Method for production of nonradioactive and stable isotope of carbon having mass number of 13
A method of manufacture, 13C. Advanced technology, applied in the field of stable isotope 13C manufacturing, can solve the problems of large devices and high reaction temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
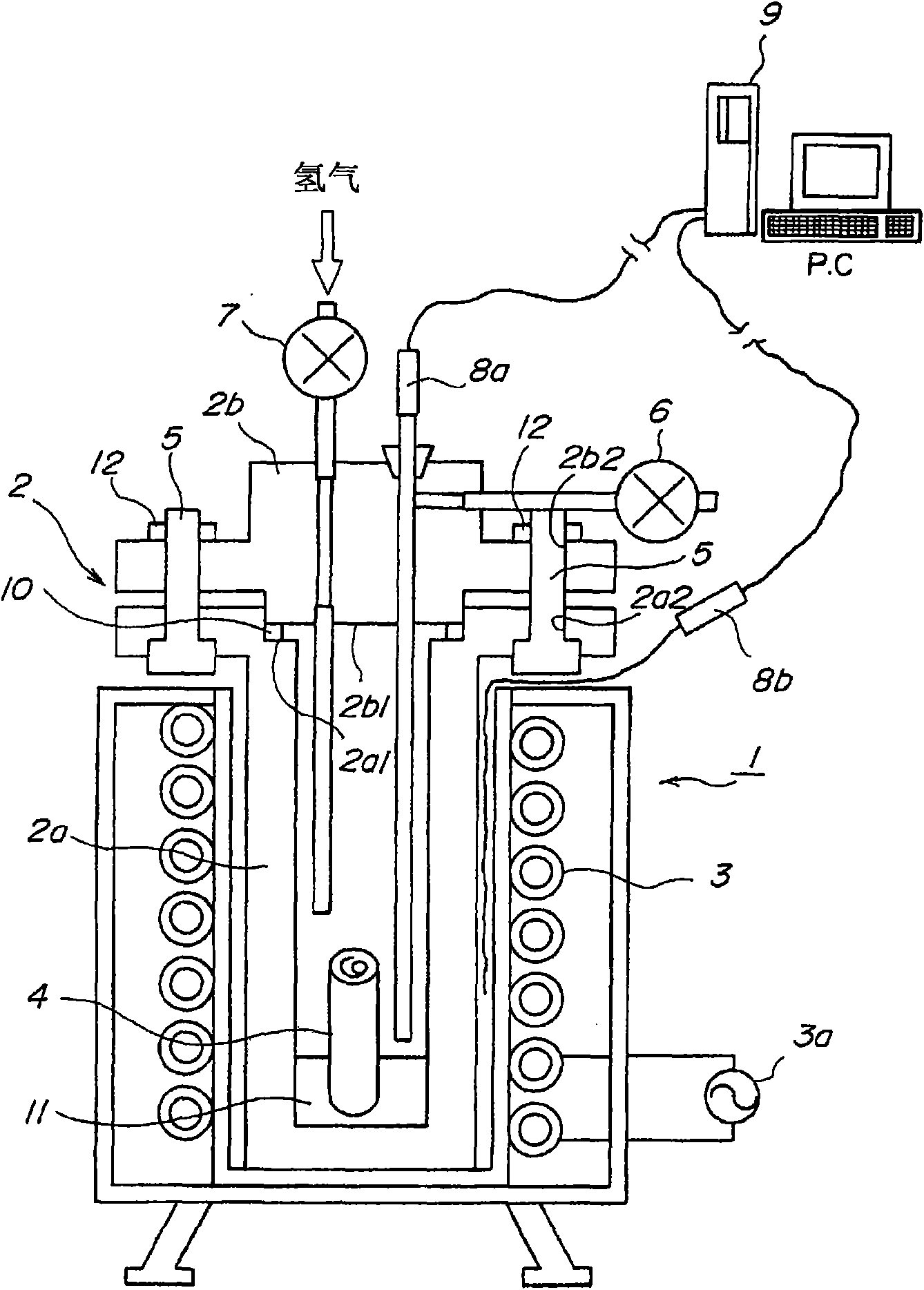
[0061] for figure 1 For the shown reactor 1, a cylindrical autoclave 2 made by INCONEL with a main body outer diameter of 56 mm, an inner diameter of 26 mm, and an inner volume of 88 cc is set in an electric heater 3 connected to a power supply 3 a to Carbon compound 11 was used as a raw material, and 12 cc of creosote oil (sulfur content rate: 0.07%) containing sulfur compounds and metal mesh platinum catalyst 4 were inserted into the autoclave main body 2a, and then the high-pressure The convex part 2b1 of the autoclave cover 2b is fitted into the recessed part 2a1 of the autoclave main body 2a, and the six bolts 5 are passed through the six positions provided at the peripheral parts of the autoclave main body 2a and the autoclave cover 2b. The holes 2a2 and 2b2 thread the nuts 12 and the bolts 5 to fix the autoclave cover 2b to the autoclave main body 2a.
