Device for detecting roundness of arc of tool tip of diamond tool with arc edge
A diamond tool and detection device technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low detection accuracy and inability to meet the requirements of high-precision tool tip arc roundness measurement, so as to improve detection accuracy, The effect of high-precision detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
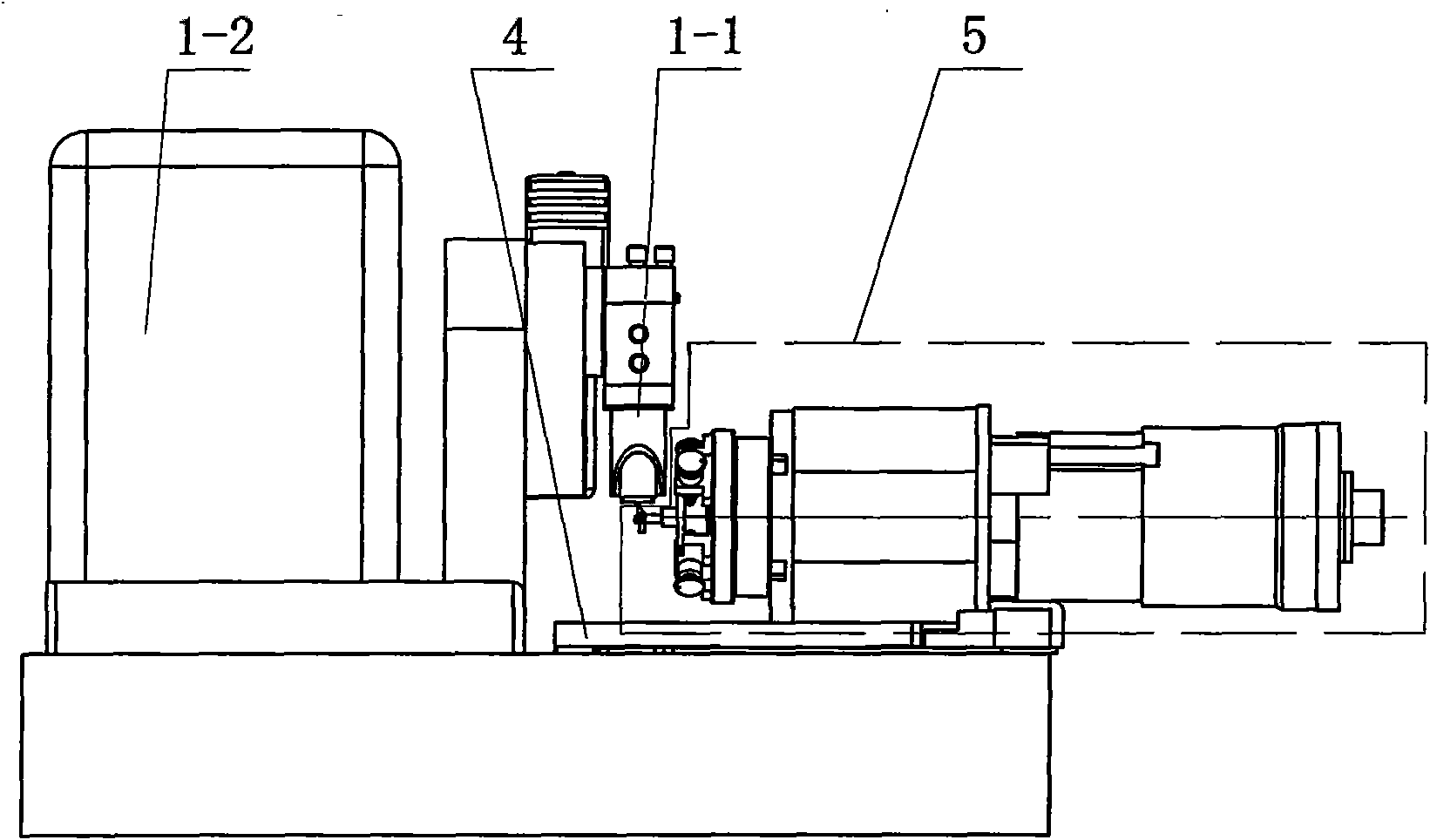
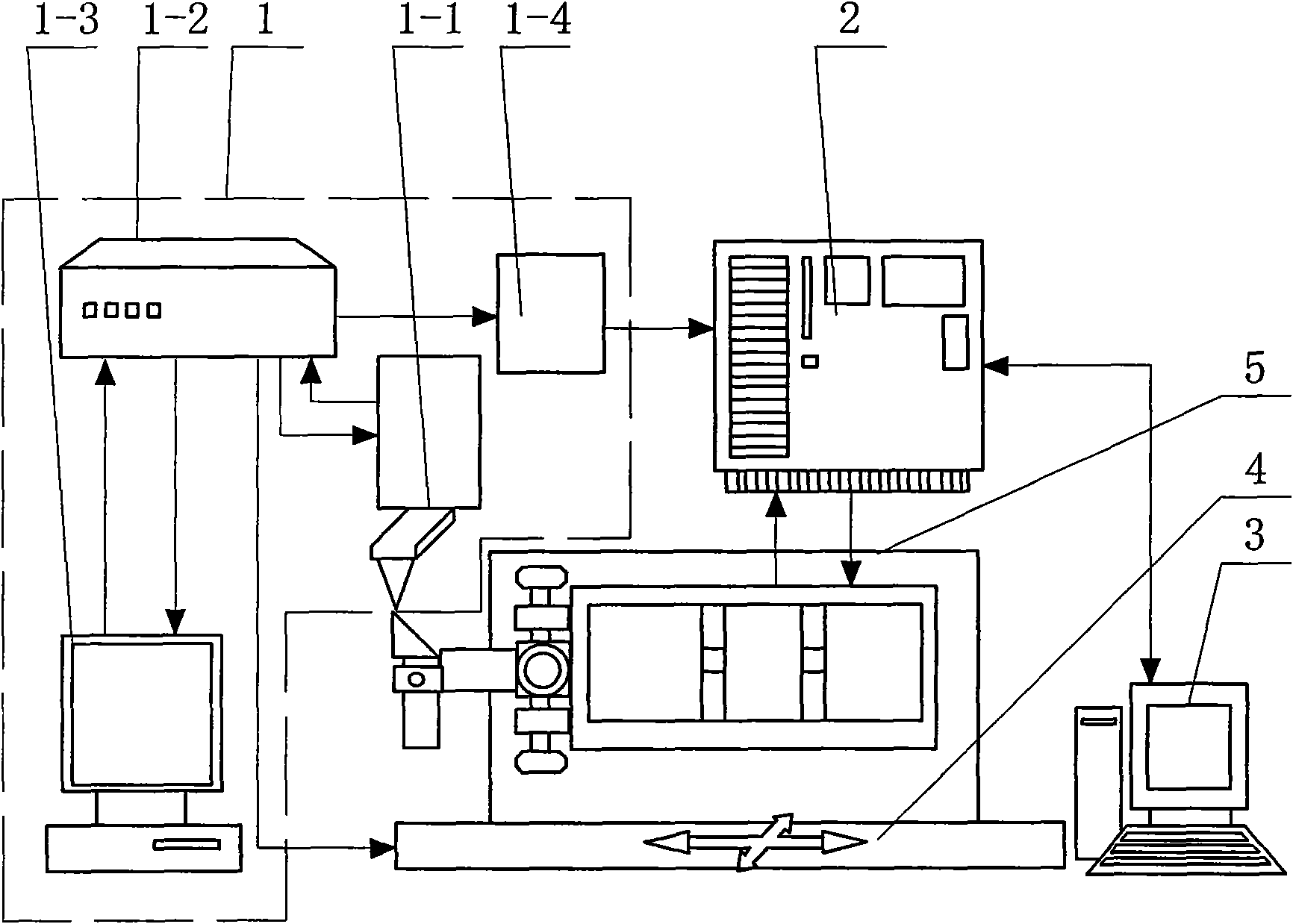
[0026] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1-Figure 3 To illustrate this embodiment, this embodiment is composed of an atomic force microscope system 1, a single-chip controller 2, a measurement control computer 3, a two-dimensional precision displacement table 4 and a rotary shaft system 5, and the rotary shaft system 5 is placed in a two-dimensional precision displacement work on stage 4;
[0027]The detection result output end of the atomic force microscope system 1 is connected to the detection result input end of the single-chip controller 2, the single-chip controller 2 is connected to the RS232 interface of the measurement control computer 3 through the RS232 interface, and the control signal output end of the single-chip controller 2 is connected to the rotary shaft system 5 The control signal input terminal of the rotary shaft system 5 is connected to the angular position signal input terminal of the microcontroller controller 2; the di...
