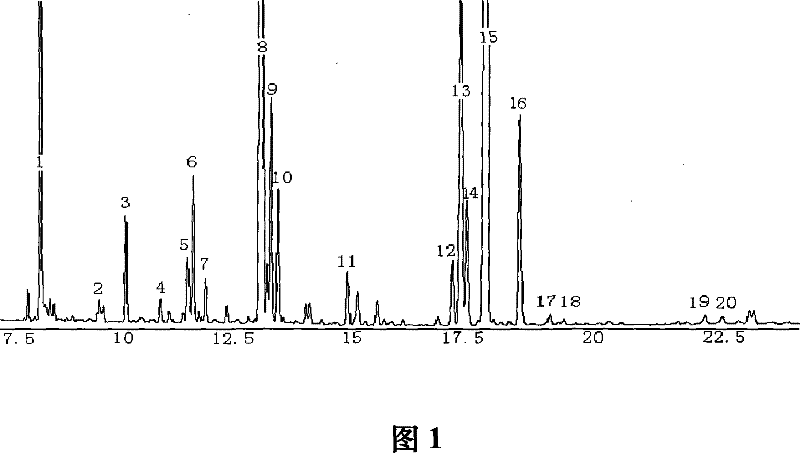
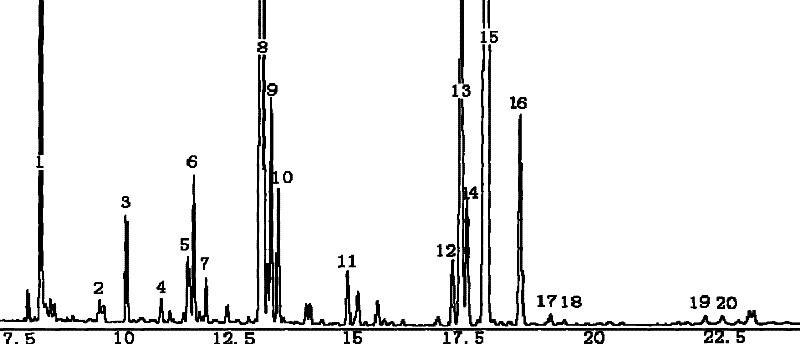
Method for analyzing fatty acid chemical composition in cortex periplocae radicis
A technology for chemical components and fatty acids, which is applied in the field of analysis of chemical components of fatty acids in Persica sativa by GC-MS technology, and can solve the problems of extraction and analysis of unseen fatty acids
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 1 Instruments, materials and reagents
[0020] 1.1 Instruments GC-MS coupled instrument (SHIMADZU 6010N GC System / SHIMADZU6010N MS System); AGBP210S electronic balance (German Satorious Company).
[0021] 1.2 Medicinal materials and reagents Cinnamon bark, purchased from Shenyang Medicinal Materials Company, was identified as authentic by Professor Sun Qishi, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. All reagents used were of analytical grade.
[0022] 2 Experimental part
[0023] 2.1 Fatty acid extraction: 100 g of Cinnamon bark is crushed and extracted with petroleum ether (60-90° C.) under reflux for 8 hours, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and evaporated to dry the solvent to obtain fatty acid.
[0024] 2.2 Methyl esterification of samples Take 2 drops of fatty acid samples, add 2 mL of 2% sodium hydroxide-methanol solution and place in a 60°C water bath for 15 minutes, then add 2 mL of boron trifluoride-diethyl...
Embodiment 2
[0035] 1 Instruments, materials and reagents
[0036]1.1 Instruments GC-MS coupled instrument (SHIMADZU 6010N GC System / SHIMADZU6010N MS System); AGBP210S electronic balance (German Satorious Company).
[0037] 1.2 Medicinal materials and reagents Cinnamon bark, purchased from Shenyang Medicinal Materials Company, was identified as authentic by Professor Sun Qishi, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. All reagents used were of analytical grade.
[0038] 2 Experimental part
[0039] 2.1 Fatty acid extraction: 100 g of Cinnamomum officinalis medicinal material was crushed and extracted with petroleum ether (60°C-90°C) for 6 hours under reflux, filtered, concentrated under reduced pressure, and evaporated to dry the solvent to obtain fatty acid.
[0040] 2.2 Methyl esterification of samples Take 2 drops of fatty acid samples, add 2 mL of 2% sodium hydroxide-methanol solution and place in a 60°C water bath for 15 minutes, then add 2 mL ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 1 Instruments, materials and reagents
[0048] 1.1 Instruments GC-MS coupled instrument (SHIMADZU 6010N GC System / SHIMADZU6010N MS System); AGBP210S electronic balance (German Satorious Company).
[0049] 1.2 Medicinal materials and reagents Cinnamon bark, purchased from Shenyang Medicinal Materials Company, was identified as authentic by Professor Sun Qishi, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University. All reagents used were of analytical grade.
[0050] 2 Experimental part
[0051] 2.1 Fatty acid extraction: Take 100 g of Cinnamomum officinalis medicinal material, pulverize and extract with petroleum ether (60°C-90°C) under reflux for 10 hours, filter, concentrate under reduced pressure, and evaporate the solvent to obtain fatty acid.
[0052] 2.2 Methyl esterification of samples Take 2 drops of fatty acid samples, add 2 mL of 2% sodium hydroxide-methanol solution and place in a 60°C water bath for 15 minutes, then add 2 mL of boro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ionization potential | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com