Manufacturing method for light-emitting diode chip substrate structure
A light-emitting diode and substrate structure technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of poor resistance to reactive ion etching of photoresist, inability to manufacture microstructure pattern substrates, and ineffective photoresist transfer and other issues, to improve the anti-dry etching ability, improve the defects, and reduce the effect of pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] First refer to Figures 1a-1g The flow chart shown is to prepare the light-emitting diode chip substrate structure. The preparation method of the LED chip substrate structure of the present invention comprises the following steps:
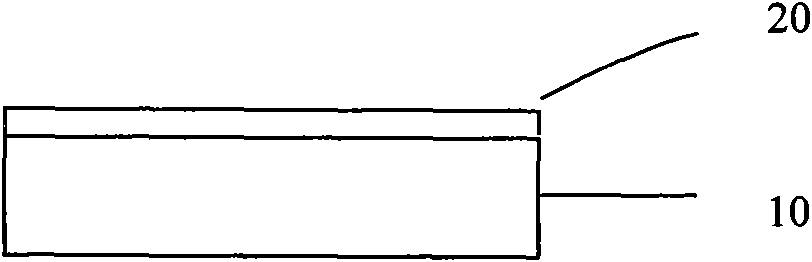
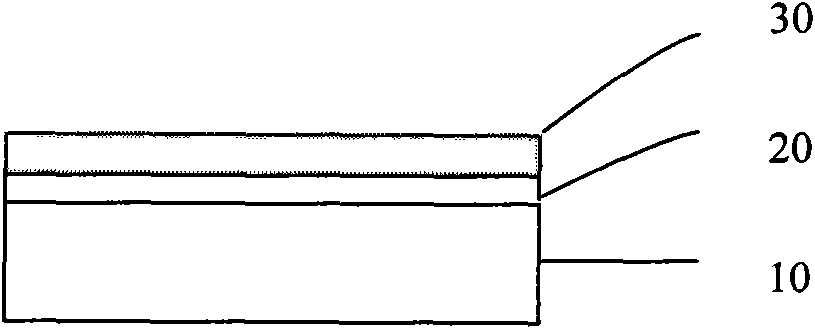
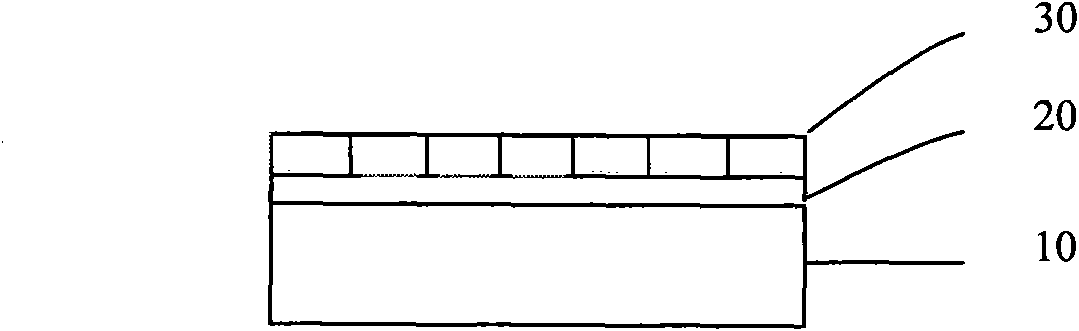
[0038] (1) A metal layer 20 is formed on the surface of the substrate 10 .
[0039] First refer to Figure 1a A metal layer 20 is formed on the surface of the substrate 10 by electron beam evaporation or sputtering technology, wherein the material of the substrate 10 is preferably sapphire. In addition, other conventional electroplating methods can also be used to form the metal layer 20 . The prepared metal layer 20 has a thickness of 1 nm, and its material is titanium. Since a layer of metal layer 20 is placed on the sapphire substrate 10 , the influence of the bond energy of the sapphire substrate 10 on the photoresist can be isolated, and the photoresist can reflow to form a more ideal pattern on the surface of the metal layer 20 .
...
Embodiment 2
[0056] First refer to Figures 1a-1g The flow chart shown is to prepare the light-emitting diode chip substrate structure. The preparation method of the LED chip substrate structure of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0057] (1) A metal layer 20 is formed on the surface of the substrate 10 .
[0058] First refer to Figure 1a A metal layer 20 is formed on the surface of the substrate 10 by electron beam evaporation or sputtering technology, wherein the material of the substrate 10 is preferably sapphire. In addition, other conventional electroplating methods can also be used to form the metal layer 20 . The prepared metal layer 20 has a thickness of 5 nm, and its material is nickel. Since a layer of metal layer 20 is placed on the sapphire substrate 10 , the influence of the bond energy of the sapphire substrate 10 on the photoresist can be isolated, and the photoresist can reflow to form a more ideal pattern on the surface of the metal layer 20 .
[...
Embodiment 3
[0075] First refer to Figures 1a-1g The flow chart shown is to prepare the light-emitting diode chip substrate structure. The preparation method of the LED chip substrate structure of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0076] (1) A metal layer 20 is formed on the surface of the substrate 10 .
[0077] First refer to Figure 1a A metal layer 20 is formed on the surface of the substrate 10 by electron beam evaporation or sputtering technology, wherein the material of the substrate 10 is preferably sapphire. In addition, other conventional electroplating methods can also be used to form the metal layer 20 . The prepared metal layer 20 has a thickness of 50 nm, and its material is aluminum. Since a layer of metal layer 20 is placed on the sapphire substrate 10 , the influence of the bond energy of the sapphire substrate 10 on the photoresist can be isolated, and the photoresist can reflow to form a more ideal pattern on the surface of the metal layer 20 . ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com