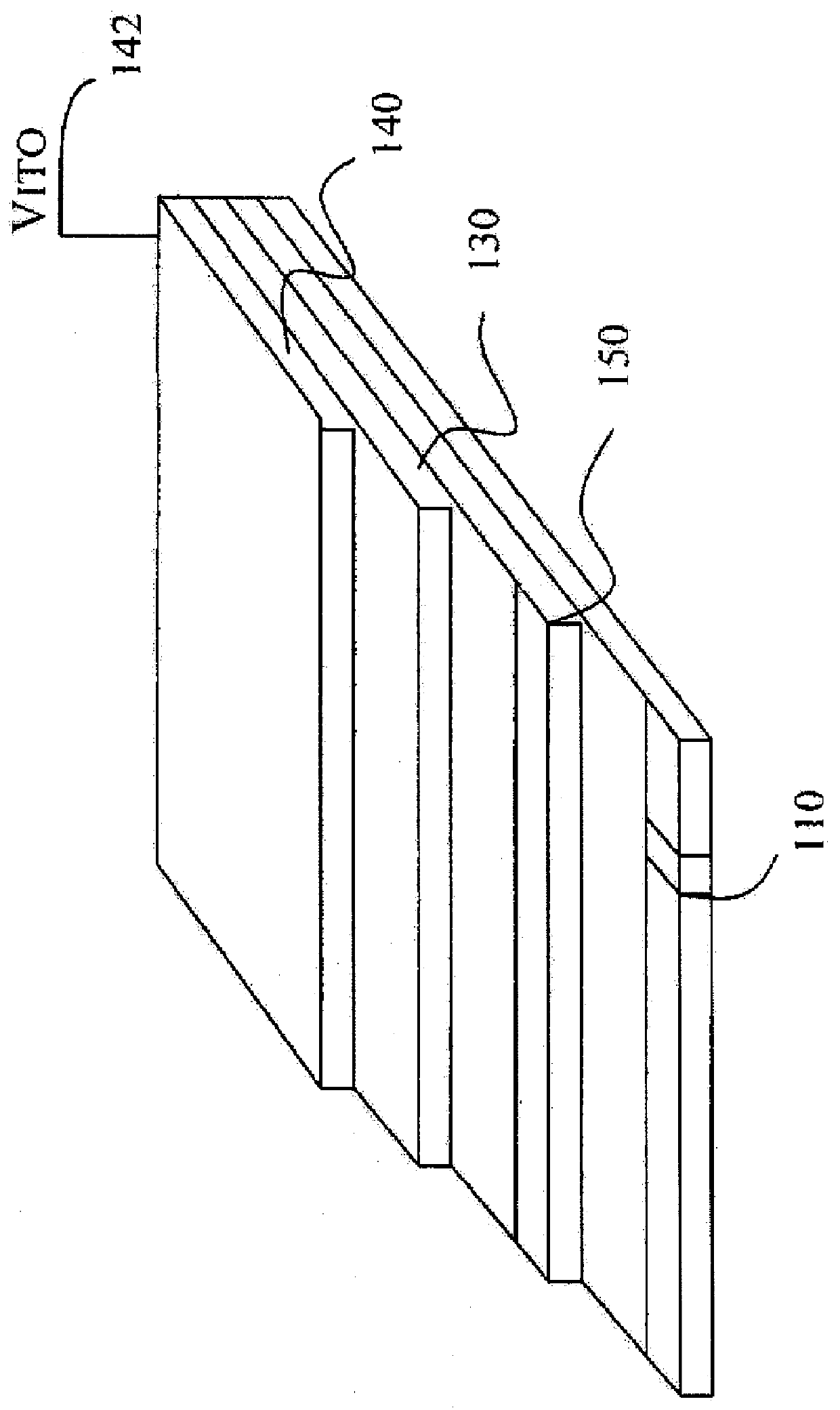
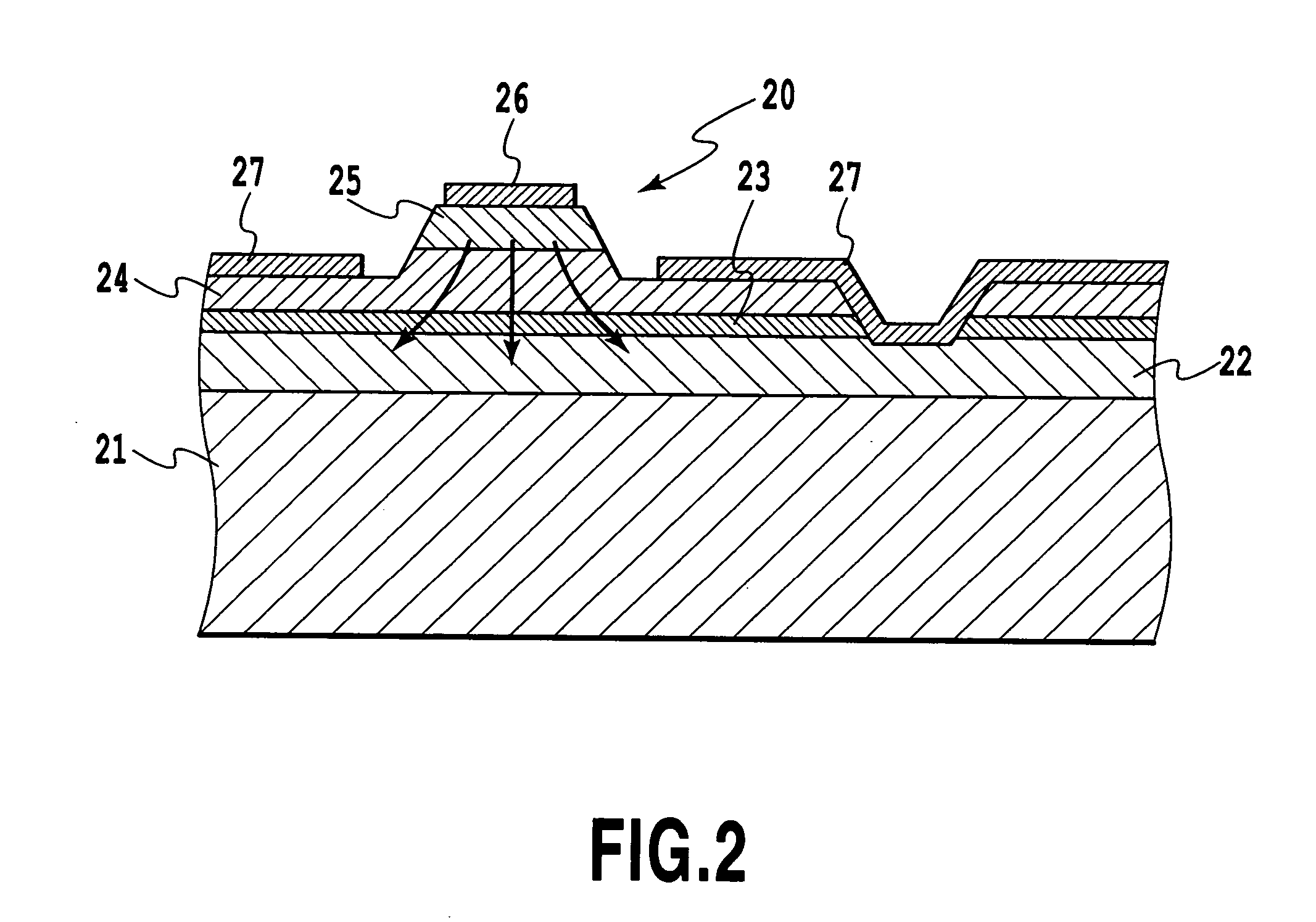
Variable-wavelength filter and variable-wavelength laser
InactiveUS20090122817A1Laser output is improvedReduce manufacturing costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersWavelength filterLength wave
Only the light at an overlapping wavelength of the transmission characteristics of at least two wavelength selecting filters is looped, and at least one of the wavelength selecting filters varies a selected wavelength. Since a loss due to the optical filters is small and there is not a loss caused by a highly reflecting film, the output of an external-resonator variable-wavelength laser can be increased. Optical circuit component (8) divides light input from external device (1) into at least two ports. Loop waveguide (11) interconnects at least ports (9, 10) divided by optical circuit component (8) in the form of a loop. At least two first wavelength selecting filters (12, 13) are inserted in series in a path of loop waveguide (11), and have periodic transmission characteristics on a frequency axis which are different from each other. At least one of first wavelength selecting filters (12, 13) varies the selected wavelength.
Owner:NEC CORP
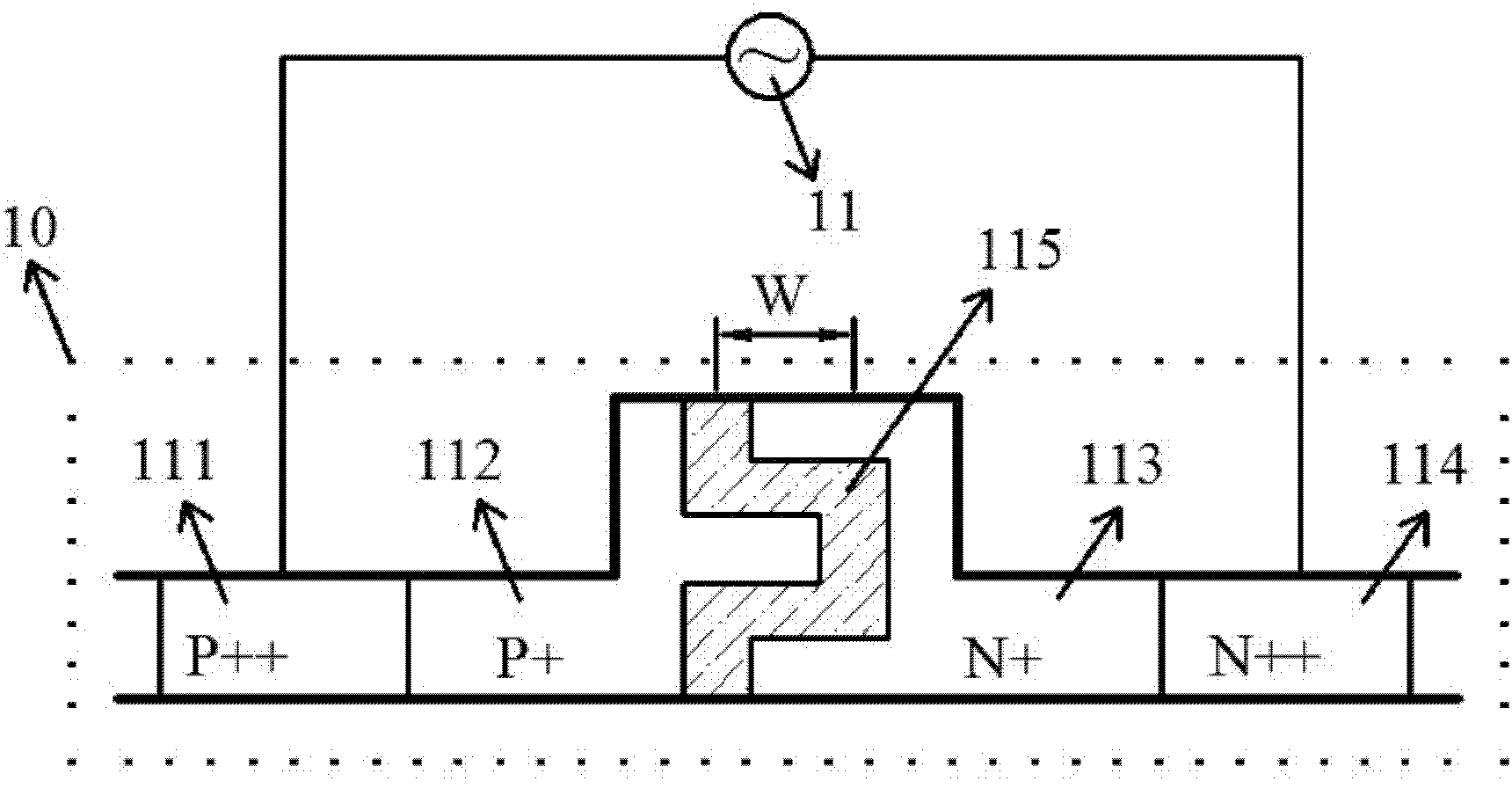
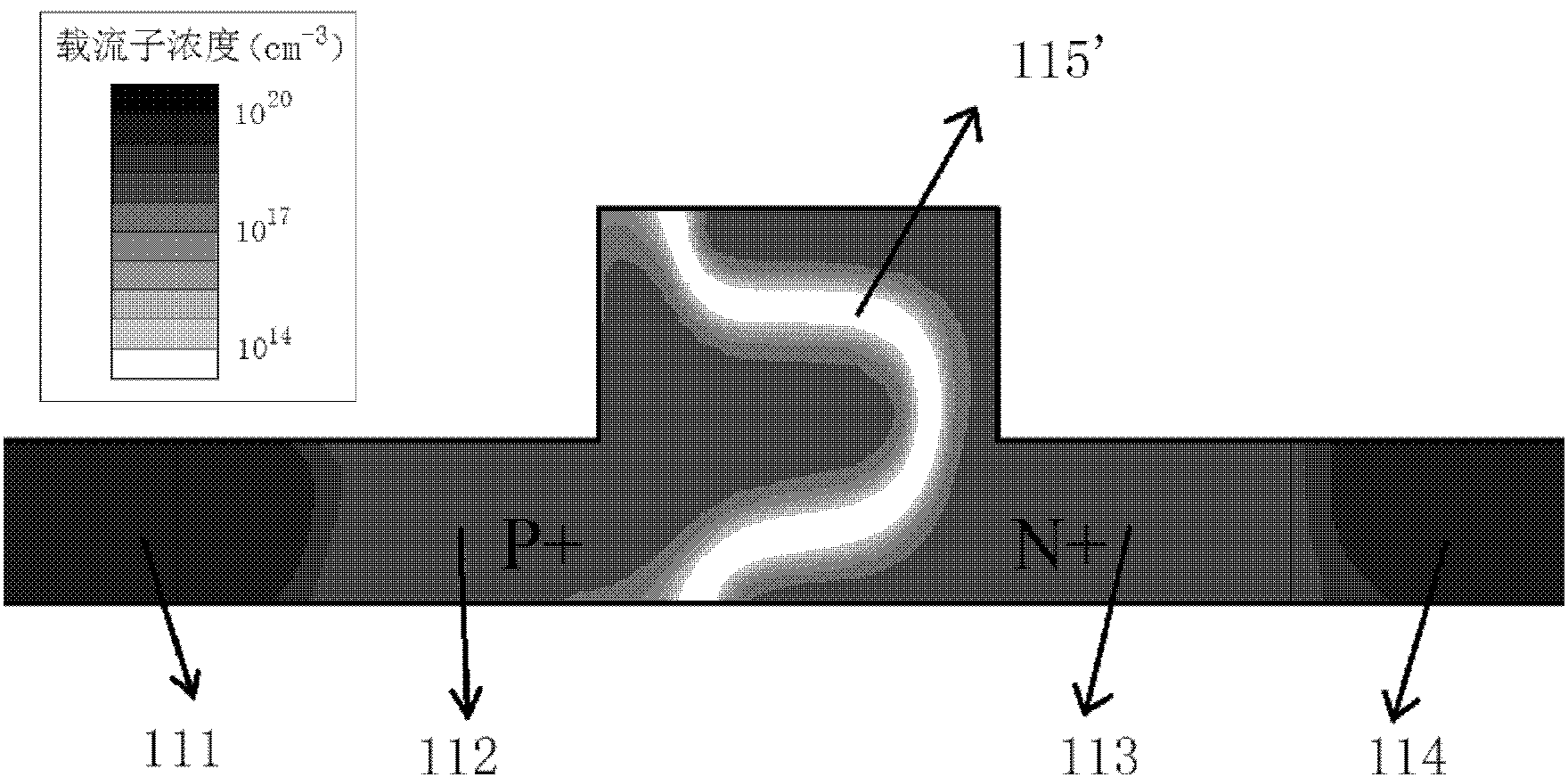
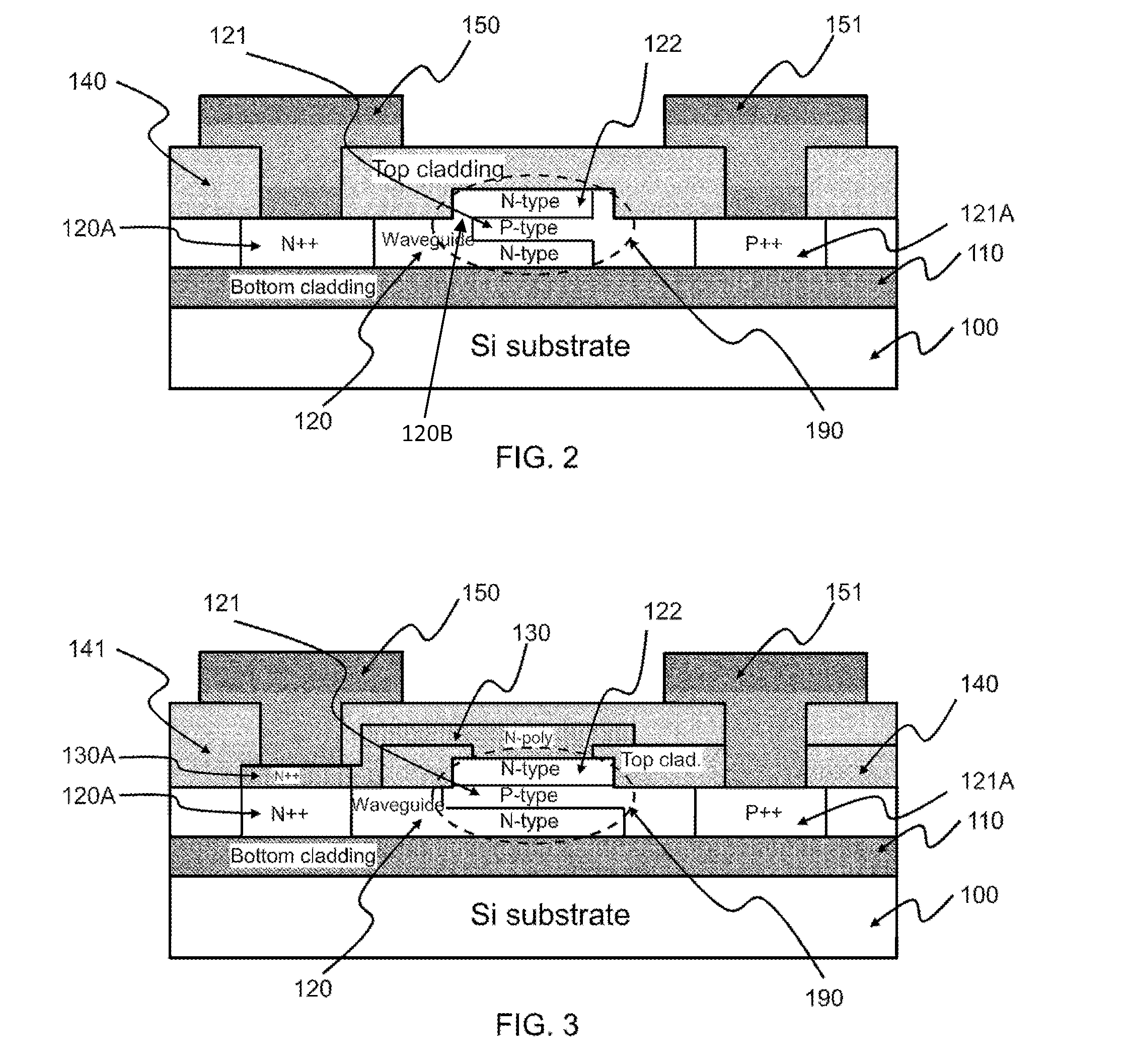
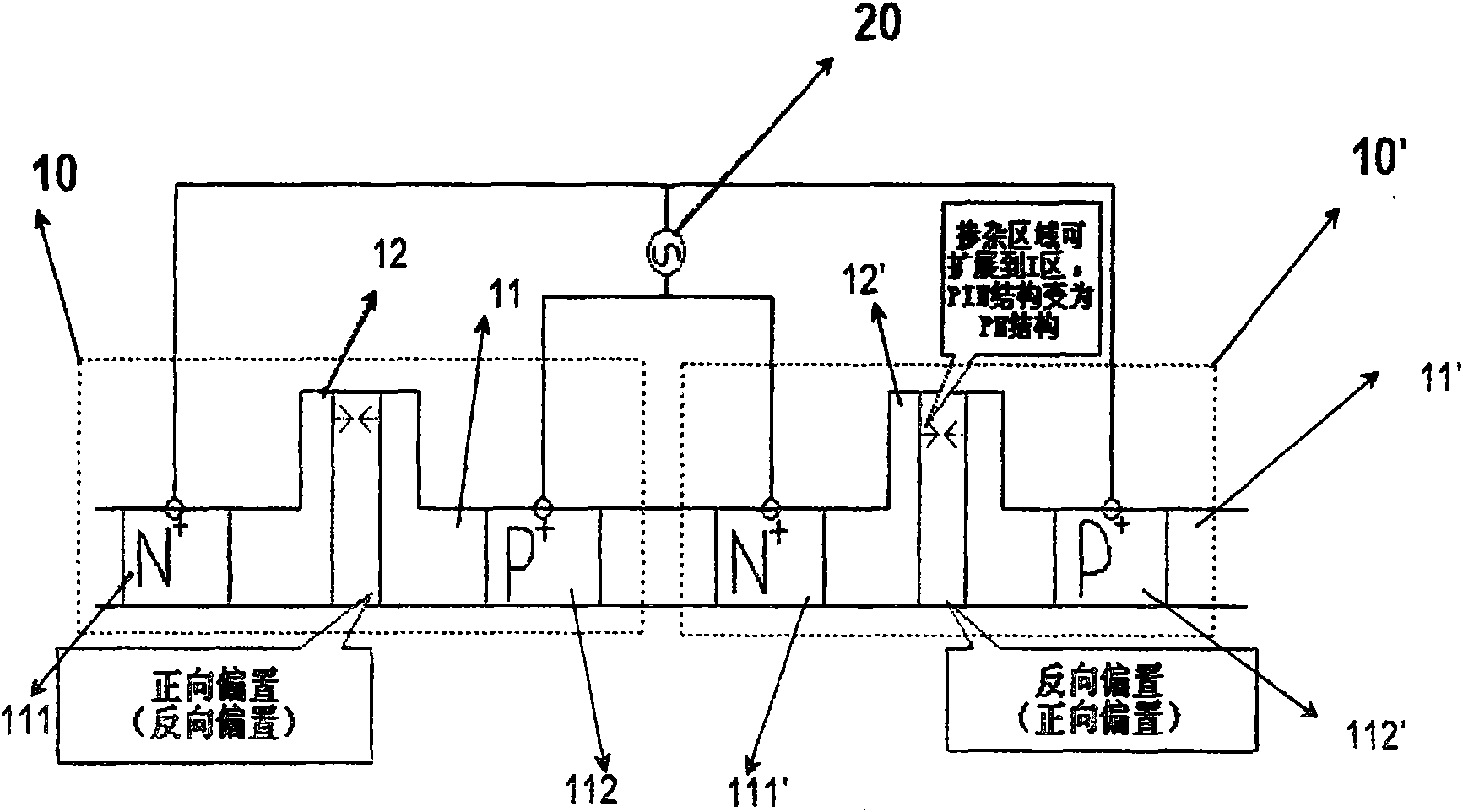
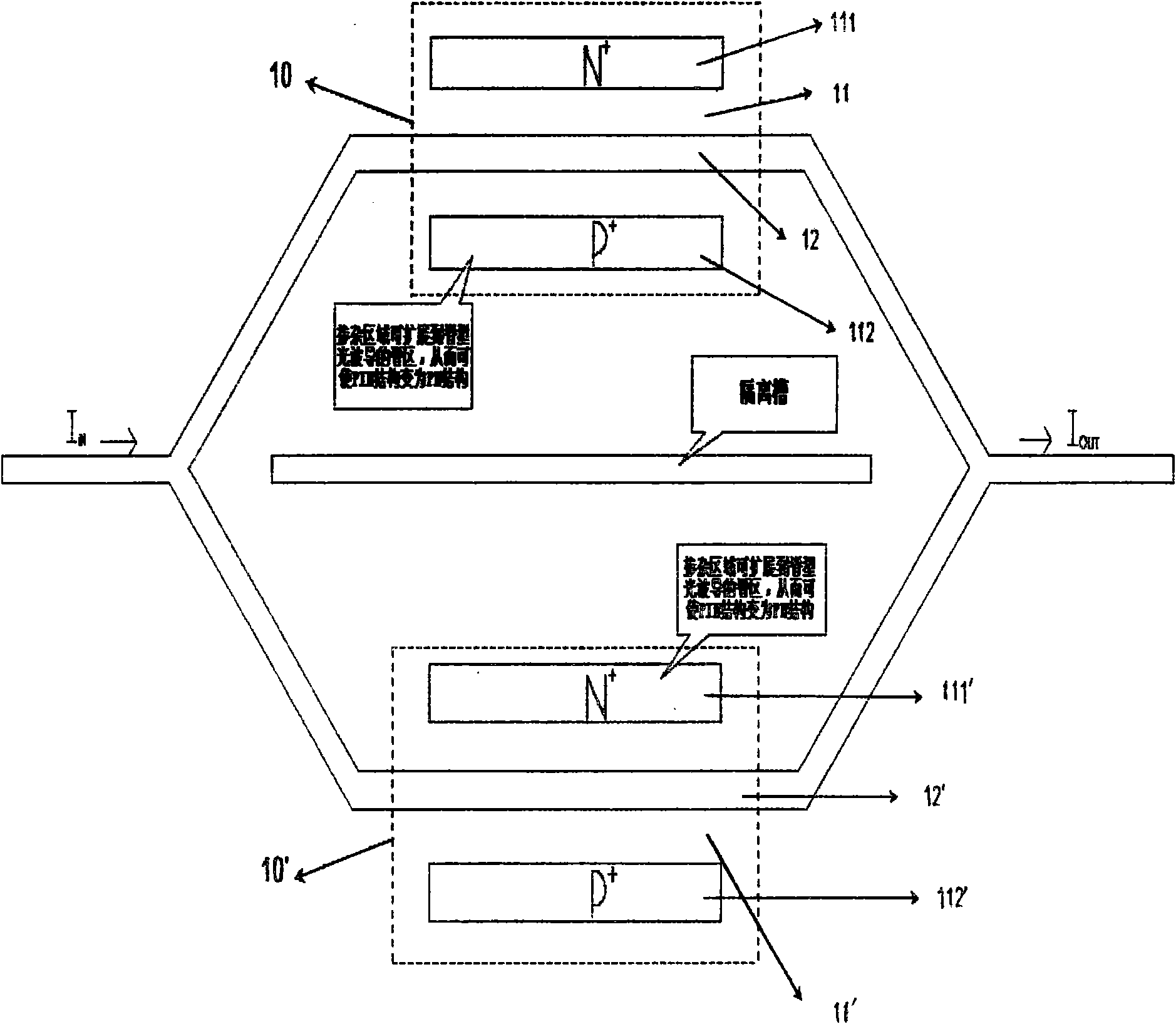
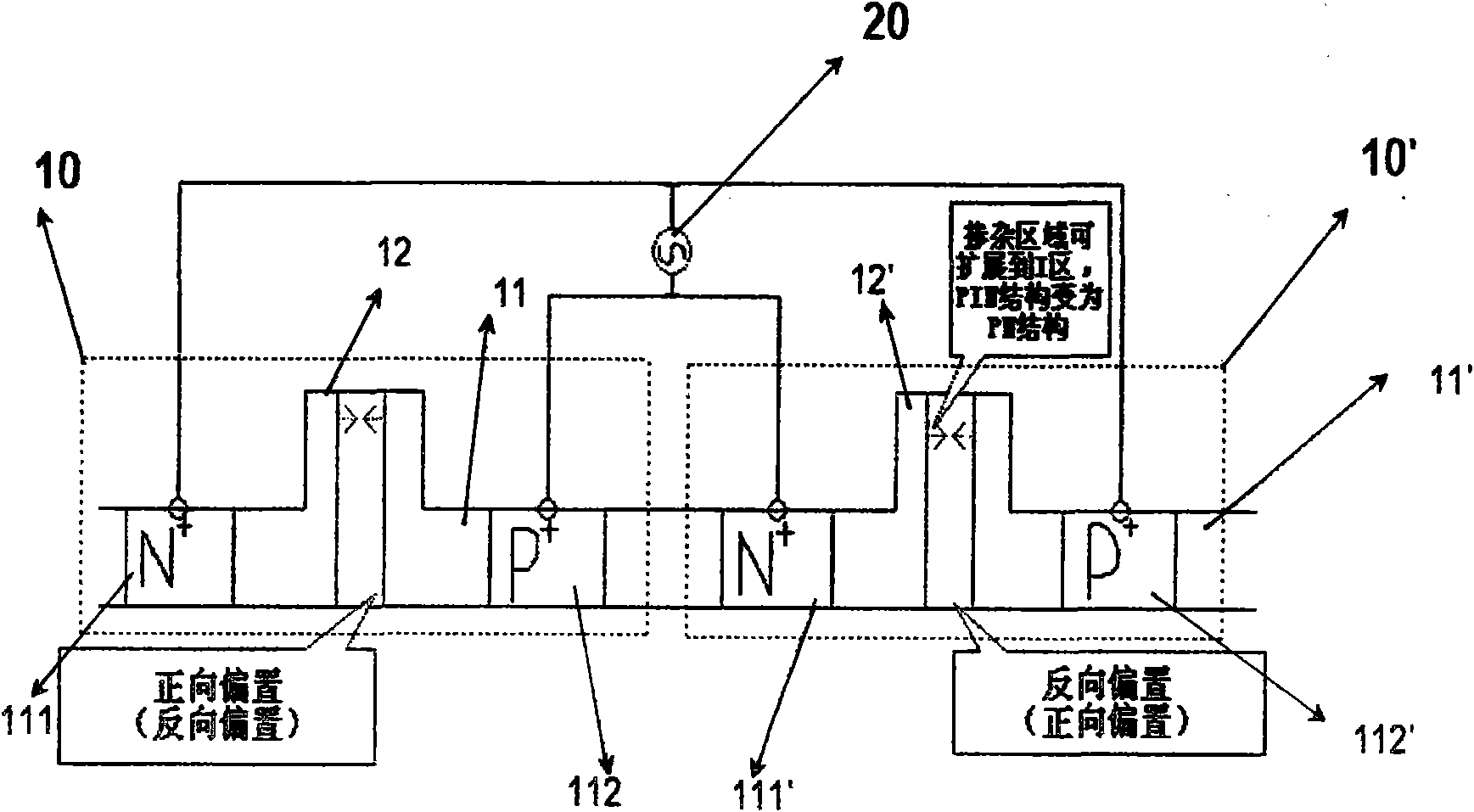
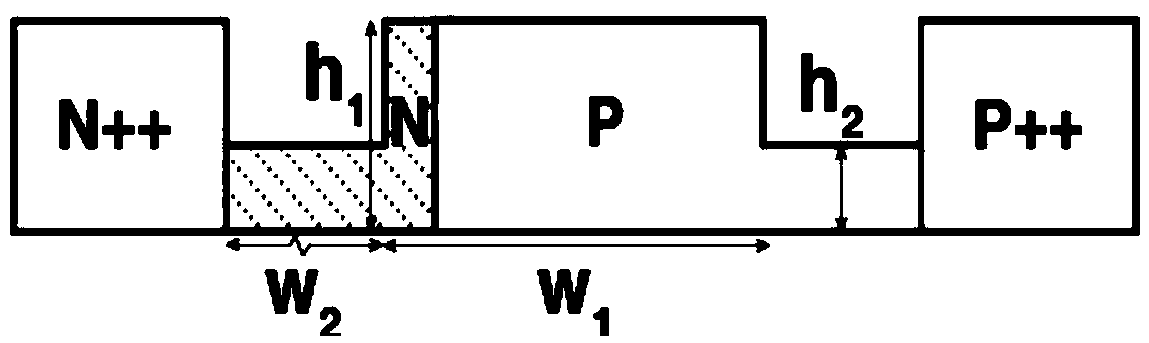
Doping structure capable of improving modulation efficiency of depletion silicon-based electrooptical modulator
InactiveCN103226252AIncrease Overlap PointsImprove modulation efficiencyNon-linear opticsOptical modulatorSilicon based
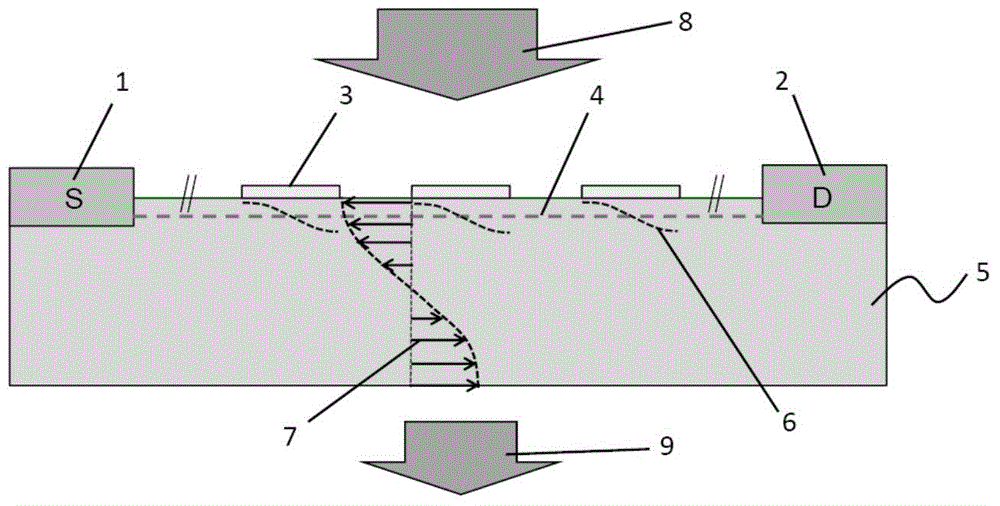
The invention discloses a doping structure capable of improving the modulation efficiency of a depletion silicon-based electrooptical modulator. The doping structure comprises a modulation area waveguide of a silicon-based electrooptical modulator, wherein the waveguide adopts a ridge-shaped optical waveguide structure; a first doping area, a second doping area, a third doping area and a fourth doping area are respectively arranged in the waveguide; a PN node electrical modulation structure shaped like the letter U is formed at the junction between the second doping area and the third doping area; and the first doping area and the fourth doping area are respectively connected with metal wires and connected with a high-frequency driving circuit. When applied to the depletion silicon-based electrooptical modulator, the doping structure can improve the modulation efficiency of the modulator and simultaneously reduce the absorption loss of carriers.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
