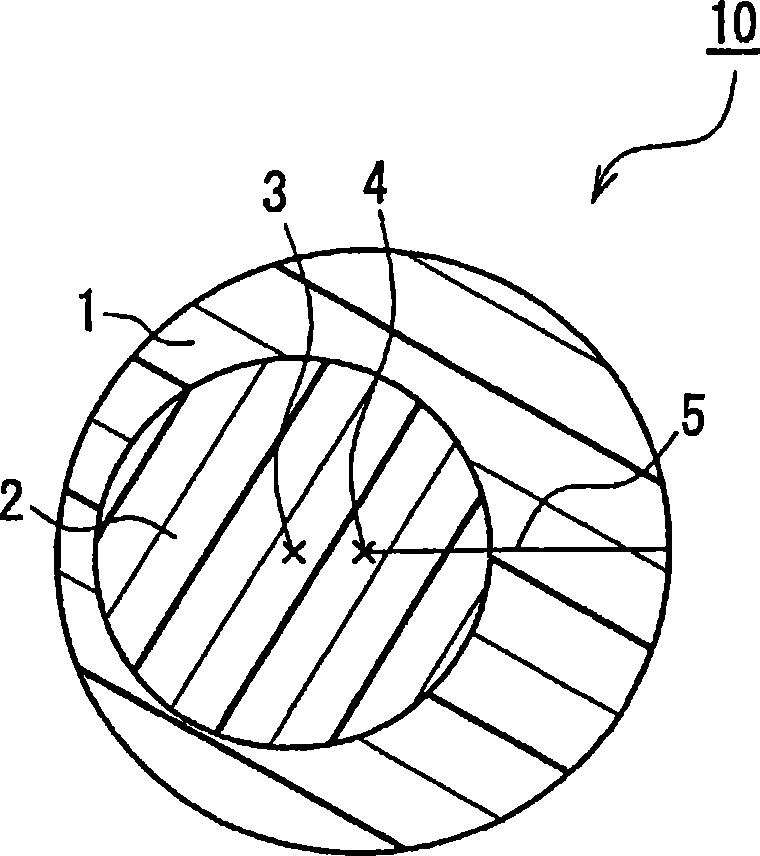
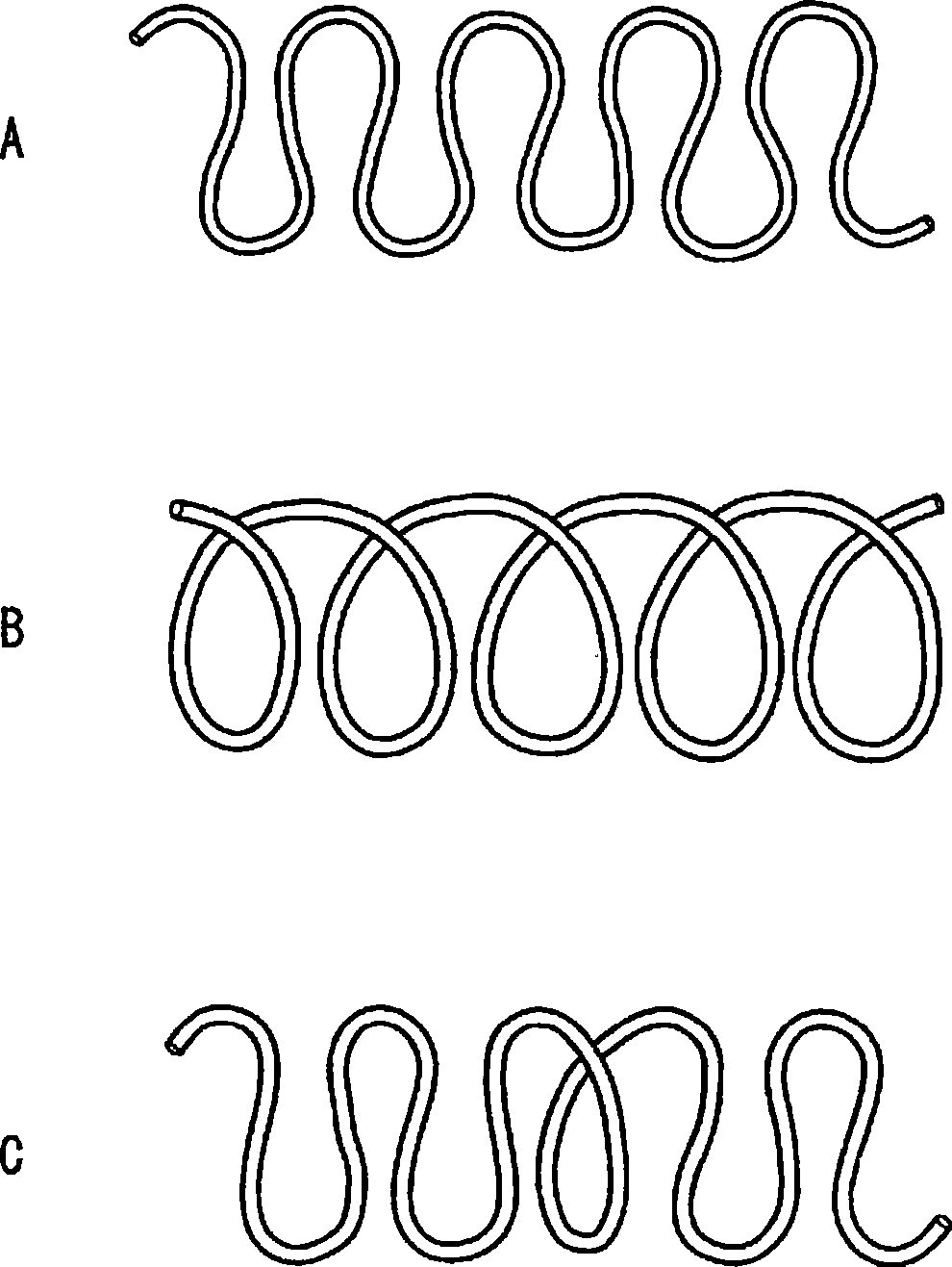Crimping conjugate fiber and non-woven fabric using the same
一种复合纤维、卷曲性的技术,应用在共轭合成聚合物人造长丝、织物、纺织等方向,能够解决无纺布蓬松度减少、耐热性低、蓬松度小等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~7、 comparative example 1~3
[0139] 1. Fiber manufacturing conditions
[0140] (A) Polymers used (abbreviations are explained below)
[0141] (1) PTT ("CORTERRA9200" manufactured by Shell Chemicals Japan Co., Ltd., glass transition point: 45°C, melting peak temperature (mp) 228°C, IV value: 0.92, melting start temperature: 213°C)
[0142] (2) PET ("T200E" manufactured by Toray Co., Ltd., mp 255°C, IV value 0.64)
[0143] (3) PP-1 ("SA03E" manufactured by Japan Polypropylene Co., Ltd., mp 160°C, MFR 20, Q value 5.6)
[0144] (4) PP-2 ("SA03B" manufactured by Japan Polypropylene Co., Ltd., mp 160°C, MFR 30, Q value 3.6)
[0145] (5) PP-3 ("SA01A" manufactured by Japan Polypropylene Co., Ltd., mp 160°C, MFR 9, Q value 3.2)
[0146] (6) PP-4 ("CJ700" manufactured by Prime Polymer Co., Ltd., mp 160°C, MFR 7, Q value 6.5)
[0147] (7) PB-1a ("PB0400" manufactured by SunAllomer, mp 123°C, MFR (190°C) 20)
[0148] (8) PB-1a ("DP0401M" manufactured by SunAllomer, mp 123°C, MFR (190°C) 15)
[0149] (9) PBT el...
Embodiment 8~15
[0172] Using the same polymer and evaluation method as in Examples 1 to 8, under the conditions described in Table 3, the conspicuously crimped conjugate fibers of Examples 8 to 11 were produced. The obtained results are shown in Table 3. In addition, 100% by mass of the crimped conjugate fibers obtained in Example 10 and Comparative Example 3 were placed in a parallel carding machine, and a cross-laid fiber web was produced using a cross-laying