Environment-friendly sea cucumber micelle feeds and preparation method thereof
An environmentally friendly, sea cucumber technology, applied in animal feed, animal feed, application and other directions, can solve the problems of water pollution, low utilization rate, high rate of feed nutrient dissolution, and achieve low cost, improved stability, good promotion and The effect of the application foreground
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
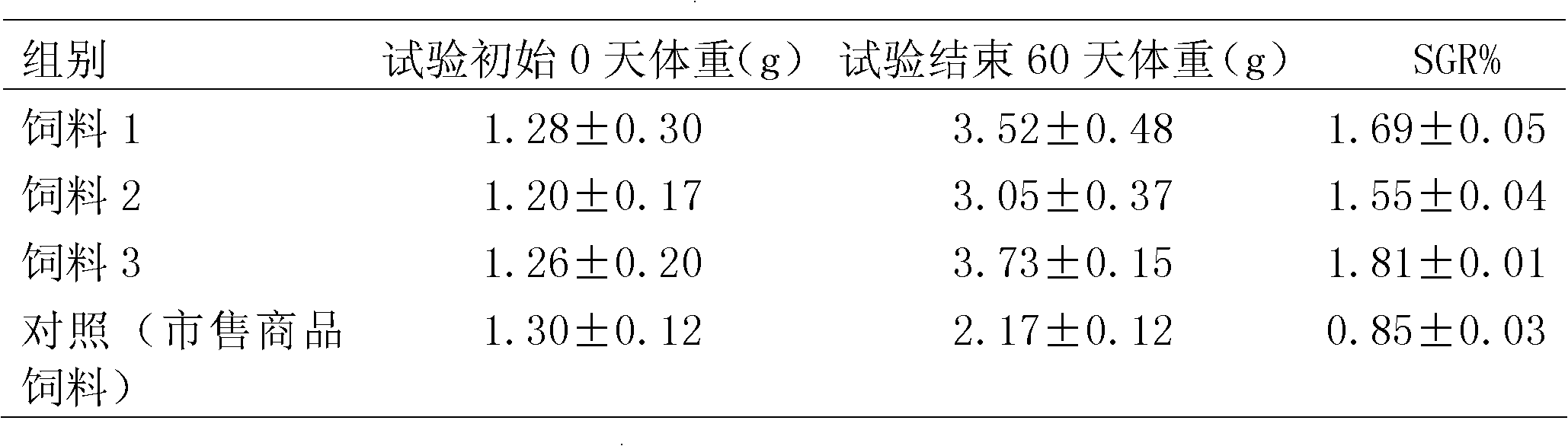
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Step 1: Feed raw materials are pretreated, dried until the water content is not higher than 15%, and coarsely crushed to 40-60 mesh.
[0019] Step 2 Weigh 3.2kg of seaweed powder, 2.8kg of fish meal, 1.2kg of soybean meal, 1.5kg of sea mud, 0.5kg of corn flour, 0.20kg of shell powder, 0.1kg of multivitamins and minerals and place them in a blender, stir and mix well to obtain Basic feed.
[0020] Step 3 Weigh 0.5 kg of cassava a-starch and add it to the basic feed obtained in step 2, place it in a mixer, fully stir and mix.
[0021] In step 4, the coarse feed powder obtained in step 3 is processed by using a high-energy vibrating mill capable of producing micro-shearing. The processing time is 20 minutes, and the particle size is 600-800 mesh as detected by a laser particle size analyzer.
[0022] Step 5: Add water according to the ratio of 1:1 by weight, mix thoroughly, and then repeatedly extrude through a tablet machine, and dry at a temperature not higher than 20°C...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Step 1: Feed raw materials are pretreated, dried until the water content is not higher than 15%, and coarsely crushed to 40-60 mesh.
[0026] Step 2 Weigh 3.2kg of seaweed powder, 2.8kg of fish meal, 1.2kg of soybean meal, 1.5kg of sea mud, 0.5kg of corn flour, 0.20kg of shell powder, 0.1kg of multivitamins and minerals and place them in a blender, stir and mix well to obtain Basic feed.
[0027] Step 3 Weigh 0.4 kg of cassava a-starch and 0.1 kg of sodium alginate and add them to the basic feed obtained in step 2, place them in a mixer, stir and mix well.
[0028] In step 4, the coarse feed powder obtained in step 3 is processed by using a high-energy vibrating mill capable of producing micro-shearing. The processing time is 20 minutes, and the particle size is 600-800 mesh as detected by a laser particle size analyzer.
[0029] Step 5: Add water according to the ratio of 1:1 by weight, mix thoroughly, and then repeatedly extrude through a tablet machine, and dry at a...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Step 1: Feed raw materials are pretreated, dried until the water content is not higher than 15%, and coarsely crushed to 40-60 mesh.
[0033] Step 2 Weigh 3.2kg of seaweed powder, 2.8kg of fish meal, 1.2kg of soybean meal, 1.5kg of sea mud, 0.5kg of corn flour, 0.20kg of shell powder, 0.1kg of multivitamins and minerals and place them in a blender, stir and mix well to obtain Basic feed.
[0034] Step 3 Weigh 0.2 kg of cassava a-starch, 0.1 kg of sodium alginate, and 0.2 kg of bentonite, add them to the basic feed obtained in step 2, place them in a mixer, and fully stir and mix them.
[0035] In step 4, the coarse feed powder obtained in step 3 is processed by using a high-energy vibrating mill capable of producing micro-shearing. The processing time is 20 minutes, and the particle size is 600-800 mesh as detected by a laser particle size analyzer.
[0036] Step 5: Add water according to the ratio of 1:1 by weight, mix thoroughly, and then repeatedly extrude through a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com