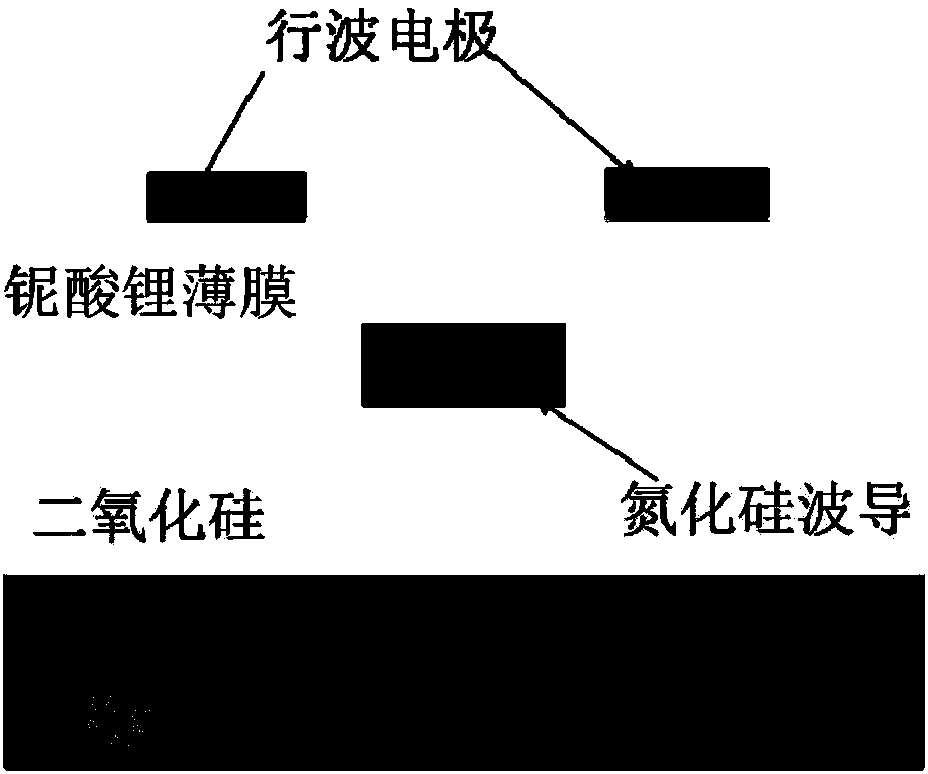
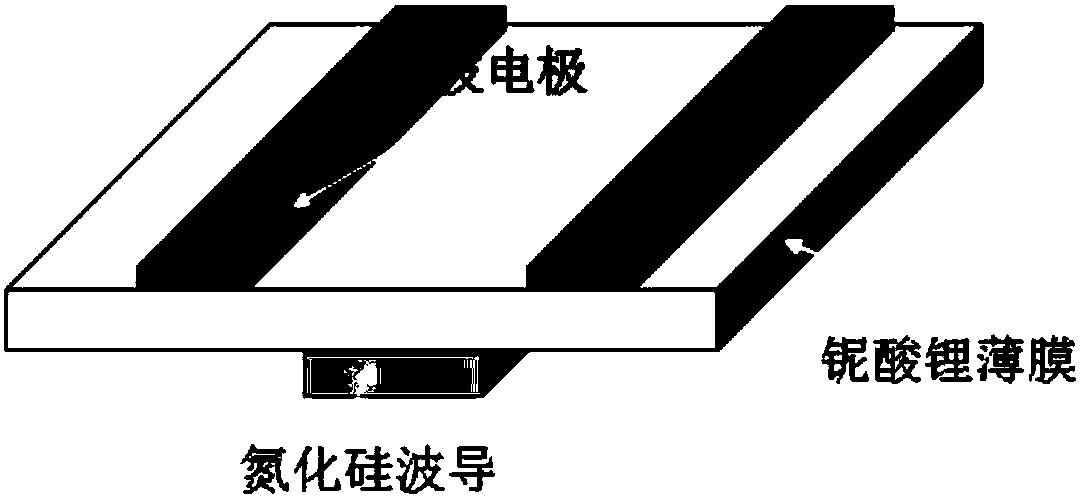
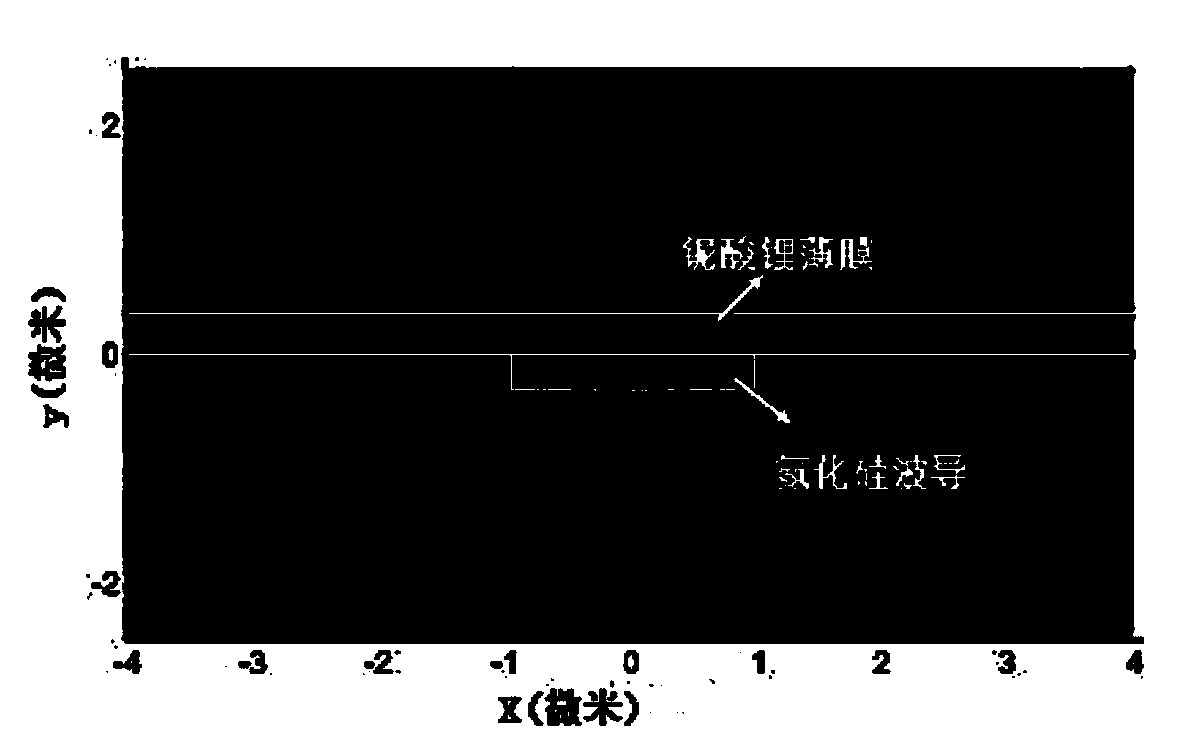
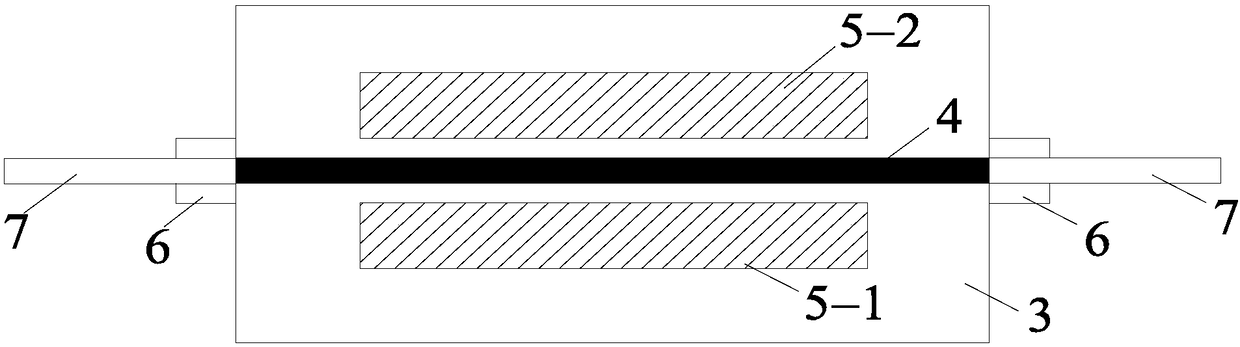
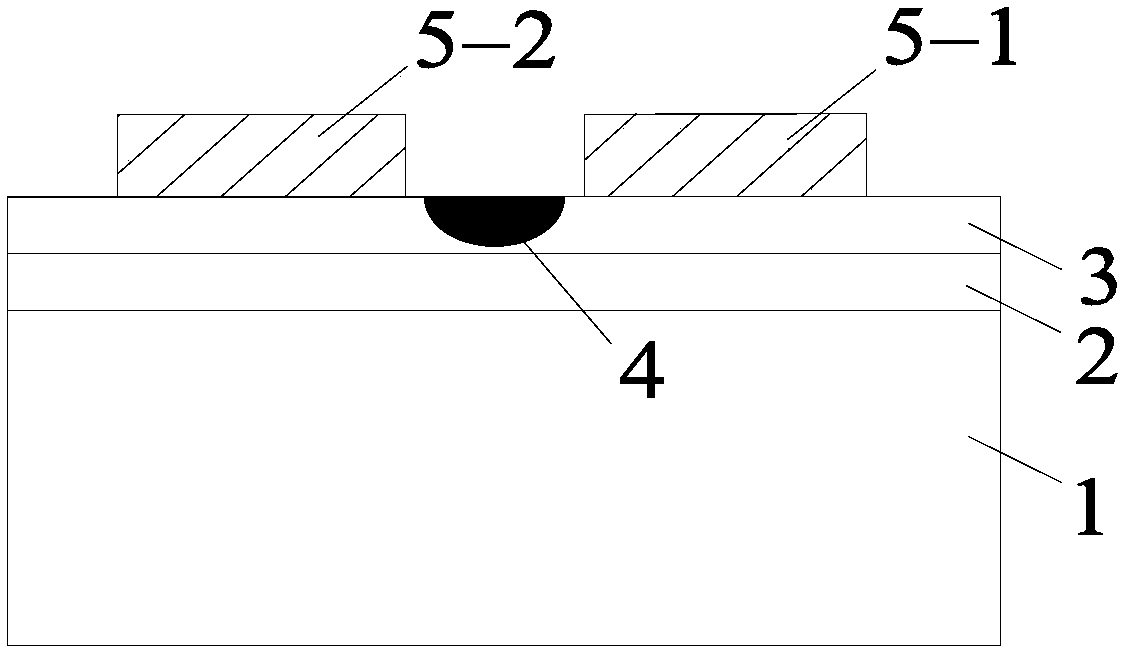
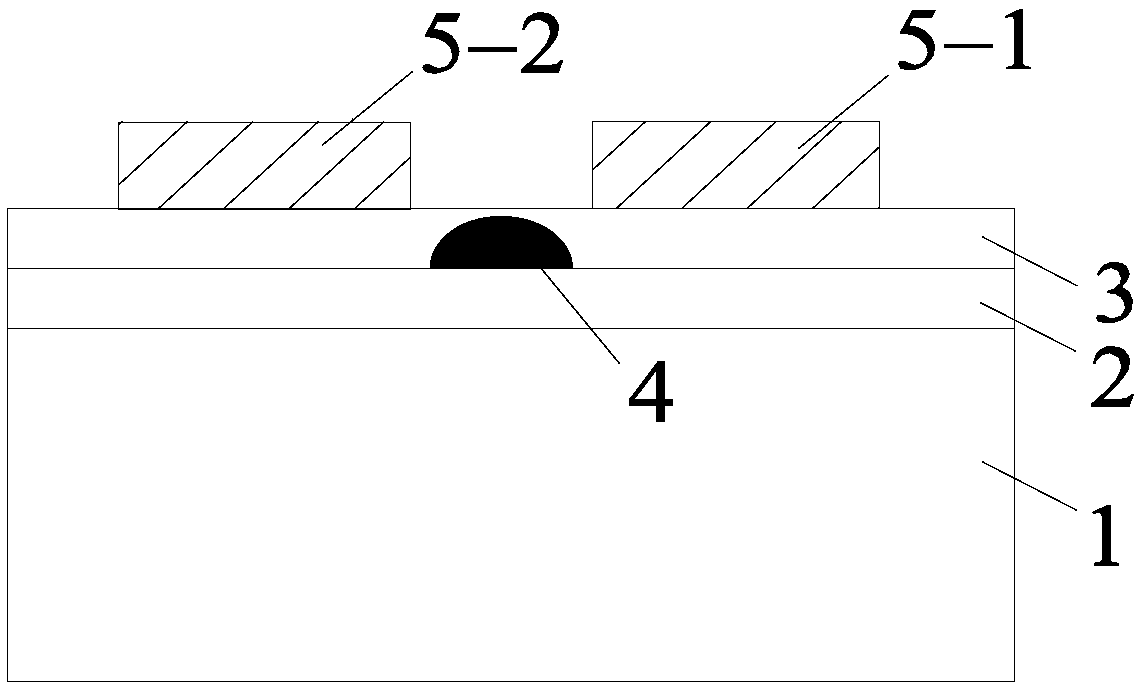
Silicon nitride-lithium niobate heterogeneous integrated waveguide device structure and preparation method of the same
InactiveCN107843957AReduce energy consumptionImprove modulation efficiencyOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsManufacturing technologySilica coating
The invention relates to a silicon nitride-lithium niobate heterogeneous integrated waveguide device structure and a preparation method of the same. The silicon nitride-lithium niobate heterogeneous integrated waveguide device structure is characterized in that a silicon nitride waveguide in a silica coating layer and a lithium niobate film on the upper surface of the silicon nitride waveguide areheterogeneously integrated to form a ridge waveguide; a traveling wave electrode is arranged on the upper surface of the lithium niobate film; the silicon nitride waveguide is crossed and coupled with the lithium niobate film on the upper surface of the silicon nitride waveguide, and a high speed electric signal is applied to the traveling wave electrode to control the phase of the light wave passing through the lithium niobate film to realize conversion from amplitude modulation of the loaded electric signal to phase modulation of an optical signal; and three-dimensional vertical integrateddesign is utilized to enable integration of the chip to be more compact, so that the space is saved; at the same time insertion loss of the light waveguide can be reduced; 100G light modulation rate can be realized; high speed modulation of the light wave in the lithium niobate film can be realized and the characteristic of low loss propagation through the silicon nitride waveguide is realized; and light modulation with excellent performance is completed. The manufacturing technology of the silicon nitride-lithium niobate heterogeneous integrated waveguide device structure is compatible with the semiconductor processing technology, is high in the modulation efficiency and low in energy consumption, and has important application prospects in the optical signal processing field and other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Silicon-based lithium niobate high-speed light modulator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108732795ARealize heterogeneous integrationReduce lossNon-linear opticsModulation bandwidthSingle crystal