machine. Next, needle punching was performed on the cross-laid fiber web at a needle depth of 5 mm and the number of penetrations shown in Table 4 (front and back are the same) using a cone knife manufactured by Fosterneedle. The obtained needle-punched nonwoven fabric was subjected to heat treatment for 30 seconds at the processing temperature shown in Table 4 using a hot air circulation type heat treatment machine to thermally fuse the sheath components to form a nonwoven fabric. Table 4 shows the results of measuring the hardness, ...
Embodiment 16~20
[0179] [Examples 16-20, Comparative Examples 1 / 2, 3, 4]
[0180] In the following examples and comparative examples, latent crimpable conjugate fibers and nonwoven fabrics using the conjugate fibers will be described.
[0181] 1. Fiber manufacturing conditions
[0182] (A) Polymers used (abbreviations are explained below)
[0183] (1) PTT ("CORTERRA9240" manufactured by Shell Chemicals Japan Co., Ltd., melting peak temperature (mp) 228°C, IV value 0.92, melting start temperature 213°C)
[0184] (2) PP-(1) ("SA03B" manufactured by Japan Polypropylene Co., Ltd., mp 160°C, MFR 30, Q value 3.6)
[0185] (3) Copolymerized PP-(1) (Nippon Polypropylene Co., Ltd. "FX4G", mp 125°C, MFR 5, Q value 5.5, binary type)
[0186] (4) Copolymerized PP-(2) ("WINTEC WFX4" manufactured by Nippon Polypropylene Co., Ltd., mp 125°C, MFR 7, Q value 2.5, metallocene catalyst, binary type)
[0187] (5) Copolymerized PP-(3) ("F794NV" manufactured by Prime Polymer Co., Ltd., mp 130°C, MFR 7, Q value ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Flow Rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melt Flow Rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com