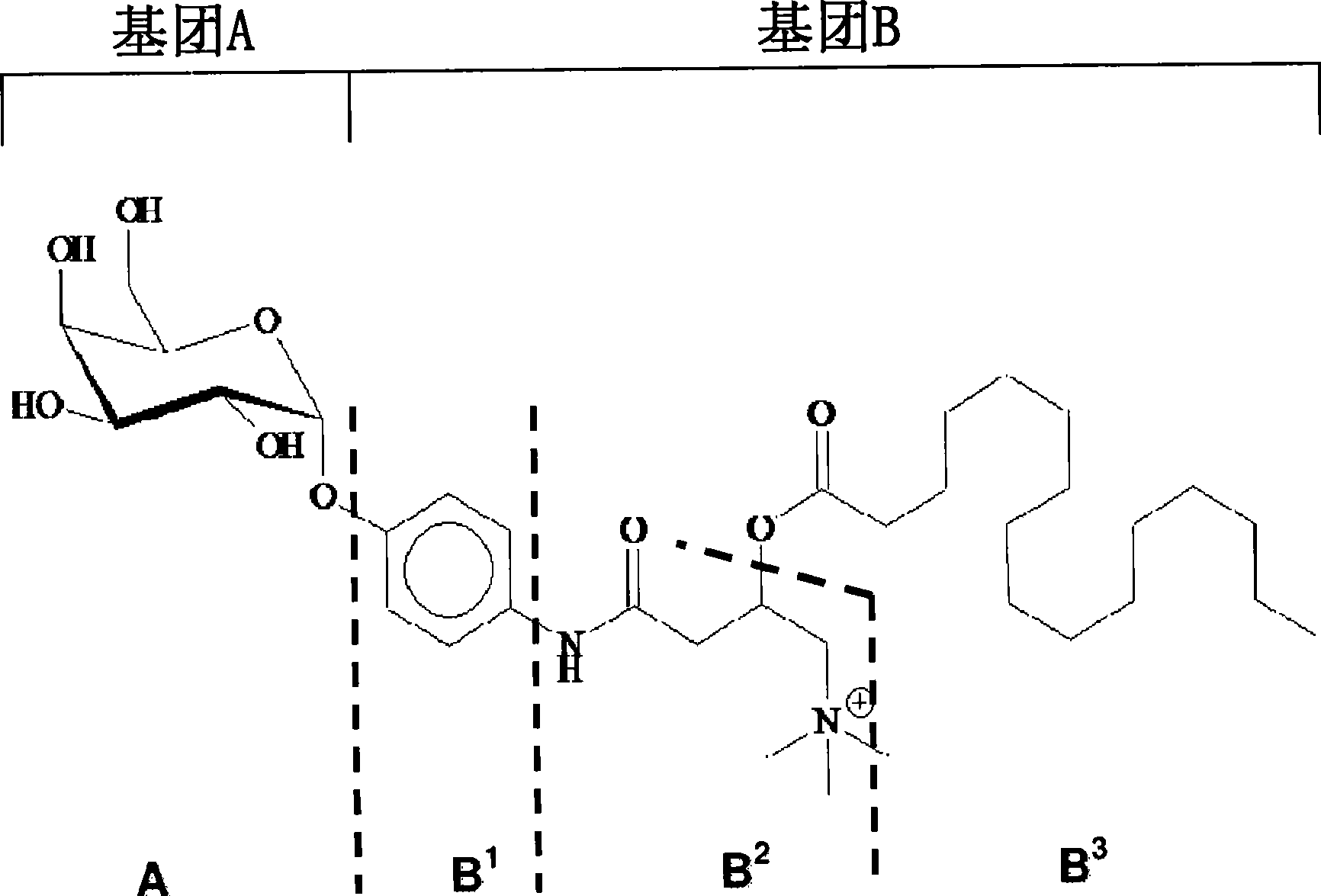
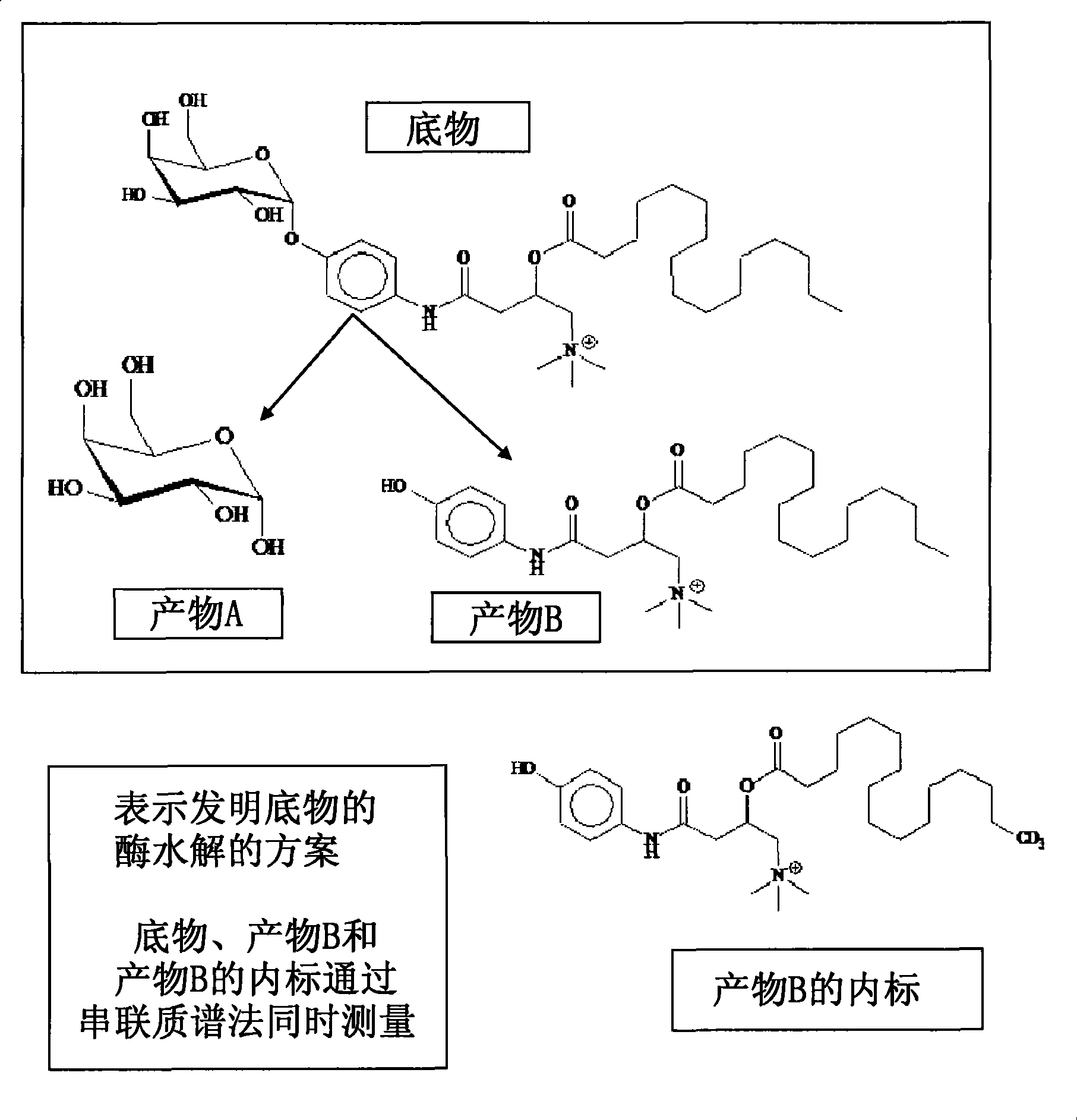
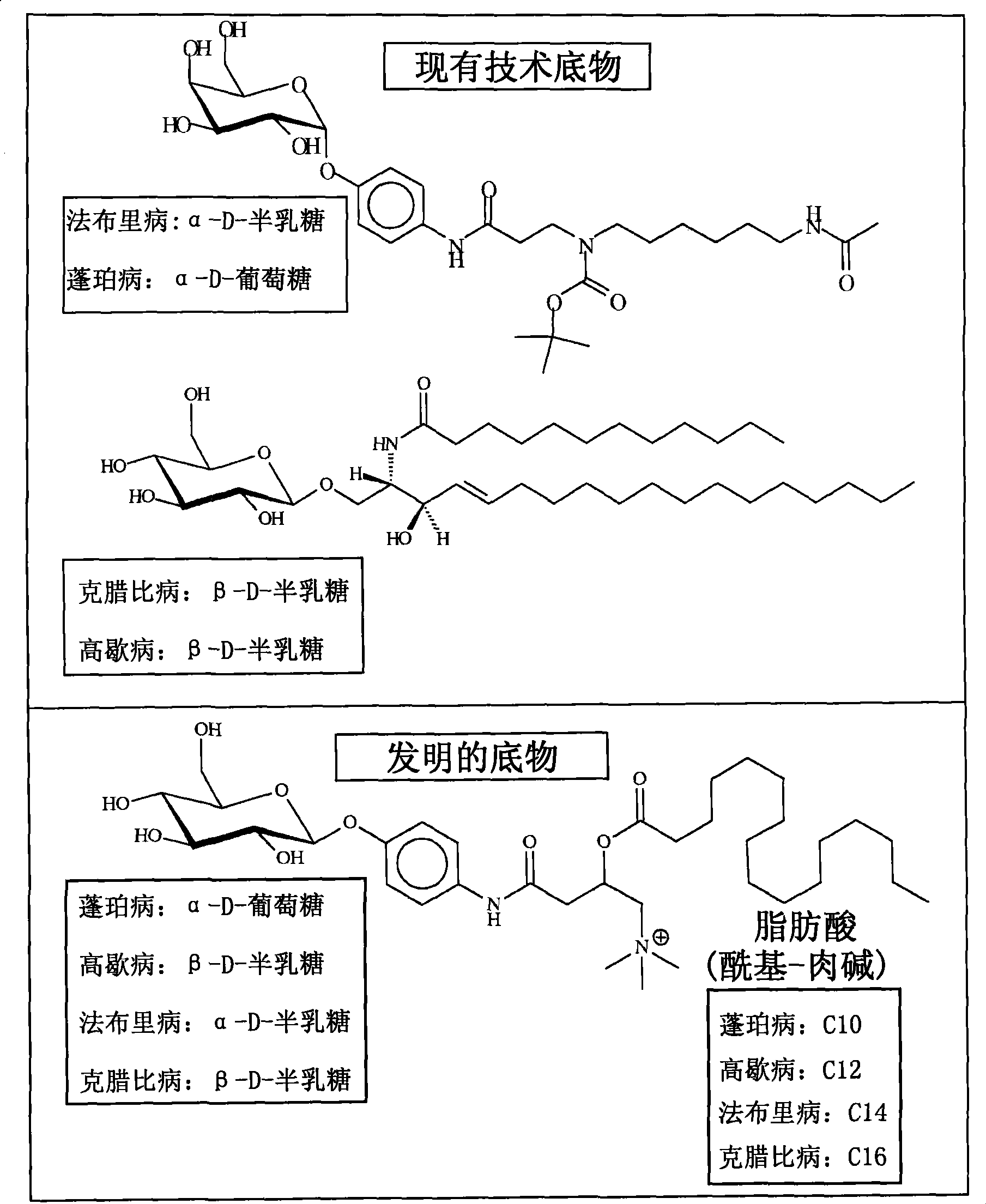
Substrates and internal standards for mass spectroscopy detection
一种底物、质谱分析的技术,应用在分析试剂和基于质谱法领域,能够解决苛刻分析成分、分析方法不容易适用于临床情况、麻烦等问题,达到时间少的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0060] For each sample, 3 mm diameter discs were punched from the dried blood area on the filter paper into the wells of microcentrifuge tubes or 96-well microtiter plates. Then, the blood disk was directly incubated with an assay solution containing a substrate for Fabry disease at a final concentration of 3 mmol / L and an internal standard at a final concentration of 0.05 mmol / L. To this analytical solution, a sodium acetate buffer at a final concentration of 0.5 mol / L was also added. The assay mixture containing the blood disk was incubated for 15 to 24 hours at 37°C with orbital shaking (150 rpm) in a thermostatted air shaker. After the incubation period, an aliquot of pure methanol (no chloroform was used) was added to each tube or well to terminate the enzyme reaction. The incubated reaction mixture