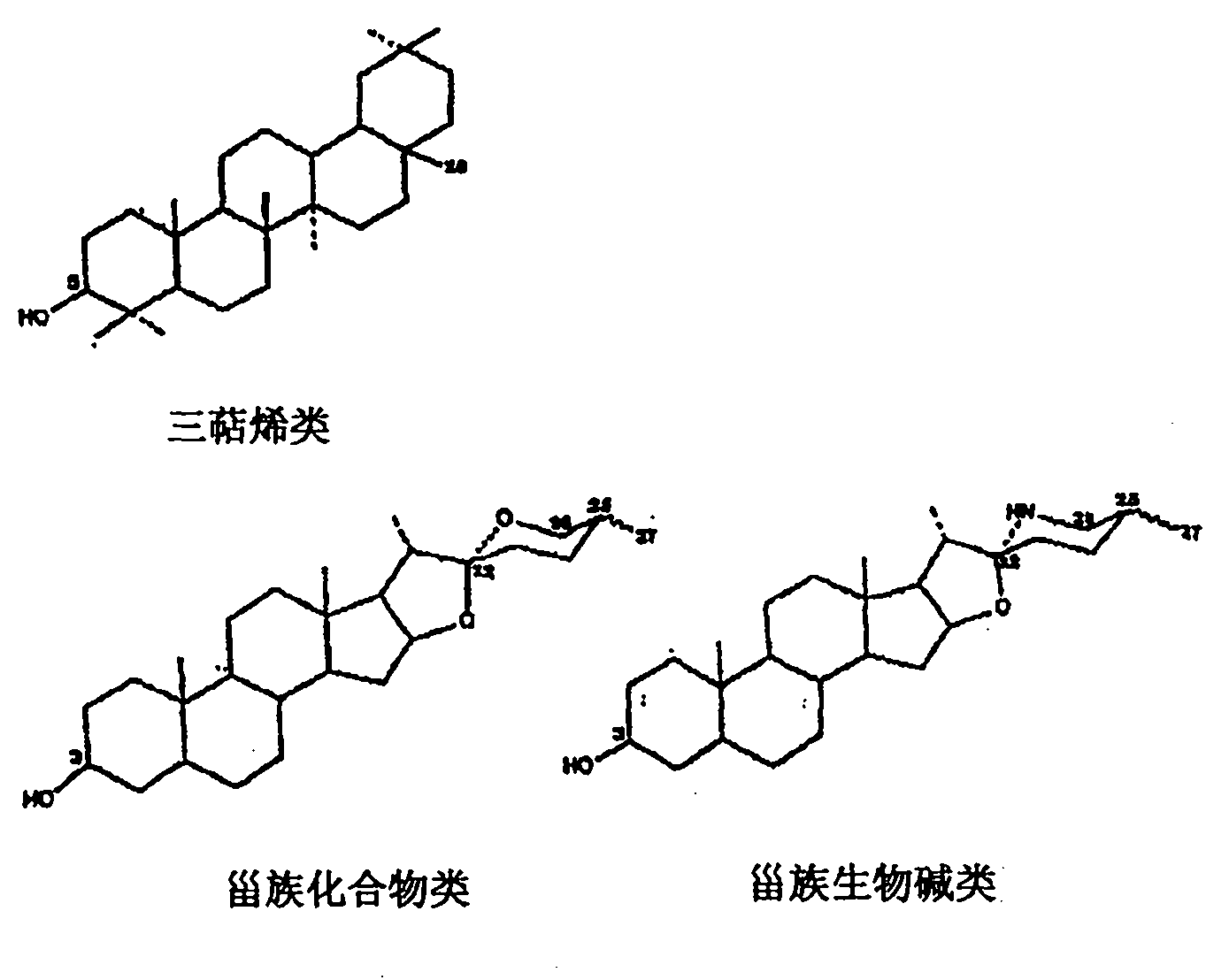
Treatment of urinary tract infections with a mixture of saponin and an antibiotic
A technique for urinary infection and antibiotics, applied to urinary system diseases, vector-borne diseases, drug delivery, etc., can solve problems such as infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
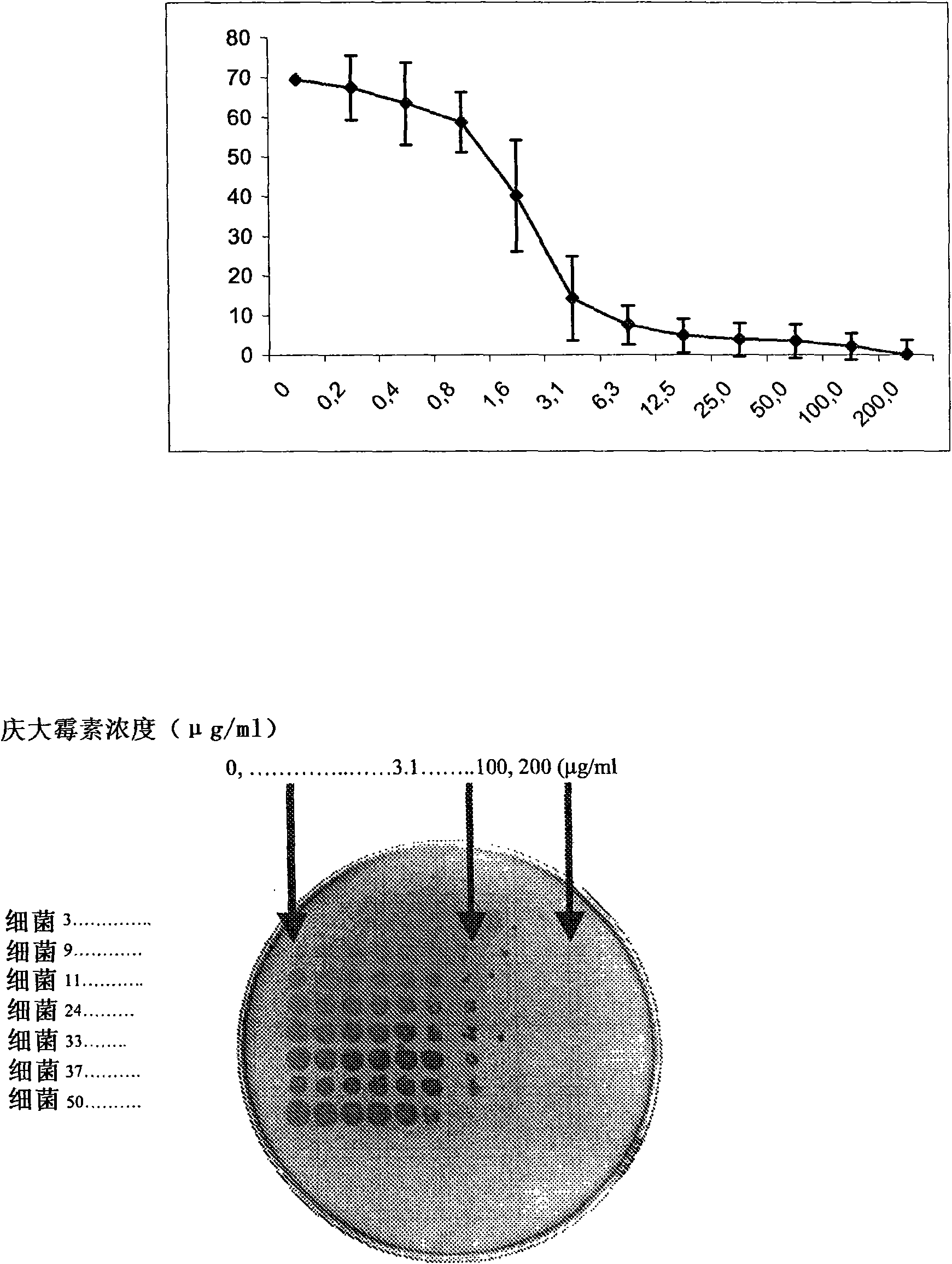
[0047] Seven different strains of wild-type E. coli bacteria were isolated from UTI patients and cultured in LuriaBroth (LB) medium under static conditions for 2 days. Methods of culturing bacteria are familiar to those skilled in the art of microbiology. The 2-day-old bacteria were diluted 100-fold in fresh sterile LB, with different concentrations of gentamicin or no gentamicin (control). Gentamicin is used as a representative antibiotic agent. The bacteria were then allowed to grow for an additional 2 hours under optimal growth conditions (shaking, 37°C) and the actual concentration of bacterial cells in the LB was measured by measuring absorbance at 600 nm. Absorbance reflects the number of bacteria. The number of bacteria is expressed relative to a control preparation without gentamicin. as image 3 As shown in the figure above, the number of bacterial cells is reduced at very low concentrations of gentamicin, showing that gentamicin is very effective in inhibiting th...
