Method for producing glutathione by use of metabolic engineering bacteria
A technology of glutathione and host bacteria, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low utilization rate of raw materials, high cost and energy consumption, low glutathione output, etc., so as to improve the utilization rate of raw materials, reduce production costs and The effect of energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
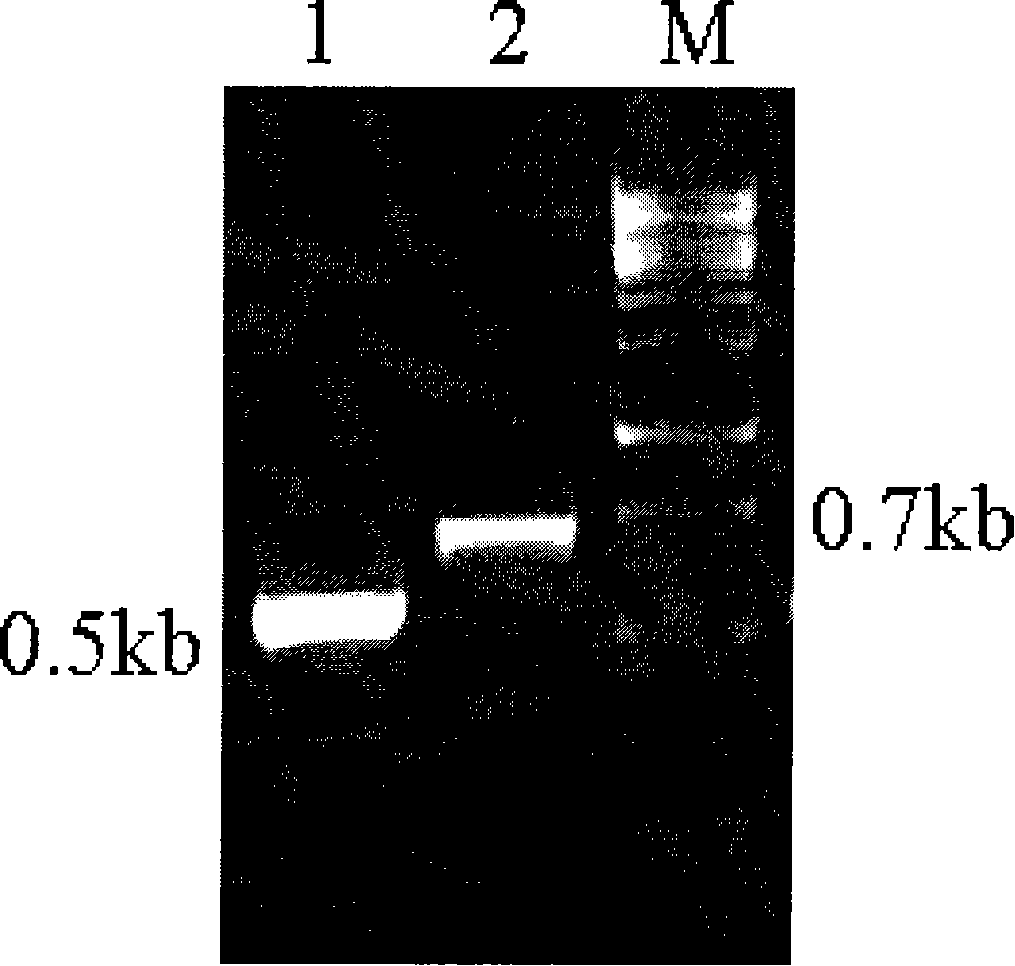
[0036] Example 1 , Construction of co-expression plasmid
[0037] 1.1. Primer design
[0038] According to the GSH1 and GSH2 sequences reported by Genebank, the following 4 primers were designed:
[0039] GSH1UP: ATCGAT ACGATGGGACTCTTAGCTTTGGG;
[0040] GSH1DNM: CAATTGTTAACATTTGCTTTCTATTG;
[0041] GSH2UP: TTCGAA ACGATGGCACACTATCCACCTTC;
[0042] GSH2DNE:GAATTCCTAGTAAAGAATAATACTGTC.
