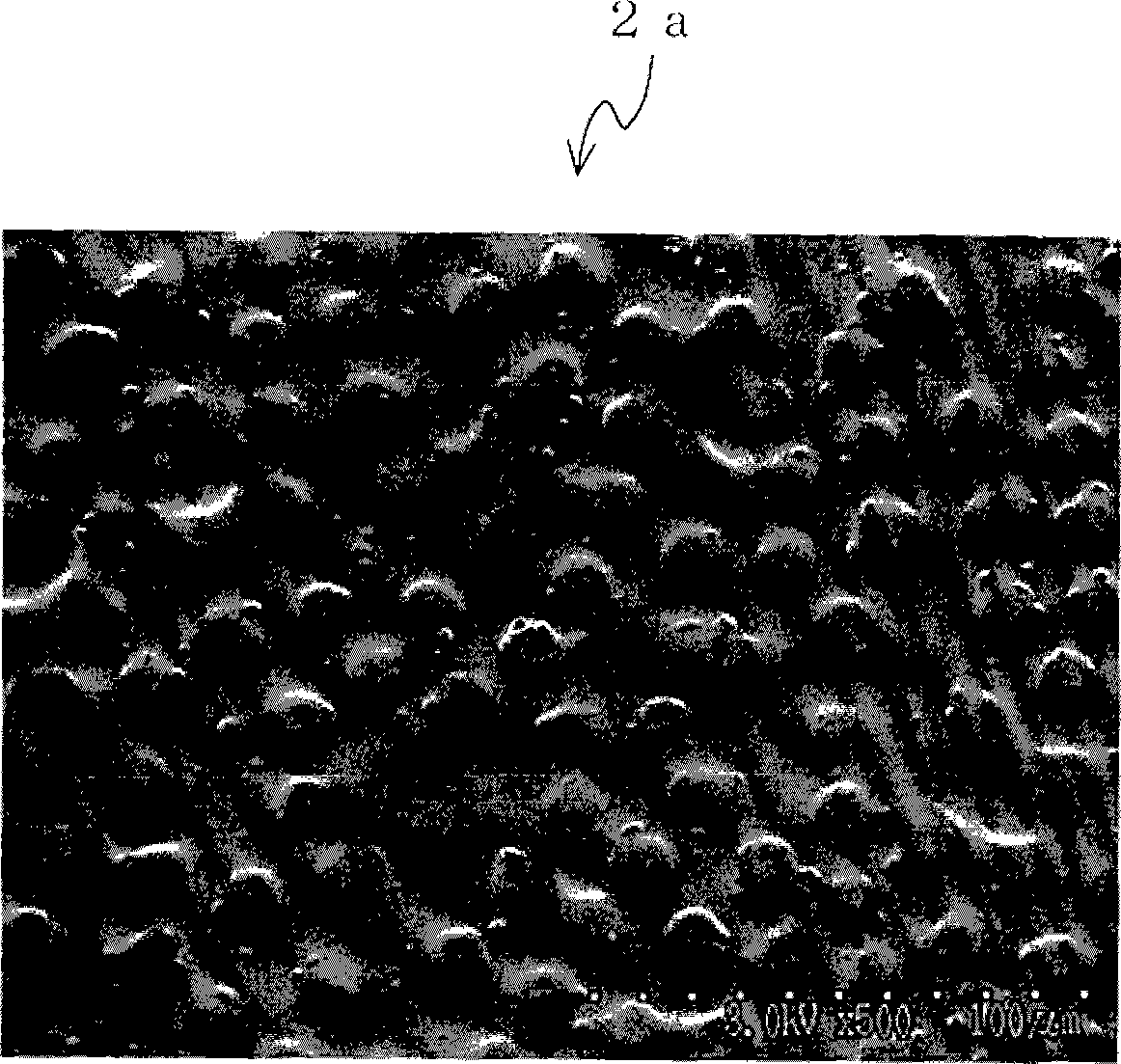
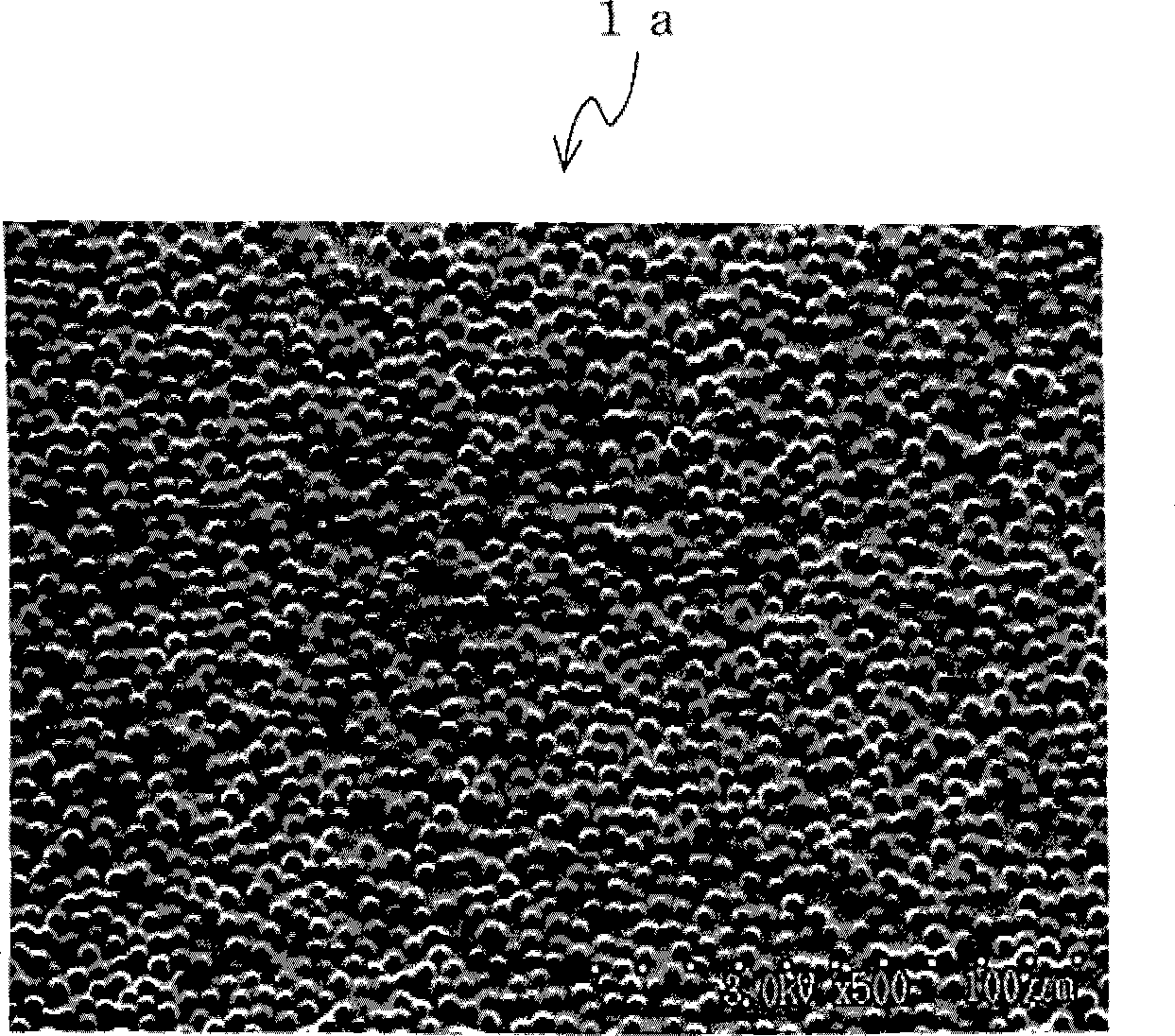
Polymer member having incompatible material maldistributed polymer layer and surface uneven tape or sheet made of the polymer member
A polymer layer, uniform distribution technology, applied in the direction of layered products, pressure-sensitive film/sheet, synthetic resin layered products, etc., can solve the problems of adverse effects, time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of excellent adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0383] The particle-combined photopolymerizable composition (A) is coated on the release-treated surface of the above-mentioned cover film so that the thickness after curing becomes 100 μm, and a particle-combined photopolymerizable composition layer is formed, which is combined with a monomer absorbing layer and The form in which the particles are in contact with the photopolymerizable composition layer is bonded to the substrate-attached monomer-absorbing sheet (A) in which the monomer-absorbing layer has been peeled off to form a laminate.
[0384] Next, ultraviolet rays (illuminance: 5 mW / cm 2 ), the particles are combined with the photopolymerizable composition layer to be photocured to form a particle-coordinated photopolymerization cured layer, thereby producing a sheet with uneven surface.
Embodiment 2