Embodiment 2
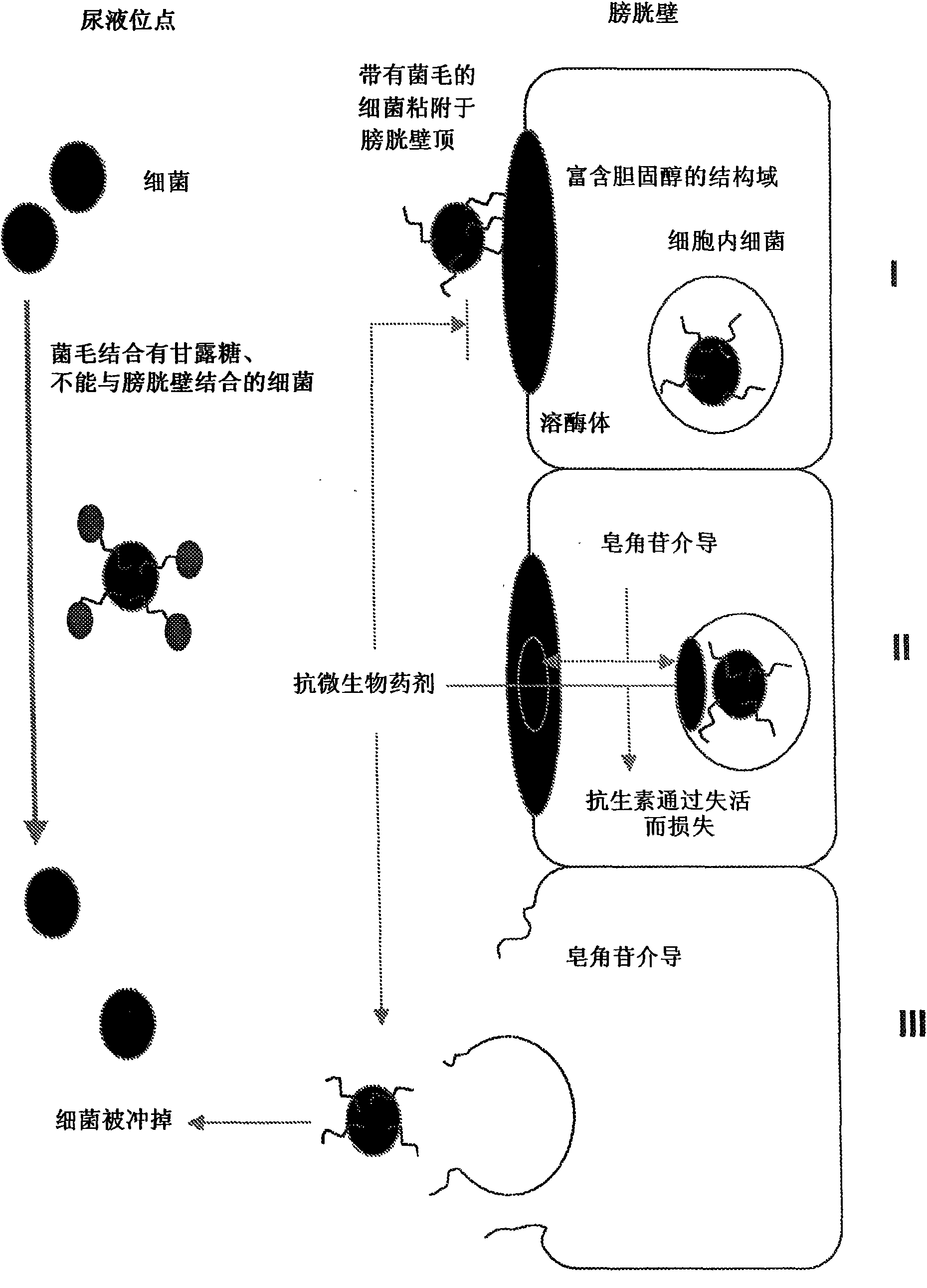
[0049] Human bladder cells were cultured and then infected with bacteria. Briefly, human bladder cells (HTB-9 from the American Tissue Culture Collection) were cultured in medium and CO 2 Incubator at 37°C until the actual experiment. The cultivation of human cells is familiar to those skilled in the biological arts. Next, varying concentrations of E. coli were added to human bladder cells. Bladder cells and bacteria were allowed to incubate together for 1 or 2 hours, then most of the loosely bound and extracellular E. coli cells (human bladder cells attached to the bottom of the cell culture flask) were removed by washing the bladder cells with PBS. Human bladder cells were exposed to 100.0 μg / ml gentamicin for 2 hours. Under normal conditions, gentamicin cannot pass through any membranes. As already shown in Example 1, the gentamicin treatment will kill all bacteria if gentamicin is accessible to the bacteria. Residual gentamicin and dead bacteria were removed by washin...
Embodiment 3
[0051] The green-stained bacteria were also infected with human bladder cells as described in Example 2 above. Infected bladder cells were then treated with ethidium bromide as explained in detail by Drevets and Campbell 1991 . Ethidium bromide will turn green-stained bacteria yellow / red if it has access to the bacteria. This experimental method allows the visual detection by microscopy of green bacteria that are not stained with ethidium bromide inside the cell as well as bacteria that are stained red / yellow outside the cell. as Figure 5 As shown, only the green-stained bacteria were located inside the bladder cells (enclosed by white lines), while the yellow / red-stained bacteria were found outside or near the human bladder cells.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com