[0062] Thereafter, the hydrogen supply valve 7 was opened to supply hydrogen gas into the autoclave 2, and the exhaus...
Embodiment 2
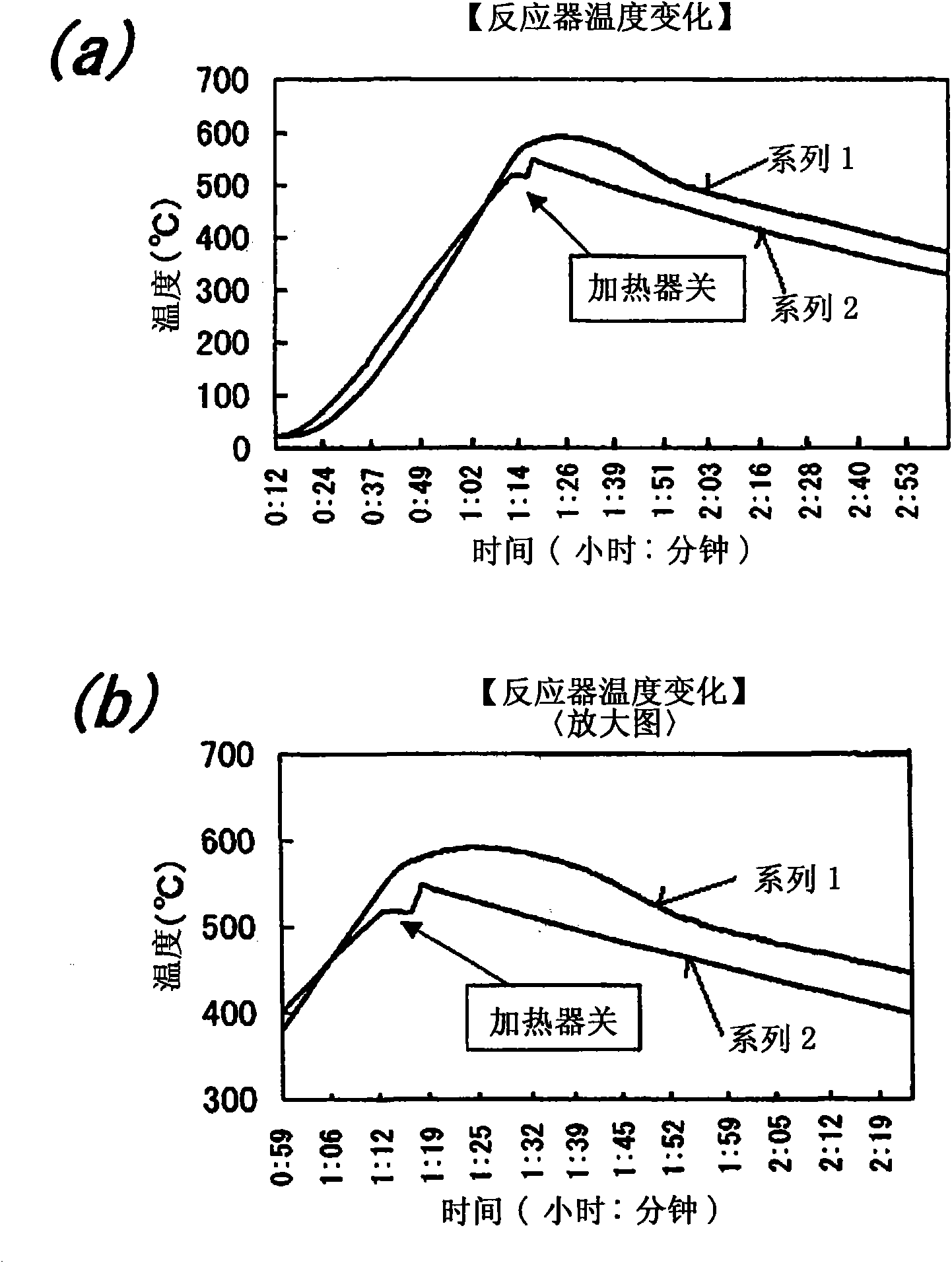
[0070] Using the high-pressure reactor and heating device having the reactor 1 used in the above-mentioned Example 1, carbon compound 11 was used as a raw material, and 12 cc of coal tar (sulfur content rate 3%) containing sulfur compounds was used instead of creosote oil to insert high pressure In the reaction kettle 2, except that, with the same operation as the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the hydrogen is heated at 100 atmospheres (1013 * 10 4 Pa) Encapsulation, the same operation was performed using the same platinum catalyst 4, the autoclave 2 was heated with the heater 3, and the temperature inside the autoclave 2 was heated from room temperature to 600°C. Such as Figure 5 As shown, the internal temperature of the autoclave 2 rises up to 660° C. at the highest.
