Method for forming microscopic structures on a substrate
A microstructure and substrate technology, applied in the direction of microstructure devices, manufacturing microstructure devices, microstructure technology, etc., can solve problems such as the use of photolithography technology and the limitation of the minimum feature size of patterned structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
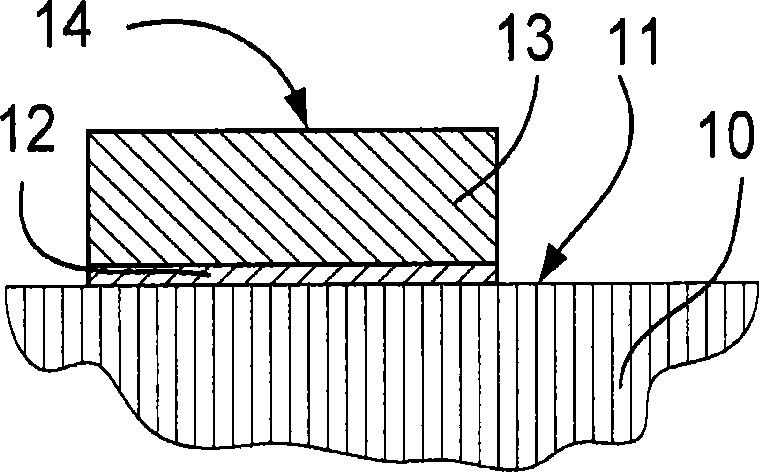
[0041] Figure 1A schematically shows a cross-section of a substrate with microstructures thereon, while Figure 1B The same substrate is shown viewed from the side where the microstructures were grown on the substrate.
