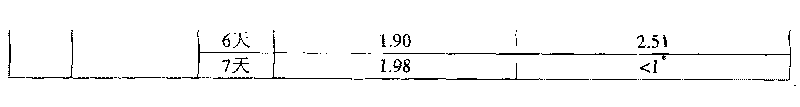Method for preparing cross-linked hyaluronic acid
A technology for cross-linking hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid, which is applied in the field of manufacturing cross-linking hyaluronic acid, can solve the problems of inability to remove the cross-linking agent, cannot effectively remove the cross-linking agent, and reduce the content of the cross-linking agent, so as to achieve a low content of the cross-linking agent. , high biocompatibility, overcoming the effect of purification steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
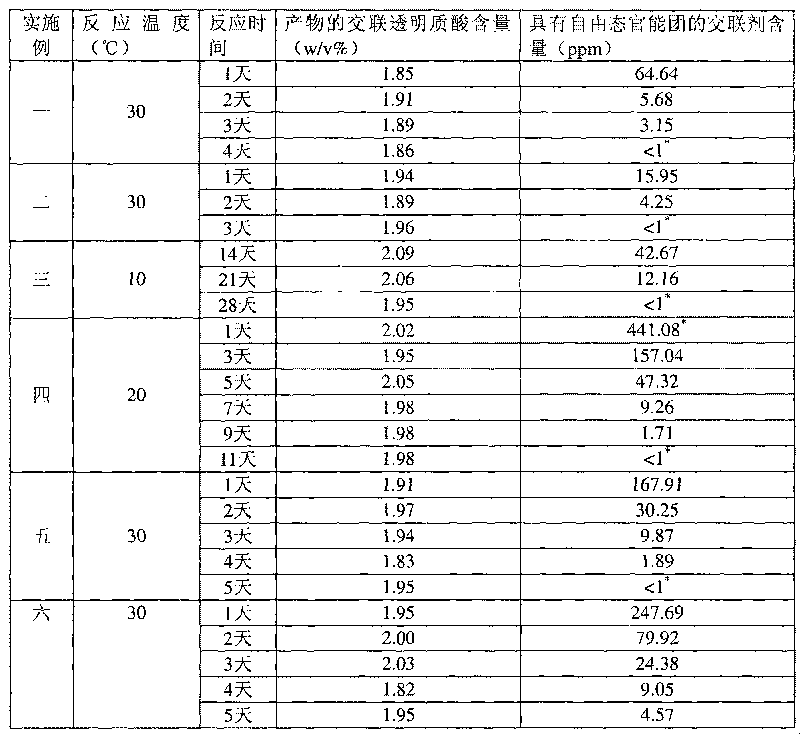
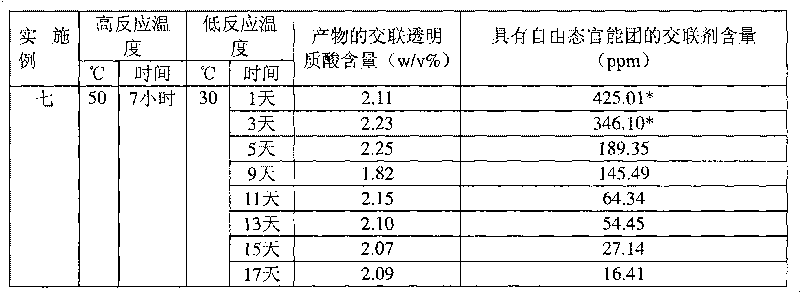
[0037] Example 1: 1,2,7,8-dioxoctane with sodium hyaluronate concentration=20w / v% HHA, alkali concentration=0.5N, reaction temperature=30°C, crosslinking agent concentration=1v / v%
[0038] Take 8.9 mL of deionized water, add 1 mL of 5N sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and 0.1 mL of crosslinking agent 1,2,7,8-dioxoctane, and add 2 g (dry weight) with an average molecular weight of 135 under magnetic stirring. Wan's sodium hyaluronate (high molecular weight hyaluronic acid, HHA), stirred at room temperature for 5 minutes, and placed in a 30°C incubator for the reaction time shown in Table 1. After the reaction, 79.2mL of 0.073M phosphate buffered saline solution and 0.8mL of 6N hydrogen chloride aqueous solution were added to the reactant with a pH value of 7.0 ± 0.2, so that after homogenization, the pH value and osmotic pressure were physiologically acceptable. After homogenizing the colloidal solution, the cross-linked hyaluronic acid product can be obtained.
[0039]The cr...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: 1,3-diepoxybutane with sodium hyaluronate concentration=20w / v% HHA, alkali concentration=0.5N, reaction temperature=30°C, crosslinking agent concentration=1v / v%
[0041] Except that the crosslinking agent was changed to 1,3-dioxetane, the other reaction conditions and the determination method of the content were the same as in Example 1. The cross-linked hyaluronic acid content and the cross-linking agent content with free state functional groups of the products obtained under different reaction times are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether with sodium hyaluronate concentration=20w / v% HHA, alkali concentration=0.25N, reaction temperature=10°C, crosslinking agent concentration=1v / v%
[0043] Take 9.4mL of deionized water, add 0.5mL of 5N sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and 0.1mL of cross-linking agent 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether, add 2 grams (dry weight) under magnetic stirring, the average molecular weight is 1.35 million Sodium hyaluronate (HHA) was stirred at room temperature for 5 minutes, and then placed in a thermostat at 10°C for reaction. After the reaction, 79.6mL of 0.1M phosphate buffer solution and 0.4mL of 6N hydrogen chloride aqueous solution were added to the resulting reactant with a pH of 79.6mL to reach a physiologically acceptable pH value and osmotic pressure after homogenization, and then After homogenizing the colloidal solution, a cross-linked hyaluronic acid product can be obtained. The determination method of the cross-linked hyaluro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com