[0043] Among them, GSH1UP and GSH1DNM are used to amplify the GSH1 coding region; GSH2UP and GSH2DNE are used to amplify the GSH2 coding region; the underlines on GSH1UP and GSH2UP indicate the AsuII restriction site and ClaI restriction site introduced on GSH1UP and GSH2UP respectively .
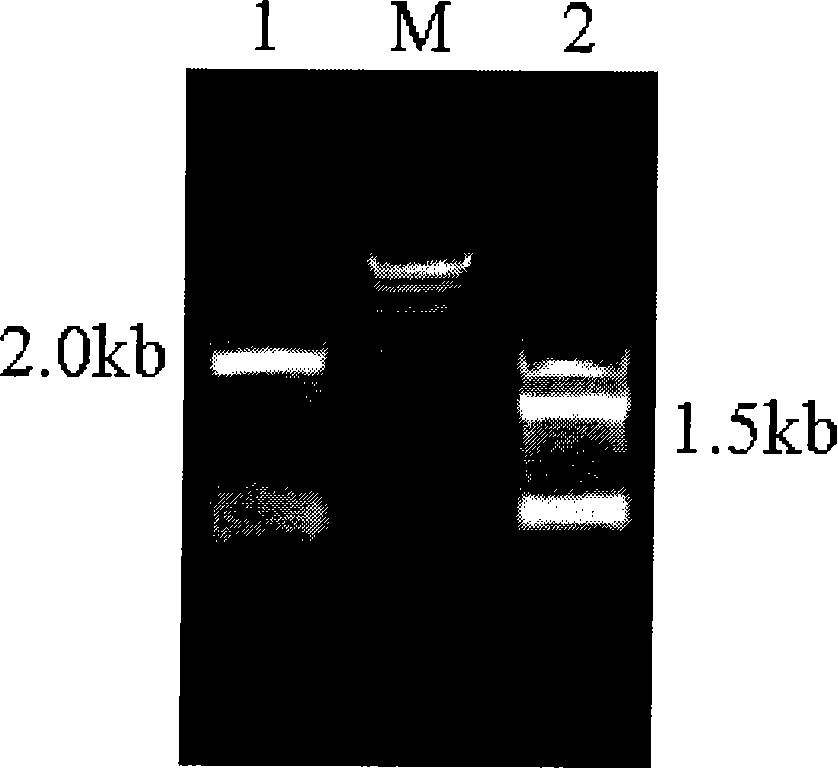
[0044] 1.2. PCR amplification of GSH1 and GSH2 sequences
[0045] The genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 was extracted.
[0046] Then, using the Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 genome as a template, the primer pair GSH1UP and GSH1DNM and the primer pair GSH2UP and GSH2DNE designed in step 1...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Example 2 , Construction of glutathione-producing Pichia strains
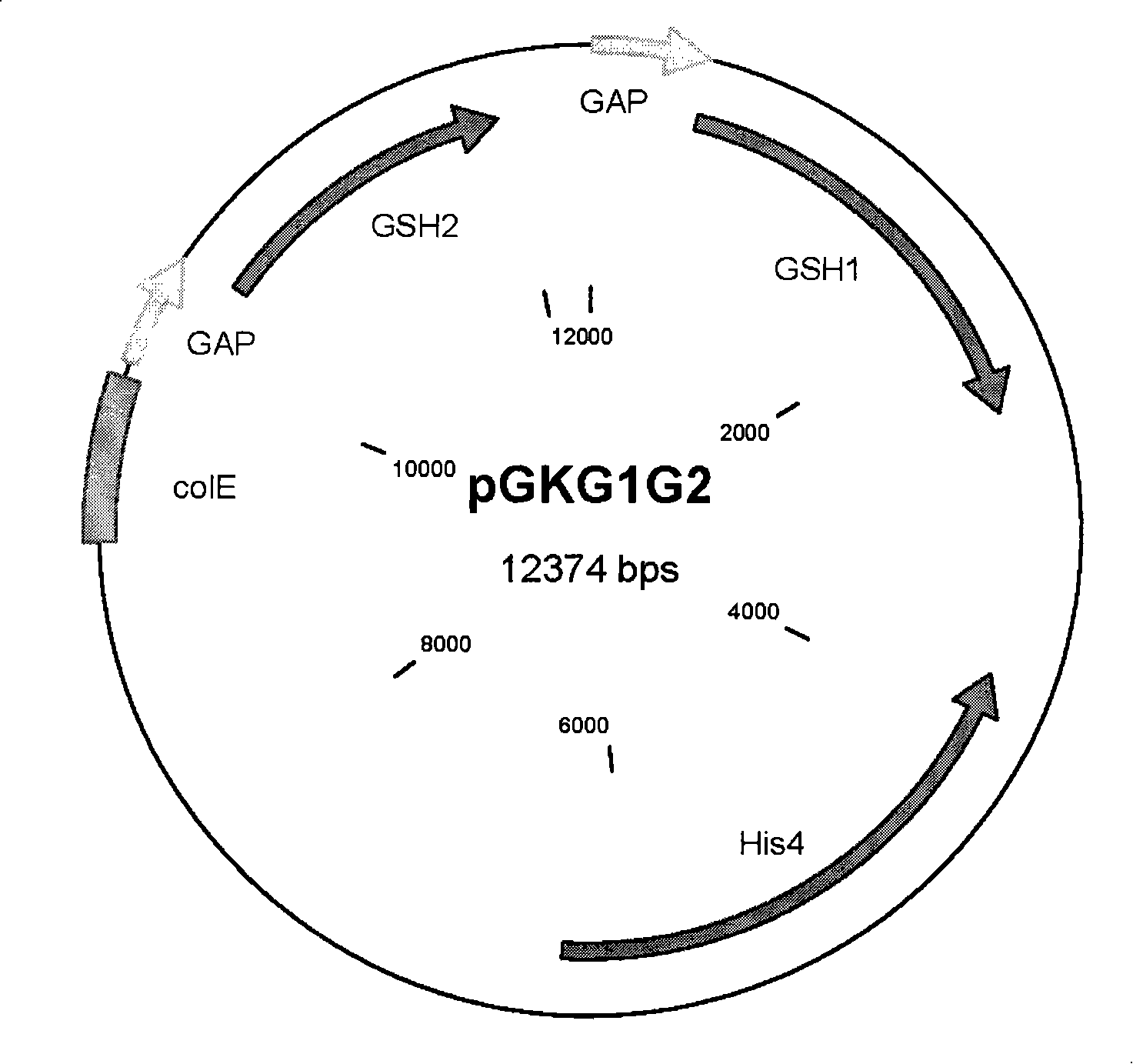
[0074] Escherichia coli carrying the plasmid pGKG1G2 was grown overnight, and the pGKG1G2 plasmid was extracted and linearized with Kpn2I. Then, the linearized pGKG1G2 plasmid was electrotransformed into the host strain GS115(his4). The solution after electroporation was spread on the MD plate without histidine, and cultured at 30°C until the transformant grew out. Among them, since GS115 (his4) is a histidine-deficient strain, it cannot grow on the MD plate without histidine, so the transformants grown on the plate are all Pichia pastoris transformed with the pGKG1G2 plasmid.
[0075] A number of transformants were picked at random, fermented and cultivated in shake flasks, and two Pichia pastoris strains with higher yields were selected, one of which was named HZ109, and the other was named HZ117. Among them, HZ109 was submitted to China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) for preservation o...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3 , HZ109 and HZ117 shake flask fermentation to produce glutathione
[0085] Single colonies of HZ109, HZ117 and HZ100 (as a control) grown on YPD plates for three days at 30°C were inserted into 5mL of YPD medium respectively, and cultured overnight at 30°C and 200rpm.
[0086] Transfer 0.25mL of bacterial liquid into 25mL of BMGY medium, culture at 30°C, 200rpm for 96h, add glycerol to 1% at 24h, 48h, and 72h, and add precursor L-cysteine to 0.01mol / L , and samples were taken at 48h, 72h, and 96h of fermentation to detect the GSH output in the culture medium, and the detection results are shown in Table 1.
[0087] Table 1. GSH production in HZ109, HZ117 and HZ100 in different time periods
[0088]
[0089] According to the results in Table 1, the yields of GSH in HZ109 and HZ117 are about twice the yield of GSH in the control HZ100, and the yields are basically similar. Therefore, in the next example, only HZ109, which has a relatively higher yield in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com