[0042] Figure 1A and 1B A substrate 10 is shown having a surface 11 on which a seed layer 12 is deposited using EBID or IBID. The seed layer is then thickened with a material 13 showing a surface 14 substantially parallel to the substrate surface using eg ALD or CVD. The substrate 10 may be a semiconductor substrate, such as a wafer or chip, showing a surface of, for example, silicon oxide, silicon nitride, or aluminum oxide. However, other materials can also be used as the substrate, such as diamond or any other material on which the seed layer can be deposited.
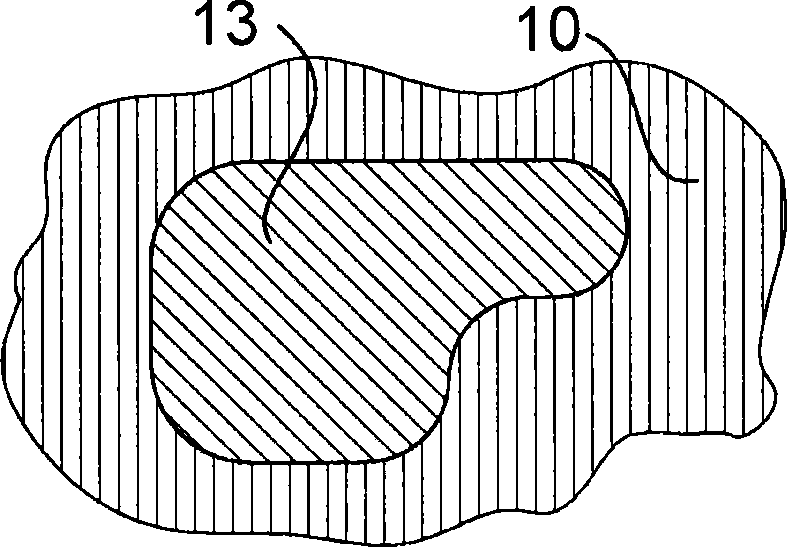
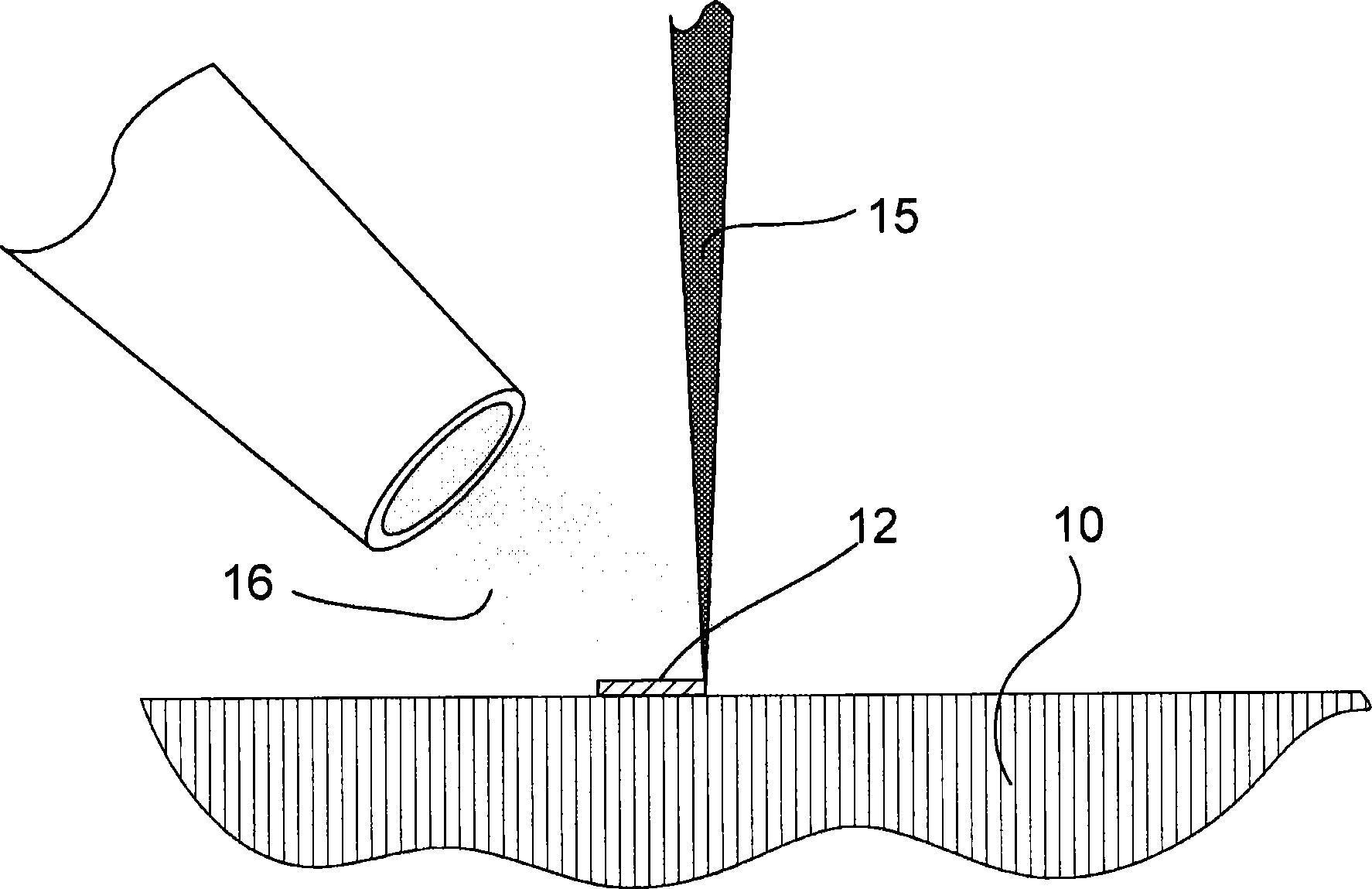
[0043] figure 2 A substrate on which a seed layer is formed is schematically illustrated.
[0044] figure 2 A substrate 10 is shown on which a focused particle beam 15 , such as an electro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com