was freed of solvent and dried down by means of a vacuum dryer before entering the mass spectrometer. For mass spectrometry analysis, the electrospray source was operated in...
Embodiment 2
[0062]The enzymatic reaction using a substrate for Pompe disease followed by mass spectrometry analysis was carried out using the method detailed in Example 1.
[0063] Figure 8 Examples are shown in which the substrates of the invention are synthesized using α-D-glucose as the sugar moiety, for example at figure 1 Those described in , thus have specificity for the lysosomal enzyme GAA (Pompe disease). The alkyl chain was chosen to contain 10 carbons for this particular example, and therefore decanoyl-carnitine was used in the synthesis of the substrate. Similarly, the corresponding internal standard was synthesized using decanoyl-carnitine, substituting 3 hydrogens for deuterium on one of the 3 methyl groups of the carnitine moiety. Using this substrate and internal standard, dried blood spot samples from two neonates—one healthy individual and the other confirmed Pompe positive—were used as Figure 5 The method of the invention described in the treatment. Alternatively,...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Figure 9 Results of processing 12 dried blood spot samples from healthy neonates and 3 from Pompe positive neonates are shown. The reagents and methods used were Figure 6 The same as those described in . Because the internal standard is introduced at a known concentration, it is possible to quantify enzyme activity by correlating the relative abundance of product and internal standard with the concentration of the internal standard. The figure shows a scatter plot of the determined enzyme activity expressed in blood units of micromoles / hour / liter for the 15 subjects studied. From this figure, it is evident that there is a clear difference between the GAA activity of healthy neonates and that of affected neonates. The activity recorded by the three Pompe patients was negligible compared to those of healthy individuals. Note that as in Figure 6 As described in , non-enzymatic hydrolysis produces a small degree of background. The data presented here are not correc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com