The invention discloses a silicon-based lithium niobate high-speed light modulator and a preparation method thereof. The modulator comprises a silicon substrate wafer, a lower silicon dioxide cladding, lithium niobate film, an optical waveguide, a metal electrode, a silicon V-shaped groove and a coupling optical fiber, wherein the lower silicon dioxide cladding is located on the upper surface of the silicon substrate wafer, and the lithium niobate film is located on the lower silicon dioxide cladding. The silicon-based lithium niobate high-speed light modulator has the advantages that heterogeneous integration of a lithium niobate single crystal body and a silicon single crystal body is achieved; by utilizing the thin-film lithium niobate wafer and the characteristics such as low dielectric constant and low dielectric loss of the lower silicon dioxide cladding, improvement of modulation rate (or modulation bandwidth) of the lithium niobate light modulator can be achieved; by utilizingthe thin-film lithium niobate wafer and the high insulativity of the lower silicon dioxide cladding, intensity increase of microwave electromagnetic fields distributed in the lithium niobate film canbe achieved, the modulation efficiency of electric fields to light fields is improved, and the driving voltage of the modulator is reduced.
Owner:天津领芯科技发展有限公司
Data Sending and Receiving Method and Data Sending and Receiving End
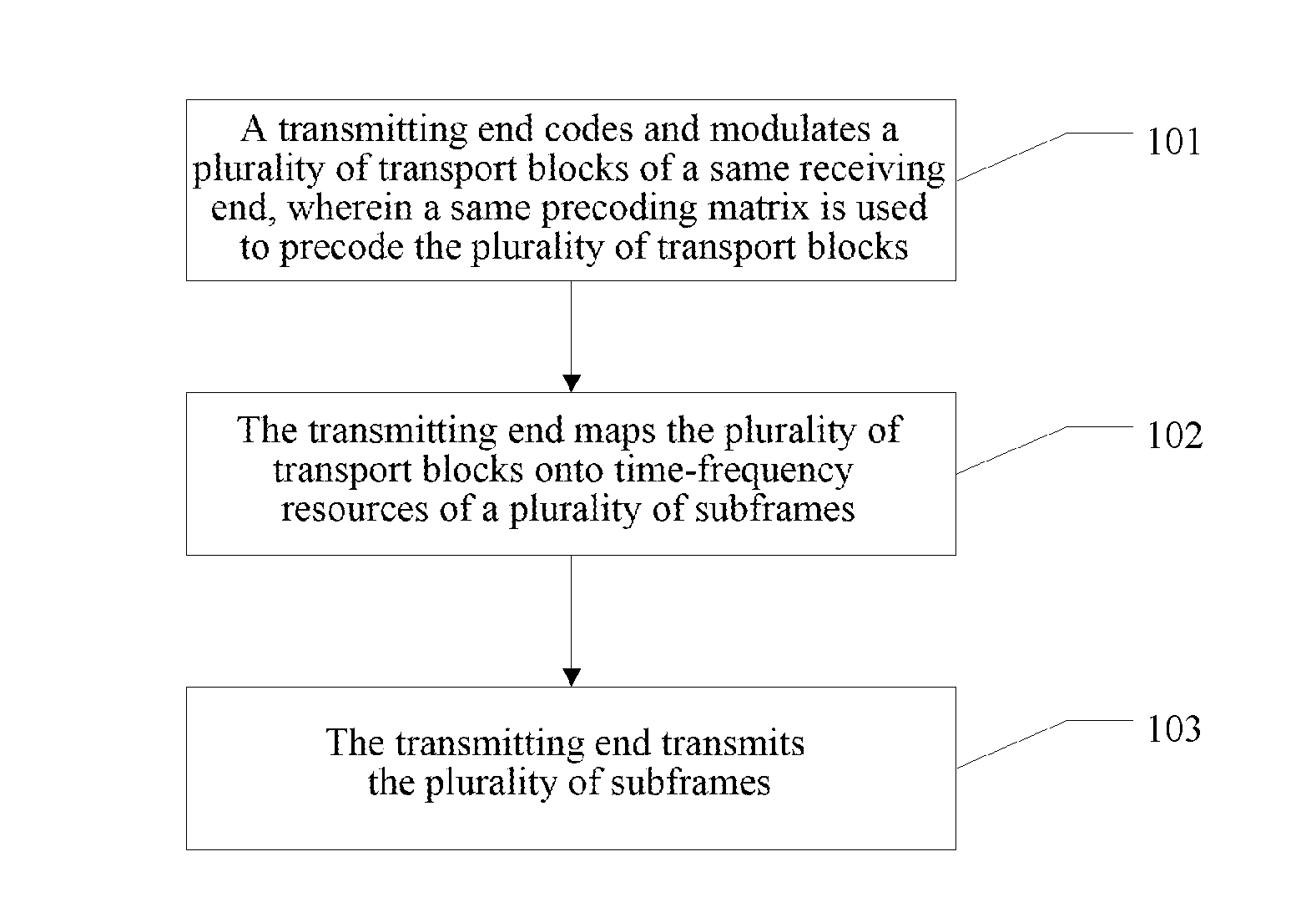
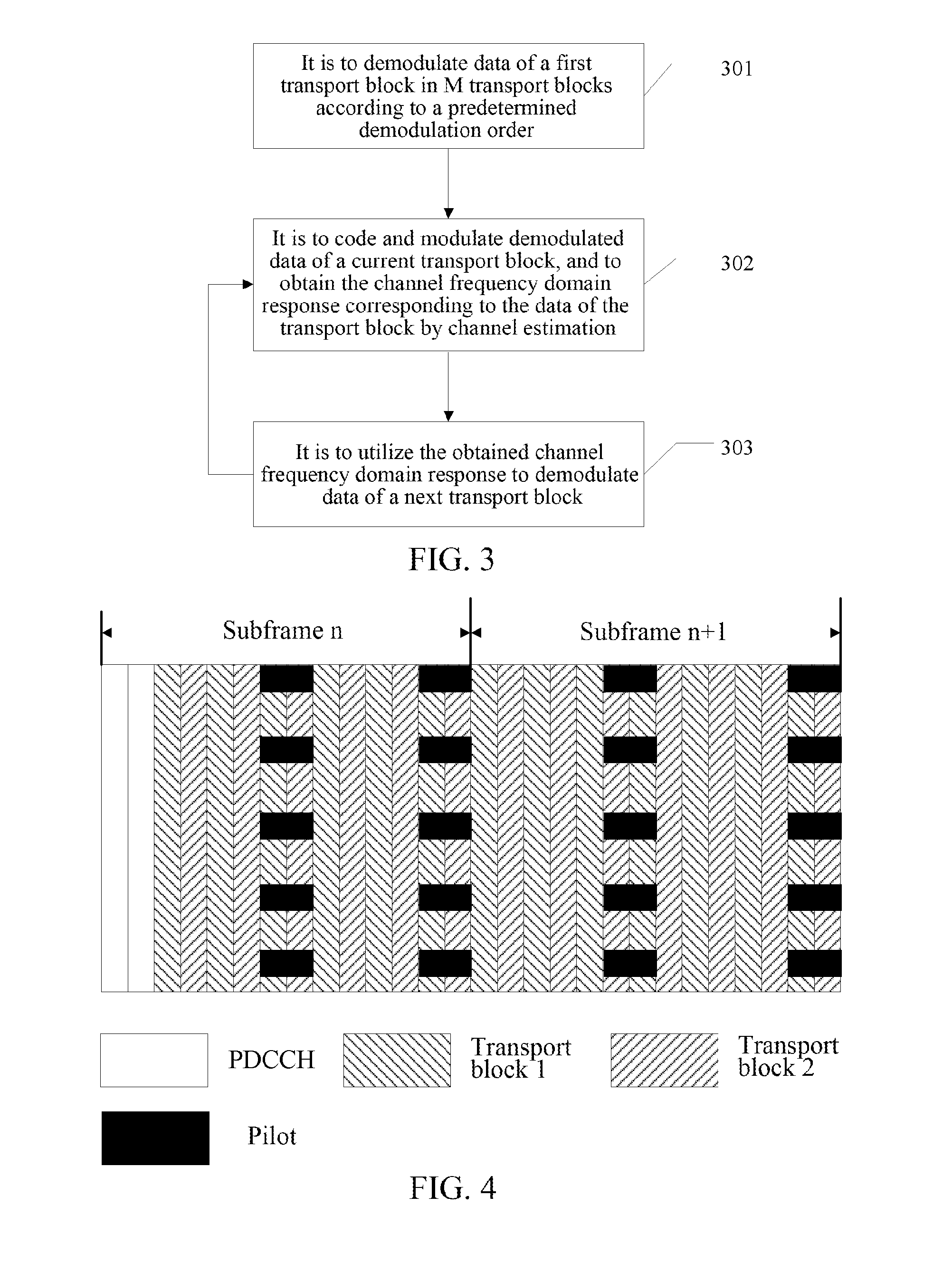
ActiveUS20160143011A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove modulation efficiencySpatial transmit diversitySignalling characterisationTelecommunicationsPrecoding matrix
Disclosed are a data transmitting, receiving method, a data transmitting end, and a data receiving end. The transmitting method includes that: a transmitting end codes and modulates a plurality of transport blocks of a same receiving end, wherein a same precoding matrix is used to precode the plurality of transport blocks; the transmitting end maps the plurality of transport blocks onto time-frequency resources of a plurality of subframes; and the transmitting end transmits the plurality of subframes.