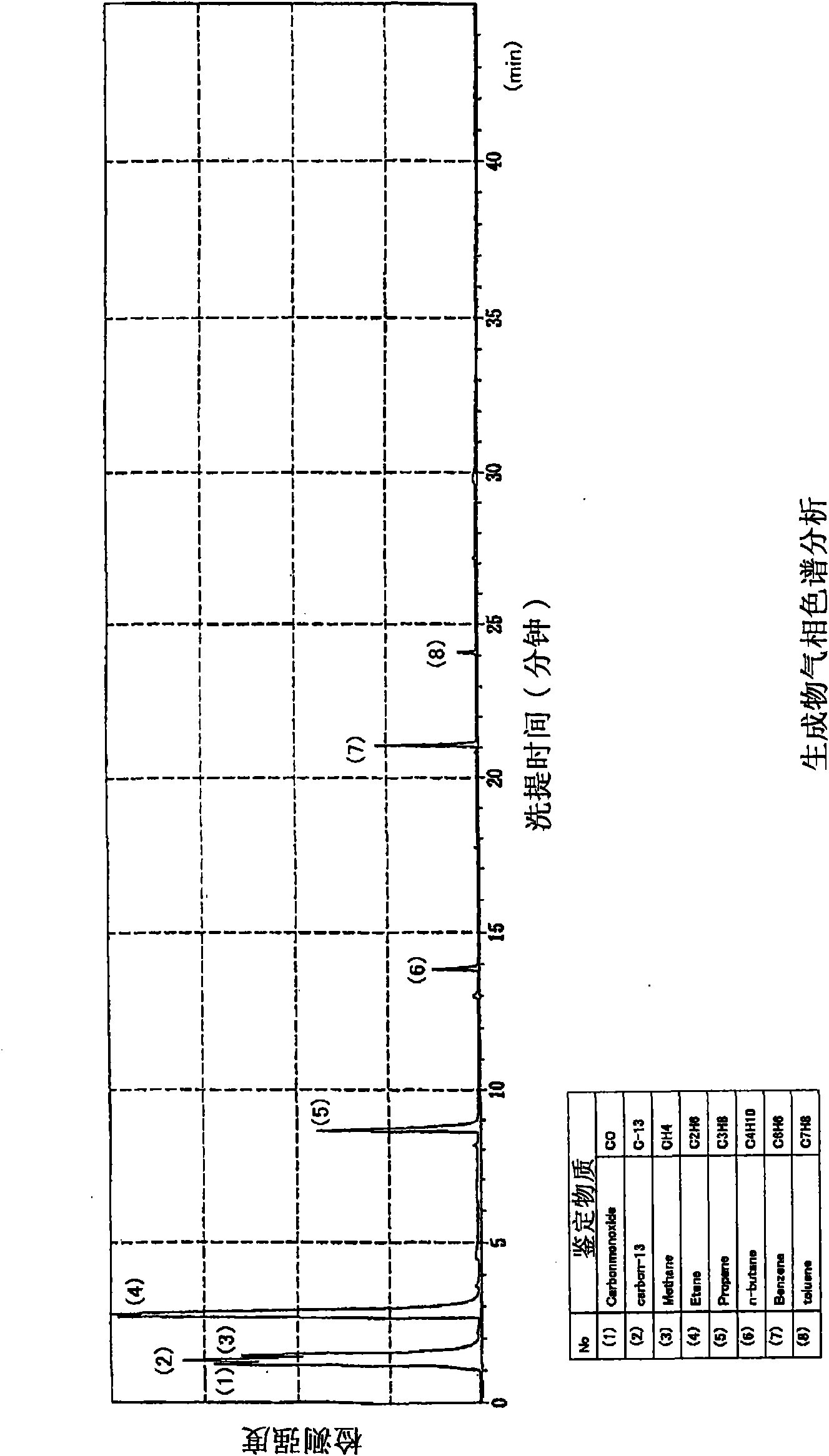
[0071] After the reaction was finished, 10 cc of solid carbon-like lumps and a small amount of liquid remained in the autoclave 2 . As in Example 1 above, gas composition analysis was performed using GC-MS (...
Embodiment 3
[0075] 1cc creosote and platinum catalyst 4 are added in the autoclave 2 of reactor 1 identical with above-mentioned embodiment 1, with the operation identical with above-mentioned embodiment 1, make hydrogen be in 1 atmospheric pressure (1013 * 10 2 Pa), and make helium at 70 atmospheres (7091×10 3 Pa), the input (power) of the heater 3 was adjusted, and the internal temperature of the autoclave 2 was set to 660°C. Such as Figure 6 As shown in (a) and (b), after the internal temperature of the autoclave 2 reaches 660° C., the internal temperature of the autoclave 2 also rises, and after the heater 3 is input, it reaches 690° C. within about 4 hours, With a temperature rise (overheating) of 30°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com