Measuring method of solar cell protective coating optical transmittance
A technology of solar cells and protective coatings, applied in the measurement of phase influence characteristics, etc., can solve the problems of in-situ testing of simulated space environments, etc., and achieve the effect of eliminating thermal annealing effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
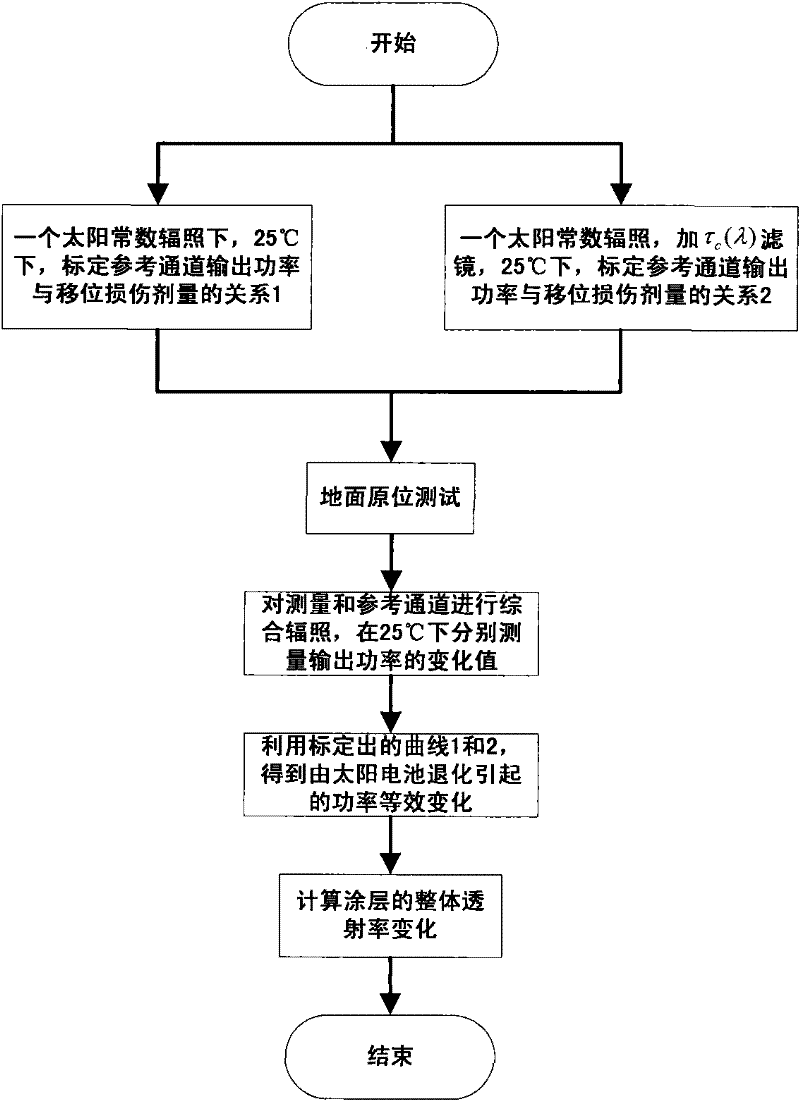
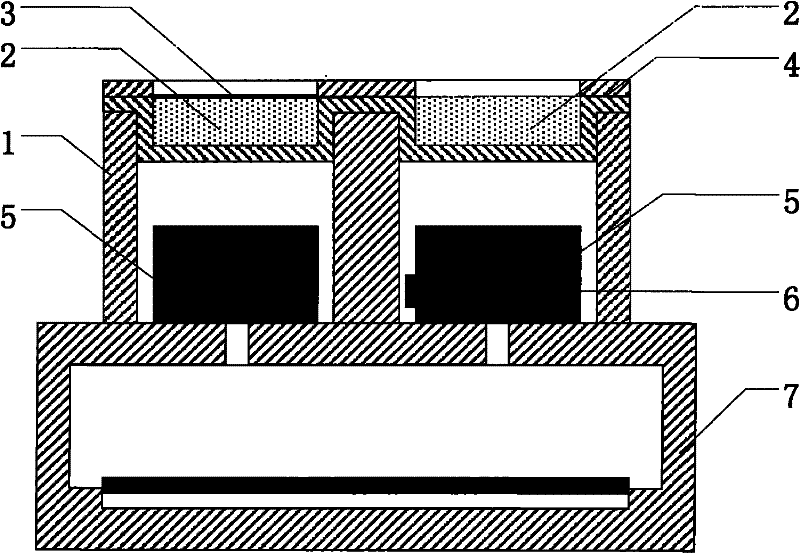
[0031] Such as figure 1 Shown, the implementation steps of the present invention are:
[0032] (1) Irradiate the cover glass with a larger particle fluence, so that its transmittance spectrum is basically unchanged in the subsequent irradiation environment.
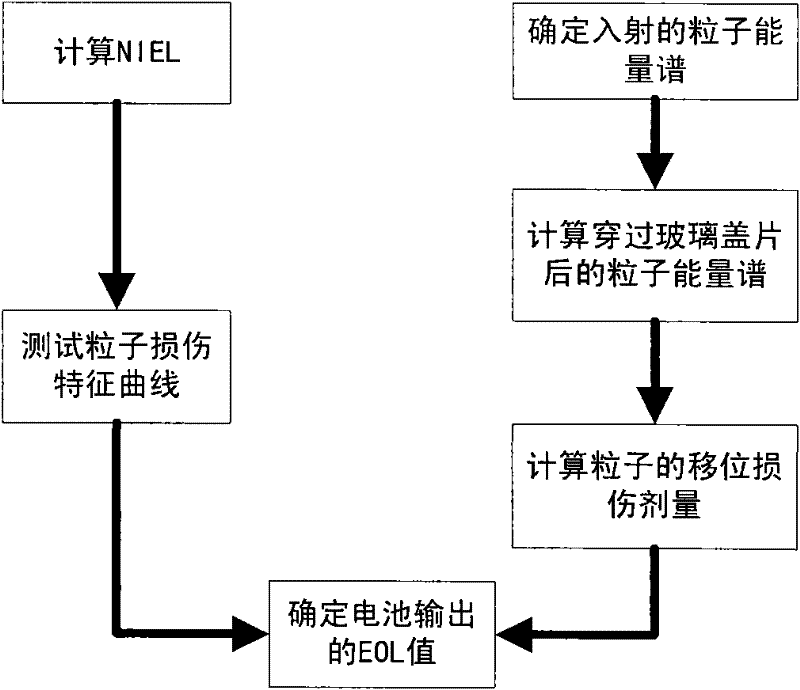
[0033] (2) Under the irradiation of a solar constant (F(λ)), when the operating temperature of the battery measured by the temperature sensor is 25°C, the reference channel is irradiated with electrons and protons of a certain energy and fluence, and the normalized value of the solar battery is obtained by calibration. The relationship between the output power and the fluence of several electrons and protons with different energies; using the method of the US Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), the relationship calibrated by the above method is converted into the particle radiation damage dose of the solar cell and its The relationship between the output power is expressed by a solar cell damage characteristic curve 1.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com