Owner:XIAN ZHONGXING NEW SOFTWARE
Dual-junction optical modulator and the method to make the same
InactiveUS20160313577A1Good ohmic contactImprove modulation efficiencyNon-linear opticsP–n junctionWaveguide
An optical device includes a substrate and an optical rib waveguide structure formed of a slab and a rib. A vertically-oriented P-N-P or N-P-N dual-junction diode is formed inside the rib waveguide, including a first doped region, a second doped region and a third doped region electrically connected to the first doped region, where two P-N junctions are formed at the boundaries of the first and the second doped regions, and the second and the third doped regions, respectively. The depletion regions of the two junctions are substantially in the center of a guided optical mode propagating at the core region through the rib waveguide. The optical device further includes a first metal contact and a second metal contact in electrical contact with the first doped region and the second doped region, respectively.
Owner:LAXENSE
Mach-zehnder type silicon optical waveguide switch based on narrow slit wave guide
InactiveCN101276068AImprove modulation efficiencySmall spacingCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionRefractive indexWaveguide
The present invention discloses a Mach-Zehnder type silica optical waveguide switch based on narrow slit waveguide. After the wave splitting of the 3dB coupler which realizes power splitting function at the input end, a first group of two spot-size converting structures are respectively connected to the interference arms of two narrow slit waveguide structures, and then are connected to the output-end interference coupler through a second group of two spot-size converting structures. A random-structure 1*2 and 2*2 optical switches are formed through the different combination of two groups of spot-size converting structures. The present invention leads to a narrow slit waveguide and fills a low refraction ratio electrooptic material in the narrow slit. The modulation facility is enlarged, and the conventional indirect electrooptic modulation of carrier injection is switched to a direct electrooptic modulation. Besides, the silicon waveguides which are at two sides of the narrow slit and are electrically insulated naturally are taken as electrodes and the distance from the electrode to the modulation area is shortened. The two characteristics can equally increase the modulation efficiency of the switch. The whole structure is compact in dimension. The invention is compatible to the CMOS processing technique and provides a novel approach for the realization of the single-chip integrated high-speed electrooptic switch.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
All-fiber electro-optical modulator based on graphene materials and method thereof
ActiveCN103176294AReduce volumeImprove modulation efficiencyNon-linear opticsOptical integrationMetal electrodes
The invention discloses an all-fiber electro-optical modulator based on graphene materials and a method of the all-fiber electro-optical modulator. The all-fiber electro-optical modulator based on the graphene materials comprises a single mode fiber, a silicon dioxide groove-type substrate, an Al2O3 transition thin layer and a graphene membrane, wherein the single mode fiber is arranged on the silicon dioxide groove-type substrate and fixed through sealed epoxy glue, a groove is formed in the single mode fiber, the Al2O3 transition thin layer is arranged in the groove, and the graphene membrane is arranged on the Al2O3 transition thin layer. Conductivity performance of graphene is changed through change of voltage applied on a metal electrode, therefore an imaginary part or a real part of an effective refractive index of a graphene composite layer structure is changed, and an electric absorption strength modulator or a phase modulator is achieved. The all-fiber electro-optical modulator based on the graphene materials and the method of the all-fiber electro-optical modulator can achieve design of the all-fiber electro-optical modulator, and have the advantages of being tiny in size, little in power consumption, low in insertion loss, high in modulating speed, beneficial for optical integration and the like. In addition, due to the fact that additional optoelectronic devices are not introduced, the all-fiber electro-optical modulator based on the graphene materials and the method of the all-fiber electro-optical modulator are suitable for being used in an all-fiber communication system and a dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Electro-optic modulator based on micro-ring Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure
InactiveCN103293715AExtend your lifeModulation speedNon-linear opticsIncident waveIntensity modulation
The invention discloses an electro-optic modulator based on a micro-ring Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure. The electro-optic modulator comprises an incident waveguide, a bending waveguide, the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure and a traveling wave electrode, the incident waveguide is a straight waveguide and used for receiving incident light and outputting emergent light, a short distance is formed between the bending waveguide and the incident waveguide, the incident light passing through the incident waveguide is coupled into the bending waveguide, the emergent light passing through the bending waveguide is coupled into the incident waveguide and outputted, an input end of the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure is connected with an input end of the bending waveguide, an output end of the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure is connected with an output end of the bending waveguide to form a micro-ring resonant cavity, the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure is used for increasing light loss of the micro-ring resonant cavity, and the traveling wave electrode is used for loading voltage to the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure, so that the Mach-Zehnder interferometer structure is used for modulating the intensity of light inputted into the structure. The MZI (Mach-Zehnder interferometer) structure is added into a micro-ring uncoupled area, and the incident light is modulated by switching over a micro-ring critical coupling state and a noncritical coupling state.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
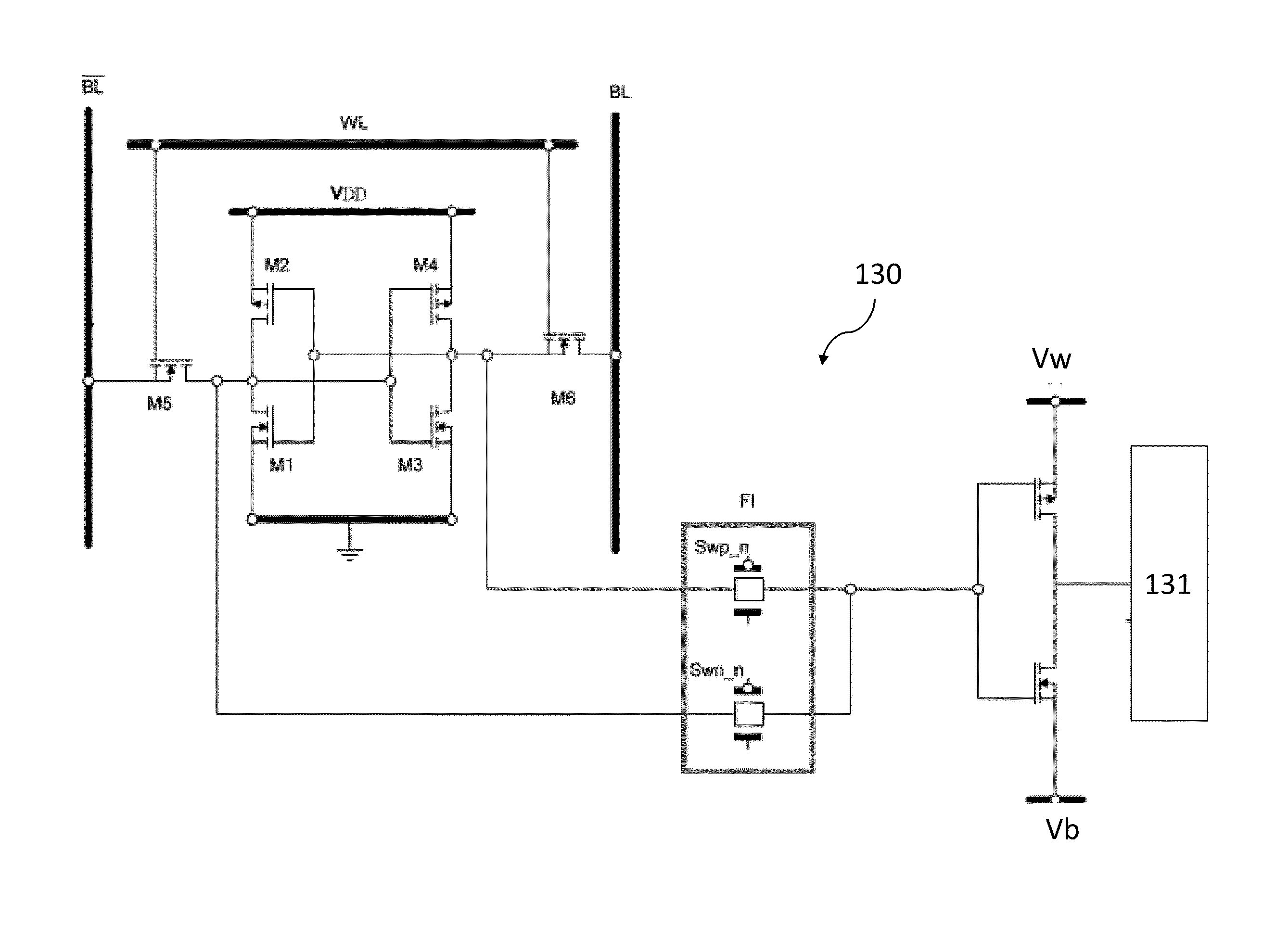
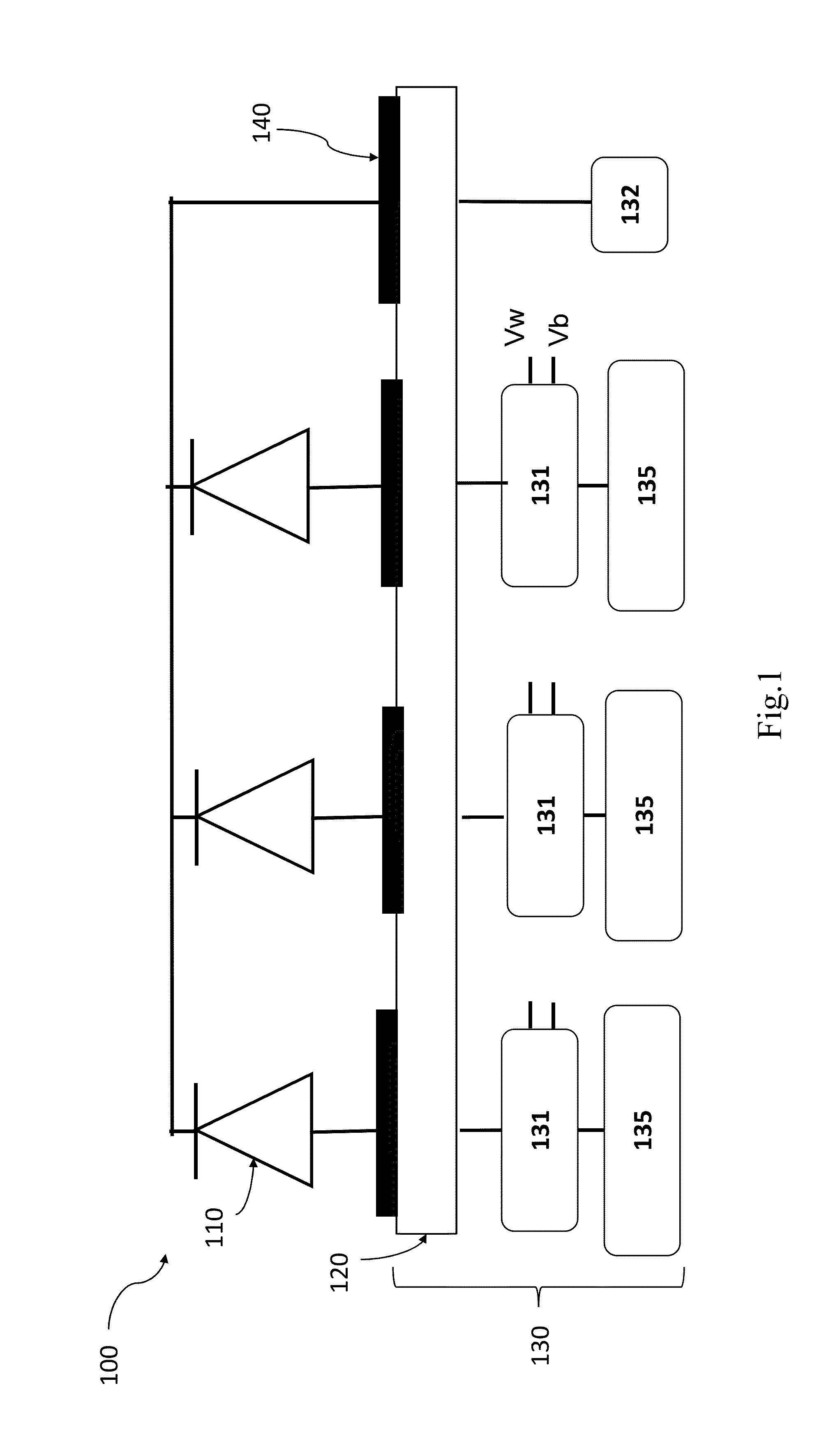
Modulation scheme for driving digital display systems
ActiveUS8421828B2Improved gray scale modulationImprove modulation efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingModulation efficiencyDisplay device
A display device and modulation scheme for applying image data to an imager. The display may use a modulation scheme wherein spacing of row write actions on the rows creates gray scale modulation, wherein one row spacing between sequential row write actions is at a first distance while another row spacing between sequential row write actions is at a distance greater than said first distance. The modulation scheme may create a series of write pointers that create a corresponding series of write planes. In some embodiments, modulation efficiency is increased allowing the use of lower frequency imaging circuits to achieve the same display image.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Electrode structure for improving speed and efficiency of MZI (Math-Zehnder Interferometer) electro-optic modulator