[0386] The particle-combined photopolymerizable composition (B) is coated on the release-treated surface of the above-mentioned cover film so that the thickness after curing becomes 50 μm, and a particle-combined photopolymerizable composition layer is formed, which is separated by a monomer-absorbing layer and The form in which the particles are in contact with the photopolymerizable composition layer is bonded to the substrate-attached monomer-absorbing sheet (A) in which the monomer-absorbing layer has been peeled off to form a laminate.
[0387] Next, 1 minute after forming the laminated body, the laminated body was irradiated with ultraviolet rays (illuminance: 5 mW / cm 2 ), the particles are combined with the photopolymerizable composition layer to be photocured to form a particle-coordinated photopolymerization cured layer, thereby producing a sheet with uneven surface.
Embodiment 3
[0389] The particle-combined photopolymerizable composition (A) is coated on the release-treated surface of the above-mentioned cover film so that the thickness after curing becomes 60 μm, and a particle-combined photopolymerizable composition layer is formed, and the monomer-absorbing layer and the The form in which the particles are in contact with the photopolymerizable composition layer is bonded to the substrate-attached monomer-absorbing sheet (B) in which the monomer-absorbing layer has been peeled off to form a laminate.
[0390] Next, 1 minute after forming the laminated body, the laminated body was irradiated with ultraviolet rays (illuminance: 5 mW / cm 2 ), the particles are combined with the photopolymerizable composition layer to be photocured to form a particle-coordinated photopolymerization cured layer, thereby producing a sheet with uneven surface.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com