Method for synthesizing high-molecular-weight polypeptide through catalysis by using hydroborated rare earth as catalyst
A technology of rare earth borohydride and high molecular weight, which is used in the field of rare earth borohydride catalysts to catalyze the synthesis of high molecular weight polypeptides. It can solve the problems of extremely high purity requirements, cumbersome steps, and the inability to realize industrialization, and achieve high activity and narrow molecular weight distribution. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
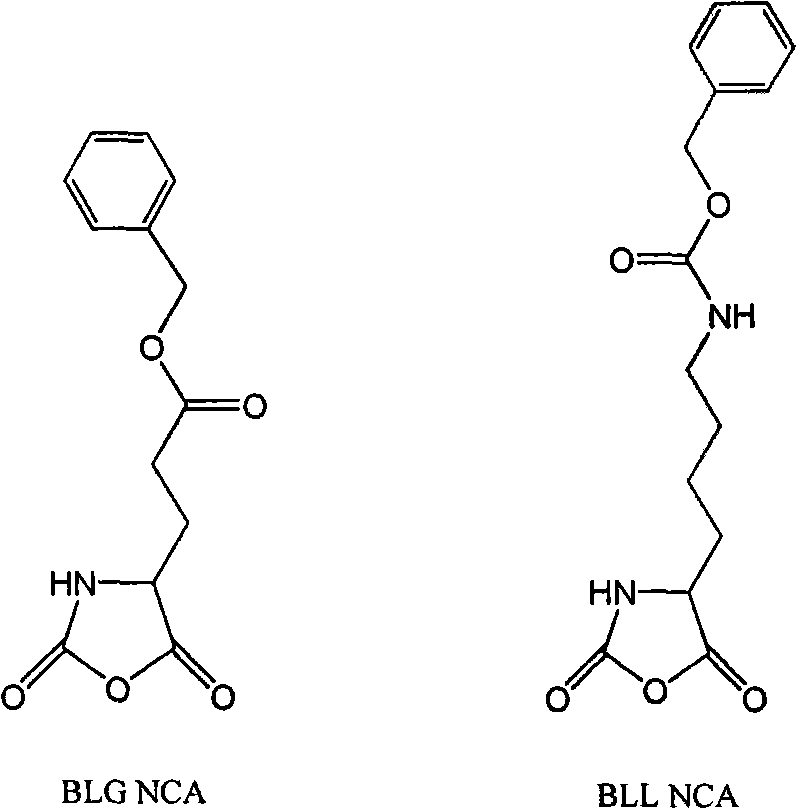
[0012] A method for catalytically synthesizing high-molecular-weight polypeptides using borohydride rare earth as a catalyst, characterized in that: borohydride rare earth Ln(BH 4 ) 3 As a catalyst, catalyzing the ring-opening polymerization of NCA monomers to obtain high molecular weight polypeptides; Ln in the catalyst is a rare earth element Sc, NCA monomers adopt BLG-NCA monomers, BLG-NCA monomers and Sc(BH 4 ) 3 The molar ratio was 20:1, the polymerization reaction temperature was -30°C, and the polymerization reaction time was 3 days. The yield of the obtained polypeptide is 83%, and the molecular weight is carried out in a Ubbelohde viscometer using the viscosity method, using dichloroacetic acid as a solvent, measured at 25°C, and the molecular weight is determined by the formula [η]=2.78×10 -5 m 0.87 calculate [6] , whose value is 29,000. The absolute molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the polymer were determined by gel permeation chromatograph...
Embodiment 2
[0014] A method for catalytically synthesizing high-molecular-weight polypeptides using borohydride rare earth as a catalyst, characterized in that: borohydride rare earth Ln(BH 4 ) 3 As a catalyst, catalyzing the ring-opening polymerization of NCA monomers to obtain high molecular weight polypeptides; the Ln in the catalyst is a rare earth element Y, and the NCA monomers adopt BLG-NCA monomers, and the BLG-NCA monomers and Y(BH 4 ) 3 The molar ratio was 400:1, the polymerization temperature was 0°C, and the polymerization time was 2.5 days. The yield of the obtained polypeptide is 88%, and the molecular weight is carried out in a Ubbelohde viscometer using the viscosity method, using dichloroacetic acid as a solvent, measured at 25°C, and the molecular weight is determined by the formula [η]=2.78×10 -5 m 0.87 calculate [6] , whose value is 66,000. The absolute molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the polymer were measured using gel permeation chromatogra...
Embodiment 3
[0016] A method for catalytically synthesizing high-molecular-weight polypeptides using borohydride rare earth as a catalyst, characterized in that: borohydride rare earth Ln(BH 4 ) 3 As a catalyst, it catalyzes the ring-opening polymerization of NCA monomers to obtain high-molecular-weight polypeptides; the Ln in the catalyst is the rare earth element La, and the NCA monomer adopts BLL-NCA monomer, and the BLL-NCA monomer and La(BH 4 ) 3 The molar ratio is 800:1, the polymerization reaction temperature is 20° C., and the polymerization reaction time is 2.0 days. The yield of the obtained polypeptide is 95%, and the molecular weight is carried out in a Ubbelohde viscometer using the viscosity method. With dichloroacetic acid as the solvent, it is measured at 25°C. The molecular weight is determined by the formula [η]=2.78×10 -5 m 0.87 calculate [6] , whose value is 79,000. The absolute molecular weight and molecular weight distribution of the polymer were measured using g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com