InactiveCN101937135AImprove modulation efficiencyNon-linear opticsPersonal identification numberLight guide
The invention relates to an electrode structure for improving the speed and the efficiency of an MZI (Math-Zehnder Interferometer) electro-optic modulator, comprising an MZI modulator structure. The MZI modulator structure comprises a first modulation arm, a second modulation arm and a high-frequency driving circuit, wherein the first modulation arm and the second modulation arm are in crestiform light guide structure and respectively comprise a first flat area, a second flat area, a first inner ridge area and a second inner ridge area, the first flat area and the second flat area at both sides of the first inner ridge area and the second inner ridge area are respectively provided with a first doping area, a second doping area, a third doping area and a fourth doping area which are in PIN (Personal Identification Number) electric modulation structure when in the first flat area and the second flat area, the second doping area and the third doping area which are adjacent to the inner sides of the first modulation arm and the second modulation arm are connected together with a metal lead to form a first electrode of the high-frequency driving circuit, and the first doping area and the fourth doping area are connected together with a metal lead to from a second electrode of the high-frequency driving circuit, both ends of which are respectively connected with the first electrode and the second electrode of the high-frequency driving circuit.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Terahertz modulator based on low-dimension electron plasma waves and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105204190AImprove modulation efficiencyEfficient modulationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsResonant cavityGrating
The invention provides a terahertz modulator based on low-dimension electron plasma waves, a manufacturing method thereof and a high-speed modulation method. The terahertz modulator comprises a plasmon and a resonant cavity. The resonance absorption mechanism is caused by electronic collective oscillation (plasma waves, namely Plasmon). In order to increase the coupling strength of the plasma waves and the plasmon, a GaN / AlGaN high-electronic-mobility transistor structure with a raster grid is integrated in a terahertz Fabry-Perot resonant cavity, plasmon polariton is formed through strong coupling of the plasmon and the resonant cavity mode. By means of the strong coupling effect, the transmission coefficient of the resonant cavity mode is the maximum at the resonance point, resonance conditions of the plasmon and the resonant cavity mode are adjusted and controlled by changing the raster pressure, and efficient and high-speed modulation for terahertz waves is achieved. The working principle and the achieving technology of the device are introduced in detail, and a good solution is provided for relevant applications.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
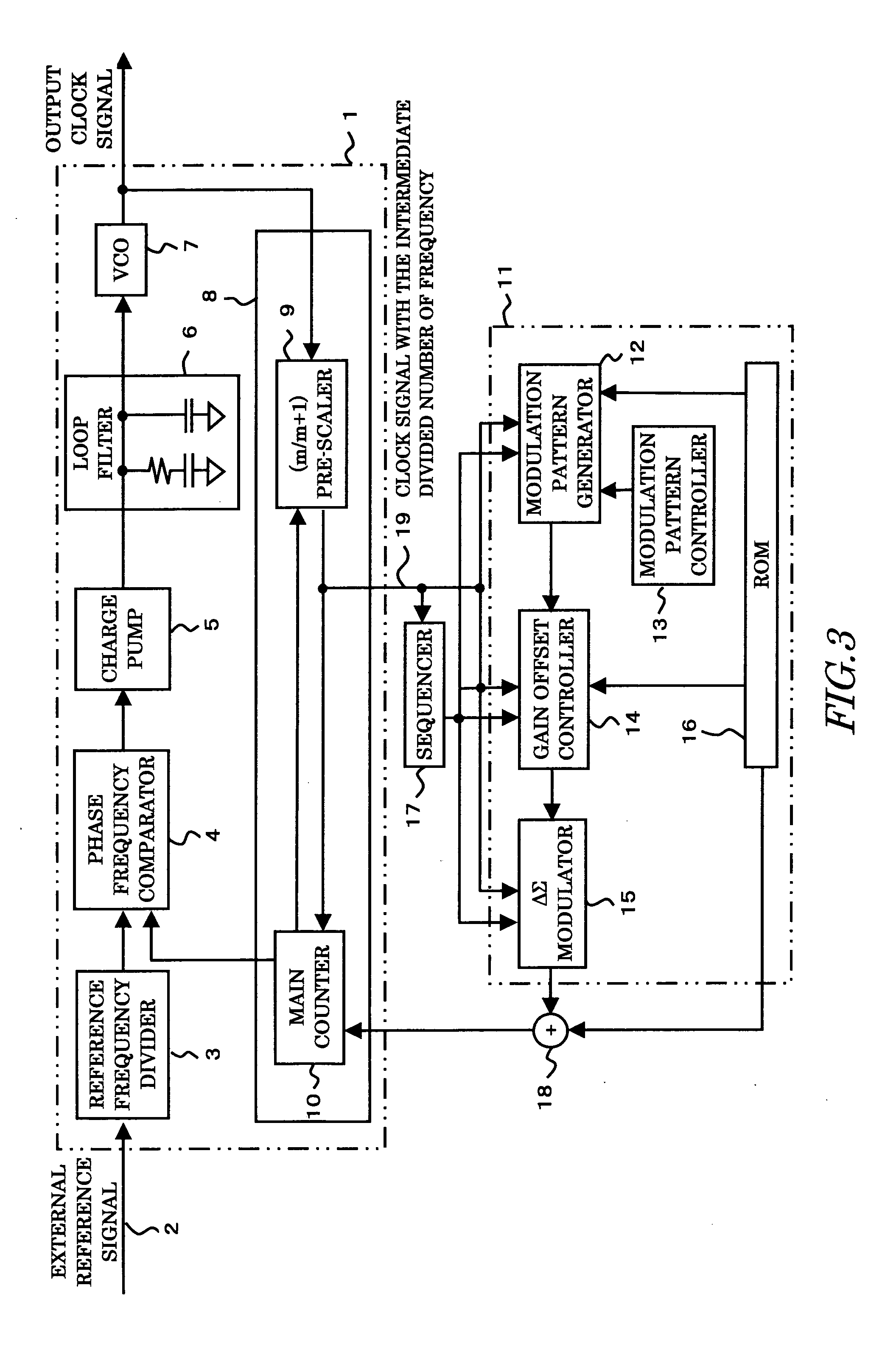
Spread spectrum type clock generation circuit for improving frequency modulation efficiency
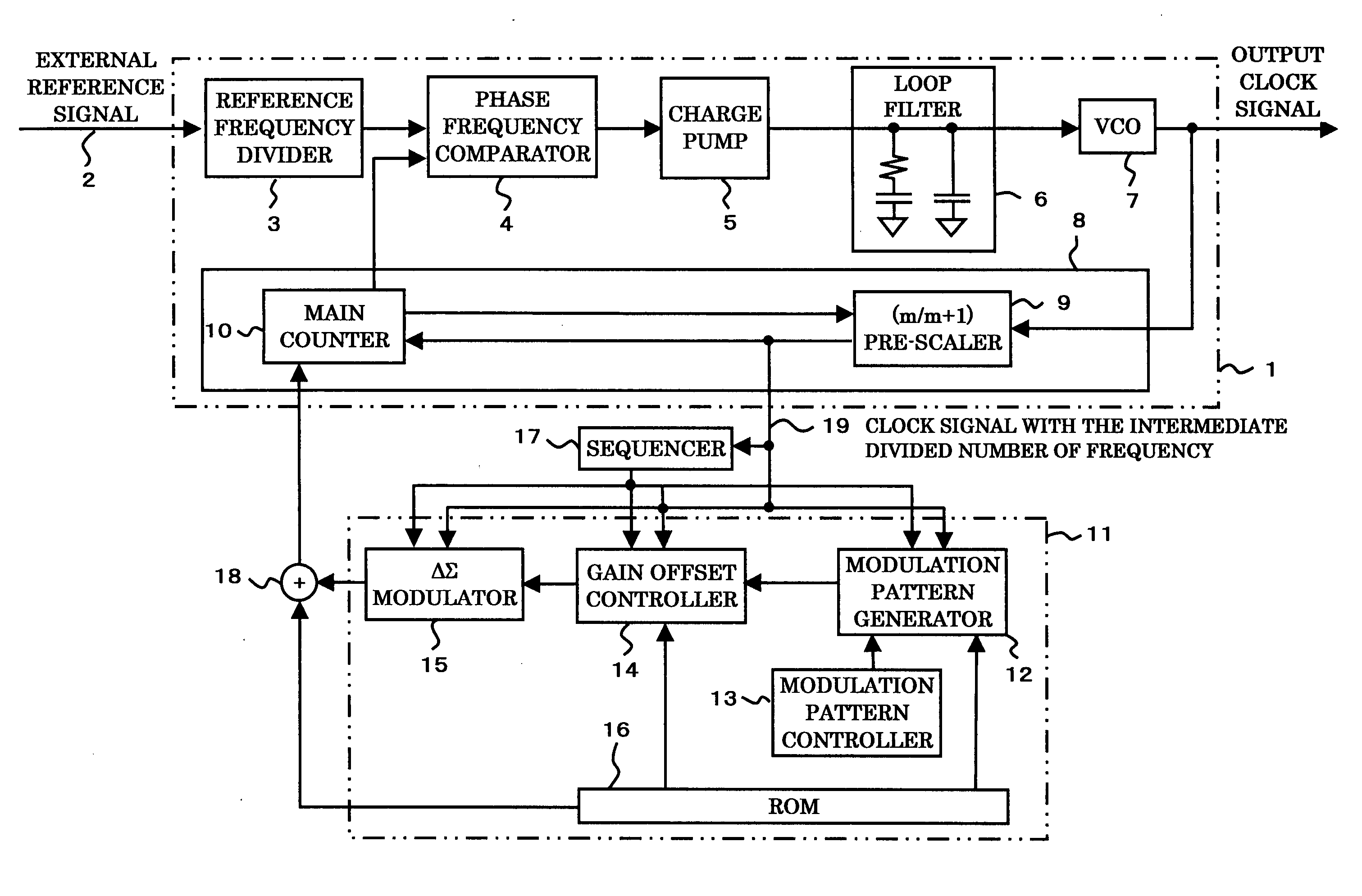
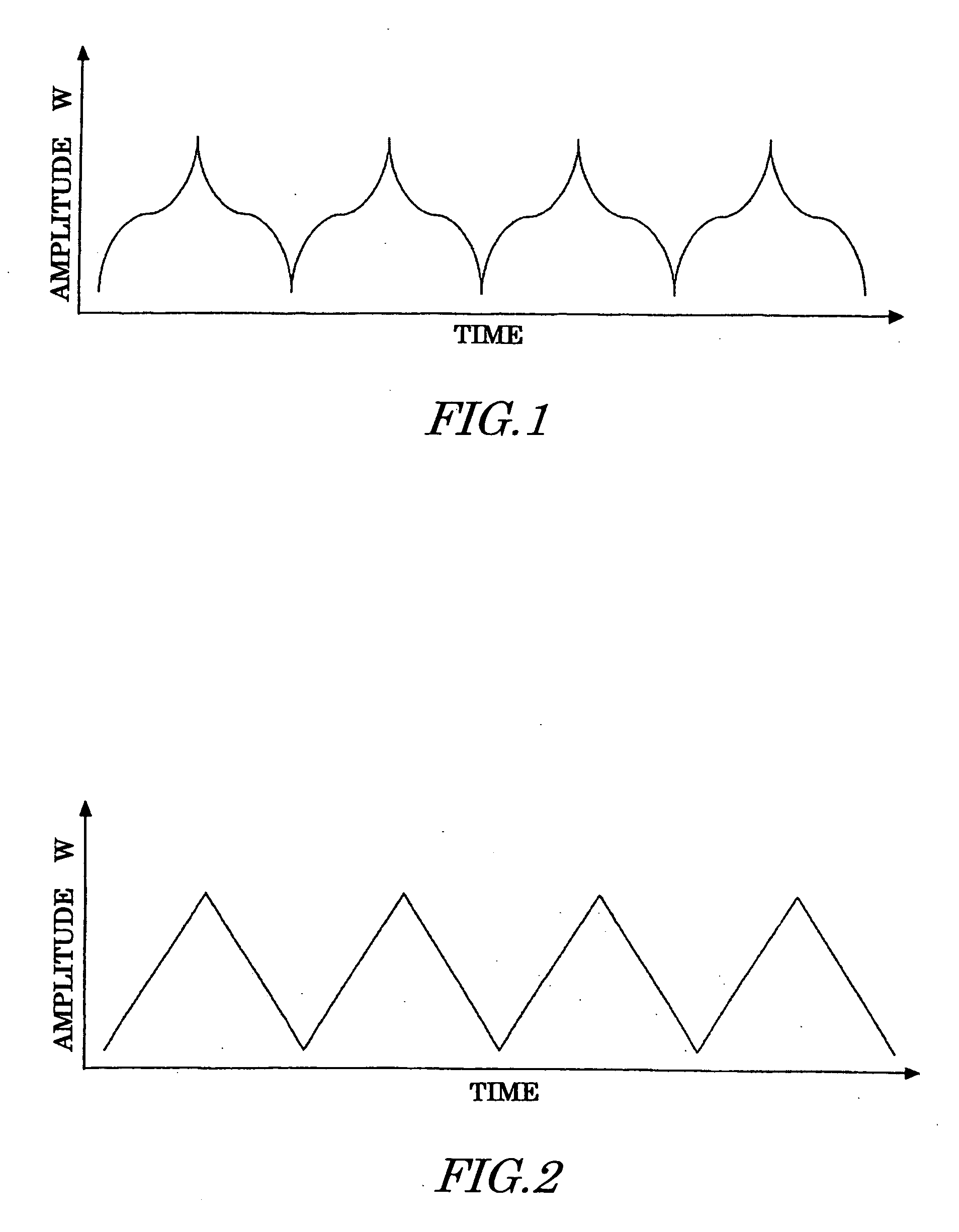
ActiveUS20050180490A1Efficient removalRemove distortionPulse automatic controlPulse duration/width modulationPhase locked loop circuitModulation pattern
The present invention provides a spread spectrum type clock generation circuit whose EMI for peripheral equipment is reduced. The clock generation circuit comprises a phase-locked loop circuit and a clock modulation circuit. The clock modulation circuit comprises a ΔΣ modulator, to frequency-modulate an output clock by modulating the frequency division number of a frequency divider in the phase-locked loop circuit by a digital circuit, and further comprises a modulation pattern controller for distributing the peak of a triangular waveform which is a modulation waveform generated by a modulation pattern generator to change the amplitude and the period thereof, thereby making it possible to eliminate dullness and distortion of a modulation waveform in a modulating method using a conventional analog circuit and to obtain an output clock having higher modulation efficiency than that in a case where a normal triangular waveform is employed in a conventional modulating method using a digital circuit.
Owner:SEIKO NPC
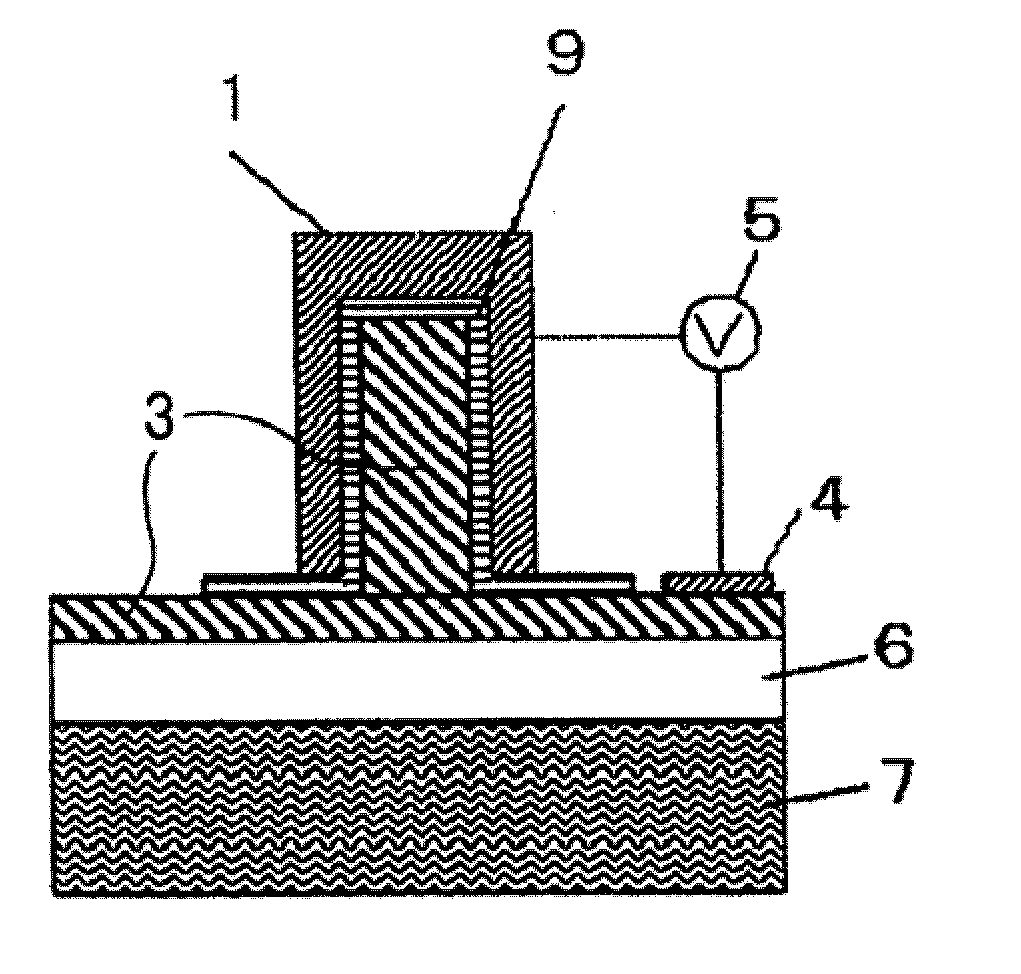
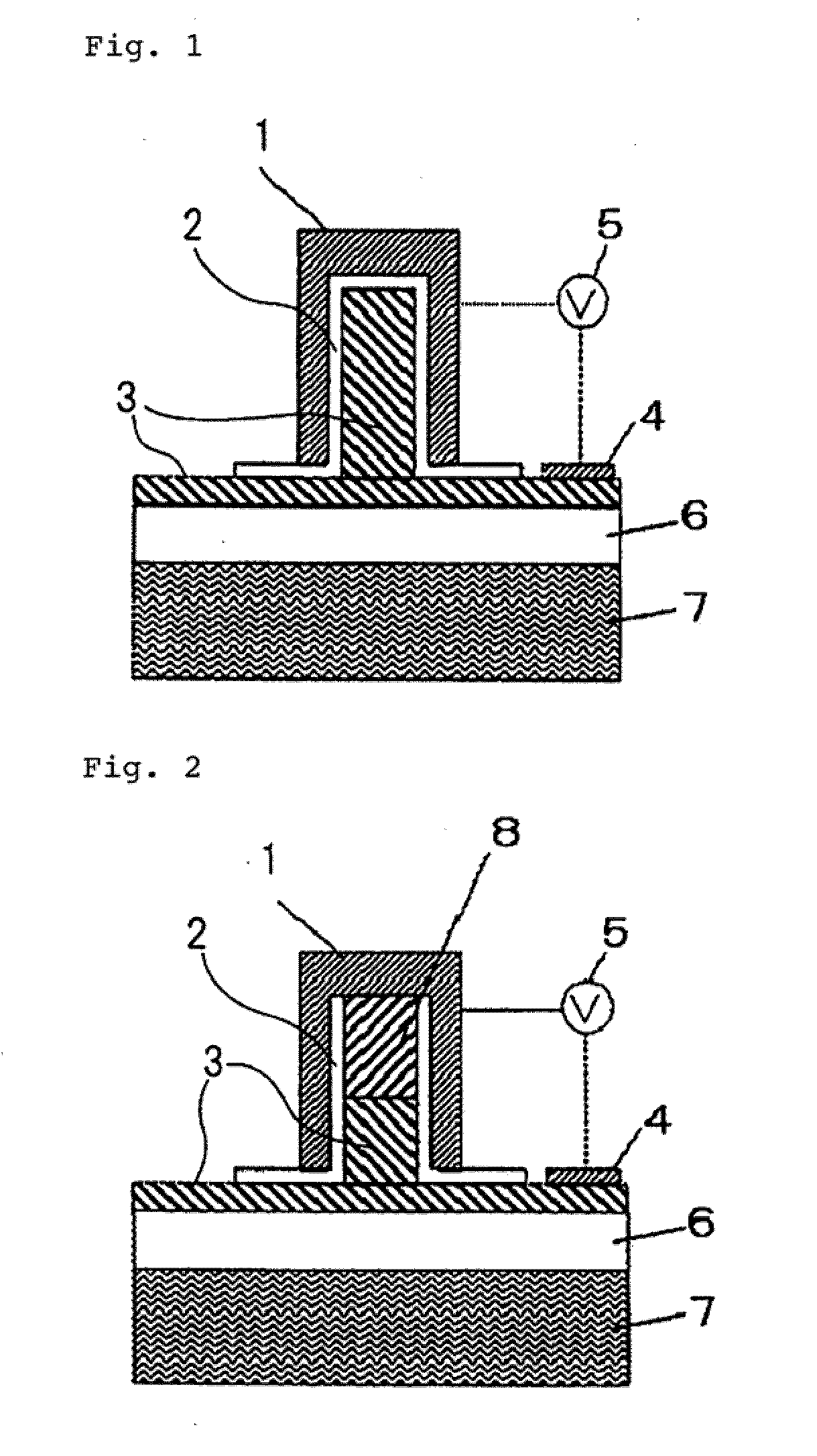
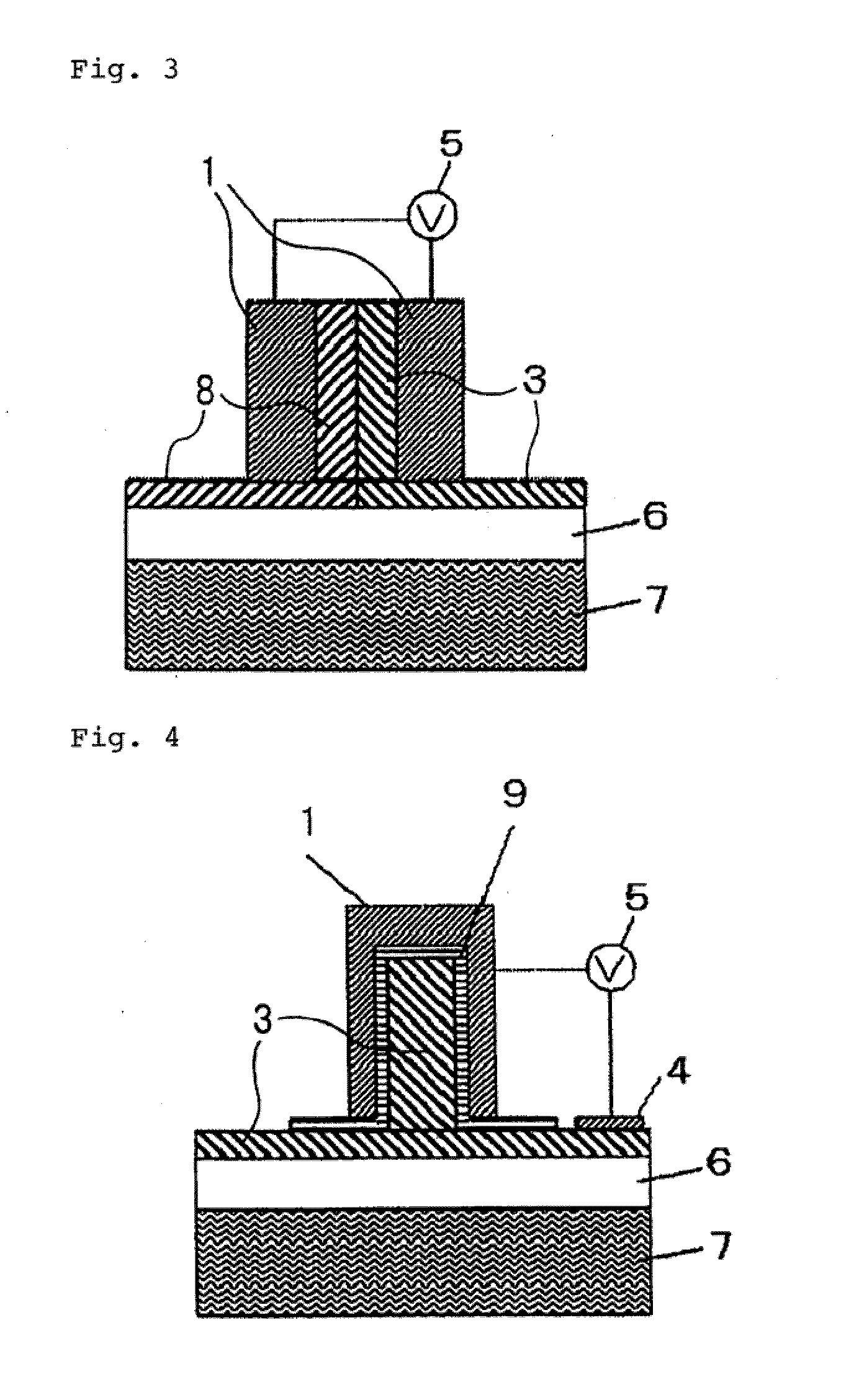
Semiconductor optical converter
ActiveUS20060159381A1Improve efficiencyIncrease the electric field strengthNanoopticsNon-linear opticsInformation processingCommunications system
A semiconductor optical converter for use principally in an optical communications system or an optical information processing system. The semiconductor optical converter comprises an n-InP clad layer (12), an optical waveguide layer (13), an SI-InP clad layer (14), and an n-InP clad layer (15) formed sequentially on an SI-INP substrate (11), characterized in that a voltage is applied from an electrode (16) connected with the n-InP clad layer (15) and ground electrode (17) connected with the n-InP clad layer (12). The semiconductor optical converter is especially applicable as a semiconductor phase modulator or a semiconductor Mach-Zehnder phase modulator operating at low voltages and having a low waveguide loss.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Optical phase modulation element and optical modulator using the same
InactiveUS20100316325A1Raise efficiencyReduce size of deviceNanoopticsCoupling light guidesOptical modulatorLight wave
Owner:NEC CORP
Low-frequency mechanical antenna based on electromechanical coupling and signal processing method
ActiveCN111478872APrecise control of carrier phaseReduce intensityMultiple carrier systemsControl theoryElectromechanical coupling
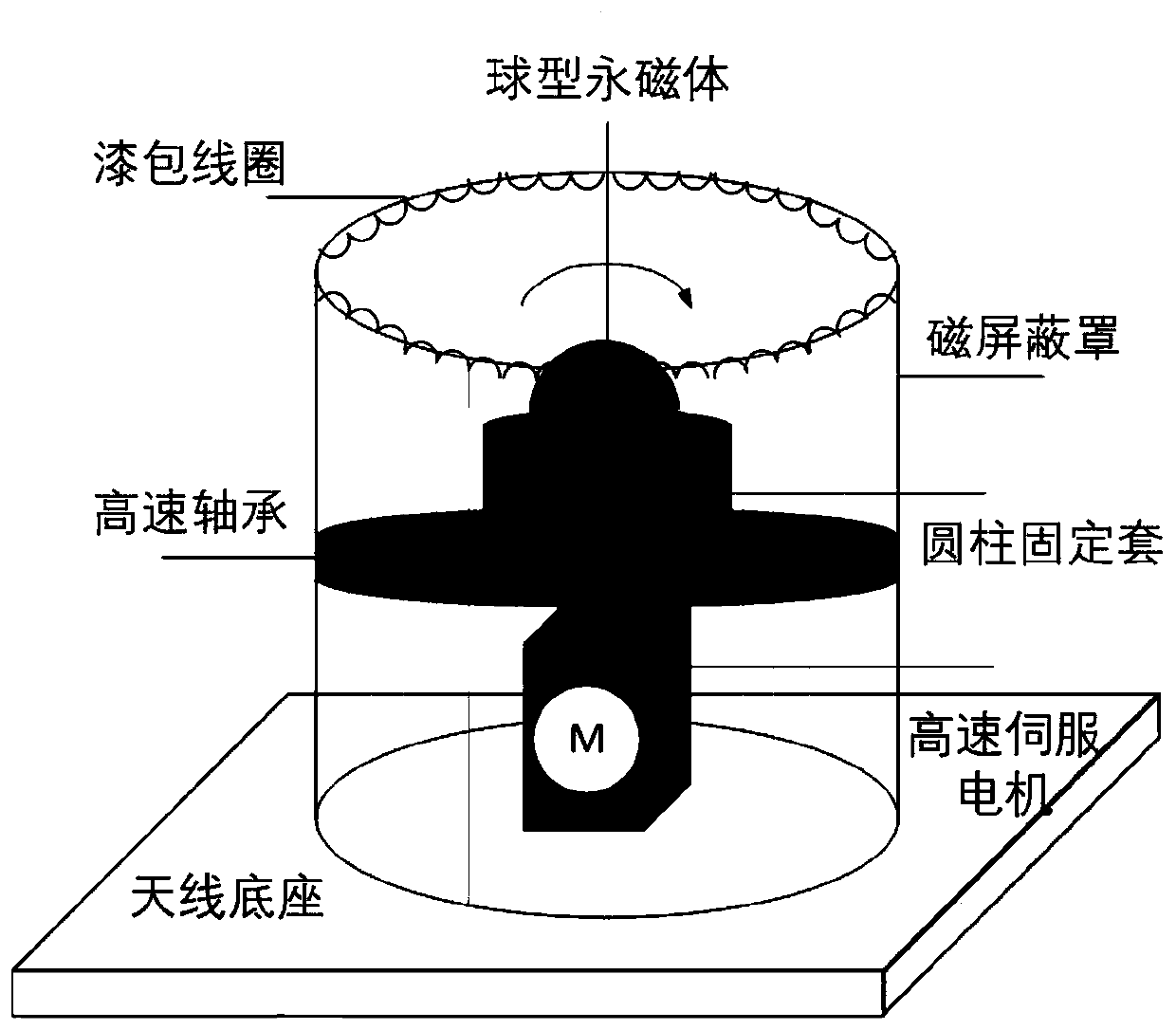
The invention discloses a low-frequency mechanical antenna based on electromechanical coupling and a signal processing method, and mainly solves the problems of poor stability and low modulation efficiency of a traditional mechanical antenna system in the prior art. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: the spherical permanent magnet is fixed by the cylindrical fixing sleeve sleeved with the motor spindle in the same diameter through the high-speed bearing, so that the operation stability is ensured; a high-speed servo motor is used for driving a spherical permanent magnet to rotate and radiating same-frequency electromagnetic waves outwards; the spherical permanent magnet is arranged in a magnetic shielding case of a signal loader, amplitude modulation information on a low-frequency magnetic field is loaded by changing the magnetic conductivity of a shielding case, a modulation signal is filtered and amplified by the signal collector, and then synchronization and demodulation are realized in the signal processor. According to the invention, the stability of a mechanical antenna rotation system is improved, a coding and modulation method adapting to a mechanical antenna modulation signal is provided, the signal processing efficiency of the antenna is effectively improved, engineering realization in information transmission application is facilitated, and the method can be used for a low-frequency wireless communication system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Three-dimensional packaging device for photonic integrated chip matching circuit