specific Embodiment approach 2
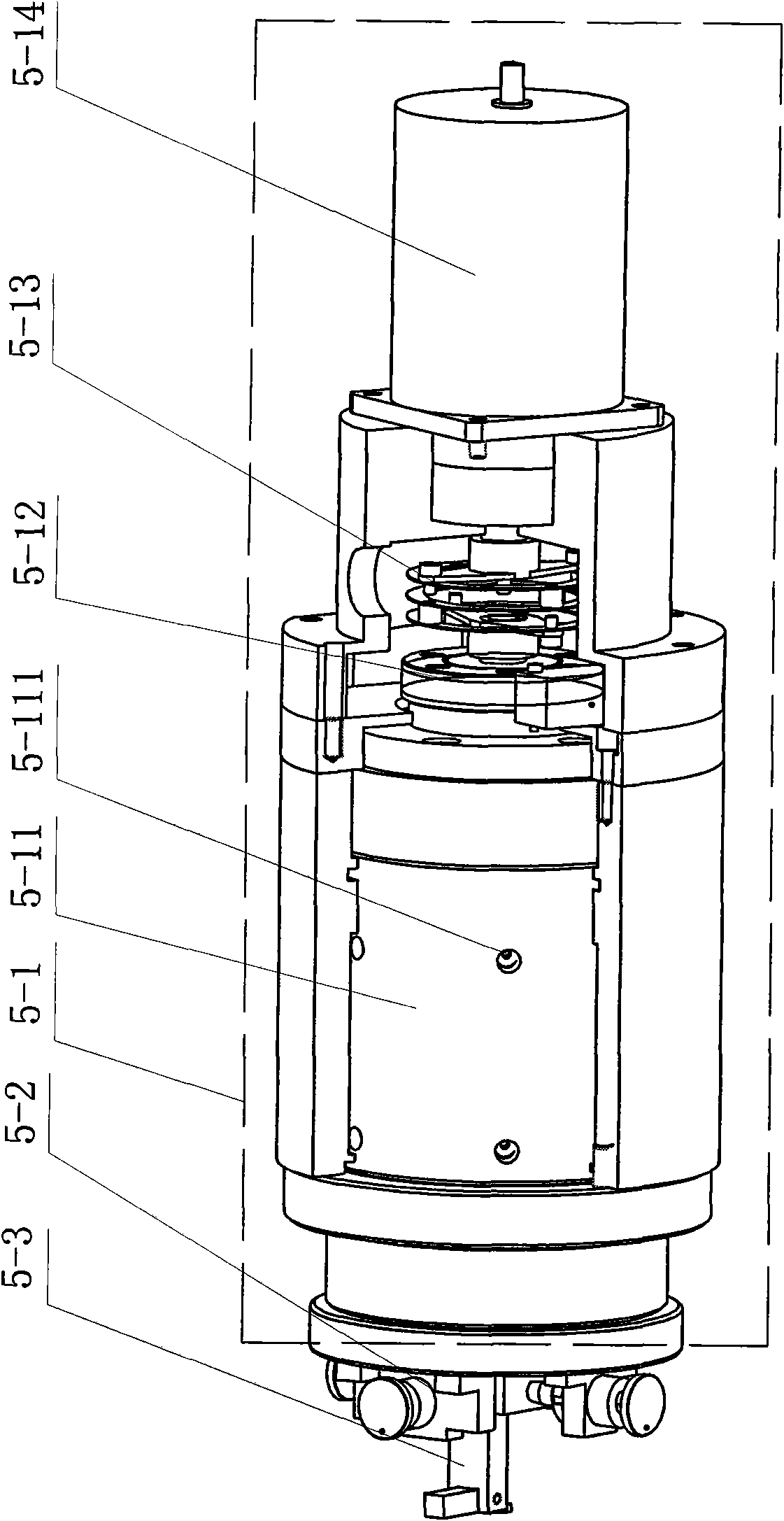
[0040] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination Figure 4 To illustrate this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the centering device 5-2 consists of a bottom disc 5-21, four positioning jackscrews 5-22, and four jacking screw seats 5 -23 and fixture holder 5-24 are formed,
[0041] The upper center of the bottom disc 5-21 is provided with a fixture fixing seat 5-24, and four jacking wire seats 5-23 are fixed on the bottom disc 5-21, and the four jacking thread seats 5-23 are fixed by the fixture fixing seat. 5-24 is the center and evenly distributed on the bottom disc 5-21, and one end of each position-adjusting top wire 5-22 passes through a top wire seat 5-23 and contacts the side wall of the clamp holder 5-24, and the opposite The central axes of the two position-adjusting jackscrews 5-22 are coincident, and the position-adjusting jacking screws 5-22 are threadedly connected with the jacking screw seat 5-23.
[0...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0045] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that six throttle holes 5-111 are evenly distributed in double rows on the outer surface of the aerostatic bearing 5-11. Other compositions and connections are the same as those in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com