ActiveCN102856302AOvercome size constraintsAdd dimensionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPhotonicsLine array
The invention discloses a three-dimensional packaging device for a photonic integrated chip matching circuit. The three-dimensional packaging device comprises a first carrier substrate, a first microwave transmission line array, a second carrier substrate, a second microwave transmission line array, an electrode array and a microwave circuit, wherein the first microwave transmission line array is evaporated on the upper surface of the first carrier substrate and used for providing bias voltage and high-frequency modulating signals for photonic integrated chips; the second carrier substrate is perpendicular to the first carrier substrate or forms a certain angle with the same so that a three-dimensional stereoscopic structure is formed; the second microwave transmission line array is evaporated on the lower surface of the second carrier substrate and is matched with an electrode of the first microwave transmission line array by welding or sintering; and the electrode array is evaporated on one side face or two opposite side faces of the second carrier substrate. The three-dimensional packaging device for the photonic integrated chip matching circuit solves the problem that a matching circuit is limited in size due to limitation on array chip spacing during integrated chip array packaging and breaks through limitations that a microwave circuit is just in a two-dimensional plane in traditional design, dimensionality of circuit design is increased, and space for designing the microwave circuit is reserved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical modulation element, optical modulator, and manufacturing method of optical modulation element
InactiveUS20180011347A1Improve modulation efficiencyImprove efficiencyNon-linear opticsEngineeringWaveguide
Provided is an optical modulation element which includes an optical waveguide. The optical waveguide includes: a rib part; a first slab part extending from the first side face of the rib part; aid a second slab part extending from the second side face of the rib part. The optical waveguide includes a first semiconductor region and a second semiconductor region which have an opposite conductive type from each other. The first semiconductor region includes an upper section, a lateral section, and a lower section. The second semiconductor region is sandwiched between the upper section and the lower section so as to be substantially in direct contact with the upper section, the lateral section, and the lower section. At least one of an end face of the upper section and an end face of the lower section flushes with the first side face of the rib part.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Double electric capacity metal oxide semiconductor silicon based high speed high modulate efficiency electro optic modulator
InactiveCN101135749AImprove modulation efficiencyShorten the lengthOptical waveguide light guideElectric capacityContact layer
The invention comprises: a substrate; a silica buried layer formed on the substrate; a p type monocrystalline silicon layer is uses as the monocrystalline silicon on the substrate; forming a grid oxide layer on both sides of the p type monocrystalline silicon layer; a p+ injection layer is formed on the p type monocrystalline silicon layer; a n type monocrystalline silicon layer is formed on the silica buried layer and the both sides of the grid oxide layer, and said n type monocrystalline silicon layer and p type monocrystalline silicon layer are combined together to form a ridge waveguide structure; a n+ injection layer formed on the planes at both sides of the n type monocrystalline silicon ridge waveguide structure; a metal contact layer is formed on middle portion of the p+ injection layer in order to form the positive and negative electrode of the modulator; a oxide layer formed on the surfaces of the n type monocrystalline silicon layer and p type monocrystalline silicon as a protective layer.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Digital type silicon optical waveguide switch based on narrow slit waveguide
InactiveCN101408646AImprove modulation efficiencySmall spacingCoupling light guidesCMOSElectrical isolation
The invention discloses a slit waveguide-based digital type silicon optical waveguide switch. The switch comprises an input waveguide structure, two branch arms of a slit waveguide structure and an output waveguide structure; the three structures are sequentially connected, a waveguide at two sides of the slit of the two branch arms of the slit waveguide structure is a silicon waveguide, the slit is filled with an electro-optic material, and the width of the two branch arms is symmetrical or asymmetrical. An input single-mode waveguide is connected with the waveguide in front of the branch by a first set of mode-spot conversion structures, and the branch arms are connected with an output single-mode waveguide by a second set of mode-spot conversion structures. The slit is filled with a low-refractive index electro-optic material by the introduced slit waveguide, thus enlarging modulation means and introducing direct electro-optic modulation; in addition, as the silicon waveguide in naturally electrical isolation at two sides of the slit is taken as an electrode, the spacing between the electrode and a modulation area is shortened. As multi-slit is introduced, the branch spacing between the two branch arms can be increased under the condition of the same device length. The switch structure is integrated into the CMOS processing technology.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Phase locked sideband beams by bias modulation of an external cavity laser diode having a grating
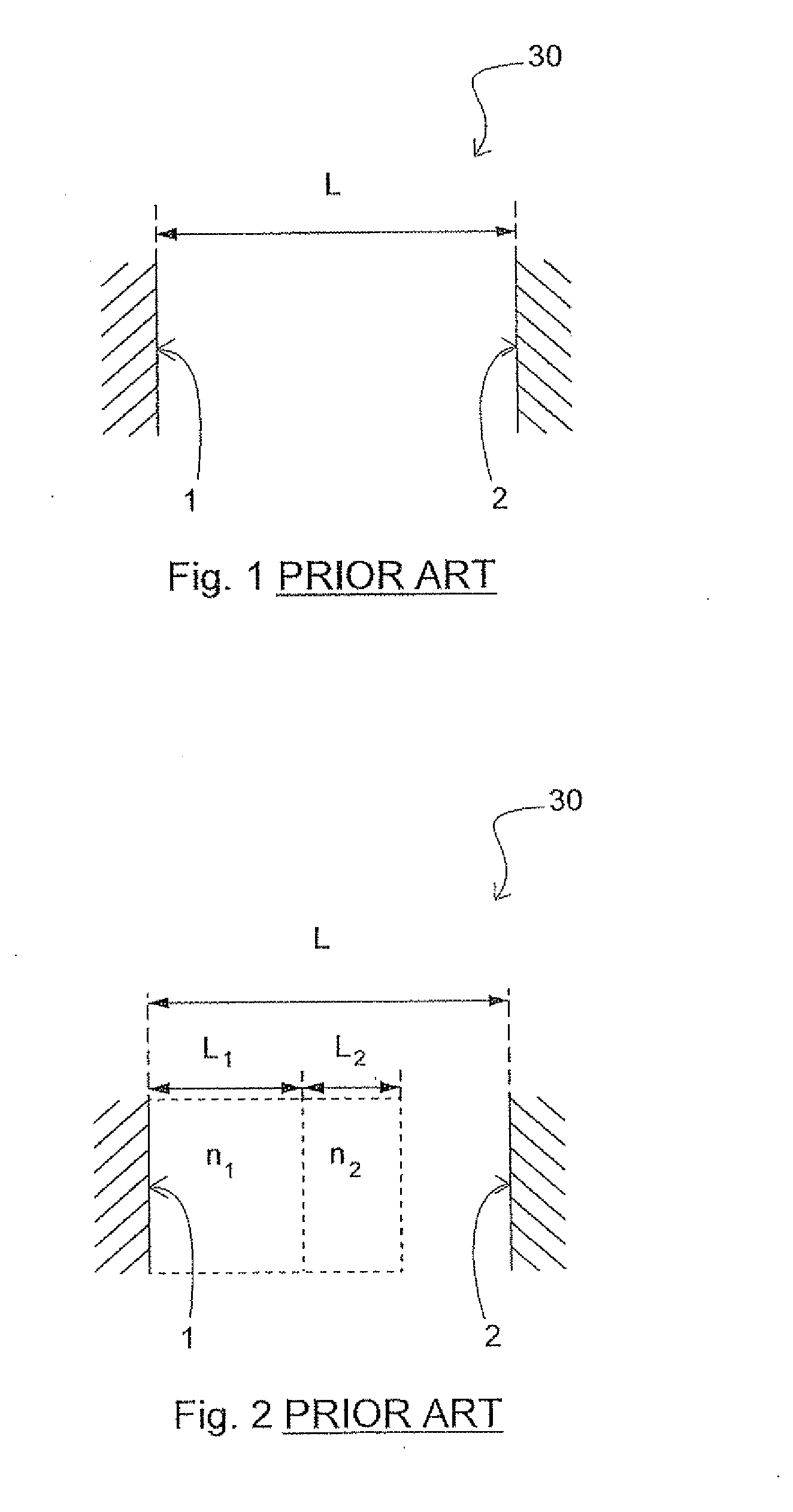
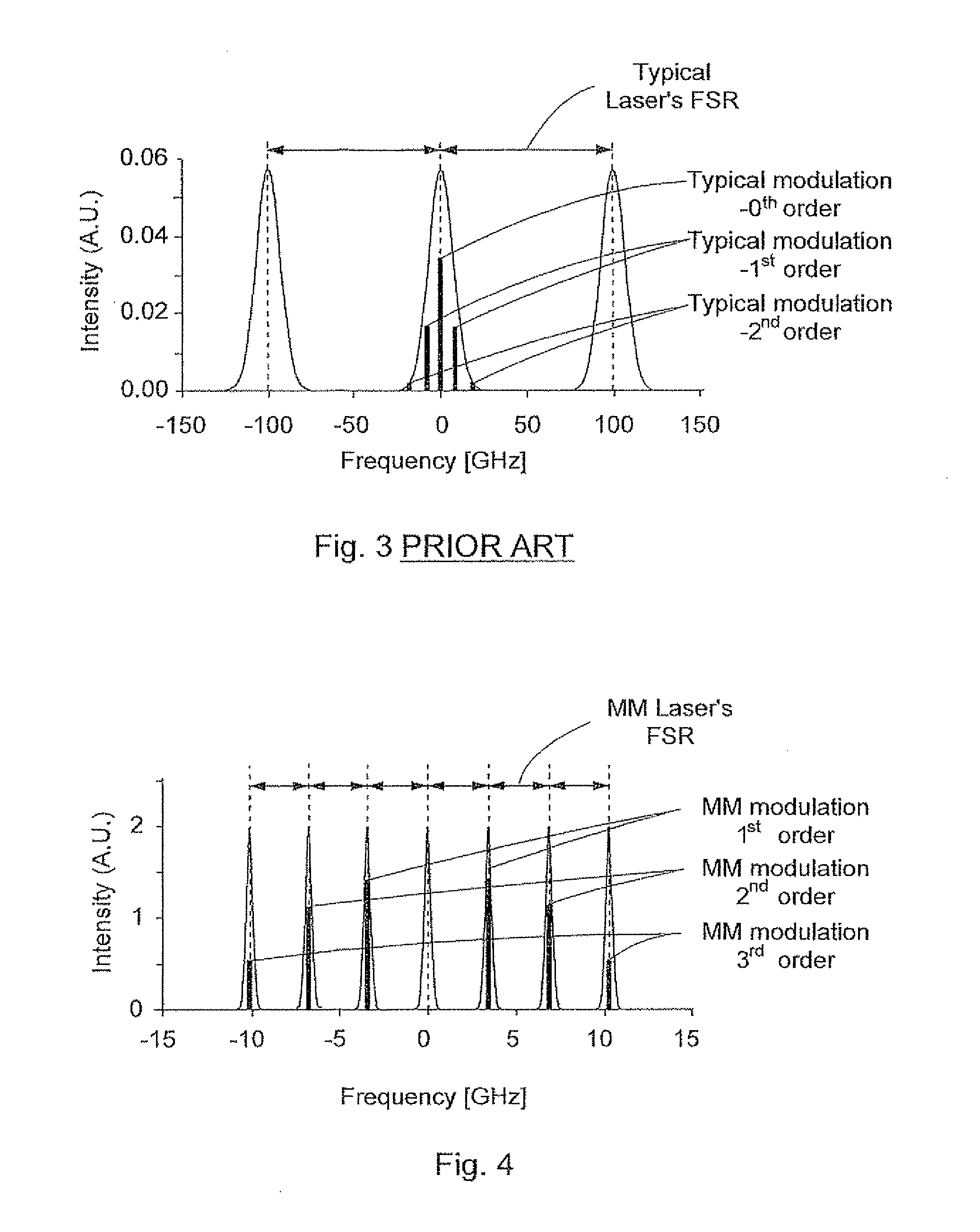
A device and a method enabling the enhancing of the modulation efficiency of lasers by matching the modulation frequency and the FSR of the laser. This is optionally achieved by eliminating the internal cavity of a laser diode (103) placed in an external cavity and matching the FSR of the external cavity to the modulation frequency. The modulation index is enhanced to and beyond the point of complete carrier suppression even at high modulation frequency and high beam intensities. The external cavity comprises a grating (107), the cavity length being adjusted with a PZT (108) and a translation stage (109). The laser diode (103) is driven by a bias current (110) from a driver (115) and a modulation current (111) from a modulation driver (116).
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
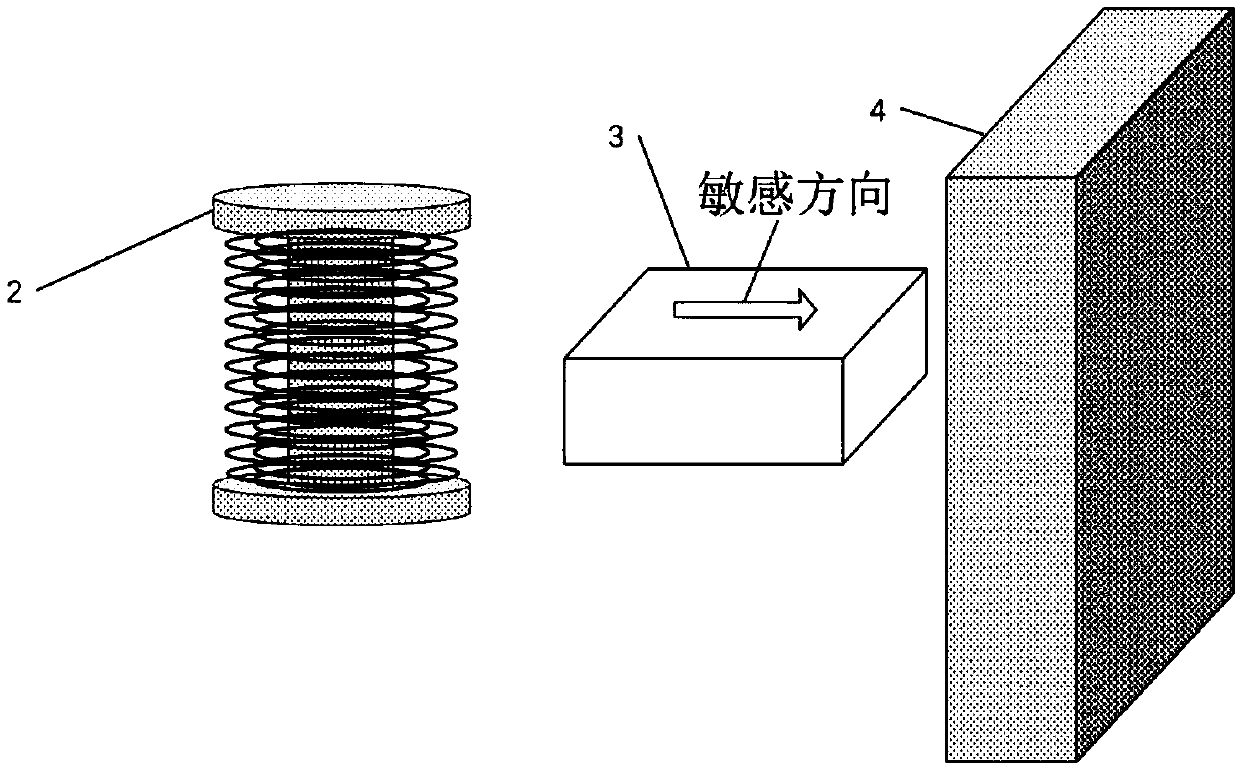
Low-frequency noise suppression device and method for tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor
ActiveCN109556647AReduce the effects of noiseEliminate the effects ofInstrumentsPeriodic alternatingLow noise
The invention discloses a low-frequency noise suppression device and method for a tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor. The device comprises a sensitive structure, wherein the sensitive structure comprises a micro coil, the tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor and a soft magnetic conductor which are sequentially disposed on a same horizontal line; the axial direction of the micro coil is perpendicular to the horizontal line; the micro coil and the tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor are spaced by a preset distance, and the sensitive direction of the tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor isperpendicular to the axial direction of the micro coil; an oscillating circuit, which is connected to the micro coil to drive the micro coil to generate a periodic alternating magnetic field; and a low-noise circuit, wherein the low-noise circuit is connected with the tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor and is used for processing an output signal of the tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor. According to the low-frequency noise suppression device for the tunnel magnetoresistive effect sensor provided by the invention, low-frequency noises can be suppressed, the signal-to-noise ratio and thedetection sensitivity are improved, the performance is stable, and the cost is low.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Electroabsorption optical modulator
InactiveUS20180373067A1Highly efficient optical couplingImprove modulation efficiencyNon-linear opticsModulation efficiencyOptical coupling
An electroabsorption optical modulator capable of realizing optical coupling with a Si waveguide with high efficiency, improving modulation efficiency, reducing light absorption by an electrode layer and achieving low optical loss includes first Si layer 34 of a first conductive type and second Si layer 35 of a second conductive type disposed parallel to substrate 31 and GeSi layer 51 stacked on the first and second Si layers.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Photonic and electric devices on a common layer
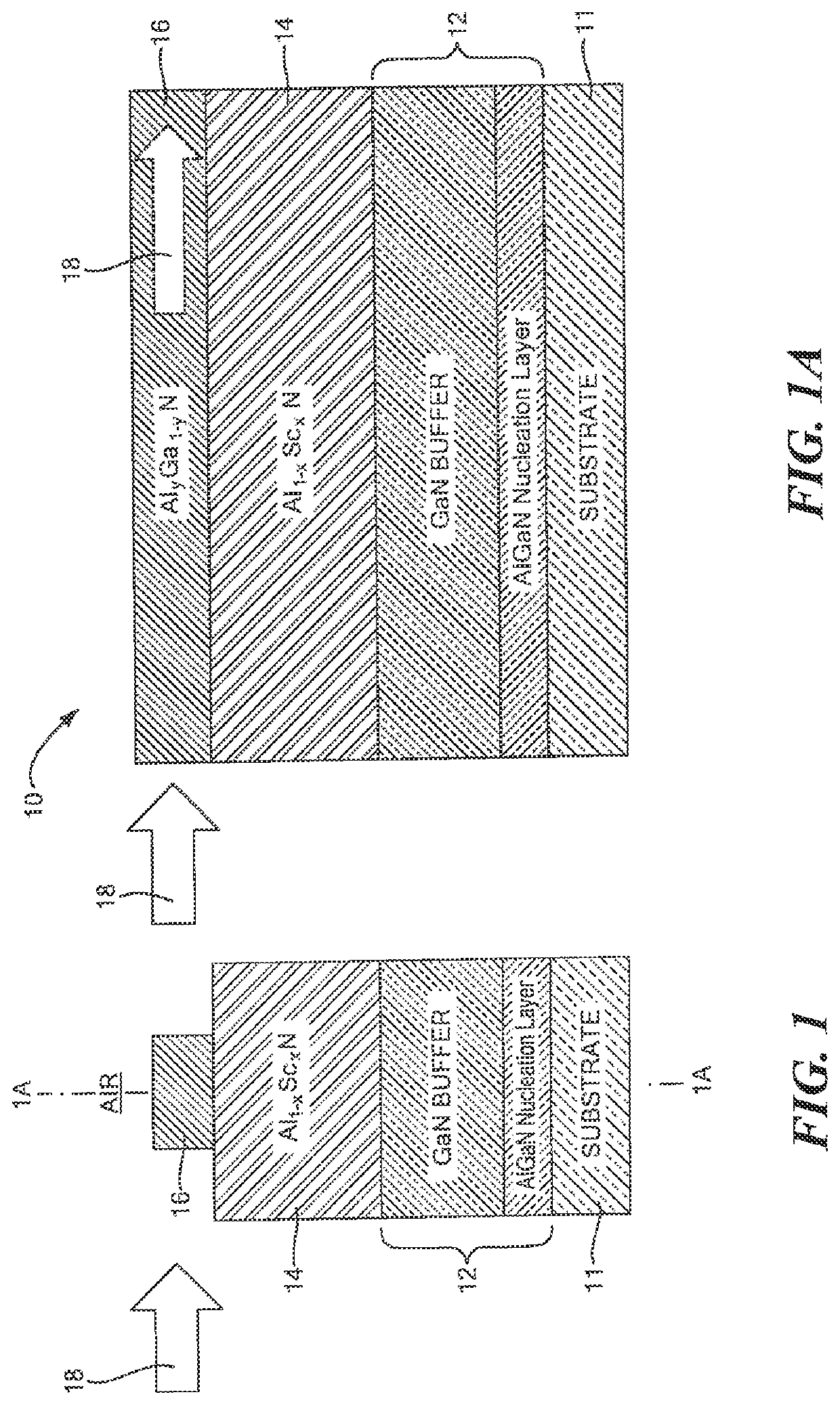
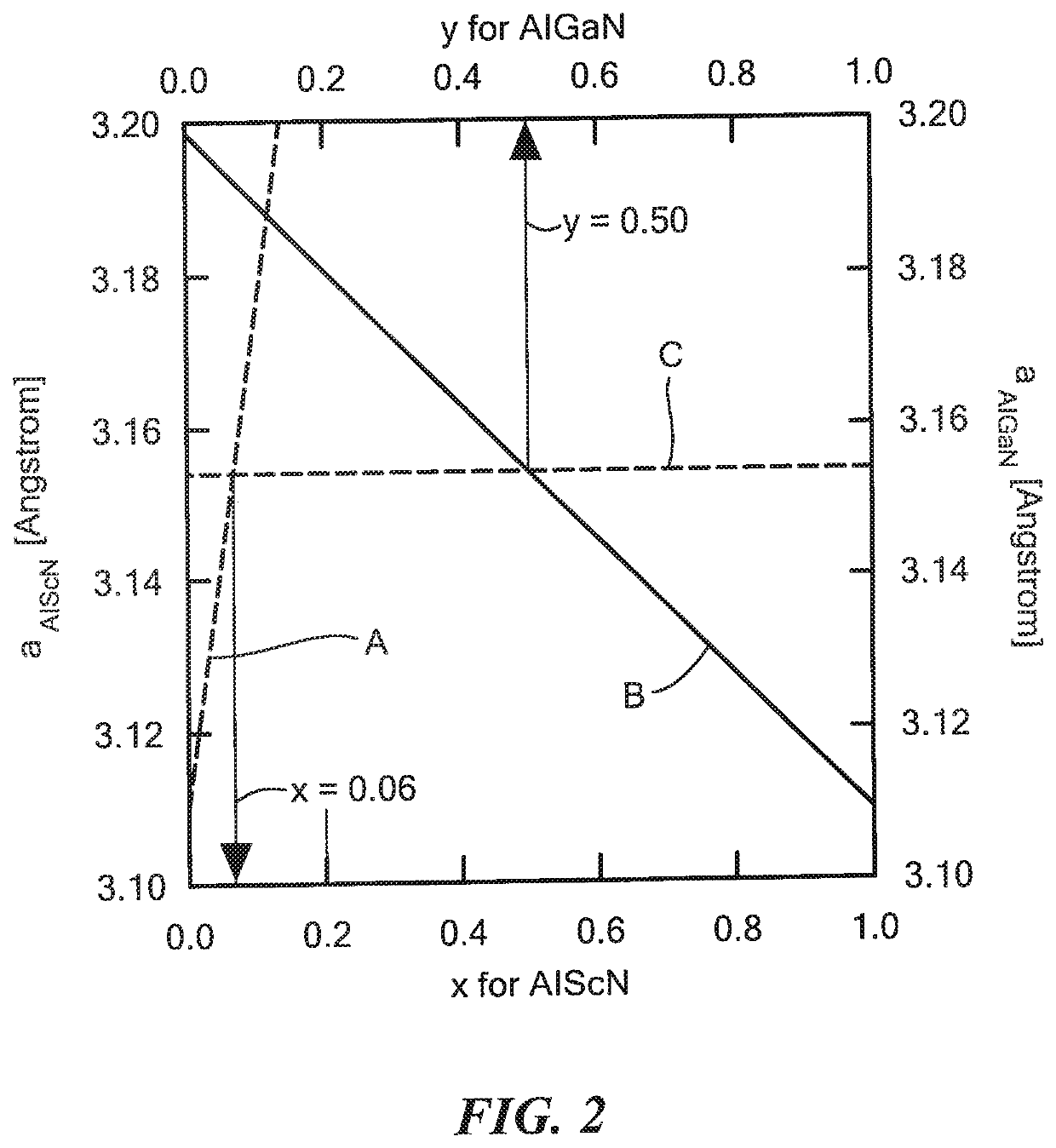
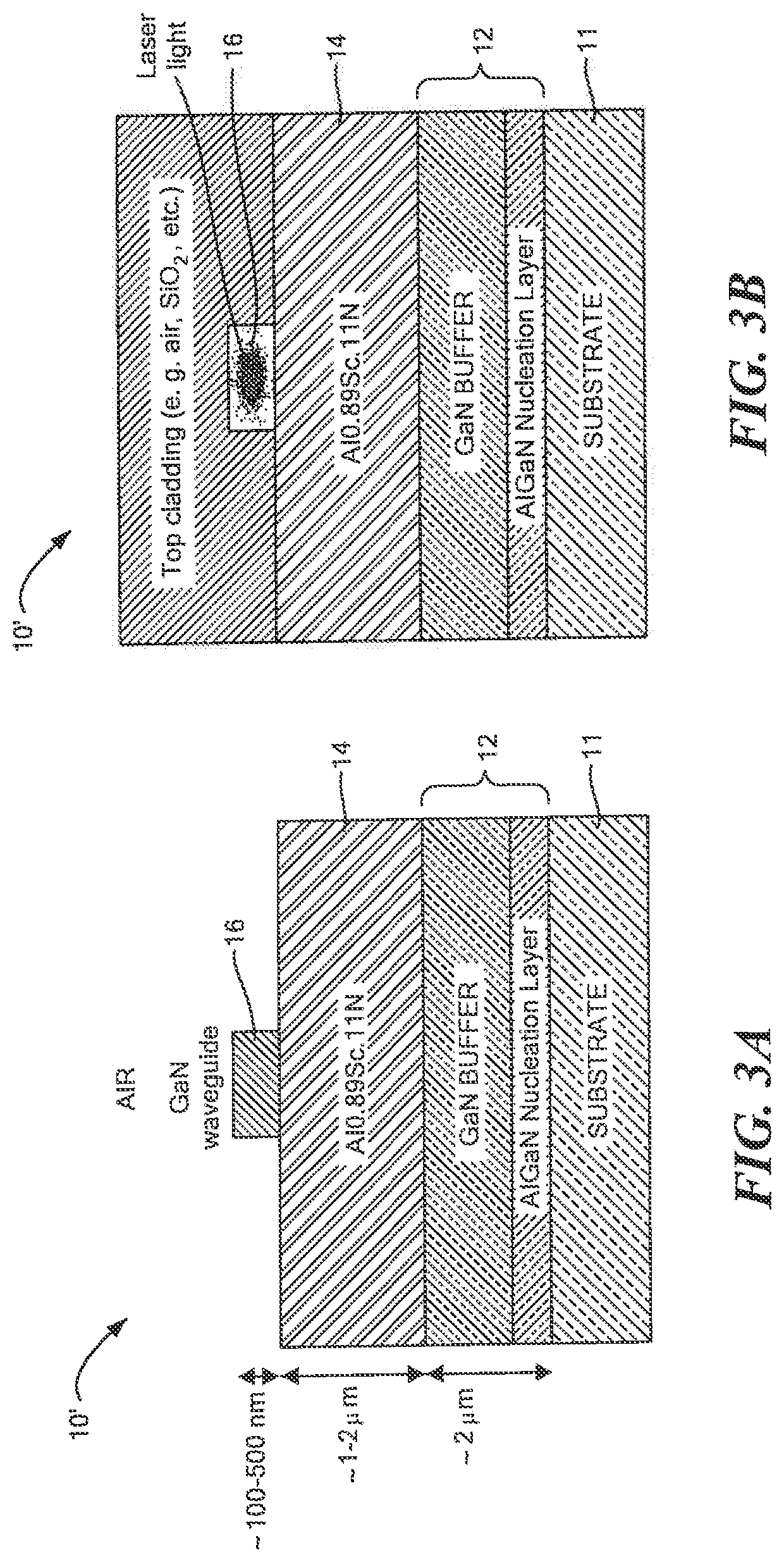
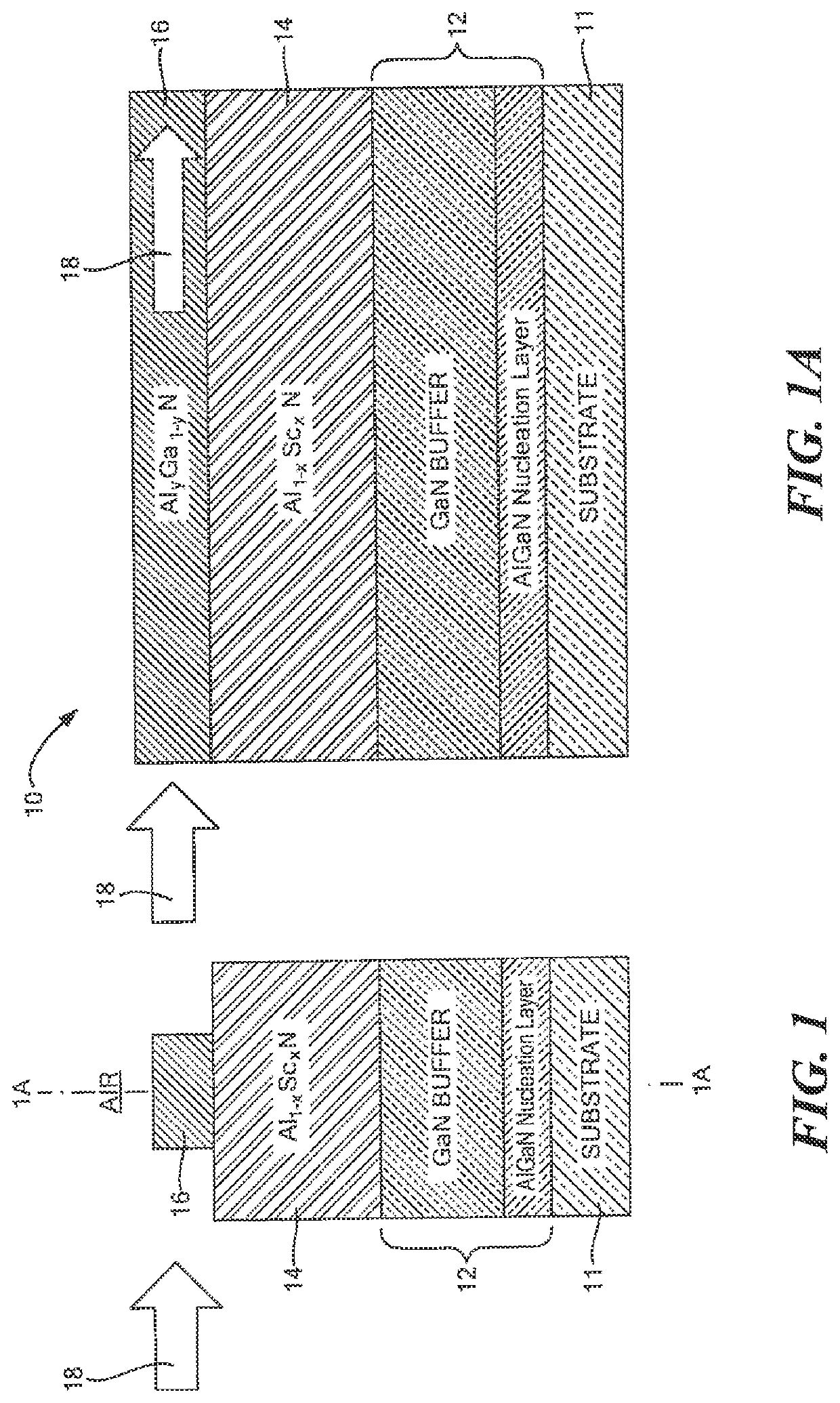
ActiveUS20190346624A1Improve efficiencyQuality improvementOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsPhotonicsScandium
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP +1
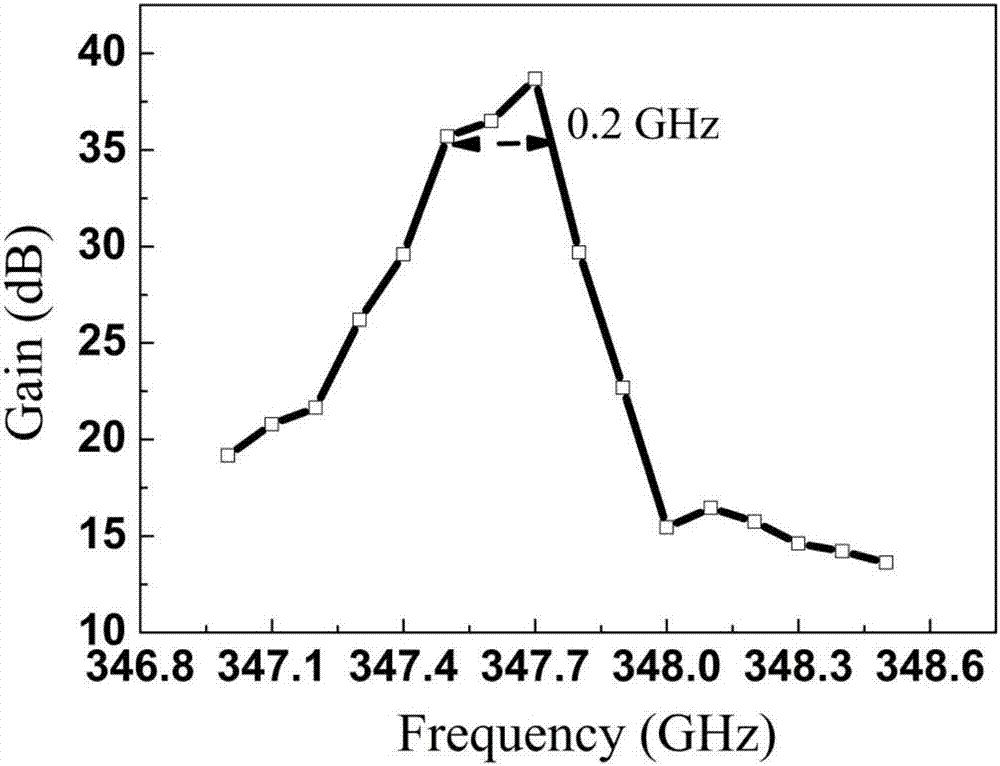
Extended interaction klystron and production method thereof
ActiveCN107068518AAvoid strong vibrationImprove working bandwidthKlystronsCold cathode manufactureKlystronResonant cavity
The invention belongs to the field of high-performance terahertz radiation sources, and provides an extended interaction klystron and a production method thereof. The extended interaction klystron comprises an input resonant cavity, an output resonant cavity, and N intermediate resonant cavities. The input resonant cavity is communicated with an input waveguide. The output resonant cavity is communicated with an output waveguide. Electron beam channels communicated with one another are arranged at the centers of the input resonant cavity, the output resonant cavity and the N intermediate resonant cavities. The cycle lengths of the resonant clearances of the N intermediate resonant cavities are different or partially different. N is a positive integer greater than 1. The problem that the existing extended interaction klystron has a very narrow working band and high in-cavity power density is solved. An electron beam is tuned by different resonant frequencies when passing through the intermediate resonant cavities. Thus, the working bandwidth of the whole device is improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Fourier laminated microimaging device and method
ActiveCN109581643AImprove coherenceSame luminous intensityMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesMicroscopic imageBeam angle
In order to solve the technical problems of low efficiency and low resolution of the existing Fourier laminated microimaging technology to recover sample images, the invention provides a Fourier laminated microimaging device and method. The device comprises a computer, and a laser, a collimating lens, a liquid crystal beam deflecting device, a sample stage, a microscope objective, a pipe mirror and a camera, which are sequentially arranged along an optical path from bottom to top; an outgoing beam center of the collimating lens and the center of the liquid crystal beam deflecting device are both coincident with the optical axis of the microscope objective; the liquid crystal beam deflecting device modulates the angle of a beam incident on a sample to be tested according to a computer control instruction; and the beams of two adjacent angles separately illuminate the sample, the diffraction spectrum information obtained on a Fourier plane of the microscope objective has an overlapping ratio greater than or equal to 50%; the camera collects a microscopic image corresponding to each beam angle incident on the sample to be tested according to computer control instruction; and the computer is also used for performing fusion reconstruction on the microscopic images obtained by the camera at different beam angles to obtain a final sample image.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Focal length-adjustable terahertz metasurface lens and preparation method and application thereof
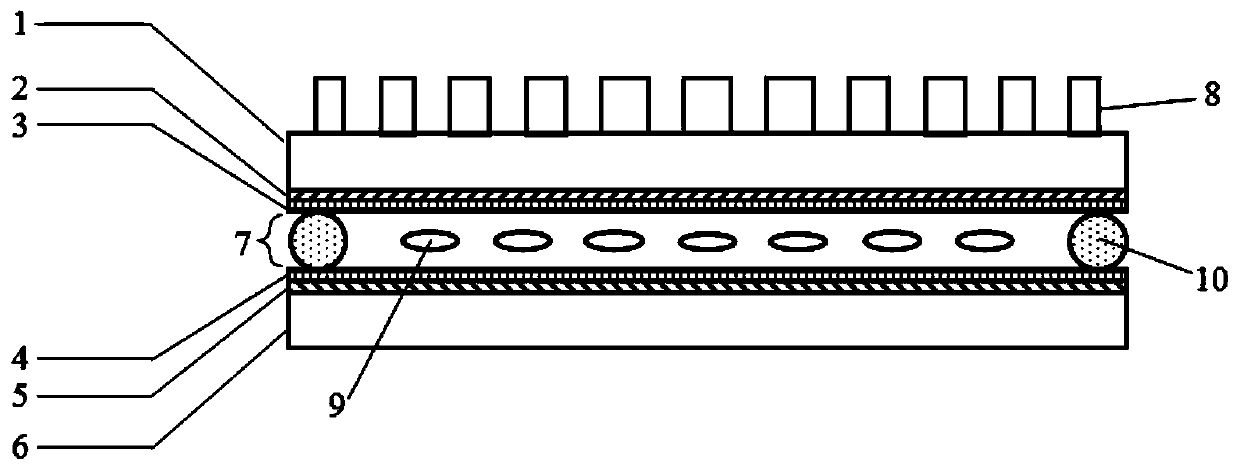
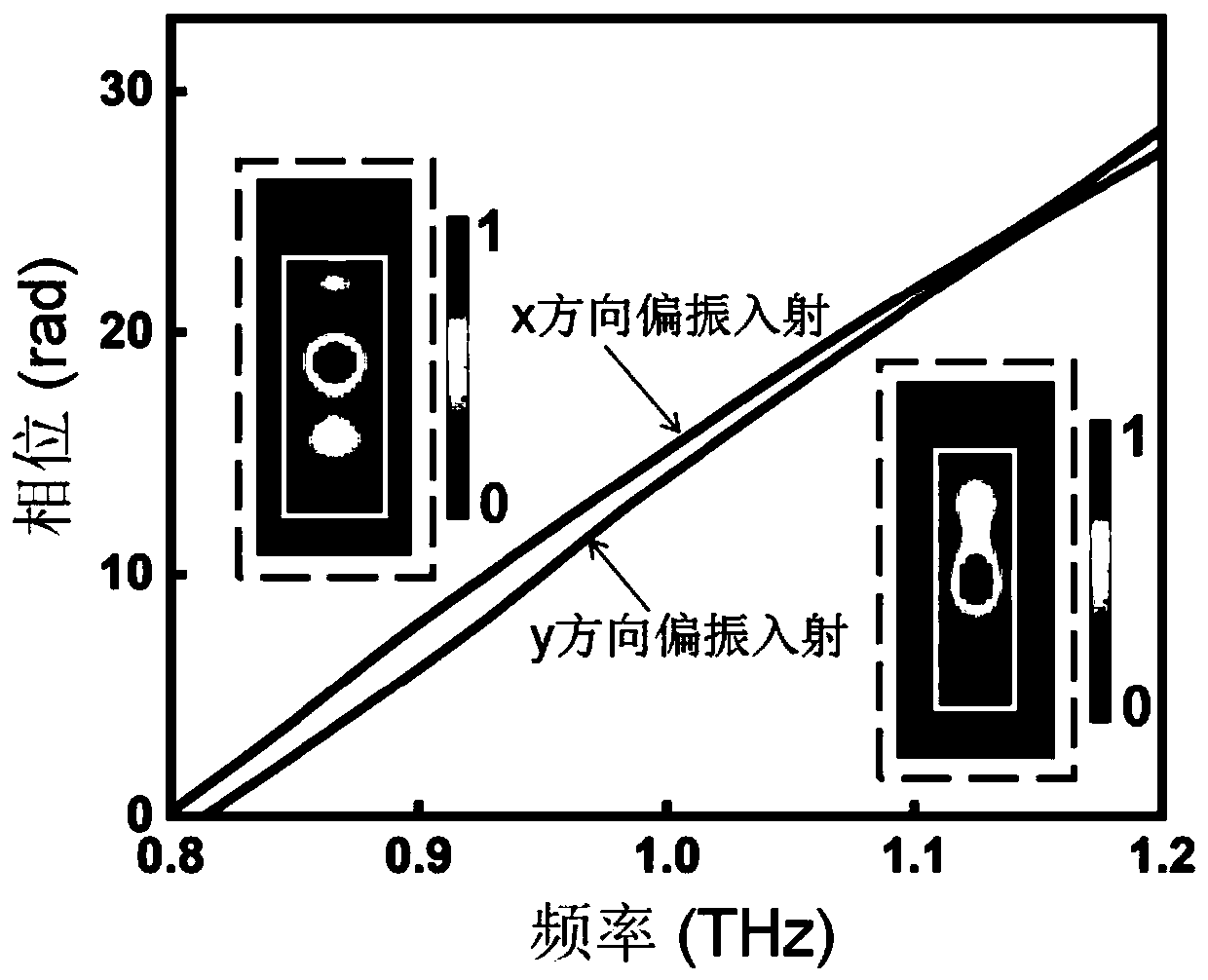
ActiveCN111399261ASolve functionImprove modulation efficiencyNon-linear opticsPolarization multiplexedDielectric layer
The invention discloses a focal length-adjustable terahertz metasurface lens and a preparation method and application thereof. The focal length-adjustable terahertz metasurface lens comprises a substrate and a dielectric layer which are oppositely arranged, a first electrode layer, a second electrode layer, a first orientation layer, a second orientation layer and a liquid crystal layer. A dielectric metasurface layer is arranged on the side, away from the substrate, of the dielectric layer, and the liquid crystal layer is arranged between the first orientation layer and the second orientationlayer; the first orientation layer and the second orientation layer have the same orientation direction are both have uniform orientations in a plane, and form an angle of 45 degrees with the transverse axis direction or the longitudinal axis direction; the orientation direction of the liquid crystal layer is induced by the orientation layer and is the same as the orientation direction of the orientation layer. Dynamic switching of the focal length of the lens can be realized through integration of the polarization multiplexing meta-lens and the electrically tunable liquid crystal wave plate,the dynamic switching of the function realizes the multifunctional adjustable terahertz meta-lens, and the technical problem of single function and application of the terahertz device in the prior art is solved.
Owner:南京南辉智能光学感控研究院有限公司
Photonic devices
ActiveUS20190346705A1Improve efficiencyQuality improvementOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsPolymer sciencePhotonics
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP +1
Inclined PN junction doped structure of silica-based electro-optic modulator
ActiveCN105511120AImprove modulation efficiencyReduce modulation energy consumptionNon-linear opticsModulation efficiencyElectrical connection
The invention relates to a doped structure of a silica-based electro-optic modulator. The doped structure comprises a modulation region waveguide of the silica-based electro-optic modulator, wherein the waveguide comprises a first heavily doped region, a second lightly doped region, a third lightly doped region and a fourth heavily doped region in sequence in the first direction; the second lightly doped region and the third lightly doped region form at least one longitudinally inclined PN junction and at least one transversely inclined PN junction, and the longitudinal direction is perpendicular to the transverse direction; a first included angle is formed between the longitudinal direction and the first direction and is larger than 0 degree and smaller than 90 degrees. The doped structure can lower modulation energy consumption while improving modulation efficiency of the silica-based electro-optic modulator, make all doped regions in the core area of the waveguide achieve electrical connection directly through the lateral waveguide, and guarantee high-speed modulation performance of a system.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method For Modulating A Micro-Led Display
InactiveUS20140368561A1Improve scaleImprove modulation efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareLED display
A micro-LED display device and modulation scheme for applying image data to an imager. The micro-LED display, including a plurality of micro-LED pixels disposed in rows and columns array, may use a modulation scheme. The method includes using row write actions to write data to said rows of micro-LED pixels; and using spacing of row write actions to create grey scale modulation, wherein one spacing between sequential row write actions is at a first distance while another spacing between sequential row write actions is at a second distance greater than said first distance.
Owner:JASPER DISPLAY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com